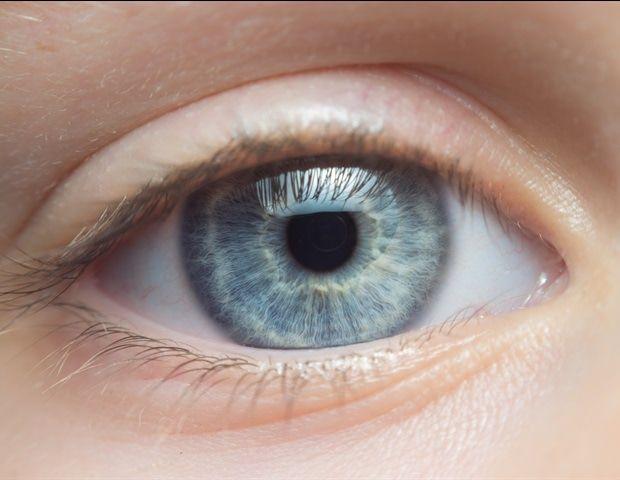
AI-Powered Oculomics: Revolutionizing Cardiovascular Risk Assessment Through Retinal Imaging
3 Sources
3 Sources
[1]
AI-driven oculomics assesses HbA1c for cardiovascular risk
By Dr. Priyom Bose, Ph.D.Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc.Oct 10 2024 Integrating AI with oculomics shows promise in predicting diabetes, with the study revealing that diverse datasets can help develop more accurate and trustworthy models to assess HbA1c levels, enhancing patient care in clinical settings. Study: Development of oculomics artificial intelligence for cardiovascular risk factors: A case study in fundus oculomics for HbA1c assessment and clinically relevant considerations for clinicians. Image Credit: Stas Ponomarencko / Shutterstock.com Oculomics is a relatively new and powerful technology that integrates ophthalmic features to identify biomarkers that can be used to predict systemic diseases. A recent Asia-Pacific Journal of Ophthalmology pilot study investigates the potential advantages of incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) with oculomics. Using oculomics for HbA1c estimation The objective of the current study was to apply oculomics to fundus images to assess glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels. The percentage of HbA1c is typically used to diagnose and monitor the progression of diabetes. Despite its widespread use, HbA1c measurements can be inaccurate in some instances, such as in patients with comorbidities like sickle cell anemia, those who have recently received a blood transfusion, or pregnant patients. In the current study, a total of 6,118 fundus images were obtained, 1,138 of which were diagnosed as normal. Initially, the researchers compared the performance of a monolithic model to ensemble architecture and its reliability and bias from the effects of age and sex. The VGG19 model, which is based on convolutional neural networks (CNN), exhibited the best performance across all metrics. Compared to the single model, the ensemble model showed a performance improvement of about 2%. For the model to be reliable, its size as compared to the dataset size must be carefully considered. In the current study, the VGG19 model outperformed other larger models, which may be due to the dataset size, as complex and more extensive models require larger amounts of data to accurately estimate parameters. It is also crucial to evaluate reliability along other dimensions than just performance on a single testing set, as safety-critical applications of AI could significantly impact patient health and safety. The effects of age and gender on model performance Higher accuracy was observed in the model that was trained on samples obtained from both youth and seniors as compared to those where the training set comprised a single group. While developing AI solutions, the ability of a model to show robust and reliable performance across a diverse population is crucial for minimizing bias. The performance was best when the training set included both sexes. In fact, a 5% degradation was observed when the model was trained on either males or females alone. An additional model was trained to output gender from fundus images. The model was associated with an overall accuracy of 87%; however, this exceptional performance could be attributed to potential bias in the training dataset. Grad-CAM, a well-known interpretable AI technique, was used to identify key features of the fundus images that provide important insights for various classification labels. These results complemented those produced in previous studies and emphasized the need for a diverse dataset to deliver reliable and robust performance. Challenges in developing trustworthy AI in oculomics The study findings confirm the importance of high-quality and diverse datasets to train models, which will ultimately improve their robust and reliable performance in different conditions. Model outputs should also be transparent to ensure healthcare providers can understand and trust their predictions. Ensuring fairness and addressing bias in model predictions is also extremely important. The future of AI in oculomics Adaptability to diverse clinical environments and compliance with regulatory guidelines is fundamental to ensure the trustworthy deployment of AI in oculomics. Maintaining transparency also supports the development of explainable and interpretable AI models in which medical practitioners can easily understand the logic of their predictions. AI models may experience performance degradation due to out-of-distribution (OOD) inputs or unforeseen clinical scenarios during deployment. However, incorporating continuous learning frameworks could mitigate this issue. Anomaly detection algorithms may also serve as a safeguard; therefore, models should be periodically updated to introduce novel and diverse data. These efforts have the potential to sustain the accuracy and relevance of AI applications in clinical environments. In the future, AI systems for oculomics must be developed to enhance human-centered healthcare by simplifying clinicians' workflows, improving patient health outcomes, and raising the quality of care provided. To this end, ongoing collaboration among various stakeholders is necessary throughout the development and implementation phases to reach AI's full potential in transforming healthcare delivery. Journal reference: Ong, J., Jang, K. J., Baek, S. J., et al. (2024) Development of oculomics artificial intelligence for cardiovascular risk factors: A case study in fundus oculomics for HbA1c assessment and clinically relevant considerations for clinicians. Asia-Pacific Journal of Ophthalmology 13(4); 100095. doi:10.1016/j.apjo.2024.100095
[2]
Leveraging AI to analyze retinal images for cardiovascular risk assessment
A recent position paper in the Asia-Pacific Journal of Ophthalmology explores the transformative potential of artificial intelligence (AI) in ophthalmology. With fundus photography enabling the visualization of retina at the back of the eye, the potential of AI in providing systemic disease biomarkers is becoming a reality. When fundus images are of sufficient quantity and quality, it becomes possible to train AI systems to detect elevated HbA1c levels -- an important marker for high blood sugar that is traditionally obtained with blood draws, which indicates a heightened risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. This process leverages the emerging field of oculomics, which studies ophthalmic biomarkers to gain insights into systemic health. In their manuscript, titled "Development of Oculomics Artificial Intelligence for Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Case Study in Fundus Oculomics for HbA1c Assessment and Clinically Relevant Considerations for Clinicians," this multi-institutional team explores the potential of oculomics and highlights pertinent topics for clinicians to consider as we move into an era where artificial intelligence has the potential to enhance systemic health through eye care. Their discussion is supported by preliminary research results from a pilot study that trained AI models to predict HbA1c levels based on fundus images. This study evaluated various factors -- such as AI model size and architecture, the presence of diabetes, and patient demographics (age and sex) -- and their impact on AI performance. One of the study observations was that biased training samples for an oculomics model, such as a pool of predominantly older patients, can degrade model performance. The results of the case study highlight the importance of developing trustworthy AI models for assessing cardiovascular risk factors while addressing the challenges and problems that must be overcome prior to clinical adoption, as well as advancing reliable oculomics technology. "By leveraging AI to analyze retinal images for cardiovascular risk assessment," says Al-Aswad, "we aim to bridge a crucial gap in early disease detection. "This method not only enhances our ability to identify at-risk individuals but also holds promise for transforming how we manage chronic conditions such as diabetes. By focusing on practical applications of this technology, we are advancing towards more personalized and preventative health care solutions." "While these advancements hold promise, it is also of utmost importance for clinicians and researchers to develop and employ these techniques in a responsible manner, as this will benefit patient care the most in the end," adds Kuk Jin Jang, a postdoctoral researcher in the Penn Research in Embedded Computing and Integrated Systems Engineering (PRECISE) Center at the University of Pennsylvania. "Our collaboration serves to further understand how we can responsibly leverage this revolutionary technology to benefit patients in the future. It is a testament to the collaborative advances formed when health care and engineering come together to work towards responsible AI for patient care," says Joshua Ong, a resident physician at the University of Michigan and PRECISE Center affiliate. "I am incredibly grateful for our multidisciplinary team for coming together to bring this paper and topic to the forefront." "This collaboration reflects a deep commitment to advancing health care through innovative AI applications," adds PRECISE Center Director Insup Lee, Cecilia Fitler Moore Professor in Computer and Information Science at Penn Engineering. "By combining our expertise, we are paving the way for significant improvements in patient care and the overall management of long-term health challenges." Led by Lama Al-Aswad, Professor of Ophthalmology and Irene Heinz Given and John La Porte Given Research Professor of Ophthalmology II, of the Scheie Eye Institute, the work represents a collaboration among researchers from Penn Engineering, Penn Medicine, the University of Michigan Kellogg Eye Center, St. John Eye Hospital in Jerusalem, and Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine in Korea.
[3]
AI revolutionizes ophthalmology with oculomics for cardiovascular risk assessment
University of Pennsylvania School of Engineering and Applied ScienceOct 4 2024 A recent position paper in the Asia-Pacific Journal of Ophthalmology explores the transformative potential of artificial intelligence (AI) in ophthalmology. Led by Lama Al-Aswad, Professor of Ophthalmology and Irene Heinz Given and John La Porte Given Research Professor of Ophthalmology II, of the Scheie Eye Institute, the work represents a collaboration among researchers from Penn Engineering, Penn Medicine, the University of Michigan Kellogg Eye Center, St. John Eye Hospital in Jerusalem, and Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine in Korea. With fundus photography enabling the visualization of retina at the back of the eye, the potential of AI in providing systemic disease biomarkers is becoming a reality. When fundus images are of sufficient quantity and quality, it becomes possible to train AI systems to detect elevated HbA1c levels -; an important marker for high blood sugar that is traditionally obtained with blood draws, which indicates a heightened risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. This process leverages the emerging field of oculomics, which studies ophthalmic biomarkers to gain insights into systemic health. In their manuscript, titled "Development of Oculomics Artificial Intelligence for Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Case Study in Fundus Oculomics for HbA1c Assessment and Clinically Relevant Considerations for Clinicians," this multi-institutional team explores the potential of oculomics and highlights pertinent topics for clinicians to consider as we move into an era where artificial intelligence has the potential to enhance systemic health through eye care. Their discussion is supported by preliminary research results from a pilot study that trained AI models to predict HbA1c levels based on fundus images. This study evaluated various factors -; such as AI model size and architecture, the presence of diabetes, and patient demographics (age and sex) -; and their impact on AI performance. One of the study observations was that biased training samples for an oculomics model, such as a pool of predominantly older patients, can degrade model performance. The results of the case study highlight the importance of developing trustworthy AI models for assessing cardiovascular risk factors while addressing the challenges and problems that must be overcome prior to clinical adoption, as well as advancing reliable oculomics technology. By leveraging AI to analyze retinal images for cardiovascular risk assessment, we aim to bridge a crucial gap in early disease detection. This method not only enhances our ability to identify at-risk individuals but also holds promise for transforming how we manage chronic conditions such as diabetes. By focusing on practical applications of this technology, we are advancing towards more personalized and preventative healthcare solutions." Lama Al-Aswad, Professor of Ophthalmology and Irene Heinz Given and John La Porte Given Research Professor of Ophthalmology II, of the Scheie Eye Institute "While these advancements hold promise, it is also of utmost importance for clinicians and researchers to develop and employ these techniques in a responsible manner, as this will benefit patient care the most in the end," adds Kuk Jin Jang, a postdoctoral researcher in the Penn Research in Embedded Computing and Integrated Systems Engineering (PRECISE) Center at the University of Pennsylvania. "Our collaboration serves to further understand how we can responsibly leverage this revolutionary technology to benefit patients in the future. It is a testament to the collaborative advances formed when healthcare and engineering come together to work towards responsible AI for patient care," says Joshua Ong, a resident physician at the University of Michigan and PRECISE Center affiliate. "I am incredibly grateful for our multidisciplinary team for coming together to bring this paper and topic to the forefront." "This collaboration reflects a deep commitment to advancing healthcare through innovative AI applications," adds PRECISE Center Director Insup Lee, Cecilia Fitler Moore Professor in Computer and Information Science at Penn Engineering. "By combining our expertise, we are paving the way for significant improvements in patient care and the overall management of long-term health challenges." University of Pennsylvania School of Engineering and Applied Science Journal reference: Ong, J., et al. (2024). Development of Oculomics Artificial Intelligence for Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Case Study in Fundus Oculomics for HbA1c Assessment and Clinically Relevant Considerations for Clinicians. Asia-Pacific Journal of Ophthalmology. doi.org/10.1016/j.apjo.2024.100095.
Share
Share
Copy Link
A groundbreaking study explores the integration of AI with oculomics to predict HbA1c levels and assess cardiovascular risk factors using retinal images, potentially transforming early disease detection and chronic condition management.

AI and Oculomics: A New Frontier in Cardiovascular Risk Assessment
A recent pilot study published in the Asia-Pacific Journal of Ophthalmology has unveiled the promising potential of integrating artificial intelligence (AI) with oculomics to revolutionize cardiovascular risk assessment. This groundbreaking research explores how AI can analyze retinal images to predict glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels, a crucial marker for diabetes and cardiovascular disease risk
1
.The Power of Oculomics and AI
Oculomics, an emerging field that studies ophthalmic biomarkers to gain insights into systemic health, is at the forefront of this innovation. By leveraging fundus photography, which visualizes the retina, researchers have demonstrated that AI systems can be trained to detect elevated HbA1c levels traditionally obtained through blood draws
2
.The study, led by Professor Lama Al-Aswad from the Scheie Eye Institute, involved a multi-institutional team that evaluated various AI models and factors affecting their performance. The researchers used a dataset of 6,118 fundus images, including 1,138 diagnosed as normal, to train and test their AI models
1
.Key Findings and Implications
The study revealed several important insights:
-
Model Performance: The VGG19 model, based on convolutional neural networks (CNN), showed the best performance across all metrics. An ensemble model approach improved performance by about 2% compared to a single model
1
. -
Dataset Diversity: The research emphasized the critical importance of diverse datasets in training AI models. Models trained on samples from both youth and seniors, as well as both sexes, showed higher accuracy and robustness
1
. -
Bias Mitigation: The study highlighted the need to address potential biases in AI models. For instance, a model trained to predict gender from fundus images achieved 87% accuracy, but this could be attributed to potential bias in the training dataset
1
.
Related Stories
Challenges and Future Directions
While the results are promising, the researchers acknowledge several challenges in developing trustworthy AI in oculomics:
-
Data Quality: High-quality and diverse datasets are crucial for training robust and reliable models
3
. -
Transparency: Ensuring model outputs are transparent and interpretable is essential for healthcare provider trust
1
. -
Adaptability: AI models must be adaptable to diverse clinical environments and comply with regulatory guidelines
1
. -
Continuous Learning: Incorporating continuous learning frameworks and anomaly detection algorithms could help mitigate performance degradation due to out-of-distribution inputs
1
.
The Road Ahead
The integration of AI and oculomics holds immense potential for transforming healthcare delivery. As Professor Al-Aswad states, "By leveraging AI to analyze retinal images for cardiovascular risk assessment, we aim to bridge a crucial gap in early disease detection"
2
.This collaborative effort between healthcare and engineering experts paves the way for more personalized and preventative healthcare solutions. However, as Kuk Jin Jang, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Pennsylvania, emphasizes, it is crucial to develop and employ these techniques responsibly to maximize patient benefit
3
.References
Summarized by
Navi
[1]
Related Stories
AI-Powered Retina Tracker Revolutionizes Diabetic Eye Disease Screening
15 Jul 2025•Health

AI Innovations in Early Detection of Myopic Maculopathy: Protecting Millions from Vision Loss
03 Oct 2024•Health

AI Revolutionizes Diabetes Care: Personalized Treatment and Early Detection on the Horizon
26 Feb 2025•Health

Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.4, New AI Model Built for Agents and Professional Work
Technology

2
Anthropic sues Pentagon over supply chain risk label after refusing autonomous weapons use
Policy and Regulation

3
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round as questions swirl around AI bubble and profitability
Business and Economy