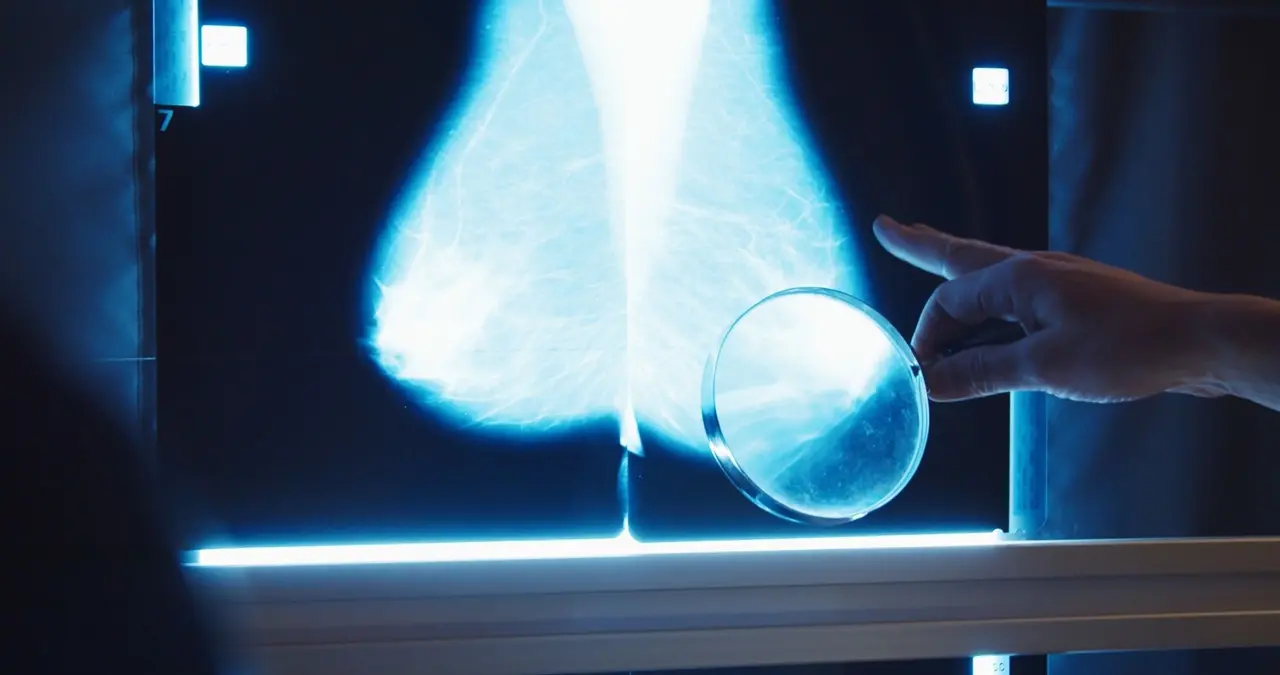
AI Revolutionizes Cancer Research: Advantages and Challenges Highlighted in New Review
2 Sources
2 Sources
[1]
AI's role in cancer research: Review highlights advantages and limitations
Significant advancements in understanding the molecular and cellular mechanisms of tumor progression have been made, yet challenges remain. Traditional imaging techniques like MRI, CT, and mammography are limited by the need for professional curation, which is time-consuming. Genetic changes associated with cancer could serve as diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive biomarkers, but their translation into clinical practice is hindered by variations in metastasis, treatment responses, and resistance. New therapeutic strategies, while efficient, face issues due to cancer heterogeneity. Artificial intelligence (AI) offers solutions to these challenges, with extensive applications in drug development, cancer prediction, diagnosis, and the analysis of next-generation sequencing data. AI algorithms can identify genetic mutations or signatures for early cancer detection and targeted therapies. However, developing and implementing accurate AI models in clinical settings is challenging due to data heterogeneity, biases, and privacy concerns. Despite these, AI has demonstrated improved clinical decision-making. Artificial intelligence, a collection of methods and techniques, has become increasingly important in cancer research. A new review published in Frontiers of Medicine discusses the advantages and limitations of various AI methods. The publication provides an overview of the usage of these methods over the past decade, as well as guidelines on incorporating AI models into clinical settings and the potential of pre-trained language models in personalizing cancer care strategies. AI methods discussed include machine learning (ML), which encompasses unsupervised and supervised learning. Supervised learning, which includes regression and classification, is widely used in cancer research. Traditional ML models like Bayesian networks, support vector machines, and random forests continuously incorporate data to produce outcomes. Deep learning, a subset of ML, uses multiple hidden layers to identify complex patterns in data. Natural language processing (NLP), another AI algorithm, targets narrative texts to extract useful information for decision-making. AI models in cancer research use multi-omics and clinical information from various sources, with classification being the most common task. These models are validated and assessed using receiver operating characteristic analysis, which computes area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, and precision. AI methods have been developed to handle large volumes of data, requiring increased cloud computing and storage power. The review also discusses the application of AI in drug development, where models predict drug responses using multi-omics data. Additionally, AI has been used to extract information from electronic health records, addressing the challenge of analyzing messy data. Despite the progress, there are limitations to AI applications in cancer research. Choosing the appropriate algorithm is complex and depends on data type and complexity. Integrating AI into clinical settings requires detailed application explanations and transparency of algorithms. Monitoring the quality of AI tools for robust performance is crucial. The review emphasizes the need for further transparency and guidance on software scrutiny, cost-effectiveness, retraining of data sets, and conditions required for using AI systems. In conclusion, AI has significantly impacted cancer research, and addressing challenges and validating AI-generated results can direct the future of oncology research. The review highlights the progress of AI methods in cancer-related applications and the potential of explainable AI, personalized medicine, and non-invasive AI tools for early cancer detection. As AI continues to evolve, it holds great potential in revolutionizing cancer detection and improving patient outcomes.
[2]
AI revolutionizes cancer research with advanced tools
Frontiers JournalsDec 13 2024 Significant advancements in understanding the molecular and cellular mechanisms of tumor progression have been made, yet challenges remain. Traditional imaging techniques like MRI, CT, and mammography are limited by the need for professional curation, which is time-consuming. Genetic changes associated with cancer could serve as diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive biomarkers, but their translation into clinical practice is hindered by variations in metastasis, treatment responses, and resistance. New therapeutic strategies, while efficient, face issues due to cancer heterogeneity. Artificial intelligence (AI) offers solutions to these challenges, with extensive applications in drug development, cancer prediction, diagnosis, and the analysis of next-generation sequencing data. AI algorithms can identify genetic mutations or signatures for early cancer detection and targeted therapies. However, developing and implementing accurate AI models in clinical settings is challenging due to data heterogeneity, biases, and privacy concerns. Despite these, AI has demonstrated improved clinical decision-making. Artificial intelligence, a collection of methods and techniques, has become increasingly important in cancer research, with various AI methods being detailed in this review, including their advantages and limitations. The review provides an overview of the usage of these methods over the past decade, as well as guidelines on incorporating AI models into clinical settings and the potential of pre-trained language models in personalizing cancer care strategies. AI methods discussed include machine learning (ML), which encompasses unsupervised and supervised learning. Supervised learning, which includes regression and classification, is widely used in cancer research. Traditional ML models like Bayesian networks, support vector machines, and random forests continuously incorporate data to produce outcomes. Deep learning, a subset of ML, uses multiple hidden layers to identify complex patterns in data. Natural language processing (NLP), another AI algorithm, targets narrative texts to extract useful information for decision-making. AI models in cancer research utilize multi-omics and clinical information from various sources, with classification being the most common task. These models are validated and assessed using receiver operating characteristic analysis, which computes area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, and precision. AI methods have been developed to handle large volumes of data, requiring increased cloud computing and storage power. The review also discusses the application of AI in drug development, where models predict drug responses using multi-omics data. Additionally, AI has been used to extract information from electronic health records, addressing the challenge of analyzing messy data. Despite the progress, there are limitations to AI applications in cancer research. Choosing the appropriate algorithm is complex and depends on data type and complexity. Integrating AI into clinical settings requires detailed application explanations and transparency of algorithms. Monitoring the quality of AI tools for robust performance is crucial. The review emphasizes the need for further transparency and guidance on software scrutiny, cost-effectiveness, retraining of data sets, and conditions required for using AI systems. In conclusion, AI has significantly impacted cancer research, and addressing challenges and validating AI-generated results can lead the future of oncology research. The review highlights the progress of AI methods in cancer-related applications and the potential of explainable AI, personalized medicine, and non-invasive AI tools for early cancer detection. As AI continues to evolve, it holds great potential in revolutionizing cancer detection and improving patient outcomes. Frontiers Journals Journal reference: Murmu, A., & Győrffy, B. (2024) Artificial intelligence methods available for cancer research. Frontiers of Medicine. doi.org/10.1007/s11684-024-1085-3.
Share
Share
Copy Link
A comprehensive review published in Frontiers of Medicine explores the transformative role of AI in cancer research, detailing its applications, benefits, and limitations in areas such as drug development, diagnosis, and personalized care.

AI's Growing Impact on Cancer Research
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing cancer research, offering innovative solutions to longstanding challenges in the field. A comprehensive review published in Frontiers of Medicine highlights the significant advancements and potential limitations of AI applications in oncology
1
2
.Addressing Traditional Limitations
Traditional cancer research methods face several obstacles. Imaging techniques like MRI, CT, and mammography require time-consuming professional curation. Genetic biomarkers, while promising, are hindered by variations in metastasis and treatment responses. AI presents solutions to these challenges, with applications spanning drug development, cancer prediction, diagnosis, and analysis of next-generation sequencing data
1
.AI Methods in Cancer Research
The review discusses various AI methods employed in cancer research:
- Machine Learning (ML): Encompasses supervised and unsupervised learning techniques.
- Deep Learning: A subset of ML using multiple hidden layers to identify complex data patterns.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Extracts useful information from narrative texts for decision-making
1
2
.
These AI models utilize multi-omics and clinical information from diverse sources, with classification being the most common task. Validation of these models involves receiver operating characteristic analysis, computing metrics such as area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, and specificity
1
.Applications and Advancements
AI has shown promising results in several areas:
- Drug Development: AI models predict drug responses using multi-omics data.
- Electronic Health Records: AI extracts valuable information from messy clinical data.
- Genetic Analysis: AI algorithms identify mutations for early cancer detection and targeted therapies
1
2
.
Related Stories
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its potential, AI faces several hurdles in cancer research:
- Algorithm Selection: Choosing appropriate algorithms is complex, depending on data type and complexity.
- Clinical Integration: Implementing AI in clinical settings requires transparency and detailed explanations.
- Data Issues: Heterogeneity, biases, and privacy concerns pose challenges in developing accurate AI models
1
2
.
Future Directions
The review emphasizes the need for:
- Increased Transparency: Better guidance on software scrutiny and AI system usage conditions.
- Cost-effectiveness Analysis: Evaluating the economic impact of AI implementation.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular retraining of datasets to maintain AI tool quality
1
2
.
As AI continues to evolve, it holds great promise for revolutionizing cancer detection and improving patient outcomes. The potential of explainable AI, personalized medicine, and non-invasive AI tools for early cancer detection points towards a transformative future in oncology research
1
2
.References
Summarized by
Navi
[2]
Related Stories
Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.4, New AI Model Built for Agents and Professional Work
Technology

2
Pentagon's Anthropic showdown exposes who controls AI guardrails in military contracts
Policy and Regulation

3
Anthropic challenges Pentagon supply chain risk label in court over AI usage restrictions
Policy and Regulation