Malicious Chrome extensions disguised as AI assistants steal data from 300,000+ users
7 Sources
7 Sources
[1]
30+ Chrome extensions disguised as AI chatbots steal secrets
More than 30 malicious Chrome extensions installed by at least 260,000 users purport to be helpful AI assistants, but they steal users' API keys, email messages, and other personal data. Even worse: many of these are still available on the Chrome Web Store as of this writing. Some of these extensions impersonate specific chatbots such as Claude, ChatGPT, Gemini, and Grok, while others claim to be more generic AI assistant tools to help users summarize documents, write messages, and provide Gmail assistance. Despite different names and extension IDs, they all use the same underlying codebase and permissions, and all 32 extensions communicate with infrastructure under the tapnetic[.]pro domain, according to LayerX Security, which uncovered the campaign and named it AiFrame. Some of them were published under new IDs after earlier versions were removed. For example, AI Sidebar (gghdfkafnhfpaooiolhncejnlgglhkhe), which had 50,000 users at the time of LayerX Security's report, appeared after the earlier Gemini AI Sidebar (fppbiomdkfbhgjjdmojlogeceejinadg), which had 80,000 users, was removed from the Chrome Web Store. The Register found that the re-uploaded extension (gghdfkafnhfpaooiolhncejnlgglhkhe) is now listed with 70,000 users as of publication. Google did not immediately respond to The Register's inquiries about the malicious extensions. All 32 extension IDs are listed in LayerX's report, so be sure to check it out before adding any AI assistant extension to your browser. Another extension that is still available at the time of this writing is called AI Assistant (nlhpidbjmmffhoogcennoiopekbiglbp) and has 60,000 users. This one, which garnered the "Featured" badge on the Chrome Web Store, points users to a remote domain (claude.tapnetic.pro). It has an iframe overlay that visually appears as the extension's interface, and this iframe allows the operator to load remote content, changing the UI and logic, and silently adding new capabilities at any time without any Chrome Web Store update required. "When instructed by the iframe, the extension queries the active tab and invokes a content script that extracts readable article content using Mozilla's Readability library," LayerX Security researcher Natalie Zargarov wrote. "The extracted data includes titles, text content, excerpts, and site metadata." The extension then sends this data - including authentication details for any page the user is viewing - back to the remote iframe. In addition to snarfing up all sorts of page content from every website a user visits, this particular extension also supports speech recognition. It transcribes the user's words and sends them back to the remote page for the operator to read. Interestingly, nearly half of the extensions target Gmail and share the same Gmail integration codebase. This allows the extension to read visible email content directly from the DOM and extract message text via textContent from Gmail's conversation view. This includes email thread content and even draft or compose-related text, which is then sent to remote servers. "The campaign exploits the conversational nature of AI interactions, which has conditioned users to share detailed information," Zargarov said in an email. "By injecting iframes that mimic trusted AI interfaces, they've created a nearly invisible man-in-the-middle attack that intercepts everything from API keys to personal data before it ever reaches the legitimate service." ®
[2]
Fake AI Chrome extensions with 300K users steal credentials, emails
A set of 30 malicious Chrome extensions that have been installed by more than 300,000 users are masquerading as AI assistants to steal credentials, email content, and browsing information. Some of the extensions are still present in the Chrome Web Store and have been installed by tens of thousands of users, while others show a small install count. Researchers at browser security platform LayerX discovered the malicious extension campaign and named it AiFrame. They found that all analyzed extensions are part of the same malicious effort as they communicate with infrastructure under a single domain, tapnetic[.]pro. According to them, the most popular extension in the AiFrame campaign had 80,000 users and was called Gemini AI Sidebar (fppbiomdkfbhgjjdmojlogeceejinadg), but it is no longer on the Chrome Web Store. However, BleepingComputer found that other extensions with thousands of users are still present on Google's repository for Chrome extensions. It should be noted that the names may be different in some cases, but the identification is the same. LayerX found that all 30 extensions share the same internal structure, JavaScript logic, permissions, and backend infrastructure. The malicious browser add-ons do not implement AI functionality locally; instead, they deliver the promised feature by rendering a full-screen iframe to load content from a remote domain. This, by itself, is risky, as publishers can change the extensions' logic at any time without pushing an update - just like in the case of Microsoft Office Add-ins - thus avoiding a new review. In the background, the extensions extract page content from websites the user visits, including sensitive authentication pages, using Mozilla's Readability library. LayerX says that a subset of 15 extensions specifically targets Gmail data, using a dedicated content script that runs at 'document_start' on 'mail.google.com' and injects UI elements. The script reads visible email content directly from the DOM and repeatedly extracts email thread text via '.textContent.' The researchers note that even email drafts can be captured. "When Gmail-related features such as AI-assisted replies or summaries are invoked, the extracted email content is passed into the extension's logic and transmitted to third-party backend infrastructure controlled by the extension operator," LayerX explains in a report today. "As a result, email message text and related contextual data may be sent off-device, outside of Gmail's security boundary, to remote servers." The extensions also feature a remotely triggered voice recognition and transcript generation mechanism using the 'Web Speech API,' returning the results to the operators. Depending on the granted permissions, the extensions may even siphon conversations from the victim's environment. BleepingComputer has contacted Google for a comment on LayerX findings, but we have not received a response by publication time. It is recommended to check LayerX's list of indicators of compromise for the complete set of malicious extensions. If compromise is confirmed, users should reset passwords for all accounts.
[3]
30 fake AI Chrome extensions caught stealing passwords and more
Users should only install official AI applications from trusted developers and use antivirus software to protect against such sophisticated scams. Security experts have uncovered a number of dangerous extensions for the Chrome browser. A total of 30 extensions belonging to the AiFrame campaign have been identified as dangerous, appearing to offer AI services but actually designed to intercept sensitive information. To date, the extensions have been installed by over 260,000 users through the official Chrome Web Store. At times, they were even shown among recommended extensions, as the creators were able to circumvent important security measures. Security researchers at LayerX Security explain how the extensions work in their analysis. They employ server-side interfaces that are embedded in the code and function as privileged proxies. This gives them extensive permissions, such as scanning and copying content (including sensitive details like passwords and bank info) from active browser tabs and sending it to the extension's operators.
[4]
300,000+ Chrome users installed these malicious extensions posing as AI assistants -- delete them right now
Extensions promised quick access to AI but were actually stealing emails, passwords and more Although people are now much more careful with the apps they install on their smartphones, the same can't be said for the extensions in their web browser. Case in point: Over 300,000 Chrome users installed 30 malicious extensions thinking they were a quick and easy way to get access to their favorite AI assistants -- but instead, opened them up to having their data stolen. As reported by BleepingComputer, these malicious extensions pose as AI assistants in order to gain a foothold in a user's browser. From there, they are able to siphon off all kinds of sensitive data in the background including passwords, email content and browsing info. Here's everything you need to know about this new campaign including the malicious extensions themselves and the steps you need to take right now if you accidentally installed one of them in your browser. This new set of malicious extensions was discovered by researchers at the browser security company LayerX which dubbed them AiFrame (more on that in a bit). After analyzing all of the bad extensions in question, the firm found that they are all part of the same campaign and use a single domain to communicate with the cybercriminals behind it. Here are the malicious extensions posing as popular AI assistants and tools with the most installs: It's worth noting that the names of some of these extensions may be different but you can find the full list at the bottom of LayerX's report and their unique identifiers (which look like this "gghdfkafnhfpaooiolhncejnlgglhkhe") there. According to BleepingComputer, the most popular malicious extension Gemini AI Sidebar has already been removed from the Chrome Web Store while some of the others haven't been taken down yet but likely will soon. If you installed any of these extensions in Chrome -- or any other Chromium-based browser for that matter -- you need to delete them immediately. To do so, click on the three-dot menu in the upper right corner of your browser, then Extensions and Manage Extensions. Here you'll see a full list of all of your installed extensions with a search bar at the top to make it easier to find and remove any of these malicious ones. Just like a malicious app on your phone, rogue extensions give cybercriminals a 'backdoor' to your browser and the sensitive data inside it. Think of these tools as a Trojan Horse: they lure you in with the promise of easy access to popular AI assistants, but while the 'gift' of the AI tool works perfectly on the surface, malicious code (the 'soldiers') is secretly operating in the background to scrape your emails, passwords, and private chatbot conversations. During its investigation, LayerX found that all 30 of these extensions have the same internal structure, JavaScript logic, permissions and backend infrastructure, which suggests they were created by the same person or group. While they do all technically 'work', they do so by using a full-screen iframe to load content from a remote domain instead of locally. This makes them extra risky because their creator could change how they function at any time just by sending out an update. Of these AiFrame extensions, 15 of them specifically target victims' Gmail data through a dedicated content script that extracts the text from email threads and according to LayerX, even draft emails can be captured. If that wasn't bad enough, these malicious extensions also have a remotely triggered voice recognition and transcript generation mechanism. When enabled, it can be used to record real life conversations right from a victim's computer, putting not just their data but what they say to themselves or others around them at risk too. Despite Google's best efforts, malicious extensions still manage to slip through the cracks and end up on the Chrome Web Store. For this reason, you always need to be extra careful when downloading any new browser extension. Although it's best to stick to well-known extensions from trusted brands, there are times when a smaller extension from a lone developer does exactly what you need to solve a problem. I've been in this situation myself and during those times, I do several things first before installing it. Besides checking an extension's rating and reviews, I also recommend doing a bit of digging into the developer to gauge whether or not they're legit. Since even good extensions can go bad, you want to make sure that your Windows PC is protected with the best antivirus software and that you're using the best Mac antivirus software on your Apple computer. That way, if an extension is spreading malware or other viruses, they'll be detected and stopped before they can do any damage. If you use a lot of extensions and are constantly installing new ones and other AI tools, it might also be a good idea to consider investing in one of the best identity theft protection services. Not only can they help you get your identity back if it's stolen but they can also help you recover any funds lost to scams or cyberattacks. AI assistants and tools can really help speed up your workflow while allowing you to do things you couldn't without them. However, just like with any other new technology, you want to be careful while being especially wary of any extension that promises a quick fix or access to something you normally wouldn't be able to use. When in doubt, it's best to chat with your favorite AI assistant in a browser window instead of using an extension because that way, the rest of your browsing data won't be at risk.
[5]
Fake Chrome AI extensions targeted over 300,000 users to steal emails, personal data and more - here's what we know
Over 300,000 downloads; popular add-ons included AI Sidebar, AI Assistant, and ChatGPT Translate Security researchers have discovered more than 30 malicious Chrome extensions that posed as GenAI add-ons, but were actually surveillance and content-stealing tools. The experts from LayerX reported dozens of Chrome extensions of the Google Chrome Web Store, all posing as AI tools and assistants. While on the surface they work as indented, in the background, they are exfiltrating everything they see in the web browser to a third-party server. As LayerX explained, the extensions use Mozilla's Readability library to extract the text, titles, and metadata of any page a user visits, including internal corporate or private authenticated pages. In other words, they act as spies looking over their victims' shoulders. When they view a website, or Gmail, the extension "reads" the text on the screen and then sends it to a hidden window inside the extension. In fact, there is a specific subset of 15 extensions that includes code to read and extract email content and even draft messages from the Gmail interface. The attackers also went to lengths to avoid being seen or scrutinized. At the same time, they made sure they could push updates to the extensions without triggering any alarms. They did this by using full-screen iframes to load content remotely, instead of running features locally. Since the interface and logic are loaded from a remote server, they can change the extension's behavior at any time without needing to push an update through the Chrome Web Store. BleepingComputer made a list of the most popular among the malicious add-ons, so if you have any of these installed, make sure to delete them and refresh your passwords: AI Sidebar (gghdfkafnhfpaooiolhncejnlgglhkhe) - 70,000 users AI Assistant (nlhpidbjmmffhoogcennoiopekbiglbp) - 60,000 users ChatGPT Translate (acaeafediijmccnjlokgcdiojiljfpbe) - 30,000 users AI GPT (kblengdlefjpjkekanpoidgoghdngdgl) - 20,000 users ChatGPT (llojfncgbabajmdglnkbhmiebiinohek) - 20,000 users AI Sidebar (djhjckkfgancelbmgcamjimgphaphjdl) - 10,000 users Google Gemini (fdlagfnfaheppaigholhoojabfaapnhb) - 10,000 users In total, the 30 extensions were downloaded more than 300,000 times. Via BleepingComputer
[6]
These Malicious AI Assistants in Chrome Are Stealing User Credentials
Always vet extensions carefully -- don't just rely on a familiar name like ChatGPT. AI-powered browser extensions continue to be a popular vector for threat actors looking to harvest user information. Researchers at security firm LayerX have analyzed multiple campaigns in recent months involving malicious browser extensions, including the widespread GhostPoster scheme targeting Chrome, Firefox, and Edge. In the latest one -- dubbed AiFrame -- threat actors have pushed approximately 30 Chrome add-ons that impersonate well-known AI assistants, including Claude, ChatGPT, Gemini, Grok, and "AI Gmail." Collectively, these fakes have more than 300,000 installs. The Chrome extensions identified as part of AiFrame look like legitimate AI tools commonly used for summarizing, chat, writing, and Gmail assistance. But once installed, they grant attackers wide-ranging remote access to the user's browser. Some of the capabilities observed include voice recognition, pixel tracking, and email content readability. Researchers note that extensions are broadly capable of harvesting data and monitoring user behavior. Though the extensions analyzed by LayerX used a variety of names and branding, all 30 were found to have the same internal structure, logic, permissions, and backend infrastructure. Instead of implementing functionality locally on the user's device, they render a full-screen iframe that loads remote content as the extension's interface. This allows attackers to push changes silently at any time without a requiring Chrome Web Store update. LayerX has a complete list of the names and extension IDs to refer to. Because threat actors use familiar and/or generic branding, such as "Gemini AI Sidebar" and "ChatGPT Translate," you may not be able to identify fakes at first glance. If you have an AI assistant installed in Chrome, go to chrome://extensions, toggle on Developer mode in the top-right corner, and search for the ID below the extension name. Remove any malicious add-ons and reset passwords. As BleepingComputer reports, some of the malicious extensions have already been removed from the Chrome Web Store, but others remain. Several have received the "Featured" badge, adding to their legitimacy. Threat actors have also been able to quickly republish add-ons under new names using the existing infrastructure, so this campaign and others like it may persist. Always vet extensions carefully -- don't just rely on a familiar name like ChatGPT -- and note that even AI-powered add-ons from trusted sources can be highly invasive.
[7]
Fraudulent AI Assistants Target User Information | PYMNTS.com
By completing this form, you agree to receive marketing communications from PYMNTS and to the sharing of your information with our sponsor, if applicable, in accordance with our Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions. According to a report Monday (Feb. 16) by cybersecurity publication Dark Reading, these extensions claim to offer the abilities of an artificial intelligence (AI) assistant, while stealing users' personal information in secret. The report cites research from security firm LayerX, which found 30 Google Chrome extensions that are carbon copies of each other, aside from some superficial branding differences, many of which have tens of thousands of downloads each. While these extensions purport to act as AI assistants, they are in fact there to steal email content, browser content and anything else the user willingly offers them. "While we've seen [similar tactics] used by malicious extensions in the past, what is new and concerning is how it's being applied," says LayerX security researcher Natalie Zargarov. "Instead of spoofing banks or email logins, attackers are now impersonating artificial intelligence interfaces and developer tools, places where users are conditioned to paste application programming interface (API) keys, tokens and sensitive data without hesitation." The research found 30 tools, with names like "Gemini AI Sidebar," "ChatGPT Translate," or more generic monikers like "AI Assistant," which amassed more than 260,000 downloads. PYMNTS has contacted Google for comment but has not yet gotten a reply. The findings come at a time when -- as PYMNTS wrote last month -- AI is "pushing intervention earlier in the attack cycle by identifying coordinated behavior and emerging risk signals before fraud scales." As covered here, companies are ramping up their use of AI to guard against suspicious activities, even as they deal with an increasing risk from shadow AI, third-party agents and apps that could subject the businesses to cyber risks. Research from PYMNTS Intelligence has found a gap between companies' belief in their defenses against AI-powered fraud and the prevalence of those fraud cases. While nearly all companies surveyed said they were confident in their protections, nearly 59% said they were struggling with bot-driven fraud. This gap is especially pronounced in the financial services sector, where 60.6% of companies have seen bot traffic rise in the past year, according to the PYMNTS Intelligence report "The Hidden Costs of 'Good Enough': Identity Verification in the Age of Bots and Agents." "Many assume their fraud controls are mature because they've passed compliance audits or updated authentication steps," PYMNTS wrote. "But the report's findings show that fraudsters' use of artificial intelligence -- from deepfakes to credential stuffing -- is evolving faster than those defenses. What looks compliant may, in practice, be porous."
Share
Share
Copy Link
More than 30 malicious Chrome extensions posing as AI assistants have infected over 300,000 users, stealing passwords, emails, and browsing data. Discovered by LayerX Security and dubbed the AiFrame campaign, these extensions impersonate ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and other popular AI tools while extracting sensitive information through hidden iframe overlays. Many remain available on the Chrome Web Store despite ongoing reports.
Malicious Chrome Extensions Target Users Through AI Assistant Disguise
A widespread cybersecurity threat has emerged as more than 30 malicious Chrome extensions disguised as AI chatbots have been installed by at least 300,000 users, according to research from LayerX Security
1
2
. The AiFrame campaign, as researchers have named it, represents a sophisticated attempt to steal credentials and emails by exploiting the growing popularity of AI assistants5
. These extensions impersonate well-known services including ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and Grok, while others present themselves as generic AI tools promising to summarize documents, write messages, and provide Gmail assistance1
.
Source: BleepingComputer
What makes this threat particularly concerning is that many of these extensions remain available on the Chrome Web Store at the time of reporting, with some even earning the "Featured" badge
1
. The most popular extension, AI Sidebar, currently shows 70,000 users, while AI Assistant has 60,000 users, and ChatGPT Translate has 30,000 users . Google has not responded to inquiries about the malicious extensions as of publication1
.How the AiFrame Campaign Operates to Steal Sensitive User Data
All 32 extensions in the AiFrame campaign share identical underlying codebases, permissions, and backend infrastructure, communicating with servers under the tapnetic[.]pro domain
1
2
. Rather than implementing AI functionality locally, these extensions deliver promised features by rendering a full-screen iframe that loads content from a remote domain2
. This iframe overlay visually appears as the extension's interface but enables operators to remotely update their malicious functionalities at any time without requiring Chrome Web Store approval1
.
Source: TechRadar
When instructed by the iframe, extensions query the active tab and invoke a content script that extracts readable article content using Mozilla's Readability library
1
. The extracted data includes titles, text content, excerpts, and site metadata from every website users visit, including sensitive authentication pages3
. This information, along with authentication details, is transmitted back to remote servers controlled by the extension operators1
. The extensions also support speech recognition through the Web Speech API, transcribing users' words and sending them to remote pages for operators to read1
4
.Gmail Targeting and Man-in-the-Middle Attacks Raise Concerns
Nearly half of the extensions—15 in total—specifically target Gmail and share the same Gmail integration codebase
1
2
. These extensions run a dedicated content script at 'document_start' on mail.google.com, allowing them to read visible email content directly from the DOM2
. The script repeatedly extracts message text via textContent from Gmail's conversation view, capturing email thread content and even draft or compose-related text1
. When Gmail-related features such as AI-assisted replies or summaries are invoked, the extracted email content is transmitted to third-party backend infrastructure outside Gmail's security boundary2
."The campaign exploits the conversational nature of AI interactions, which has conditioned users to share detailed information," explained LayerX Security researcher Natalie Zargarov. "By injecting iframes that mimic trusted AI interfaces, they've created a nearly invisible man-in-the-middle attack that intercepts everything from API keys to personal data before it ever reaches the legitimate service"
1
. This approach represents a significant evolution in browser security threats, leveraging user trust in AI assistants to execute data exfiltration at scale5
.
Source: PCWorld
Related Stories
Immediate Action Required for Affected Users
Users who have installed any of these extensions should delete them immediately by accessing Chrome's Extensions menu and checking against LayerX's complete list of indicators of compromise
2
4
. After removal, affected individuals should reset passwords for all accounts, as the extensions may have captured authentication credentials across multiple services2
. The persistence of these extensions on the Chrome Web Store, despite affecting over 300,000 users, highlights ongoing challenges in browser security and the need for more robust vetting processes3
. Security experts recommend installing only official AI applications from trusted developers and using antivirus software to protect against such sophisticated scams3
. The incident serves as a reminder that while users have become more cautious with smartphone apps, browser extensions often receive less scrutiny despite having similarly broad access to sensitive information4
.References
Summarized by
Navi
[1]
[2]
[4]
Related Stories
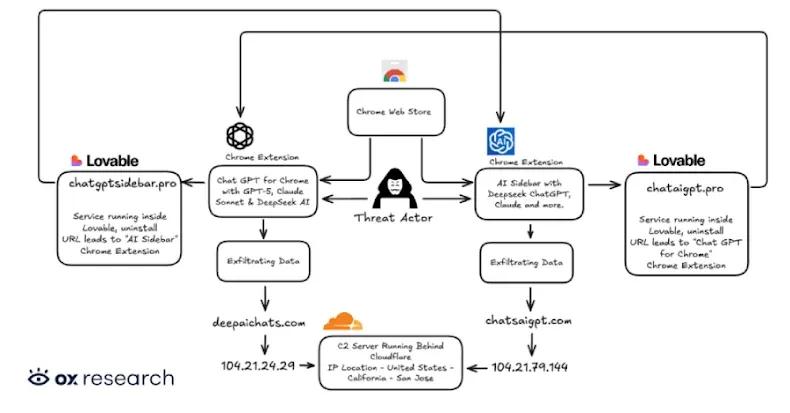
Two Chrome Extensions Caught Stealing AI Chats from 900,000 ChatGPT and DeepSeek Users
07 Jan 2026•Technology
Browser extensions with 8 million users caught secretly harvesting AI conversations
17 Dec 2025•Technology

Chrome Gemini vulnerability allowed malicious extensions to hijack AI and spy on users
02 Mar 2026•Technology

Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.4, New AI Model Built for Agents and Professional Work
Technology

2
Anthropic sues Pentagon over supply chain risk label after refusing autonomous weapons use
Policy and Regulation

3
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round as questions swirl around AI bubble and profitability
Business and Economy





