AI-Assisted Creation of Comprehensive Human Cell Map Unveils New Protein Functions
2 Sources
2 Sources
[1]
A comprehensive map of the human cell
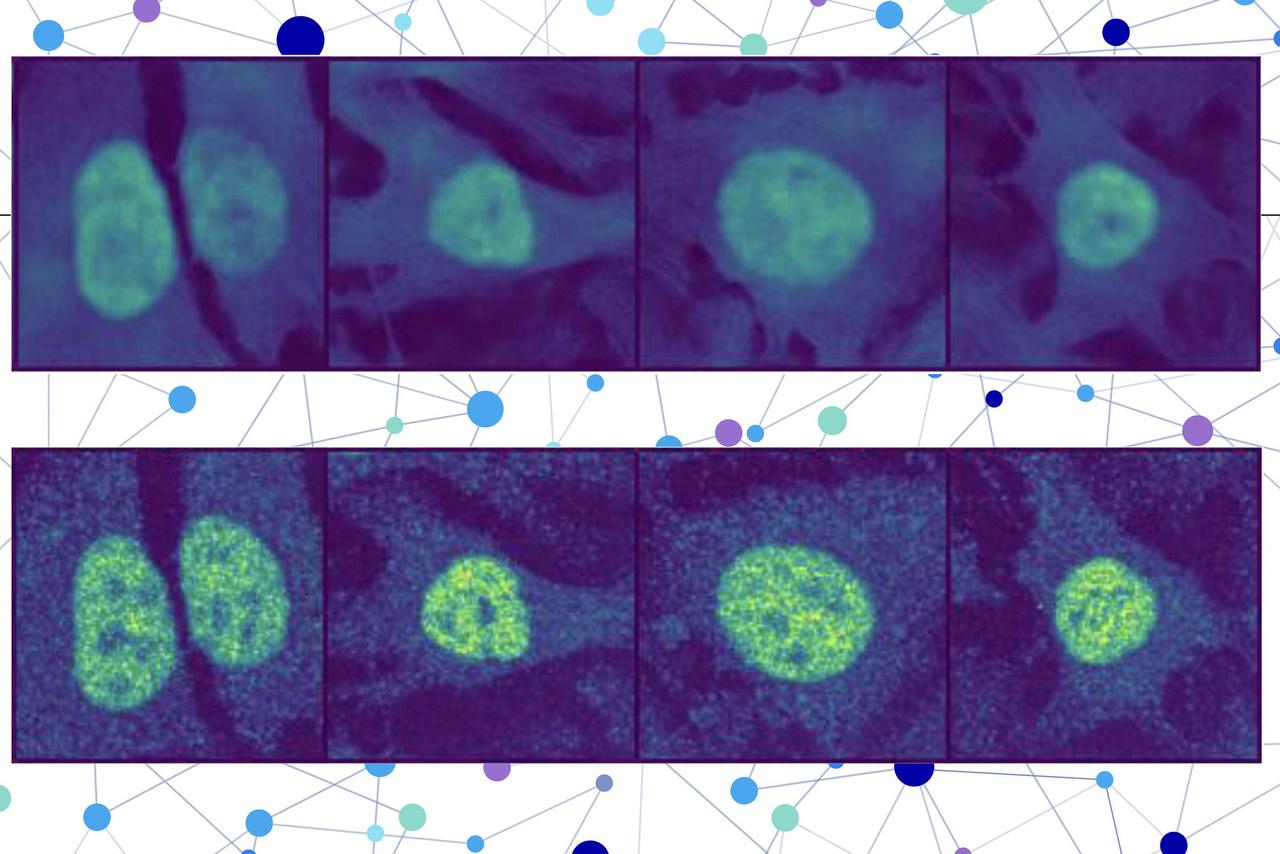
Scientists have attempted to map the human cell since the first microscope was invented more than 400 years ago. But many components of the cell still remain uncharted. "We know each of the proteins that exist in our cells, but how they fit together to then carry out the function of a cell still remains largely unknown across cell types," said Leah Schaffer, Ph.D., a postdoctoral research scholar at UC San Diego School of Medicine. Now, Schaffer and her colleagues at UC San Diego -- in collaboration with researchers at Stanford University, Harvard Medical School and the University of British Columbia -- have created a comprehensive, interactive map of U2OS cells, which are associated with pediatric bone tumors. They combined high-resolution microscope imaging and biophysical interactions of proteins to map the subcellular architecture and protein assemblies in the cell. The map revealed previously unknown protein functions and will help the researchers understand how mutated proteins contribute to diseases such as childhood cancers. It will also serve as a reference for developing maps of other cell types. The study will be published on April 9, 2025 in Nature. "Based on cell biology 101 and textbook pictures of cells, you might think that we understand everything about a cell. But what's remarkable is that for no human cell type do we really have a proper parts catalog and assembly manual," said co-senior author Trey Ideker, Ph.D., a professor of medicine, adjunct professor in Jacobs School of Engineering and member of Moores Cancer Center at UC San Diego. The researchers used a technique called affinity purification to isolate individual proteins and document their interactions with other proteins. In addition, they analyzed more than 20,000 images of the interior of cells marked with fluorescent dye to light up the location of proteins of interest from the Human Protein Atlas. Combining these data for more than 5,100 proteins revealed 275 distinct protein assemblies of different sizes within U2OS cells. "Historically, scientists have been biased by the notion that one gene codes for one protein that has one function," said co-senior author Emma Lundberg, Ph.D., associate professor of bioengineering and of pathology at Stanford University. "However, there is now an increasing number of known multifunctional proteins, and while we're probably still underestimating how many there are, this study demonstrates the importance of multimodal data integration to reveal these multifunctional properties." The researchers discovered 975 previously unknown functions for proteins in the map. For example, C18orf21 -- a recently discovered protein whose function was previously unknown -- appears to be involved with RNA processing, according to the study, and the DPP9 protein, known to cut proteins at specific regions, is implicated in interferon signaling, which is important for fighting infection. The model drew upon a huge knowledge base it absorbed from the scientific literature on proteins, according to co-first author Clara Hu, a biomedical sciences doctoral candidate in Ideker's lab. The researchers asked GPT-4 -- a large language model artificial intelligence tool similar to ChatGPT -- for the function of individual proteins and how they worked together in protein assemblies. This took a fraction of the time it would take a human researcher, says Hu. This GPT-4-based analysis tool, recently published in Nature Methods, summarized the common theme of each protein assembly and proposed names for them, which were used in the cell map. "We're able to, in an unbiased manner, really look at how these parts fit together and how to look at them in the context of disease," said Schaffer. In fact, by locating mutated proteins on the cell map, the researchers were able to identify 21 assemblies frequently mutated in childhood cancer. Within these groups, 102 mutated proteins were found to be strongly linked to cancer development, thanks to the study. The findings have implications for how cancer research is conducted at the molecular and cellular level. "We need to stop looking at the level of individual mutations, which are very rare, sporadic, and almost never recur in the same way twice, and start looking at the common machinery inside of cells that is disrupted or hijacked by these mutations," said Ideker. Schaffer says browsing the U2OS cell map is similar to navigating an online geographical map. "You're able to really explore, zoom in, and see what proteins are part of these different communities, and then see where those communities are located," she said. "As you increase resolution, you can see even more detail-level information," said Hu. The team is currently working on resolving the map even further so that users can zoom in as much as they want at a high resolution. The researchers think the U2OS cell atlas will not only facilitate a better understanding of childhood cancers, but will also provide a blueprint for scientists who want to map other cell types, use artificial intelligence tools to uncover the function of poorly-understand proteins and protein complexes, and decipher the mechanisms behind a wide variety of disease processes. Additional co-authors on the study include: Gege Qian, Dorothy Tsai, Nicole M. Mattson, Katherine Licon, Robin Bachelder, Yue Qin, Xiaoyu Zhao, Christopher Churas, Joanna Lenkiewicz, Jing Chen from University of California San Diego, Kei Ono, Peter Zage, all at UC San Diego; Kyung-Mee Moon and Leonard J. Foster at University of British Columbia; Abantika Pal, Neelesh Soni, Andrew P. Latham Aji Palar, Andrej Sali, and Ignacia Echeverria at University of California San Francisco; Steven P. Gygi, Laura Pontano Vaites, Edward L. Huttlin, and J. Wade Harper at Harvard Medical School; Anthony Cesnik, Ishan Gaur, Trang Le, William Leineweber, Ernst Pulido at Stanford University. The study was funded, in part, by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) (grants: Bridge2AI Program OT2 OD032742, U54 CA274502, R01GM083960, P41GM109824, U24 HG006673), Schmidt Futures, the Wallenberg Foundation (2021.0346) and the Göran Gustafsson Foundation.
[2]
Interactive map of the human cell reveals previously unknown protein functions
Scientists have attempted to map the human cell since the first microscope was invented more than 400 years ago. But many components of the cell still remain uncharted. " We know each of the proteins that exist in our cells, but how they fit together to then carry out the function of a cell still remains largely unknown across cell types," said Leah Schaffer, Ph.D., a postdoctoral research scholar at UC San Diego School of Medicine. Now, Schaffer and her colleagues at UC San Diego -- in collaboration with researchers at Stanford University, Harvard Medical School and the University of British Columbia -- have created a comprehensive, interactive map of U2OS cells, which are associated with pediatric bone tumors. The study was published in Nature. They combined high-resolution microscope imaging and biophysical interactions of proteins to map the subcellular architecture and protein assemblies in the cell. The map revealed previously unknown protein functions and will help the researchers understand how mutated proteins contribute to diseases such as childhood cancers. It will also serve as a reference for developing maps of other cell types. "Based on cell biology 101 and textbook pictures of cells, you might think that we understand everything about a cell. But what's remarkable is that for no human cell type do we really have a proper parts catalog and assembly manual," said co-senior author Trey Ideker, Ph.D., a professor of medicine, adjunct professor in Jacobs School of Engineering and member of Moores Cancer Center at UC San Diego. The researchers used a technique called affinity purification to isolate individual proteins and document their interactions with other proteins. In addition, they analyzed more than 20,000 images of the interior of cells marked with fluorescent dye to light up the location of proteins of interest from the Human Protein Atlas. Combining these data for more than 5,100 proteins revealed 275 distinct protein assemblies of different sizes within U2OS cells. "Historically, scientists have been biased by the notion that one gene codes for one protein that has one function," said co-senior author Emma Lundberg, Ph.D., associate professor of bioengineering and of pathology at Stanford University. "However, there is now an increasing number of known multifunctional proteins, and while we're probably still underestimating how many there are, this study demonstrates the importance of multimodal data integration to reveal these multifunctional properties." The researchers discovered 975 previously unknown functions for proteins in the map. For example, C18orf21 -- a recently discovered protein whose function was previously unknown -- appears to be involved with RNA processing, according to the study, and the DPP9 protein, known to cut proteins at specific regions, is implicated in interferon signaling, which is important for fighting infection. The model drew upon a huge knowledge base it absorbed from the scientific literature on proteins, according to co-first author Clara Hu, a biomedical sciences doctoral candidate in Ideker's lab. The researchers asked GPT-4 -- a large language model artificial intelligence tool similar to ChatGPT -- for the function of individual proteins and how they worked together in protein assemblies. This took a fraction of the time it would take a human researcher, says Hu. This GPT-4-based analysis tool, published in Nature Methods, summarized the common theme of each protein assembly and proposed names for them, which were used in the cell map. "We're able to, in an unbiased manner, really look at how these parts fit together and how to look at them in the context of disease," said Schaffer. In fact, by locating mutated proteins on the cell map, the researchers were able to identify 21 assemblies frequently mutated in childhood cancer. Within these groups, 102 mutated proteins were found to be strongly linked to cancer development, thanks to the study. The findings have implications for how cancer research is conducted at the molecular and cellular level. "We need to stop looking at the level of individual mutations, which are very rare, sporadic, and almost never recur in the same way twice, and start looking at the common machinery inside of cells that is disrupted or hijacked by these mutations," said Ideker. Schaffer says browsing the U2OS cell map is similar to navigating an online geographical map. "You're able to really explore, zoom in, and see what proteins are part of these different communities, and then see where those communities are located," she said. "As you increase resolution, you can see even more detail-level information," said Hu. The team is currently working on resolving the map even further so that users can zoom in as much as they want at a high resolution. The researchers think the U2OS cell atlas will not only facilitate a better understanding of childhood cancers, but will also provide a blueprint for scientists who want to map other cell types, use artificial intelligence tools to uncover the function of poorly understood proteins and protein complexes, and decipher the mechanisms behind a wide variety of disease processes.
Share
Share
Copy Link
Scientists have developed an interactive map of human cells using AI, revealing previously unknown protein functions and assemblies. This breakthrough has significant implications for understanding diseases like childhood cancers.

Groundbreaking Human Cell Map Created with AI Assistance
In a significant scientific breakthrough, researchers have developed a comprehensive, interactive map of human cells, revealing previously unknown protein functions and assemblies. The study, published in Nature on April 9, 2025, combines high-resolution microscope imaging, biophysical protein interactions, and artificial intelligence to create a detailed "parts catalog and assembly manual" for U2OS cells, which are associated with pediatric bone tumors
1
.Collaborative Effort and Innovative Techniques
The research team, led by scientists from UC San Diego, Stanford University, Harvard Medical School, and the University of British Columbia, employed a variety of cutting-edge techniques to create this groundbreaking cell map
2
. They used affinity purification to isolate individual proteins and document their interactions, analyzed over 20,000 fluorescent-dyed cell images, and integrated data from more than 5,100 proteins to reveal 275 distinct protein assemblies within U2OS cells.AI-Powered Analysis and Discovery
One of the most innovative aspects of this research was the use of GPT-4, a large language model AI tool, to analyze the vast amount of scientific literature on proteins. This AI-assisted approach allowed researchers to quickly determine the functions of individual proteins and how they work together in protein assemblies, significantly accelerating the research process
1
.New Insights into Protein Functions
The study uncovered 975 previously unknown functions for proteins. For example, the recently discovered protein C18orf21, whose function was previously unknown, was found to be involved in RNA processing. Additionally, the DPP9 protein, known for cutting proteins at specific regions, was implicated in interferon signaling, which is crucial for fighting infections
2
.Implications for Cancer Research
By mapping mutated proteins on the cell map, the researchers identified 21 assemblies frequently mutated in childhood cancer, with 102 mutated proteins strongly linked to cancer development. This finding has significant implications for cancer research, suggesting a shift in focus from individual mutations to the common cellular machinery disrupted by these mutations
1
.Related Stories
Interactive and Expandable Map
The U2OS cell map is designed to be interactive, allowing users to explore and zoom in on different protein communities and their locations within the cell. The research team is currently working on improving the map's resolution to provide even more detailed information
2
.Future Applications and Research Directions
This groundbreaking cell atlas is expected to have far-reaching implications beyond childhood cancer research. It provides a blueprint for mapping other cell types, using AI tools to uncover functions of poorly understood proteins and protein complexes, and deciphering mechanisms behind various disease processes
1
.References
Summarized by
Navi
[1]
Related Stories
Human Cell Atlas Project Leverages AI to Transform Understanding of Disease
21 Nov 2024•Science and Research

AI Model Predicts Protein Location in Human Cells, Advancing Disease Research and Drug Development
16 May 2025•Science and Research
AI-Powered CellTransformer Creates Most Detailed Mouse Brain Map to Date
07 Oct 2025•Science and Research
Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.4, New AI Model Built for Agents and Professional Work
Technology

2
Anthropic sues Pentagon over supply chain risk label after refusing autonomous weapons use
Policy and Regulation

3
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round as questions swirl around AI bubble and profitability
Business and Economy





