AI-Powered Video Analysis Reveals New Biomarkers for Tinnitus Severity
3 Sources
3 Sources
[1]
Facial Movements and Pupils Reveal Tinnitus Severity - Neuroscience News
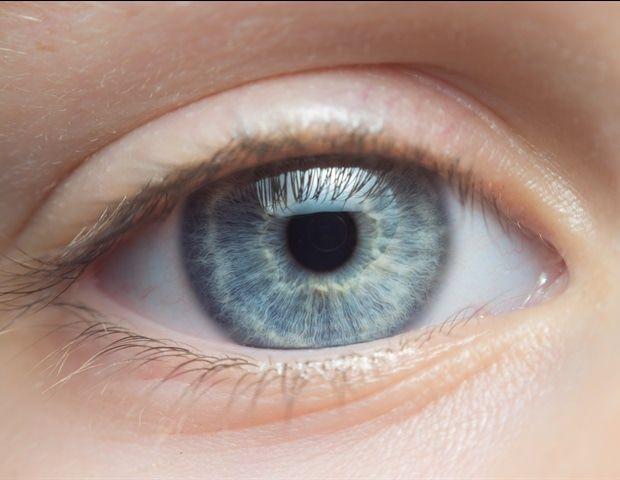
Summary: Researchers have identified new biomarkers for tinnitus by tracking pupil dilation and subtle facial movements linked to distress levels. Using AI-powered video analysis, they found that severe tinnitus sufferers showed constant pupil dilation and reduced facial responses to sounds, indicating heightened vigilance and chronic distress. These objective markers offer a breakthrough for a condition long measured only by subjective questionnaires. The findings could pave the way for consumer-friendly diagnostic tools and help advance clinical trials and therapies targeting tinnitus. Researchers at Mass General Brigham have identified new biomarkers for tinnitus by measuring pupil dilation and subtle facial movements that correlate with the level of distress caused by the disorder. Published in Science Translational Medicine, the findings could lead to placebo-controlled treatment studies that have largely been not feasible due to lack of objective measures. "Imagine if cancer severity were determined by giving patients a questionnaire -- this is the state of affairs for some common neurological disorders like tinnitus," said corresponding author Daniel Polley, PhD, vice chair for basic science research and director of the Eaton-Peabody Laboratories at Mass Eye and Ear, a member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system. "For the first time, we directly observed a signature of tinnitus severity. When we began this study, we didn't know if sounds would elicit facial movements; so, to discover that these movements not only occur, but can provide the most informative measure to date of tinnitus distress, is quite surprising." Tinnitus presents as persistent phantom sounds like ringing, buzzing or clicking, that affect about 12% of the general population and 25% of individuals ages 65 and older. Though many learn to live with it and consider it a nuisance, an estimated 15% of sufferers have tinnitus so disabling that it disrupts sleep, mental health, and daily functioning. Until now, there's been no objective way to differentiate these experiences. In addition to more standard measures of hearing and auditory brain function, Dr. Polley and his team turned their attention more downstream to the sympathetic nervous system -- the body's "fight, flight, or freeze" mechanism -- to look for outward, involuntary signs of distress in people with tinnitus that might be "hidden in plain sight." They knew that the pupil dilation was a sign of increased arousal and that involuntary facial movements could provide a window into threat assessment. The researchers hypothesized that people with debilitating tinnitus are chronically in vigilance mode, reacting to everyday sounds as if they are threats. To test this, they recruited 97 participants with normal hearing, which included 47 with varying levels of tinnitus and sound sensitivity and 50 healthy volunteers that served as controls. Video recordings were made while participants listened to pleasant, neutral, or distressing and unpleasant sounds (like coughing fits, yelling, or a baby crying). Using artificial intelligence (AI)-powered software, they detected rapid and subtle involuntary facial movements -- twitches in the cheeks, eyebrows, or nostrils -- correlated with reported tinnitus distress levels. When combined with pupil dilation data, the predictive power increased even more. In people with severe tinnitus, pupils dilated extra wide at all sounds (pleasant, neutral, or unpleasant), while facial movements were blunted in response to the same sounds. People without tinnitus or with less bothersome tinnitus by contrast showed exaggerated pupil dilation and facial movements only to the most unpleasant sounds. The measures also predicted individual questionnaire scores for hyperacusis severity (reduced sound tolerance), though the results were not as accurate as tinnitus severity. "What's really exciting is this vantage point into tinnitus severity didn't require highly specialized brain scanners; instead, the approach was relatively low-tech.," said Polley, who also is also director of Mass Eye and Ear's Lauer Tinnitus Research Center. "If we can adapt this approach to consumer-grade electronics, they could be put to use in hearing health clinics, as objective measures in clinical trials and by the public at large." The study's main limitation was its participant pool. To demonstrate the potential uses of their video-based approach, researchers had to exclude many individuals with co-occurring issues like hearing loss, advanced age, or mental health challenges, which are commonly associated with complex and severe tinnitus. Future research will aim to include these more at-risk populations. Dr. Polley and his lab are now using these biomarkers to develop new therapies that combine neural stimulation with immersive software environments designed to eliminate or significantly reduce the loudness of the tinnitus phantom sound. "These biomarkers get to the root of the distress," said Dr. Polley. "While imaging might show hyperactive brain regions in tinnitus patients, these biomarkers reveal body-wide threat evaluation systems that are operating outside of their normal range, leading to the distressful symptoms they experience." Authorship: Additional Mass General Brigham authors include Samuel S. Smith, Kelly N. Jahn, Jenna A. Sugai, and Ken E. Hancock of Mass Eye and Ear's Eaton-Peabody Laboratories. Disclosures: Polley is on the advisory board of the American Tinnitus Association, Hyperacusis Research Ltd, and Tinnitus Quest. Jahn is on the advisory board of Hyperacusis Research Ltd and Hyperacusis Central. Funding: This research was funded by the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders grants P50DC015857 and K01DC019647, and a ASHFoundation New Investigators Research Grant. Objective Autonomic Signatures of Tinnitus and Sound Sensitivity Disorders Hypersensitivity, phantom percepts, and sensory reactivity are core features of many neurological disorders. Direct, objective measurements of these features have proven difficult to identify, leaving subjective questionnaires as the primary means of assessing sensory disorder severity. Here, we studied neurotypical adults (n = 50) or adults with sound sensitivity and tinnitus (ringing of the ears) (n = 47) and discovered a previously unidentified set of objective measurements that predicted individual differences in the Tinnitus Handicap Inventory (THI) and Hyperacusis Questionnaire (HQ). A neurophysiological assessment of central auditory gain demonstrated an elevation in participants with tinnitus and sound sensitivity but no association with symptom severity. Instead, accurate predictors of individual THI and HQ scores were identified in pupil dilations and facial movements elicited by emotionally evocative sounds. These findings highlight autonomic signatures of disrupted affective sound processing in persons with tinnitus and sound sensitivity disorders and introduce new approaches for their objective measurement.
[2]
Do You Have Tinnitus? The Answer Might Be Written In Your Face
By Dennis Thompson HealthDay ReporterTHURSDAY, May 1, 2025 (HealthDay News) -- Subtle facial gestures linked to the body's fight-or-flight response could be used to help diagnose people with tinnitus, a new study says. Video recordings showed that people with tinnitus experienced facial twitches and pupil dilation in response to certain sounds, researchers reported April 30 in the journal Science Translational Medicine. This is the first time researchers have found a marker that could be used to identify tinnitus in people suffering from the hearing problem, researchers said. "Imagine if cancer severity were determined by giving patients a questionnaire - this is the state of affairs for some common neurological disorders like tinnitus," senior investigator Daniel Polley, director of Mass Eye and Ear's Lauer Tinnitus Research Center in Boston, said in a news release. "For the first time, we directly observed a signature of tinnitus severity," Polley said. "When we began this study, we didn't know if sounds would elicit facial movements; so, to discover that these movements not only occur, but can provide the most informative measure to date of tinnitus distress, is quite surprising." Tinnitus is the medical term for ringing in the ears, but it also can present as other persistent phantom sounds like buzzing or clicking, researchers said in background notes. Tinnitus affects about 12% of people, including 25% of seniors 65 and older. Most learn to live with the nuisance, but about 15% of people have tinnitus so severe that it disrupts their sleep, mental health and everyday function, researchers said. For this study, researchers hypothesized that people with debilitating tinnitus might exist in constant fight-or-flight mode, reacting to everyday sounds as though they were threats. The team recruited 47 folks with varying levels of tinnitus and compared them to 50 healthy people who served as a control group. The people were videotaped as they listened to pleasant, neutral or distressing sounds. The unpleasant sounds included coughing fits, yelling or a baby crying. Using artificial intelligence (AI) software, they looked for rapid and subtle involuntary facial movements, like twitches in the cheeks, eyebrows or nostrils. Researchers found that these twitches correlated with the levels of distress that participants had reported from tinnitus in questionnaires. Further, the pupils of people with severe tinnitus dilated extra wide at all sounds, be they pleasant or unpleasant, researchers report. The pupils of people without tinnitus or with less bothersome tinnitus only responded to the most unpleasant sounds. Combining the facial twitches with pupil dilation, researchers found they could accurately identify people most tormented by tinnitus. "What's really exciting is this vantage point into tinnitus severity didn't require highly specialized brain scanners; instead, the approach was relatively low-tech," Polley said. "If we can adapt this approach to consumer-grade electronics, they could be put to use in hearing health clinics, as objective measures in clinical trials and by the public at large." Researchers are now using this test to develop ways to eliminate or significantly reduce the loudness of the phantom sounds from tinnitus. "These biomarkers get to the root of the distress," said Polley. "While imaging might show hyperactive brain regions in tinnitus patients, these biomarkers reveal body-wide threat evaluation systems that are operating outside of their normal range, leading to the distressful symptoms they experience."
[3]
Tinnitus clues may be hiding in your face, researchers say
Subtle facial gestures linked to the body's fight-or-flight response could be used to help diagnose people with tinnitus, a new study says. Video recordings showed that people with tinnitus experienced facial twitches and pupil dilation in response to certain sounds, researchers reported April 30 in the journal Science Translational Medicine. This is the first time researchers have found a marker that could be used to identify tinnitus in people suffering from the hearing problem, researchers said. "Imagine if cancer severity were determined by giving patients a questionnaire - this is the state of affairs for some common neurological disorders like tinnitus," senior investigator Daniel Polley, director of Mass Eye and Ear's Lauer Tinnitus Research Center in Boston, said in a news release. "For the first time, we directly observed a signature of tinnitus severity," Polley said. "When we began this study, we didn't know if sounds would elicit facial movements; so, to discover that these movements not only occur, but can provide the most informative measure to date of tinnitus distress, is quite surprising." Tinnitus is the medical term for ringing in the ears, but it also can present as other persistent phantom sounds like buzzing or clicking, researchers said in background notes. Tinnitus affects about 12% of people, including 25% of seniors 65 and older. Most learn to live with the nuisance, but about 15% of people have tinnitus so severe that it disrupts their sleep, mental health and everyday function, researchers said. For this study, researchers hypothesized that people with debilitating tinnitus might exist in constant fight-or-flight mode, reacting to everyday sounds as though they were threats. The team recruited 47 folks with varying levels of tinnitus and compared them to 50 healthy people who served as a control group. The people were videotaped as they listened to pleasant, neutral or distressing sounds. The unpleasant sounds included coughing fits, yelling or a baby crying. Using artificial intelligence (AI) software, they looked for rapid and subtle involuntary facial movements, like twitches in the cheeks, eyebrows or nostrils. Researchers found that these twitches correlated with the levels of distress that participants had reported from tinnitus in questionnaires. Further, the pupils of people with severe tinnitus dilated extra wide at all sounds, be they pleasant or unpleasant, researchers report. The pupils of people without tinnitus or with less bothersome tinnitus only responded to the most unpleasant sounds. Combining the facial twitches with pupil dilation, researchers found they could accurately identify people most tormented by tinnitus. "What's really exciting is this vantage point into tinnitus severity didn't require highly specialized brain scanners; instead, the approach was relatively low-tech," Polley said. "If we can adapt this approach to consumer-grade electronics, they could be put to use in hearing health clinics, as objective measures in clinical trials and by the public at large." Researchers are now using this test to develop ways to eliminate or significantly reduce the loudness of the phantom sounds from tinnitus. "These biomarkers get to the root of the distress," said Polley. "While imaging might show hyperactive brain regions in tinnitus patients, these biomarkers reveal body-wide threat evaluation systems that are operating outside of their normal range, leading to the distressful symptoms they experience."
Share
Share
Copy Link
Researchers have discovered new objective measures for tinnitus severity using AI-powered video analysis of facial movements and pupil dilation, potentially revolutionizing diagnosis and treatment of this common hearing disorder.
Breakthrough in Tinnitus Research: AI-Powered Video Analysis Reveals New Biomarkers
Researchers at Mass General Brigham have made a significant breakthrough in tinnitus research, identifying new biomarkers that could revolutionize how the condition is diagnosed and treated. The study, published in Science Translational Medicine, used AI-powered video analysis to detect subtle facial movements and pupil dilation that correlate with tinnitus severity
1
.The Challenge of Measuring Tinnitus
Tinnitus, a condition characterized by persistent phantom sounds like ringing or buzzing in the ears, affects approximately 12% of the general population and 25% of individuals over 65. Until now, the severity of tinnitus has been primarily assessed through subjective questionnaires, making it challenging to conduct placebo-controlled treatment studies
2
.Innovative Approach: Facial Movements and Pupil Dilation
The research team, led by Dr. Daniel Polley, hypothesized that individuals with severe tinnitus might be in a constant state of vigilance, reacting to everyday sounds as if they were threats. To test this, they recruited 97 participants: 47 with varying levels of tinnitus and 50 healthy controls
3
.Participants were video-recorded while listening to pleasant, neutral, and distressing sounds. Using AI software, researchers analyzed:
- Rapid and subtle involuntary facial movements
- Pupil dilation in response to various sounds
Key Findings
The study revealed several important insights:
- Facial twitches correlated with reported tinnitus distress levels
- Severe tinnitus sufferers showed constant pupil dilation for all sounds
- Individuals without tinnitus or with mild cases only showed exaggerated responses to unpleasant sounds
By combining facial movement and pupil dilation data, researchers could accurately identify those most affected by tinnitus
1
.Related Stories
Implications for Diagnosis and Treatment
This breakthrough offers several potential benefits:
- Objective measurement of tinnitus severity
- Improved clinical trial design for tinnitus treatments
- Potential for consumer-friendly diagnostic tools
Dr. Polley emphasized the significance of these findings: "For the first time, we directly observed a signature of tinnitus severity. These biomarkers reveal body-wide threat evaluation systems that are operating outside of their normal range, leading to the distressful symptoms they experience"
2
.Future Directions
The research team is now using these biomarkers to develop new therapies combining neural stimulation with immersive software environments. These treatments aim to eliminate or significantly reduce the loudness of phantom sounds associated with tinnitus
1
.While the study's main limitation was its selective participant pool, future research will aim to include more diverse populations, including those with hearing loss, advanced age, or mental health challenges commonly associated with complex tinnitus cases
3
.References
Summarized by
Navi
[1]
[3]
Related Stories
Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.4, New AI Model Built for Agents and Professional Work
Technology

2
Anthropic sues Pentagon over supply chain risk label after refusing autonomous weapons use
Policy and Regulation

3
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round as questions swirl around AI bubble and profitability
Business and Economy