AI Model Detects Fatty Liver Disease in Chest X-Rays, Revolutionizing Early Diagnosis
2 Sources
2 Sources
[1]
AI sees what doctors miss: Fatty liver disease hidden in chest x-rays
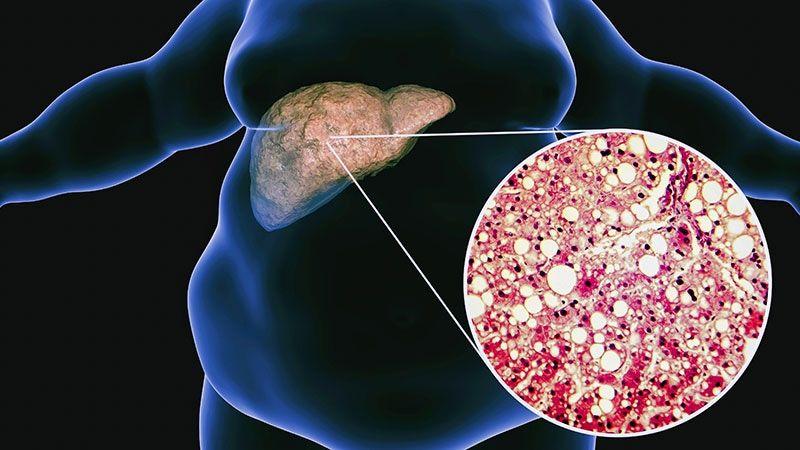
Currently, standard tests for diagnosing fatty liver disease include ultrasounds, CTs, and MRIs, which require costly specialized equipment and facilities. In contrast, chest X-rays are performed more frequently, are relatively inexpensive, and involve low radiation exposure. Although this test is primarily used to examine the condition of the lungs and heart, it also captures part of the liver, making it possible to detect signs of fatty liver disease. However, the relationship between chest X-rays and fatty liver disease has rarely been a subject of in-depth study. Therefore, a research group led by Associate Professor Sawako Uchida-Kobayashi and Associate Professor Daiju Ueda at Osaka Metropolitan University's Graduate School of Medicine developed an AI model that can detect the presence of fatty liver disease from chest X-ray images. In this retrospective study, a total of 6,599 chest X-ray images containing data from 4,414 patients were used to develop an AI model utilizing controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) scores. The AI model was verified to be highly accurate, with the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) ranging from 0.82 to 0.83. "The development of diagnostic methods using easily obtainable and inexpensive chest X-rays has the potential to improve fatty liver detection. We hope it can be put into practical use in the future," stated Professor Uchida-Kobayashi.
[2]
AI detects fatty liver disease with chest X-rays
Fatty liver disease, caused by the accumulation of fat in the liver, is estimated to affect one in four people worldwide. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications, such as cirrhosis and liver cancer, making it crucial to detect early and initiate treatment. Currently, standard tests for diagnosing fatty liver disease include ultrasounds, CTs, and MRIs, which require costly specialized equipment and facilities. In contrast, chest X-rays are performed more frequently, are relatively inexpensive, and involve low radiation exposure. Although this test is primarily used to examine the condition of the lungs and heart, it also captures part of the liver, making it possible to detect signs of fatty liver disease. However, the relationship between chest X-rays and fatty liver disease has rarely been a subject of in-depth study. Therefore, a research group led by Associate Professor Sawako Uchida-Kobayashi and Associate Professor Daiju Ueda at Osaka Metropolitan University's Graduate School of Medicine developed an AI model that can detect the presence of fatty liver disease from chest X-ray images. The findings are published in the journal Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging. In this retrospective study, a total of 6,599 chest X-ray images containing data from 4,414 patients were used to develop an AI model utilizing controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) scores. The AI model was verified to be highly accurate, with the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) ranging from 0.82 to 0.83. "The development of diagnostic methods using easily obtainable and inexpensive chest X-rays has the potential to improve fatty liver detection. We hope it can be put into practical use in the future," stated Professor Uchida-Kobayashi.
Share
Share
Copy Link
Researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University have developed an AI model that can accurately detect fatty liver disease from chest X-ray images, potentially offering a more accessible and cost-effective diagnostic tool.
AI Innovation in Fatty Liver Disease Detection
Researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University's Graduate School of Medicine have developed a groundbreaking artificial intelligence (AI) model capable of detecting fatty liver disease from chest X-ray images. This innovative approach could revolutionize the early diagnosis of a condition that affects approximately one in four people worldwide
1
2
.The Challenge of Fatty Liver Disease Diagnosis
Fatty liver disease, characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver, can lead to severe complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer if left untreated. Early detection is crucial for timely intervention and treatment. However, current standard diagnostic methods present significant challenges:
- Ultrasounds, CT scans, and MRIs are the primary tools for diagnosis
- These methods require costly specialized equipment and facilities
- Access to these diagnostic tools may be limited in some healthcare settings
Leveraging Chest X-Rays for Liver Disease Detection
Source: ScienceDaily
The research team, led by Associate Professors Sawako Uchida-Kobayashi and Daiju Ueda, recognized an opportunity in the ubiquity of chest X-rays:
- Chest X-rays are more frequently performed than specialized liver scans
- They are relatively inexpensive and involve low radiation exposure
- While primarily used for lung and heart examinations, chest X-rays also capture part of the liver
Despite this potential, the relationship between chest X-rays and fatty liver disease had rarely been studied in depth until now
1
2
.Related Stories
Development of the AI Model

Source: Medical Xpress
The study, published in the journal Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging, details the development of the AI model:
- A retrospective study design was employed
- 6,599 chest X-ray images from 4,414 patients were utilized
- The AI model was developed using controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) scores
- The model demonstrated high accuracy, with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) ranging from 0.82 to 0.83
1
2
Implications and Future Prospects
This innovative approach to fatty liver disease detection holds significant promise for improving healthcare outcomes:
- Increased accessibility to diagnosis, especially in resource-limited settings
- Potential for earlier detection and intervention
- Cost-effective screening method using existing chest X-ray infrastructure
Professor Uchida-Kobayashi expressed optimism about the practical applications of this technology, stating, "The development of diagnostic methods using easily obtainable and inexpensive chest X-rays has the potential to improve fatty liver detection. We hope it can be put into practical use in the future"
1
2
.As this AI model moves towards practical implementation, it could significantly enhance the early detection and management of fatty liver disease, potentially improving health outcomes for millions of people worldwide.
References
Summarized by
Navi
[2]
Related Stories
AI Algorithm Detects Undiagnosed Early-Stage Liver Disease, Promising Improved Patient Care
18 Nov 2024•Health

AI Revolutionizes Heart Disease Detection: From ECGs to Hidden Conditions
17 Jul 2025•Health
AI Tool Revolutionizes Disease Detection in CT Scans Through Opportunistic Screening
05 Dec 2024•Health

Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.4, New AI Model Built for Agents and Professional Work
Technology

2
Anthropic sues Pentagon over supply chain risk label after refusing autonomous weapons use
Policy and Regulation

3
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round as questions swirl around AI bubble and profitability
Business and Economy