OpenAI Transforms ChatGPT into an App Platform, Revolutionizing AI-Driven Commerce
24 Sources
24 Sources
[1]
OpenAI and the race for AI-driven commerce | TechCrunch
OpenAI held its annual dev day on Monday, where the company rolled out its plan to build apps into ChatGPT. The demo was impressive, showing how programs like Spotify and Figma can be called or discovered without leaving the ChatGPT window. With so much of the tech world barreling towards AI integration, OpenAI's demo was the best picture yet of what an AI-first internet might actually look like, with interfaces like ChatGPT querying information and executing commands directly. If you're watching closely, you may have noticed that there's a lot of room in this system for money to change hands. Just last week, the company launched Instant Checkout, an agentic shopping system that serves as payment infrastructure for one-off purchases, plugging in any stores that sell through Shopify, Etsy or Stripe. Now, apps provides the front-end infrastructure, letting service providers build their own interface into ChatGPT. In short, OpenAI now has all the pieces in place for AI-driven commerce, establishing ChatGPT as a place customers go to buy and retailers go to sell. It's a huge new line of business for the company -- and one with huge implications for the tech industry. In this world, OpenAI's isn't just competing with Google and Anthropic, but with Amazon and Wal-Mart. If you look at OpenAI's pending app partners in the launch announcement, you can see how far the vision reaches. ChatGPT will be able to call you a cab through Uber, book a trip on Expedia, call a plumber or locksmith through Thumbtack, order groceries from Instacart, prepared food from Doordash, or big-box goods from Target. Without too much more work, ChatGPT could become a portal for most of its users' discretionary spending. If it works, this would be worth a lot more than just a $20-a-month subscription. The precise terms of the arrangement are still unclear, but like any app store, OpenAI is well positioned to get a portion of any money spent on its platform. ChatGPT is also recommending products, drawing on its wealth of data about its users, which tips the balance of power between OpenAI and retailers even more. In Ben Thompson's terms, ChatGPT becomes a super-aggregator, funneling customers to retailers and providing an entry point for ever-larger amounts of commerce. OpenAI has lots of potential lines of business to pursue, but it's no exaggeration to say that AI-driven commerce is one of the most lucrative options. OpenAI isn't the only company with an eye on this prospect. On the same day as the ChatGPT announcement, Adobe released a report predicting that this year's holiday would be dominated by AI-assisted shopping, with shoppers turning to chatbots instead of search engines to find the best deals available. A separate report from Mastercard dubbed agentic commerce as a "new competitive arena" for finance. Google has already launched its own competing protocol for agentic commerce called AP2, which arrives with a broader scope but less momentum than OpenAI's version. The simplest version of AI-driven shopping is using ChatGPT to find products in place of search: if you're looking for a canvas tennis shoe under $80, ChatGPT can find it for you just as easily as Google Search. But AI systems don't need to be passive. The AP2 specification includes a provision for agent-initiated purchases, if you want an agent to buy concert tickets as soon as they become available, say, or book a flight as soon as it falls below a certain price. Of course, there could be agents on the other side of the transaction too, negotiating with purchasing agents for the best deal, and willing to bundle goods under the right circumstances. If retailers and customers are willing to take the leap, the changes could extend pretty far beyond a simple "buy" button. The biggest unanswered question is whether the shopping public will actually be interested. AI shopping is obviously attractive to OpenAI, and companies like Stripe and Mastercard see plenty of benefit in it too -- but users haven't shown much interest in agentic shopping systems beyond simple product searches. But then, they haven't had a chance to; these systems aren't even properly available now, and it will be months before the average user can try out a fully agentic shopping system. When they finally do, there will be a lot riding on how they react.
[2]
OpenAI launches apps inside of ChatGPT | TechCrunch
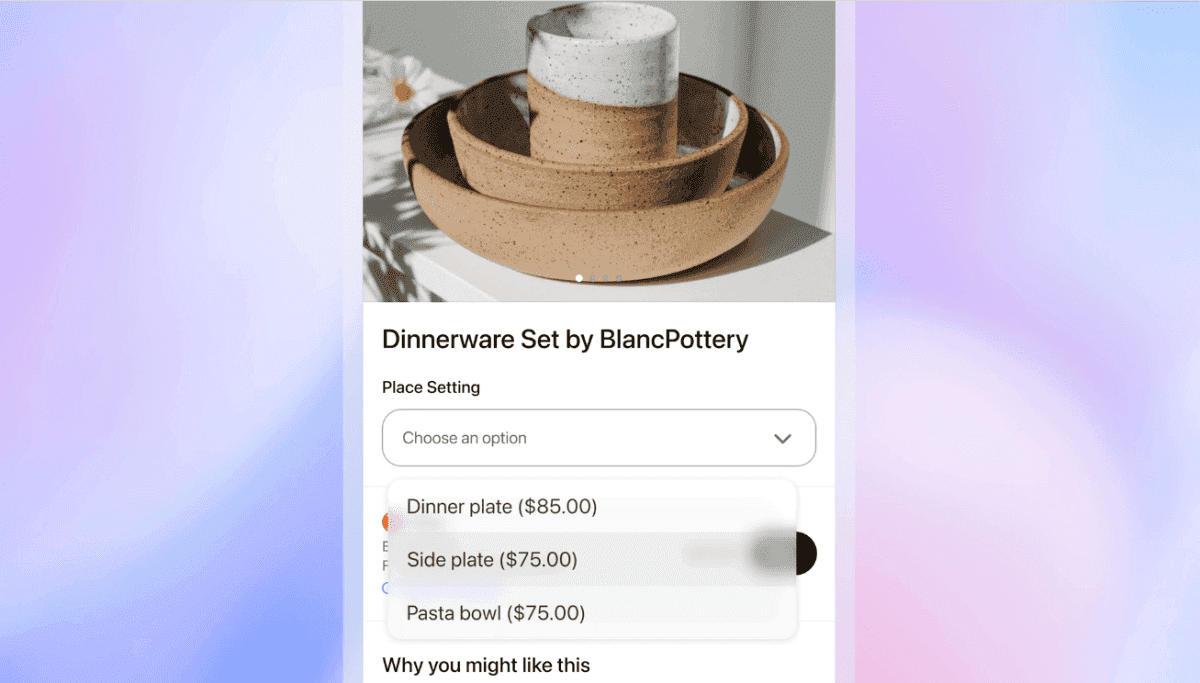
OpenAI is launching a new way for developers to build applications inside of ChatGPT. Starting Monday, users in ChatGPT will be able to access interactive applications from companies like Spotify, Figma, Coursera, Zillow, and Canva. OpenAI is also launching a preview of the Apps SDK on Monday, the developer-facing toolkit to build these apps. OpenAI made the announcement at its annual developer conference, DevDay 2025. "We want ChatGPT to be a great way for people to make progress, to be more productive, more inventive, to learn faster, to do whatever they're trying to do in their lives better," said CEO Sam Altman. "[Apps inside of ChatGPT] will enable a new generation of apps that are interactive, adaptive, and personalized, that you can chat with." The new system is OpenAI's latest attempt to build an ecosystem of apps around its flagship AI product, ChatGPT. The launch follows OpenAI's previous attempts to let developers build interactive applications, such as through its GPT Store. Unlike that product, which asked ChatGPT users to access a separate app store, Monday's launch puts apps directly in ChatGPT's responses, and lets users call up different applications in their everyday conversations. This gives developers better distribution for the apps they build, and aims to make a richer experience for users in ChatGPT. By calling out the names of different apps, users can draw in content from a variety of services. For example, ChatGPT users can say "Figma, turn this sketch into a workable diagram" to call up the Figma app. Users can also call up the Coursera app by asking, "Coursera, can you teach me something about machine learning." In a demo of Zillow's application, users could access for apartments in their area within a specific price range. ChatGPT then pulled up an interactive map showing options, and users could talk with ChatGPT to learn more about each one. ChatGPT will also surface relevant apps when they could be helpful to a user. If someone asks for a playlist for a party this weekend, ChatGPT may call up the Spotify app in the conversation. OpenAI says the new system is built using the Model Context Protocol (MCP), which allows developers to connect their data sources to an AI systems. ChatGPT apps can also trigger actions, and render a fully interactive UI in the chatbot's responses. Certain apps are able to display videos in ChatGPT, which will be pinned to the top of the web-page and can be altered based on user requests. If users are already subscribed to a product, they'll be able to login to their account directly in ChatGPT to access certain features. Altman also says OpenAI will support ways to monetize apps inside of ChatGPT in the future, including through the company's recently launched Instant Checkout feature in ChatGPT.
[3]
ChatGPT wants to act more like an OS -- as it transforms into an app platform
Nick Turley, Head of ChatGPT, says it will act more like an operating system. Over the past year, numerous developments have occurred in the AI space, including agentic assistants that can carry out tasks on your behalf and more seamless, multimodal ways to interact with chatbots. Yet, the way you can interact with ChatGPT has remained mostly unchanged: it's an AI chatbot with a traditional Q&A format. That may change soon. Also: OpenAI DevDay event: Agent Kit, Apps SDK, ChatGPT, and more At OpenAI DevDay 2025, the company took the stage to unveil a range of updates designed to help developers build and deploy AI solutions more efficiently. A major highlight was the launch of the Apps SDK, which, in simple terms, enables developers to build actual Apps within the ChatGPT interface. This is a glimpse into the next phase of OpenAI's core product, which Nick Turley, Head of ChatGPT, told me in a press Q&A would function like an OS. "What you're going to see over the next six months is an evolution from an app that is really useful into something that feels a little bit more like an operating system where you can access business services and you can access software, both the existing software they're used to, but more importantly and most excitingly, new software that's been built natively on top of ChatGPT." During the DevDay keynote, we already got a glimpse of what this could possibly look like through ChatGPT App pilot partner demos. For example, Alexi Christakis, a software engineer at OpenAI, led a live demo showcasing the integration of the Canva app within ChatGPT. He was able to request that Canva create a poster directly within the chatbot, which was able to produce four posters in line. He later had Canva convert the posters into a slide deck, again using a simple ChatGPT prompt. Also: OpenAI's Sora 2 app soars to No. 1 in the App Store - why there's a feeding frenzy to try it This, of course, isn't OpenAI's first stab at apps, with experiences such as custom chatbots or GPTs previously available within the chatbot. However, those were mostly limited to an inline chatbot text exchange. A distinguishing factor of the new apps is their deep integration into the ChatGPT experience. When announcing the Apps SDK during the keynote, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman said it was opening app building to developers to "enable a new generation of apps that are interactive, adaptive, and personalized that you can chat with." Another example of this interactivity was highlighted in the Zillow app demo, where Christakis was able to filter down the house results he wanted by simply using a text prompt. This is a far more seamless experience than having to select multiple different toggles on the Zillow website to achieve the desired results. Being able to view apps in full-screen was also another major upgrade, opening the opportunity for more developers to build experiences within ChatGPT that are more consistent with the app. At launch, the App SDK partners include household names such as Booking.com, Canva, Coursera, Figma, Expedia, and Spotify, with 11 additional partners expected to join later in the year. The App SDK is now available in preview for developers starting today. Later this year, developers will be able to submit apps for review to be listed. Also: OpenAI's Altman calls AI sector 'bubbly', but says we shouldn't worry - here's why All users, regardless of subscription tier, can access these apps. To activate the app, simply start a message to ChatGPT with the name of an available app at the beginning of the prompt. The chatbot will also suggest relevant chatbots based on your conversation. In the future, these apps may also leverage agentic features that perform tasks proactively on your behalf. Regardless of what the apps are actually built to do, Turley reassured users that what ChatGPT is capable of doing will be "greatly expanded" and should feel "meaningfully different."
[4]
You Can Now Add Spotify, Zillow to ChatGPT, But Don't Call It an App Store
When he's not battling bugs and robots in Helldivers 2, Michael is reporting on AI, satellites, cybersecurity, PCs, and tech policy. Don't miss out on our latest stories. Add PCMag as a preferred source on Google. ChatGPT can now run third-party apps, including Spotify, for an experience that OpenAI says is closer to an operating system than an app store. At its DevDay conference today, OpenAI said the app support goes beyond offering plugins for the chatbot. A key difference is that a user can access the apps within the ChatGPT prompt. This includes displaying "interactive interfaces you can use right in the chat," the company says. "The magic of this new generation of apps in ChatGPT is how they blend familiar interactive elements-like maps, playlists, and presentations-with new ways of interacting through conversation," OpenAI wrote in a blog post. For example, a user can query ChatGPT to access Spotify to list and play popular tracks from the streaming app. In a demo at the developer conference, the company also showed that a user could access Zillow directly within ChatGPT to search and display property listings. In addition, ChatGPT can also suggest a user try out an app. The company is rolling out the feature starting today for all logged-in ChatGPT users outside of the European Union, including on free accounts.The first supported apps include Booking.com, Canva, Coursera, Figma, Expedia, Spotify, and Zillow. "What you're going to see over the next six months is an evolution of ChatGPT from an app that is really, really useful to something that'll be a bit more like an operating system, where you can access different services, you can access software," OpenAI's head of ChatGPT, Nick Turley, said during a Q&A with the press. This will include both existing software and new software "built natively on top of ChatGPT," which promises to offer a different experience. Also today, OpenAI revealed that ChatGPT has now grown to over 800 million weekly active users. "I imagine you're starting your day with ChatGPT," Turley said. He suggested the chatbot has become an entry point for the web for some users. The news also raises a question about how ChatGPT will recommend the apps users should run. For now, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman told the press the company doesn't want to break user trust by recommending unworthy apps. "We're hyper aware of the need to be careful," he said. In the meantime, the company is trying to get companies on board by offering a new apps software development kit, which is arriving in preview mode. Users can expect other apps to launch in the coming weeks, including Target, DoorDash, Instacart, Uber, and Uber Eats. "For Uber Eats, ChatGPT will detect when a user wants to place an Uber Eats order, confirm details like delivery address, and then display nearby restaurant and menu options directly in ChatGPT," Uber said. "To complete their order, users will then be prompted to launch the Uber Eats app directly from ChatGPT." Disclosure: Ziff Davis, PCMag's parent company, filed a lawsuit against OpenAI in April 2025, alleging it infringed Ziff Davis copyrights in training and operating its AI systems.
[5]
OpenAI opens ChatGPT to referring queries to developer apps
Integrate your apps via their Apps SDK and maybe they'll send you some business OpenAI on Monday pitched its coding tools to software developers in the hope of generating the usage and revenue necessary to recoup the vast sums it spends to create and run its AI services. CEO Sam Altman presided over OpenAI DevDay 2025 at San Francisco's Fort Mason Center, the third such event since the company began chewing through massive amounts of costly cloud computing to resell scraped data as service. "Today, 4 million developers have built with OpenAI," said Altman in a streamed presentation. "More than 800 million people use ChatGPT every week, and we process over six billion tokens per minute on the API, thanks to all of you. AI has gone from something people play with to something people build with every day." That hasn't been enough to turn a profit. According to The Information, OpenAI generated $4.3 billion in revenue in the first half of 2025, 16 percent more than all of 2024, and reported a net loss of $13.5 billion, up from $3.1 billion during the same period a year ago. OpenAI did not respond to a request to confirm those figures. But Altman insists that there's never been a better time to build software applications with OpenAI, and he provided some details on how the AI giant aims to help developers do that. Altman and underlings went on to describe: Here's a rundown of the most important and interesting bits. Apps SDK provides a way to discover and invoke apps through the ChatGPT interface. "When someone's using ChatGPT, you'll be able to find an app by asking for it by name," Altman explained. "For example, you could sketch out a product flow for ChatGPT and then say 'Figma, turn the sketch into a workable diagram.' The Figma app will take over, respond, and complete the action." (In a sign of how desperate investors are to get in on the AI boom, Figma's stock went up 16 percent after Altman talked about them in his presentation.) Functionally, the idea is similar to an Android Intent - a way to pass data from one mobile app to another. But OpenAI aims to generalize this sort of cross-app communication so it works on a broader level, through natural language. And it is doing so in a way that will have economic implications for app developers. To participate, developers have to set up metadata that informs ChatGPT about their app's functions, create an MCP server to handle communication with ChatGPT, and connect the MCP server to ChatGPT. They have a substantial incentive to do so given the size of the ChatGPT audience - integration is a prerequisite for having ChatGPT surface apps. However, app makers who agree to entrust distribution to a third party may find themselves at the mercy of that entity, as Apple's App Store and Google Play have demonstrated. Developers comfortable with that tradeoff will be able to register their apps so that ChatGPT can route queries to those apps when the topic and metadata suggest a match. Alexi Christakis, a member of OpenAI's technical staff, explained how ChatGPT app discovery works when the user hasn't tried the app before; it requires user consent to connect the app to your ChatGPT conversation. AgentKit provides a way to configure workflows to be carried out by agents (models running tools in a loop). The Agent Builder offers visual flowcharting to connect models with data and tools. The Connector Registry provides an administrative panel governing how ChatGPT and the API get linked to other services, such as pre-built connectors for Dropbox, Google Drive, Sharepoint, and Microsoft Teams, and third-party MCP servers. "AgentKit is a complete set of building blocks available in the OpenAI platform designed to help you take agents from prototype to production," said Altman. "It is everything you need to build, deploy, and optimize Agentic workflows with way less friction." Altman described how grocery chain Albertson's built an agent using AgentKit. Faced with a scenario in which ice cream sales had dropped unexpectedly by 32 percent, the grocery chain would typically have undertaken a long process of reporting and spreadsheet data analysis, he said. "Now, an associate can just ask the agent what's going on," Altman said. "The agent will look at the full context of everything it can discover - seasonality, historical trends, external factors - and it will give a recommendation." He didn't address whether the resulting recommendation would reverse the sales slump or how it might compare to slower human data analysis. The utility of AI intervention was also left unaddressed in a demonstration of Agent Builder by OpenAI technical staff member Christina Huang. She created an agent to recommend sessions at OpenAI's DevDay in less than eight minutes. Whether this low-code experience produced something of value depends on whether this is the sort of task one prefers to delegate to a hastily-assembled web page widget or whether it's the sort of challenge one might manage without aid. Altman concluded, "We want OpenAI to be a great platform for this new era of building. We think things are going to get pretty incredible pretty soon."
[6]
New platform, familiar risks: Zillow and Expedia bet on OpenAI's ChatGPT apps rollout
Zillow and Expedia were among the first companies to launch apps inside OpenAI's ChatGPT this week, securing early positions in what analysts are already calling the potential "Windows of AI." The move puts the iconic Seattle brands in a new ecosystem with more than 800 million weekly users, making them part of what one report called the AI "super app" of the future. But past platform shifts raise a key question: Are these companies booking a seat on a rocket ship, or are they ceding control to a new gatekeeper that could one day put its own interests first? OpenAI announced the new app platform at its annual DevDay in San Francisco, saying that developers can now build full-fledged applications within ChatGPT using a new software development kit, or SDK. The idea is to create a new category of conversational apps that work directly in the chat flow, including interactive features accessible in ChatGPT. During a live demo, for example, an engineer prompted Canva to create a poster for a dog-walking business and later asked Zillow to show homes for sale in Pittsburgh, which generated an interactive map from the real estate site inside the chat. "Zillow is the only real estate app available in ChatGPT," the company crowed in a news release. "Zillow worked with OpenAI as one of the first partners to build an app in ChatGPT, underscoring its trusted brand, scale and track record of turning technology breakthroughs into consumer-first innovations." Expedia's new ChatGPT app, announced in conjunction with the OpenAI platform launch, will allow users to plan trips by asking for flights and hotels directly in the chat. The apps handle the discovery and planning phases within ChatGPT, handing users off to the partner sites to take the final steps, like booking a room or scheduling a home tour. OpenAI framed the new Apps SDK as a full-stack platform for developers, offering tools to connect data, trigger actions, and present interactive interfaces directly inside ChatGPT. CEO Sam Altman said the goal is to "help developers rapidly scale products" by reaching hundreds of millions of users -- a message that echoed the early days of mobile app stores and hinted at OpenAI's ambitions to create a new operating system for the AI era. But that ambition is already raising bigger questions about potential trade-offs. In his Platformer newsletter, Casey Newton compared OpenAI's ambitions to Facebook's troubled "social graph," warning that the "AI graph may prove even riskier" to digital privacy given that ChatGPT stores users' most private conversations. Newton also asked whether long-term economic incentives -- i.e., will OpenAI auction off app placement in the future? -- could eventually warp the user experience at the cost of ChatGPT's usefulness. In The Information's nightly briefing, Martin Peers questioned whether app developers have a real incentive to participate if it means diminishing their direct traffic and their ability to sell ads. As it related to the specific integrations, however, much of the reaction was positive. On the Vendor Alley real estate technology blog, Greg Robertson recalled Zillow (and Expedia) co-founder Rich Barton mentioning that having Zillow's app featured in Apple keynotes was a big boost, both for attracting the attention of consumers and for internal morale at Zillow. Referencing the applause that followed OpenAI's Zillow demo, Robertson wrote, "That's the sound of Zillow winning the real estate AI race. Everyone else is now playing catch up."
[7]
OpenAI Goes All-In on Vibe Coding, Says 'Mature Experiences' Are on the Horizon
OpenAI's DevDay 2025 featured a major focus on vibe coding. The company, which boasts that it now has more than 800 million weekly active users for ChatGPT, announced a variety of new tools for developers during its annual event in San Francisco. Headlining the announcements: the ability to build with apps directly in ChatGPT (including eventually allowing "mature experiences" once age verification is in place) and the introduction of a toolkit that will help users build and deploy their own AI agents. In OpenAI's apparent effort to turn ChatGPT into a full-on frontend development environment, the company announced its new Apps SDK (Software Development Kit) that will allow devs to pull in supported third-party apps to complete tasks. In a demo, the company showed ChatGPT working with Zillow to generate a map of homes available for sale in Pittsburgh. Zillow created an interactive map based on the prompt, and the user was able to ask additional questions based on the map. The functionality should allow users to create tools using third-party apps, which they can preview directly within ChatGPT. According to OpenAI, Apps SDK is available immediately for Free, Go, Plus, and Pro plans. Support will be available out of the gate for Booking.com, Canva, Coursera, Figma, Expedia, Spotify, and Zillow. The company also said that it plans to offer support for DoorDash, OpenTable, Target, and Uber in the near future. For now, users will only be able to make and use the apps in preview, but it plans to allow developers to submit apps later this year, with a directory for apps planned so that developers can share their vibe-based creations. There are lots of details yet to come regarding what comes from Apps SDK. Altman promised monetization guidelines, for instance, are in the pipeline. Also on the way: "mature experiences." According to OpenAI's App developer guidelines, "Apps must be suitable for general audiences, including users aged 13â€"17. Apps may not explicitly target children under 13." But that won't be the case forever. "Support for mature (18+) experiences will arrive once appropriate age verification and controls are in place," it reads. The company recently introduced age verification tools designed to shift underage users into a ChatGPT experience with much stricter guidelines following a wrongful death lawsuit filed against the company by the family of a teenager who died by suicide after extensive conversations with the chatbot. It appears that once it hammers out those details, it'll open the floodgates to more "adult" functions. In addition to Apps SDK, the company also rolled out its AgentKit API (Application Programming Interface), which will allow users to build their own agentic AI tools. It's a significant expansion of OpenAI's Agent, which it introduced earlier with the promise that the system could navigate the web autonomously to complete tasks assigned to it by the user. Sticking with the vibe coding theme, AgentKit's primary feature is its Agent Builder, which allows users to program their AI agent's functionality through a visual interface. Altman described it as being like Canva for building agents, making it more accessible to those who are less technical.
[8]
OpenAI Dev Day 2025: ChatGPT becomes the new app store -- and hardware is coming
In a packed hall at Fort Mason Center in San Francisco, against a backdrop of the Golden Gate Bridge, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman laid out a bold vision to remake the digital world. The company that brought generative AI to the mainstream with a simple chatbot is now building the foundations for its next act: a comprehensive computing platform designed to move beyond the screen and browser, with legendary designer Jony Ive enlisted to help shape its physical form. At its third annual DevDay, OpenAI unveiled a suite of tools that signals a strategic pivot from a model provider to a full-fledged ecosystem. The message was clear: the era of simply asking an AI questions is over. The future is about commanding AI to perform complex tasks, build software autonomously, and live inside every application, a transition Altman framed as moving from "systems that you can ask anything to, to systems that you can ask to do anything for you." The day's announcements were a three-pronged assault on the status quo, targeting how users interact with software, how developers build it, and how businesses deploy intelligent agents. But it was the sessions held behind closed doors, away from the public livestream, that revealed the true scope of OpenAI's ambition -- a future that includes new hardware, a relentless pursuit of computational power, and a philosophical quest to redefine our relationship with technology. From chatbot to operating system: The new 'App Store' The centerpiece of the public-facing keynote was the transformation of ChatGPT itself. With the new Apps SDK, OpenAI is turning its wildly popular chatbot into a dynamic, interactive platform, effectively an operating system where developers can build and distribute their own applications. "Today, we're going to open up ChatGPT for developers to build real apps inside of ChatGPT," Altman announced during the keynote presentation to applause. "This will enable a new generation of apps that are interactive, adaptive and personalized, that you can chat with." Live demonstrations showcased apps from partners like Coursera, Canva, and Zillow running seamlessly within a chat conversation. A user could watch a machine learning lecture, ask ChatGPT to explain a concept in real-time, and then use Canva to generate a poster based on the conversation, all without leaving the chat interface. The apps can render rich, interactive UIs, even going full-screen to offer a complete experience, like exploring a Zillow map of homes. For developers, this represents a powerful new distribution channel. "When you build with the Apps SDK, your apps can reach hundreds of millions of chat users," Altman said, highlighting a direct path to a massive user base that has grown to over 800 million weekly active users. In a private press conference later, Nick Turley, head of ChatGPT, elaborated on the grander vision. "We never meant to build a chatbot," he stated. "When we set out to make ChatGPT, we meant to build a super assistant and we got a little sidetracked. And one of the tragedies of getting a little sidetracked is that we built a great chatbot, but we are the first ones to say that not all software needs to be a chatbot, not all interaction with the commercial world needs to be a chatbot." Turley emphasized that while OpenAI is excited about natural language interfaces, "the interface really needs to evolve, which is why you see so much UI in the demos today. In fact, you can even go full screen and chat is in the background." He described a future where users might "start your day in ChatGPT, just because it kind of has become the de facto entry point into the commercial web and into a lot of software," but clarified that "our incentive is not to keep you in. Our product is to allow other people to build amazing businesses on top and to evolve the form factor of software." The rise of the agents: Building the 'do anything' AI If apps are about bringing the world into ChatGPT, the new "Agent Kit" is about sending AI out into the world to get things done. OpenAI is providing a complete "set of building blocks... to help you take agents from prototype to production," Altman explained in his keynote. Agent Kit is an integrated development environment for creating autonomous AI workers. It features a visual canvas to design complex workflows, an embeddable chat interface ("Chat Kit") for deploying agents in any app, and a sophisticated evaluation suite to measure and improve performance. A compelling demo from financial operations platform Ramp showed how Agent Kit was used to build a procurement agent. An employee could simply type, "I need five more ChatGPT business seats," and the agent would parse the request, check it against company expense policies, find vendor details, and prepare a virtual credit card for the purchase -- a process that once took weeks now completed in minutes. This push into agents is a direct response to a growing enterprise need to move beyond AI as a simple information retrieval tool and toward AI as a productivity engine that automates complex business processes. Brad Lightcap, OpenAI's COO, noted that for enterprise adoption, "you needed this kind of shift to more agentic AI that could actually do things for you, versus just respond with text outputs." The future of code and the Jony Ive bBombshell Perhaps the most profound shift is occurring in software development itself. Codex, OpenAI's AI coding agent, has graduated from a research preview to a full-fledged product, now powered by a specialized version of the new GPT-5 model. It is, as one speaker put it, "a teammate that understands your context." The capabilities are staggering. Developers can now assign Codex tasks directly from Slack, and the agent can autonomously write code, create pull requests, and even review other engineers' work on GitHub. A live demo showed Codex taking a simple photo of a whiteboard sketch and turning it into a fully functional, beautifully designed mobile app screen. Another demo showed an app that could "self-evolve," reprogramming itself in real-time based on a user's natural language request. But the day's biggest surprise came in a closing fireside chat, which was not livestreamed, between Altman and Jony Ive, the iconic former chief design officer of Apple. The two revealed they have been collaborating for three years on a new family of AI-centric hardware. Ive, whose design philosophy shaped the iPhone, iMac, and Apple Watch, said his creative team's purpose "became clear" with the launch of ChatGPT. He argued that our current relationship with technology is broken and that AI presents an opportunity for a fundamental reset. "I think it would be absurd to assume that you could have technology that is this breathtaking, delivered to us through legacy products, products that are decades old," Ive said. "I see it as a chance to use this most remarkable capability to full-on address a lot of the overwhelm and despair that people feel right now." While details of the devices remain secret, Ive spoke of his motivation in deeply human terms. "We love our species, and we want to be useful. We think that humanity deserves much better than humanity generally is given," he said. He emphasized the importance of "care" in the design process, stating, "We sense when people have cared... you sense carelessness. You sense when somebody does not care about you, they care about money and schedule." This collaboration confirms that OpenAI's ambitions are not confined to the cloud; it is actively exploring the physical interface through which humanity will interact with its powerful new intelligence. The Unquenchable Thirst for Compute Underpinning this entire platform strategy is a single, overwhelming constraint: the availability of computing power. In both the private press conference and the un-streamed Developer State of the Union, OpenAI's leadership returned to this theme again and again. "The degree to which we are all constrained by compute... Everyone is just so constrained on being able to offer the services at the scale required to get the revenue that at this point, we're quite confident we can push it pretty far," Altman told reporters. He added that even with massive new hardware partnerships with AMD and others, "we'll be saying the same thing again. We're so convinced... There's so much more demand." This explains the company's aggressive, multi-billion-dollar investment in infrastructure. When asked about profitability, Altman was candid that the company is in a phase of "investment and growth." He invoked a famous quote from Walt Disney, paraphrasing, "We make more money so we can make more movies." For OpenAI, the "movies" are ever-more-powerful AI models. Greg Brockman, OpenAI's President, put the ultimate goal in stark economic terms during the Developer State of the Union. "AI is going to become, probably in the not too distant future, the fundamental driver of economic growth," he said. "Asking 'How much compute do you want?' is a little bit like asking how much workforce do you want? The answer is, you can always get more out of more." As the day concluded and developers mingled at the reception, the scale of OpenAI's project came into focus. Fueled by new models like the powerful GPT-5 Pro and the stunning Sora 2 video generator, the company is no longer just building AI. It is building the world where AI will live -- a world of intelligent apps, autonomous agents, and new physical devices, betting that in the near future, intelligence itself will be the ultimate platform.
[9]
OpenAI: "We never meant to build a chatbot"
Why it matters: OpenAI is following the playbook of Apple, Google, Microsoft and Meta, aiming to turn its product into platforms where developers invest time and money. Driving the news: OpenAI on Monday announced its second effort to allow developers to build apps that run within ChatGPT. * Starting Monday, a handful of apps will appear in ChatGPT -- including Spotify, Zillow, Figma, Canva and Booking.com -- through a partnership with OpenAI. * Next, OpenAI will open ChatGPT to all app developers willing to follow the guidelines it detailed on Monday. The company said it will start reviewing and listing those apps "later this year." * OpenAI promised developers will be able to make money -- somehow -- but how that money will change hands remains murky. * "I would expect us to try a lot of things over the next few months and then, hopefully, we'll find what most of the market wants," Altman told reporters. The big picture: ChatGPT head Nick Turley told Axios that OpenAI sees a chance to expand its popular chatbot into a core way people interact with their devices. * "It's not inconceivable to me that over time, you perceive ChatGPT to be a type of operating system," Turley said in an interview. * "Now, literally speaking, it's obviously running on something; it's not a real OS in that sense," he said. * Turley suggested that ChatGPT will be both an "access point to get into other pieces of software" and a place for developers to innovate. "So, in that sense, it's very much becoming an operating system." Flashback: This isn't OpenAI's first time opening up ChatGPT to developers. * OpenAI launched custom GPTs and its ChatGPT store at its first developer event in 2023. * There was an initial wave of interest in the store, but it largely became a tool for companies to build their own apps for internal use, with no clear way for developers to make money. Between the lines: Just because OpenAI is trying to turn ChatGPT into a platform doesn't mean everything will be done in a conversational chat interface, Turley said during a question-and-answer session with reporters earlier in the day. * "Not all software needs to be a chatbot," Turley said in response to a question from Axios. "Not all interaction with the commercial world needs to be a chatbot." * ChatGPT, Turley said, wasn't even meant to be OpenAI's big bet. "We never meant to build a chatbot," he said. "We meant to build a super assistant and we got a little sidetracked." * Turley said that spending all your time in a chatbot would be a dystopian future, but he sees a path to broadening the experience. * "If we can evolve ChatGPT the right way, if we can let people build into it, then maybe you will be spending a lot of time in ChatGPT, the sort of operating system," Turley told Axios in a follow-up interview. "But it won't feel like you're in a chatbot." Yes, but: OpenAI is far from alone in wanting to be the next platform. * Google, Microsoft and Apple, whose operating systems power the vast majority of phones and computers, are keen to extend those positions into the AI era. * Meanwhile, the tech giants who missed out on the mobile revolution -- Meta and Amazon -- are also keen to position themselves at the center of whatever comes after the phone. * And then there are countless startups who themselves dream of being the next tech giant. The intrigue: Just what hardware we'll be using in a few years' time also remains unsettled. PCs and phones probably won't be going away, but they are likely to be complemented by new devices, including smart glasses.
[10]
OpenAI: You can use third-party apps like Spotify and Canva in ChatGPT
OpenAI and CEO Sam Altman want ChatGPT to evolve beyond a conversational tool into a full-fledged digital assistant -- one that can use other apps for you. The company announced a new initiative to create a "new generation of apps in ChatGPT," allowing users to connect and interact directly with third-party services inside the chatbot. The new feature was unveiled during OpenAI's Dev Day, during which the company showcased several live demos highlighting how this could work in practice. In one example, ChatGPT connected to Spotify to generate a playlist based on the user's favorite songs, created and saved automatically within the Spotify app. Another demo showed an OpenAI engineer tagging Canva in the chat to design a poster for a dog-walking business. After specifying that it should look whimsical and bright with a sans-serif font, ChatGPT returned multiple poster options generated through Canva. The system prompts users for permission the first time an app is connected, but once approved, it can use that app freely in future chats. OpenAI also demonstrated educational and real estate integrations, like creating a machine learning lesson plan via Coursera and finding homes for sale in Pittsburgh through Zillow. Starting today, ChatGPT users can connect to apps including Spotify, Canva, Booking.com, Expedia, Coursera, Zillow, and Figma. Altman added that more integrations, such as DoorDash and Uber, are coming later this year. Additionally, developers will soon be able to submit their own apps for review and publication within ChatGPT. OpenAI also plans to launch a dedicated app directory, giving users an easier way to discover and install integrations. As for monetization, Altman says the company will share more details in the near future. This push marks a key step in OpenAI's broader vision of agentic AI, especially after the company recently introduced Instant Checkout, a feature that lets users make purchases directly in chat.
[11]
ChatGPT gets apps: now you can book a trip, build slides, and make playlists without leaving the chat
Users can access apps like Spotify, Canva, and Zillow directly within conversations with the AI chatbot OpenAI is reshaping ChatGPT to be a whole platform full of apps, going well beyond the usual chatbot setup. The newest feature makes ChatGPT a conversational app store with potentially huge ramifications for how people engage with it. ChatGPT has been moving toward a more proactive approach to answering requests for a while, but the inclusion of third-party apps provided by the likes of Booking.com, Canva, Coursera, Expedia, Figma, Spotify, and Zillow, makes it so you can simply mention a task in a chat and ChatGPT can now call on the relevant services without you needing to click on a link. For instance, you could ask for a new Spotify playlist or help make a real estate listing for Zillow and have it set up on those respective platforms without leaving ChatGPT. And you don't even have to specify which app you want. Mention planning a trip, and ChatGPT might suggest the Expedia or Booking.com app. Or if you're asking about designing a logo, you might see Figma appear as part of ChatGPT's answer. ChatGPT becomes a central command center where conversations turn into actions with a single prompt. The obvious comparison here is to smartphones and the early days of the Apple App Store. But even on your phone, you have to go find and open an app to use it. With ChatGPT apps, the software comes to you based on context as much as by name. You don't open the app. The app joins the conversation. Of course, it's also a power play by OpenAI. After all, becoming a platform, OpenAI now owns the interface and possibly the app economy within it. Much like how Google controls search traffic or how Apple controls mobile distribution, OpenAI could soon determine which apps appear in ChatGPT, how they're ranked, and what it takes to be discoverable. The change is rolling out today for all ChatGPT users, except those within the EU for now. OpenAI says it plans to expand the roster of third-party partners throughout the year, aided by how developers can start building their own apps right now using the SDK. OpenAI hasn't yet laid out exactly how app developers will earn money from this new ecosystem, but a revenue model is inevitable. From the user's perspective, using one of these new ChatGPT apps looks less like installing software and more like inviting a useful guest into your chat. The first time you use a new app, ChatGPT will ask for permission and show you what data it plans to share, with a prompt to connect your accounts if needed. Once connected, these apps are interactive and will offer all sorts of help based on what you've discussed with ChatGPT. Still, if OpenAI's vision pans out, we may look back on today as the day AI stopped being a service and started becoming a storefront.
[12]
OpenAI unveils ChatGPT app integration feature
OpenAI on Monday unveiled a new feature for ChatGPT, the leading generative AI model with 800 million weekly users, enabling it to interact with everyday apps like Spotify and Booking.com. Chief Executive Sam Altman announced the new tool to a crowd of enthusiastic developers gathered in San Francisco for the company's annual "Developer Day." The new feature, Apps SDK, allows ChatGPT to interact with various apps to select music, search for real estate or explore hotel and flight booking sites. Initial partners including Booking.com, Canva, Coursera, Figma, Expedia, Spotify and Zillow launched Monday in markets where their services operate. Additional partners, including Uber, AllTrails and DoorDash, are expected later this year. However, the feature is not yet available in Europe, where rules on deployment of data-heavy AI tools are stricter. The move marks a significant expansion of ChatGPT's capabilities, blending traditional interactive elements like maps and playlists with conversational AI. Users could, for example, ask "Spotify, make a playlist for my party this Friday" and have the music streaming app intervene within the chat. ChatGPT can also suggest apps when relevant to the conversation. For example, if a user is discussing buying a new home, ChatGPT can turn to the Zillow app to browse listings matching their budget on an interactive map inside ChatGPT.
[13]
ChatGPT can now run apps and it forever changes how you get work done
Imagine a future where you don't even have to open the dedicated website or the mobile app of a service, and everything can be done within ChatGPT. Well, that future is finally here. OpenAI has today announced what it calls "apps you can chat with, right inside ChatGPT." The big shift So far, ChatGPT has relied on a system of connectors, where you could link ChatGPT with a third-party service such as Gmail, Drive, Dropbox, and Notion, among others. However, the list of supported services has been extremely limited. Now, OpenAI will let any developer build apps that can be directly accessed within the ChatGPT dialog box. More importantly, you just need to describe the task at hand and name the app to get it done. "You can discover them when ChatGPT suggests one at the right time, or by calling them by name. Apps respond to natural language and include interactive interfaces you can use right in the chat," says the company. Recommended Videos OpenAI is kicking off app support in ChatGPT with partners such as Booking.com, Canva, Coursera, Figma, Expedia, Spotify, and Zillow. These apps will be available to all users, whether they are on the free tier, or pay for a Go, Plus, or Pro subscription. The key takeaway Support for apps that can be summoned right within the ChatGPT command box and getting work done by simply describing it is quite convenient. For example, you can just type something like "Booking, show me homestays for three people over the weekend starting on September 19," and the AI chatbot will do the bidding. OpenAI has already released the SDK so that developers can start building their apps for ChatGPT atop the open Model Context Protocol (MCP) standard. In the coming months, OpenAI will start taking submissions of these apps, which will also offer monetization opportunities, just like the App Store or Google Play Store. This is a huge move as these apps essentially turn ChatGPT into its own ecosystem, just like Android and iOS. And now that ChatGPT already commands 800 million active users, it has a vast ecosystem ready to experience apps in an entirely new and conversational way.
[14]
OpenAI Just Turned ChatGPT Into an App Platform - Decrypt
Together the features shift ChatGPT from chatbot to software platform, aiming to anchor developers -- and users -- inside OpenAI's walled garden. OpenAI is turning ChatGPT into more than a chatbot. It's recasting it as a platform -- one where apps and autonomous agents run inside your conversations. At its developer conference today, the company unveiled two marquee upgrades designed to make ChatGPT the hub for both work and code. A new App SDK lets third parties build fully interactive apps that live inside chats -- so users can book flights through Expedia, design graphics in Canva, or pull listings from Zillow without ever leaving the window. And AgentKit, a drag-and-drop builder for autonomous AI agents, allows developers to design workflows that reason, retrieve data, and act on their own -- all locked within OpenAI's ecosystem. Together, the updates mark OpenAI's most aggressive push yet to transform ChatGPT from a conversational assistant into a full-blown platform -- part super-app, part operating system for reasoning. "Since our first Dev Day we've been working to open up ChatGPT to developers, and we've tried things like GPTs, and adopted standards like MCP (Model Context Protocol)," Altman said in the Opening Keynote in San Francisco earlier today. "Some of that stuff has worked, some hasn't. And today we are going to open up ChatGPT for developers to build real apps inside of ChatGPT." OpenAI's gambit is simple: If the world already runs on apps, then get people to use them inside GPT. Each "app" can respond to natural language cues, call APIs, and return structured results -- effectively giving ChatGPT plug-in-like powers without the clunkiness of a plug-in store. It's a vision borrowed from both WeChat and Salesforce AppExchange: centralize user attention, make third-party services interoperable, and turn ChatGPT into an operating system for reasoning. But unlike WeChat's mini-programs -- written by engineers for fixed tasks -- OpenAI's apps live in a fuzzier zone, where intent replaces buttons and prompts replace clicks. For OpenAI, a robust app layer means more reasons for subscribers to stay inside the ChatGPT environment and fewer to defect to rival models from Anthropic, Google, or Meta. Developers, meanwhile, are offered distribution to a user base north of 200 million, plus monetization hooks via upcoming "usage tiers" and revenue-sharing programs. Under the hood, each app plugs into ChatGPT via OpenAI's new App SDK, a toolkit that handles authentication, permissions, and semantic routing. For example, if a user says, "Find me a two-bedroom in Portland with a yard," then ChatGPT can delegate the query to Zillow, pull listings, then synthesize follow-ups -- "Would you like me to check school ratings?" Opening ChatGPT to external developers introduces the oldest problem in computing: curation. Apple and Google learned that an app store without strict review becomes a spam trap; OpenAI's review process is still opaque. Then there's the UX paradox: The more capable ChatGPT becomes, the more it risks collapsing under its own ambiguity. If half a dozen apps can answer a question, then who decides which one speaks? ChatGPT Agents. The company also unveiled "AgentKit," a platform that lets developers build and deploy autonomous AI agents using a visual drag-and-drop interface. The toolkit includes Agent Builder for workflow design, ChatKit for embeddable interfaces, Evals for performance testing, and Connectors for data integration -- all locked within OpenAI's ecosystem. The move comes as developers have spent the past years jerry-rigging autonomous systems using different tools to make their AI models execute tasks. OpenAI's solution attempts to replace that fragmented approach with a single canvas where users drag blocks, connect logic, and publish production-ready agents. The interface mimics what open-source automation tool n8n has offered for years, except with one critical difference: developers can't swap in competing models. Where n8n allows model-agnostic setups that work with Claude, Gemini, or any other AI via an API key, Agent Kit chains users exclusively to OpenAI's models. Community reactions on X ranged from "OpenAI just killed n8n" to debates about whether the restrictions outweigh the convenience. OpenAI also made Codex -- its GPT-5 model customized for coding tasks -- generally available. The coding agent has seen explosive growth, with usage jumping 10x since early August 2025, serving over 40 trillion tokens in three weeks according to Sam Altman. During the stream, Altman assured that inside OpenAI, nearly all engineers use Codex, resulting in 70% more pull requests merged weekly and automatic reviews of almost every PR. The Codex integration extends to third-party apps such as Slack, where developers can tag @Codex in channels for task delegation. It gathers context, selects environments, and provides completion links. Agent Kit components are rolling out in phases. ChatKit, a chat interface for apps built on ChatGPT, and the Agent Evaluation tool are generally available. Agent Builder remains in beta, while Connectors -- which include pre-built options for Dropbox, Google Drive, SharePoint, and Microsoft Teams -- are in beta for select API, ChatGPT Enterprise, and Edu users. The platform includes open-source Guardrails libraries in Python and JavaScript for safety controls, plus Reinforcement Fine-Tuning for models like o4-mini (generally available) and GPT-5 (private beta), with custom tool calls and graders.
[15]
OpenAI announces Apps SDK allowing ChatGPT to launch and run third party apps like Zillow, Canva, Spotify
OpenAI's annual conference for third-party developers, DevDay, kicked off with a bang today as co-founder and CEO Sam Altman announced a new "Apps SDK" that makes it "possible to build apps inside of ChatGPT," including paid apps, which companies can charge users for using OpenAI's recently unveiled Agentic Commerce Protocol (ACP). In other words, instead of launching apps one-by-one on your phone, computer, or on the web -- now you can do all that without ever leaving ChatGPT. This feature allows the user to log-into their accounts on those external apps and bring all their information back into ChatGPT, and use the apps very similarly to how they already do outside of the chatbot, but now with the ability to ask ChatGPT to perform certain actions, analyze content, or go beyond what each app could offer on its own. "This will enable a new generation of apps that are interactive, adaptive and personalized, that you can chat with," Altman said. While the Apps SDK is available today in preview, OpenAI said it would not begin accepting new apps within ChatGPT or allow them to charge users until "later this year." Built atop common MCP standard Built on the open source standard Model Context Protocol (MCP) introduced by rival Anthropic nearly a year ago, the Apps SDK gives third-party developers working independently or on behalf of enterprises large and small to connect selected data, "trigger actions, and render a fully interactive UI [user interface]" Altman explained during his introductory keynote speech. The Apps SDK includes a "talking to apps" feature that allows ChatGPT and the underlying GPT-5 or other "o-series" models piloting it underneath to obtain updated context from the third-party app or service, so the model "always knows about exactly what you're user is interacting with," according to another presenter and OpenAI engineer, Alexi Christakis. Developers can build apps that: * appear inline in chat as lightweight cards or carousels * expand to fullscreen for immersive tasks like maps, menus, or slides * use picture-in-picture for live sessions such as video, games, or quizzes Each mode is designed to preserve ChatGPT's minimal, conversational flow while adding interactivity and brand presence. Early integrations with Coursera, Canva, Zillow and more... Christakis showed off early integrations of external apps built atop the Apps SDK, including ones from e-learning company Coursera, cloud design software company Canva, and real estate listings and agent connections search engine, Zillow. Altman also announced Apps SDK integrations with additional partners not demoed officially during the keynote including: Booking.com, Expedia, Figma and Spotify and in documentation, said more upcoming partners are on deck: AllTrails, Peloton, OpenTable, Target, theFork, and Uber, representing lifestyle, commerce, and productivity categories. The Coursera demo included an example of how the user onboards to the external app, including a new login screen for the app (Coursera) that appears within the ChatGPT chat interface, activated simply by a text prompt from the user asking: "Coursera can you teach me something about machine learning"? Once logged in, the app launched within the chat interface, "in line" and can render anything from the web, including interactive elements like video. Christakis explained and showed the Apps SDK also supports "picture-in-picture" and "fullscreen" views, allowing the user to choose how to interact with it. When playing a Coursera video that appeared, he showed that it automatically pinned the video to the top of the screen so the user could keep watching it even as they continued to have a back-and-forth dialog in text with ChatGPT in the typical input/output prompts and responses below. Users can then ask ChatGPT about content appearing in the video without specifying exactly what was said, as the Agents SDK pipes the information on the backend, server-side, from the connected app to the underlying ChatGPT AI model. So "can you explain more about what they're saying right now" will automatically surface the relevant portion of the video and provide that to the underlying AI model for it to analyze and respond to through text. In another example, Christakis opened an older, existing ChatGPT conversation he'd had about his siblings' dog walking business and resumed the conversation by asking another third-party app, Canva, to generate a poster using one of ChatGPT's recommended business names, "Walk This Wag," along with specific guidance about font choice ("sans serif") and overall coloration and style ("bright and colorful.") Instead of the user manually having to go and add all those specific elements to a Canva template, ChatGPT went and issued the commands and performed the actions on behalf of the user in the background. After a few minutes, ChatGPT responded with several poster designs generated directly within the Canva app, but displayed them all in the user's ChatGPT chat session where they could see, review, enlarge and provide feedback or ask for adjustments on all of them. Christakis then asked for ChatGPT to turn one of the slides into an entire slide deck so the founders of the dog walking business could present it to investors, which did it in the background over several minutes while he presented a final integrated app, Zillow. He started a new chat session and asked a simple question: "based on our conversations, what would be a good city to expand the dog walking business." Using ChatGPT's optional memory feature, it referenced the dog walk conversation and suggested Pittsburgh, which Christakis used as a chance to type in "Zillow" and "show me some homes for sale there," which called up an interactive map from Zillow with homes for sale and prices listed and hover-over animations, all in-line within ChatGPT. Clicking a specific home also opened a fullscreen view with "most of the Zillow experience," entirely without leaving ChatGPT, including the ability to request home tours and contact agents and filtering by bedrooms and other qualities like outdoor space. ChatGPT pulls up the requested filtered Zillow search as well as provides a text-based response in-line explaining what it did and why. The user can then ask follow-up questions about the specific property -- such as "how close is it to a dog park?" -- or compare it to other properties, all within ChatGPT. It can also use apps in conjunction with its Search function, searching the web to compare the app information (in this case, Zillow) with other sources. Safety, privacy, and developer standards OpenAI emphasized that apps must comply with strict privacy, safety, and content standards to be listed in the ChatGPT directory. Apps must: * serve a clear and valuable purpose * be predictable and reliable in behavior * be safe for general audiences, including teens aged 13-17 * respect user privacy and limit data collection to only what's necessary Every app must also include a clear, published privacy policy, obtain user consent before connecting, and identify any actions that modify external data (e.g., posting, sending, uploading). Apps violating OpenAI's usage policies, crashing frequently, or misrepresenting their capabilities may be removed at any time. Developers must submit from verified accounts, provide customer support contacts, and maintain their apps for stability and compliance. OpenAI also published developer design guidelines, outlining how apps should look, sound, and behave. They must follow ChatGPT's visual system -- including consistent color palettes, typography, spacing, and iconography -- and maintain accessibility standards such as alt text and readable contrast ratios. Partners can show brand logos and accent colors but not alter ChatGPT's core interface or use promotional language. Apps should remain "conversational, intelligent, simple, responsive, and accessible," according to the documentation. A new conversational app ecosystem By opening ChatGPT to third-party apps and payments, OpenAI is taking a major step toward transforming ChatGPT from a chatbot into a full-fledged AI operating system -- one that combines conversational intelligence, rich interfaces, and embedded commerce. For developers, that means direct access to over 800 million ChatGPT users, who can discover apps "at the right time" through natural conversation -- whether planning trips, learning, or shopping. For users, it means a new generation of apps you can chat with -- where a single interface helps you book a flight, design a slide deck, or learn a new skill without ever leaving ChatGPT. As OpenAI put it: "This is just the start of apps in ChatGPT, bringing new utility to users and new opportunities for developers." There remain a few big questions, namely: 1. what happens to all the data from those third-party apps as they interface with ChatGPT and its users...does OpenAI get access to it and can it train upon it? 2. What happens to OpenAI's once much-hyped GPT Store, which had been in the past promoted as a way for third-party creators and developers to create custom, task-specific versions of ChatGPT and make money on them through a usage-based revenue share model? We've asked the company about both issues and will update when we hear back.
[16]
ChatGPT Enters the Super App Era With Apps SDK | AIM
The company also announced a new no-code, drag-and-drop AI agent builder. OpenAI announced a range of new capabilities for ChatGPT at its DevDay event on October 6. The company announced a new Apps SDK, a software development kit that enables developers to allow users to chat directly with apps within ChatGPT. Developers can start building apps to work with ChatGPT using the Apps SDK preview, which is built on the open standard, the Model Context Protocol (MCP). To begin building, developers can access the documentation for guidelines and example apps, and then test apps using Developer Mode in ChatGPT. Users can access third-party applications within ChatGPT by calling them by name or discovering them when they are suggested in a conversation. The feature is available to all ChatGPT users, across all plans, except for those based in the European Union. OpenAI's pilot partners -- Booking.com, Canva, Coursera, Figma, Expedia, Spotify, and Zillow are offering their services using this feature. "More pilot partners will launch later this year, and we expect to bring apps to EU users soon," said OpenAI. For instance, users can access Booking.com through ChatGPT to plan a trip, create designs using Canva, ask follow-up questions after watching a course video on Coursera, build playlists on Spotify, and more. Other apps from partners, such as TripAdvisor, Uber, Khan Academy, Instacart, DoorDash, and more, are expected to arrive soon. OpenAI said that later this year, it will begin accepting app submissions for review and will share more details on how developers can monetise their apps. The announcement has led many to envision the future of ChatGPT as a super app. "OpenAI's APP SDK is a genius move," said Yuchen Jin, co-founder and CTO of Hyperbolic apps. "The goal: make ChatGPT the default interface for everyone, where you can talk to all your apps. ChatGPT becomes the new OS, the place where people spend most of their time," he added in his post on X. "Always wondered if the WeChat platform model could happen for apps in the US," said Ceci Stallsmith, head of marketing of Lovable, in a post on X. "Well done OAI [OpenAI] team." In addition to the Apps SDK, OpenAI also announced a new 'AgentKit', a toolkit for taking agents from prototype to production. Part of it is the Agent Builder, which provides a no-code, visual canvas interface for designing, testing, and shipping agentic workflows. This allows users to build agents using drag-and-drop components, logical flows, and frameworks like MCP. This will directly compete with platforms like Zapier, n8n, Make, and others. "Agent Builder transformed what once took months of complex orchestration, custom code, and manual optimisations into just a couple of hours," said Ramp, an expense management company, in a testimonial. "The visual canvas keeps product, legal, and engineering on the same page, slashing iteration cycles by 70% and getting an agent live in two sprints rather than two quarters." OpenAI also introduced a Connector Registry to unify data from sources like Google Drive, Dropbox, SharePoint, and Microsoft Teams into a single admin panel for ChatGPT and the API, including support for third-party MCPs. The new ChatKit tool lets developers embed chat-based agents directly into their apps and websites. OpenAI also updated its evaluation framework, allowing developers to test prompts and assess model behaviour more effectively. Agent Builder is available in beta, and the Connector Registry is currently on beta rollout to select API, ChatGPT Enterprise, and Edu customers with a Global Admin Console. ChatKit and the new Evals capabilities are generally available to all developers. Other announcements from DevDay include the general availability of OpenAI's Codex, powered by the GPT-5-Codex model. Moreover, the GPT-5 Pro model, the new Sora 2 text-to-video model, and the GPT-realtime-mini voice model are now available in API.
[17]
OpenAI announces ChatGPT apps, embedded Codex coding agent at DevDay - SiliconANGLE
OpenAI announces ChatGPT apps, embedded Codex coding agent at DevDay OpenAI will enable developers to embed their applications into ChatGPT using a new software toolkit called the Apps SDK. Executives revealed the first seven apps that integrate with the chatbot service at OpenAI's DevDay event today. In addition, the artificial intelligence provider detailed an embedded version of its Codex programming agent. Developers can use the agent to build their own coding assistants. The initial roster of embedded ChatGPT apps comprises Booking.com, Canva, Coursera, Figma, Expedia, Spotify and Zillow. Users can launch them in two ways. They can include the name of an app in a prompt or enter a request that doesn't mention a specific app, but describes a task ChatGPT could perform using a third-party service. The user experience varies by app. If a worker asks ChatGPT to turn a sketch into a diagram using Figma, the chatbot will simply display the requested diagram with a link for launching it in Figma. In contrast, requesting Booking.com hotel listings brings up a carousel that displays more than half a dozen data points about each relevant property. Embedded apps can not only perform one-off tasks but also process follow-up prompts. For example, a user could instruct ChatGPT to launch a Coursera course and then ask it to explain concepts introduced during the lecture. Developers can build embedded apps using a toolkit called the Apps SDK that launched today. OpenAI will start accepting app submissions later this year. In the same time frame, the AI provider plans to add apps from nearly a dozen major partners including publicly-traded tech firms such as Uber Technologies Inc. "The Apps SDK builds on the Model Context Protocol (MCP), the open standard that lets ChatGPT connect to external tools and data," OpenAI staffers detailed in a blog post today. "It extends MCP so developers can design both the logic and interface of their apps." The other highlight of DevDay was the launch of OpenAI's Codex coding assistant into general availability. The AI provider rolled out three new features on occasion of the update. OpenAI has added a development toolkit, Codex SDK, that companies can use to embed Codex features into their software. Building an integration requires a few lines of code. On launch, the Codex SDK can be implemented using an enhanced version of JavaScript called TypeScript. The ability to integrate Codex into external applications is rolling out alongside two pre-packaged connectors developed by OpenAI. The first enables users to launch the coding assistant from Slack. The other connector, which works with GitHub's GitHub Actions service, makes it possible to integrate Codex into CI/CD pipelines. Those are automation workflows that reduce the amount of work involved in releasing newly created code to production. Rounding out the enhancements is a set of administrative features. According to OpenAI, information technology teams can now require that developers' Codex installations use secure configuration settings. Additionally, administrators can review Codex output and delete cloud-based software environments created by the AI agent.
[18]
ChatGPT Will Now Let You Interact With Apps Like Canva and Spotify
* Sora 2 and Sora 2 Pro models are now available via API * OpenAI is also making GPT-5 Pro available via API * AgentKit is now available for developers as a modular kit OpenAI DevDay 2025 was hosted by the company on Monday, and multiple announcements for both end-users and developers were made. Among them, the biggest announcement was adding a new capability in ChatGPT that will allow users to work with third-party apps such as Canva and Spotify without leaving its interface. The San Francisco-based artificial intelligence (AI) firm also introduced AgentKit, a developer-focused tool to build, deploy, and optimise agentic workflows. Additionally, the company also made GPT-5 Pro, Sora 2, and Sora 2 Pro available via application programming interface (API). Everything Announced at the OpenAI DevDay 2025 ChatGPT Apps: Building on ChatGPT's agentic capabilities, OpenAI is now allowing software and services to connect to a new ChatGPT software development kit (SDK), which will then allow users to access these apps from the chatbot's interface. It will also let them complete certain tasks in these apps directly via text prompts. Currently, users will be able to use Booking.com, Canva, Coursera, Expedia, Figma, Spotify, and Zillow in the chatbot. However, in the coming weeks, the company plans to add support for more apps such as DoorDash, OpenTable, Target, and Uber. Apps SDK: Alongside ChatGPT apps, the company also released an open standard built on Anthropic's Model Context Protocol (MCP), dubbed Apps SDK. This will allow developers to build and test apps in ChatGPT. App submissions for publication will occur later this year. OpenAI also plans to provide users with a directory to browse these ChatGPT-based apps. The company also promised to share details about the monetisation of these apps soon. Notably, the monetisation could also pave the way for ads on ChatGPT, which was reported last month. Sora 2 and Sora 2 Pro in API: OpenAI has also made the Sora 2 and Sora 2 Pro AI models available via API. Sora 2 can generate videos in 1280x720p resolution, while Sora 2 Pro offers a resolution of up to 1792x1024p. Both models are capable of generating both landscape and portrait videos of up to 12 seconds duration. However, video input and image-to-video of real people is not supported at this time. Notably, there are three variants available. The Sora 2 model is available at the price of $0.1 (roughly Rs. 8.8) per second of generated video, while the base Sora 2 Pro will cost developers $0.3 (roughly Rs. 26.6) for the same duration. Both of these models will generate videos with a watermark. To get watermark-free videos, devs will have to opt for the advanced Sora 2 Pro model, which charges $0.5 (roughly Rs. 44.3) per second of generation. GPT-5 Pro in API: Alongside Sora, the GPT-5 Pro AI model is also available via API. The model uses more compute to think longer and provide more in-depth responses. The AI model is available in the Responses API and supports multi-turn interactions before responding to API requests. It is a fairly expensive offering with $15 (roughly Rs. 1,330) per million input tokens and $120 (roughly Rs. 10,650) for one million output tokens. AgentKit for Developers: OpenAI describes AgentKit as a modular toolkit for building, deploying, and optimising agents. Developers can build an agent workflow, connect to large language models (LLMs), add tools support, add knowledge hubs, and even create voice-based agents. Apart from this, Codex is now generally available, and the GPT-5 API requests are faster on the priority processing tier.
[19]
OpenAI ChatGPT DevDay 2025 : Bold Moves, But Are They Enough?
What happens when a tech giant like OpenAI promises to transform the way we build and interact with AI, and then the dust settles? The much-anticipated OpenAI DevDay 2025 keynote was presented by Sam Altman and team, leaving developers, organizations, and tech enthusiasts buzzing with excitement, skepticism, and plenty of questions. From the unveiling of the Apps SDK for ChatGPT to the introduction of Agent Kit, the event showcased bold strides in AI accessibility and functionality. But not every announcement landed as intended. For all the innovation on display, some features raised eyebrows, while others left attendees wondering if OpenAI's vision for the future is as seamless as it seems. In this breakdown, Sam Witteveen explores what truly stood out and what fell short at DevDay 2025. You'll discover how tools like the Apps SDK and Codex enhancements could reshape workflows and spark creativity, but also why certain promises may face hurdles in real-world adoption. Whether you're a developer eager to harness these tools or a curious observer tracking the evolution of AI, this analysis will unpack the highs, the lows, and the potential ripple effects of OpenAI's latest moves. After all, innovation isn't just about what's announced, it's about what endures. The Apps SDK for ChatGPT introduces a powerful way to create applications directly within the ChatGPT environment. This feature enables you to integrate external tools and services, such as Canva for designing presentations or Coursera for interactive learning, into ChatGPT, transforming it into a versatile hub for productivity, education, and beyond. With this SDK, you can design custom workflows, automate tasks, and build tailored solutions that align with your specific requirements. However, as the platform grows, navigating and discovering apps within ChatGPT may become increasingly challenging. Established partners like Canva or Expedia could dominate visibility, potentially overshadowing smaller developers and niche solutions. Despite these challenges, the Apps SDK offers you a unique opportunity to innovate and create applications that cater to specialized needs, fostering a more personalized and efficient user experience. Agent Kit is a comprehensive toolkit designed to simplify the development, deployment, and optimization of AI agents. It offers several key features that make it accessible to organizations with varying levels of AI expertise: These features lower the barrier to entry, allowing businesses to create internal AI agents for tasks such as customer support, workflow automation, or data analysis. OpenAI has also prioritized safety by incorporating guardrails into the Agent Kit, making sure that your AI agents operate reliably and ethically. Additional functionalities, such as email automation tools, further enhance its versatility, making it a valuable resource for organizations seeking to streamline operations or improve customer engagement. Uncover more insights about OpenAI in previous articles we have written. Codex, OpenAI's AI-powered coding assistant, has received significant updates to enhance its performance and usability. Now generally available, Codex includes new integrations, such as Slack, which improve collaboration and streamline workflows. These integrations allow you to seamlessly incorporate Codex into your existing tools, boosting productivity across teams. In addition to new features, OpenAI has introduced admin tools that provide greater control over coding projects. These tools enable you to manage tasks, monitor progress, and ensure quality across projects of varying complexity. Rather than focusing on introducing entirely new capabilities, OpenAI has refined Codex's existing features to ensure reliability and effectiveness. Whether you are working on small coding tasks or managing large-scale projects, Codex continues to serve as a dependable resource for developers. OpenAI's latest API updates focus on affordability and functionality, making real-time AI applications more accessible to developers. These updates include: These updates are designed to provide you with cost-effective tools for building innovative applications while encouraging broader adoption of AI technologies. By reducing costs and enhancing functionality, OpenAI aims to make advanced AI tools accessible to a wider range of developers and organizations. The announcements at OpenAI DevDay 2025 reflect a strong commitment to expanding the AI ecosystem, improving accessibility for developers, and reducing costs for real-time applications. Whether you are an individual developer exploring new possibilities or part of a larger organization seeking to address complex challenges, these updates offer valuable opportunities to innovate and create impactful solutions. By focusing on usability, affordability, and safety, OpenAI continues to empower you to use AI technologies effectively, shaping a future where AI-driven applications are more accessible and practical than ever before.
[20]
OpenAI Aims to Standardize How to Build AI Agents | PYMNTS.com
By completing this form, you agree to receive marketing communications from PYMNTS and to the sharing of your information with our sponsor, if applicable, in accordance with our Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions. The announcement followed other product updates, including OpenAI's move to let ChatGPT connect directly to external applications and the debut of Instant Checkout, which allows users to make purchases directly within ChatGPT. Together, these updates expand OpenAI's focus from model development to real-world enterprise and consumer transactions. AgentKit is "a complete set of tools for developers and enterprises to build, deploy and optimize agents," the release said. The platform includes Agent Builder, a visual, no-code interface that allows users to design and refine agent logic without writing software. Using a drag-and-drop structure, companies can define the logic, steps and conditions that govern how agents operate. In practice, AgentKit acts as a visual canvas for assembling agent workflows, linking data connectors and embedding chat interfaces, giving businesses a complete ecosystem for developing and governing AI systems. In commerce, the company's Instant Checkout feature demonstrates how conversational AI can directly facilitate purchases. The capability currently supports Etsy sellers in the United States and will expand to other merchants. Customers can complete orders within ChatGPT, while merchants continue to handle payment processing and fulfillment through their existing channels. The launch of AgentKit also coincides with progress in AI payments. PayOS and Mastercard announced Sept. 29 that they completed the first AI-facilitated transaction using Mastercard's tokenization framework. The system allowed an AI agent to make a verified purchase without exposing card details. PayOS said it is working with Mastercard and Visa to extend this technology to additional networks and use cases. These developments align with the industry's shift toward what is often called agentic commerce. Mastercard's Agent Pay program introduces agentic tokens, which build upon the company's tokenization capabilities and are intended to support AI agents transacting on behalf of consumers. Meanwhile, Visa Intelligent Commerce enables AI agents to securely purchase items using tokenized credentials, combining authentication, identity controls and transaction limits. AgentKit operates at the coordination layer of this ecosystem. While payment networks manage authentication and settlement, OpenAI's system structures how automated actions occur and how they are reviewed. Businesses could use it to reconcile invoices, send payment confirmations or generate financial summaries for approval, with each step logged for auditability. The introduction of AgentKit suggests that OpenAI is positioning itself within this same infrastructure layer. Rather than facilitating payments directly, it defines how AI agents can operate within verified environments already established by payment networks and enterprise platforms. OpenAI Chief Operating Officer Brad Lightcap said in a Monday interview with Bloomberg that 2025 is "the year of AI agents," referencing the company's expanding infrastructure investments and enterprise partnerships, including its collaboration with AMD. These efforts position OpenAI as a core supplier of AI automation platforms, he added. OpenAI's $500 billion valuation reflects growing investor confidence in AI systems designed for secure, operational deployment across industries.
[21]
OpenAI introduces apps such as Figma, Zillow into ChatGPT; also launches agent builder and Codex update
Microsoft-backed (NASDAQ:MSFT) OpenAI introduced a new way for users to interact with ChatGPT today with the launch of Apps SDK, which provides access to various apps within the ChatGPT dialogue window. OpenAI CEO Sam Altman revealed Apps SDK during his Apps SDK allows developers to integrate directly within ChatGPT, leading to increased app availability and user engagement. AgentKit enables rapid deployment of AI agents, while Codex SDK's now-general availability and capabilities make software creation easier and faster for businesses. Figma's shares jumped 10%, DoorDash rose nearly 4%, and other related companies saw positive movements after the announcement.
[22]
OpenAI introduces Apps and AgentKit to expand ChatGPT's agent capabilities
OpenAI has unveiled a new generation of interactive apps inside ChatGPT, alongside AgentKit -- a complete toolkit for building, deploying, and optimizing AI agents. The update expands ChatGPT's capabilities with in-chat app experiences while giving developers a unified platform to create, test, and manage agentic workflows efficiently. The new Apps in ChatGPT feature allows users to interact with third-party services directly within conversations. These apps understand natural language, include interactive elements such as maps, playlists, and slides, and appear automatically when relevant to a discussion. Users can activate an app by starting a message with its name -- for example, "Spotify, make a playlist for my party this Friday." ChatGPT will surface the app and prompt for connection approval, explaining what data may be shared. Apps can also appear contextually. For instance, during a conversation about buying a home, ChatGPT may suggest Zillow to browse property listings on an interactive map inside the chat. This update blends familiar interfaces with conversational flexibility, enabling users to create presentations with Canva, explore travel options via Expedia, or take courses from Coursera -- all without leaving ChatGPT. Early partner apps OpenAI launched the first set of integrated apps from Booking.com, Canva, Coursera, Expedia, Figma, Spotify, and Zillow, available starting today for English-language ChatGPT users outside the EU. The company said feedback from these early partners shaped the Apps SDK now available in preview for developers. Developers can build their own ChatGPT apps using the new Apps SDK, built on the Model Context Protocol (MCP) -- an open standard that connects ChatGPT to external tools and data. The SDK extends MCP to let developers define both the app's logic and interface, and connect it directly with their backend for user authentication or premium access. OpenAI has open-sourced the Apps SDK so apps created with it can run on any platform adopting the MCP standard. Documentation, design guidelines, and example repositories are also available to help developers design conversational, interactive experiences. Safety and privacy OpenAI stated that all apps in ChatGPT must comply with usage policies, partner rules, and audience-appropriate content standards. Developers are required to include clear privacy policies, collect only necessary data, and disclose all permissions. When users connect an app for the first time, ChatGPT outlines what data will be shared. Later this year, OpenAI plans to offer granular data controls so users can choose which categories of personal data apps can access. What's next for ChatGPT apps OpenAI will expand app access to ChatGPT Business, Enterprise, and Edu later this year. Developers will be able to submit apps for review and publication, and users will gain a dedicated app directory to browse and search. Apps meeting OpenAI's quality standards will be eligible for enhanced visibility, and OpenAI plans to support monetization via the upcoming Agentic Commerce Protocol for instant in-chat checkout. Alongside apps, OpenAI introduced AgentKit, a comprehensive suite that unifies tools for building, deploying, and improving AI agents. Previously, agent creation required complex orchestration, separate connectors, and manual evaluations. AgentKit simplifies this with new modules designed for faster, safer, and more reliable workflows. AgentKit integrates Guardrails, an open-source safety layer that prevents unintended agent behavior by masking or flagging personal data, detecting jailbreaks, and enforcing policy-based constraints. It also introduces new evaluation features through the Evals platform, adding: These tools help developers measure and refine agent reliability across different tasks and models. Reinforcement fine-tuning and custom grading OpenAI is expanding Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (RFT) to customize model reasoning. RFT is now generally available on o4-mini and in private beta for GPT-5. The update adds custom tool calls and custom graders, allowing developers to train agents to use tools more effectively and define evaluation criteria specific to their needs. AgentKit consolidates every step of agent creation and deployment into one system. Developers can design workflows using Agent Builder, implement logic through the Agents SDK (available for Python, Node, and Go), deploy chat experiences via ChatKit, and evaluate performance using Evals -- all within a unified ecosystem. This integration aims to make agent development faster, more reliable, and easier to scale across products and organizations. OpenAI plans to add a standalone Workflows API and new agent deployment options to ChatGPT in the coming months.
[23]
OpenAI DevDay 2025 - Apps Within ChatGPT, AI Agent Kit, etc.
At the OpenAI third annual DevDay conference, CEO Sam Altman said that the AI company is going to create an application marketplace-style directory to integrate more apps into ChatGPT's ecosystem, allowing users to access them simply by “talking to apps†without the need for visiting the primary app. The existing onboarding apps range from ed-tech and content creation platforms, to e-commerce platforms. Among others, OpenAI outlined four key features for app developers and coders at the DevDay, which are as follows: Notably, Altman revealed a few statistics to showcase the recent growth of OpenAI. For context, in 2023, the company had 2 million developers, 100 million weekly ChatGPT users, and processed about 300 million tokens per minute through its API. However, by 2025, the company said that those numbers reached 4 million developers, more than 800 million weekly users, and about 6 billion tokens per minute. OpenAI is opening ChatGPT to third-party apps through an Apps software development kit (SDK), available for preview to all non-EU users. Altman said the feature allows developers to connect their full-stack applications, enabling them to access data, trigger actions, and display a fully interactive user interface within ChatGPT. For context, the SDK is built on the open Model Context Protocol (MCP) standard. To explain, MCP provides a standardised way for AI systems to access external data, tools, and services, similar to large language models (LLMs). Altman also laid out plans for a an app marketplace-like platform to make ChatGPT more interoperable. The AI company is going to open this feature for more developers who can submit their apps for "review and publication" into a directory for the users to browse. Alexi Christakis, a Technical Staff Member at OpenAI, called this feature "talking to apps". He demonstrated how users can access ChatGPT-partnered websites, like Coursera, within the AI model by connecting their Coursera account to the chatbot. Currently, a user can connect ChatGPT to third-party apps to delegate tasks across a range of platformsincluding Booking.com, Canva, Expedia, Figma, Spotify and Zillow. The company also highlighted e-commerce within the application, as Altman said that OpenAI will launch an “agentic commerce protocol†that enables instant checkout directly within ChatGPT. He emphasised discovery and scale, saying that apps will be “displayed in line with the conversationâ€, and “can be discovered by asking for them by nameâ€. "AI has evolved from 'systems you can ask anything' to 'systems that can do anything for you'," Altman said while announcing OpenAI's Agent Kit. He added that similar progress can be seen in AI agents as they gain more “context, tools and trustâ€. He defined AgentKit as "building blocks" within ChatGPT that can take the prototype of an AI agent to production. It is a "complete set of tools for developers and enterprises" to build their own AI agents. Some aspects of this agent kit include: The blog post says that developers can enable the open-source, modular guardrails in Agent Builder to prevent "unintended or malicious behaviour" within AI models. OpenAI claims that LY Corporation, a Japanese technology and internet services company, built a work assistant agent using Agent Builder in under two hours. Meanwhile to test an agent's performance, OpenAI has the Evals API: that can enable developers to test their prompts and measure an AI model's performance. Notably, this year OpenAI has announced four new features to build Evals: Interestingly, OpenAI is also releasing Sora 2 through the API. Besides the general video generation and modification to the real camera-shot videos, Altman pointed out that Sorai is "great for concept development", saying that the general "vibe" of the product can give a visual starting point. However, it is important to note that when OpenAI launched Sora 2, it faced a lot of criticism as it blatantly used copyrighted and intellectual property-related material to generate content from user-given prompts. For context, an API allows several software applications to communicate with each other, which means that developers can send text prompts to ChatGPT from their own applications and receive ChatGPT-generated responses in return. Consequently, this can let businesses and developers integrate ChatGPT’s capabilities directly into websites, apps, or other software, automating content creation at scale without manually using ChatGPT’s main visual interface. Elsewhere, Altman announced that GPT-5 Pro, the "most intelligent model OpenAI ever shipped", is available through API. Along with this, he also announced the 70% cheaper voice model, "gpt-realtime-mini" with the same audio quality, remarking that voice interactions might become the primary way for people to interact with AI. Altman also announced that Codex is now out of general preview and "generally available". For context, it was launched as a “preview†in May 2025, and operates across integrated development environments, terminals, GitHub, and cloud platforms. Notably, it runs on GPT-5. Altman also claimed that since August, the daily messages on CodeX have jumped 10 times, highlighting that 40 trillion tokens were used. The AI company has integrated Codex with Slack, created its SDK, and enterprise control with more admin controls and dashboards, etc. It means that users can integrate their workflows into ChatGPT using the Codex SDK. Notably, users can trigger Codex by using the @codex keyword in their chat. Altman ended his keynote address saying that "you just need an idea", dismissing the need for a team to build a product.
[24]
From Canva to Coursera: Why so many apps are rushing into ChatGPT's new app ecosystem
OpenAI's latest move has officially turned ChatGPT into more than just a conversational assistant - it's now a platform. With the introduction of apps inside ChatGPT and a new Apps SDK that lets developers build directly for it, OpenAI is positioning its flagship product as a digital ecosystem where users can do everything from booking trips to building designs - without ever leaving the chat. The early lineup is impressive: Canva, Coursera, Expedia, Figma, Spotify, Zillow, and Booking.com are among the first wave of companies integrating into ChatGPT's interface. Each brings a distinct service, but their motivations converge on the same point - they all want to be where users increasingly are: inside AI conversations. Also read: DevDay 2025: OpenAI brings third-party apps inside ChatGPT, check details This isn't OpenAI's first experiment with external tools. Earlier attempts with "plugins" in 2023 hinted at the potential, but the new apps framework is more polished, more integrated, and far more ambitious. It allows users to directly invoke partner services by name - "Spotify, make me a focus playlist" or "Canva, design a poster for my café." Apps in ChatGPT are interactive and contextual. Instead of redirecting users to websites, they deliver dynamic results inside the chat window. You can preview a design, explore a course, or browse homes on Zillow, all without breaking the flow of conversation. Underneath it all sits OpenAI's Model Context Protocol (MCP), a new open standard for connecting AI systems to external data and tools. MCP is what allows ChatGPT to talk to these services securely, passing only the data required for each task. Also read: OpenAI DevDay 2025: Jony Ive hints at AI devices that 'make us happy' For platforms like Canva and Figma, ChatGPT offers a direct line to millions of users who already rely on AI for creative tasks. "If you think about how people ideate now, it often starts with a prompt," said one Canva product manager. "Integrating with ChatGPT lets us meet users at that moment of inspiration." For Coursera, the motivation is similar but more educational. A user might ask ChatGPT for help learning Python, and the assistant could instantly surface a Coursera course, preview its modules, or even enroll the user directly. The AI becomes both a tutor and a gateway to structured learning. Travel platforms like Expedia and Booking.com see this as the next phase of digital convenience. Instead of toggling between websites to compare hotels or flights, users can ask ChatGPT to summarize options, check availability, and even make reservations in one conversational flow. The rush also speaks to a bigger shift in how tech companies think about discovery. For years, app stores and search engines have been the main gateways to digital content. But as AI interfaces become more personalized, contextual, and voice-driven, traditional discovery channels risk being displaced. Being inside ChatGPT could soon be as critical as being at the top of a Google search. With the Apps SDK, developers can now build experiences that merge natural language with interactive logic, think of a Spotify playlist builder that adapts to your chat history or a design tool that evolves as you refine your prompt. OpenAI is currently offering this SDK in preview, but developers can already test and deploy apps privately through a new Developer Mode inside ChatGPT. The company promises monetization and app store-style discovery later this year, signaling an eventual ecosystem where AI-native apps could flourish. Analysts are calling it an "App Store moment" for AI, a comparison that feels apt. Apple's App Store catalyzed the mobile software revolution; OpenAI's ecosystem could do the same for AI services. Of course, all this integration comes with data considerations. Every time you connect an app, you're asked to grant permissions and view what data will be shared. OpenAI emphasizes transparency, saying apps must disclose their privacy policies and collect only what's necessary. Still, privacy experts warn that centralizing so much personal and behavioral data inside a single interface poses new challenges. OpenAI says more apps, including AllTrails, Peloton, Uber, and Target, are on the way. In the coming months, it plans to expand access to ChatGPT Plus, Team, and Enterprise users, followed by a public app directory and monetization options. For now, the message from the tech world is clear: the future of app interaction might not live on your phone's home screen - it might live in a conversation. And that's exactly where Canva, Coursera, and hundreds of other digital services want to be when the next wave of AI-native computing takes off.
Share
Share
Copy Link
OpenAI's DevDay 2025 unveils a new era for ChatGPT, introducing in-app functionality and positioning it as a potential operating system for AI-driven commerce. This move could reshape online shopping and digital interactions.
OpenAI's Vision for ChatGPT as an App Platform
At OpenAI's annual DevDay 2025, the company unveiled a groundbreaking transformation of ChatGPT, positioning it as a comprehensive app platform and potential operating system for AI-driven services
1
. This move marks a significant evolution in ChatGPT's functionality, moving beyond its traditional question-answering format to become a central hub for various digital interactions and commerce.
Source: Seeking Alpha
The Apps SDK: A New Frontier for Developers
The cornerstone of this transformation is the introduction of the Apps SDK, which allows developers to build interactive applications directly within the ChatGPT interface
2
. This new capability enables users to access services from companies like Spotify, Figma, Coursera, Zillow, and Canva without leaving the ChatGPT window. The integration is designed to be seamless, with users able to call up specific apps by name or have ChatGPT suggest relevant apps based on the conversation context3
.
Source: Digit
AI-Driven Commerce: A New Competitive Arena
OpenAI's strategic move positions ChatGPT at the forefront of AI-driven commerce. By integrating payment infrastructure through Instant Checkout and providing a front-end for service providers, OpenAI is creating a comprehensive ecosystem for online transactions
1
. This development could potentially challenge established e-commerce giants like Amazon and Walmart, as ChatGPT becomes a portal for users' discretionary spending.The Future of ChatGPT: An AI Operating System
Nick Turley, Head of ChatGPT, envisions the platform evolving into something akin to an operating system over the next six months
3
. This transformation aims to provide users with access to both existing software and new, natively built applications, offering a more integrated and personalized digital experience.Implications for Users and Developers
For users, this evolution promises a more streamlined digital experience, with the ability to perform various tasks and access multiple services through a single, AI-powered interface
4
. Developers, on the other hand, gain a new platform to build and distribute their applications, potentially reaching ChatGPT's vast user base of over 800 million weekly active users4
.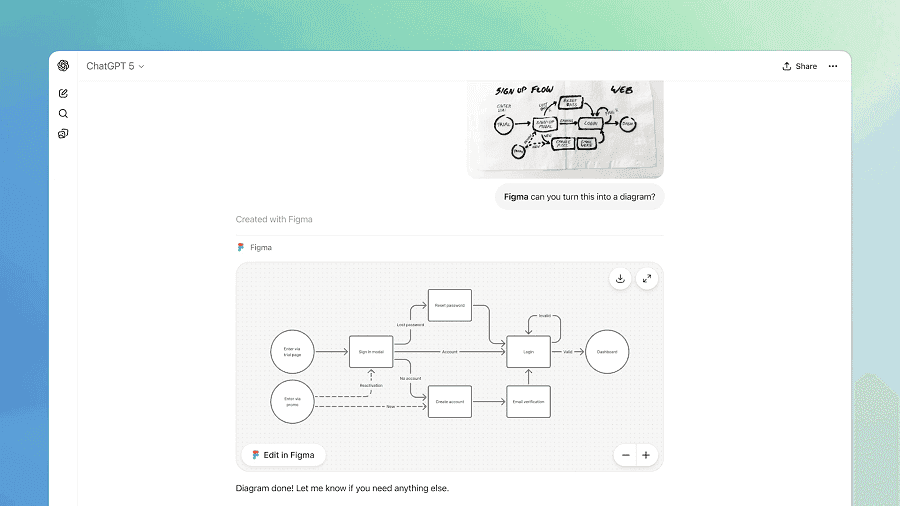
Source: SiliconANGLE
Related Stories
Challenges and Considerations
As OpenAI expands ChatGPT's capabilities, questions arise about how the platform will recommend apps and manage the potential for bias or unfair promotion
4
. Additionally, the economic model for app developers and OpenAI's role in this new ecosystem remains to be fully defined5
.The Road Ahead
With the Apps SDK now available in preview for developers, and plans to allow app submissions for review later in the year, the tech industry is poised for a new wave of AI-integrated applications . As ChatGPT continues to evolve, it may redefine how users interact with digital services and conduct online commerce, potentially reshaping the landscape of the internet itself.
References
Summarized by
Navi
[1]
[2]
[5]
Related Stories
Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.4, New AI Model Built for Agents and Professional Work
Technology

2
Anthropic takes Pentagon to court over unprecedented supply chain risk designation
Policy and Regulation

3
Meta smart glasses face lawsuit and UK probe after workers watched intimate user footage
Policy and Regulation