Google Opal integrates with Gemini to let anyone build AI mini-apps using natural language
3 Sources
3 Sources
[1]
Google's vibe-coding tool Opal comes to Gemini | TechCrunch
Google's vibe-coding tool, Opal, is making its way to Gemini. The company on Wednesday said it is integrating the tool, which lets you build AI-powered mini apps, inside the Gemini web app, allowing users to create their own custom apps, which Google calls Gems. Introduced in 2024, Gems are customized versions of Gemini designed for specific tasks or scenarios. For instance, some of Google's pre-made Gems include a learning coach, a brainstorming assistant, a career guide, a coding partner, and an editor. Opal, meanwhile, focuses on helping users create mini-apps or mix existing apps. To use the feature, users describe the app they want to make in natural language, and the tool will use the different Gemini models to create it. Now, Opal is directly available from Gemini on the web, where it's found in the Gems manager. The tool has a visual editor that lays out the steps required to create an application. From the editor, users can rearrange steps and link them together, without writing code. Google notes that the visual editor also includes a new view in Gemini that will take the user's written prompts and turn them into a list of steps. This makes it even easier to build apps and see how they work. For more advanced customization options, users can move from Gemini to the Advanced Editor at opal.google.com. The mini apps can be reused after they're created. Known as "vibe-coding," using AI to program and make apps has skyrocketed in popularity over the past couple of years. The market now has apps from startups like Lovable and Cursor, as well as offerings from AI providers like Anthropic and OpenAI. There are also tools focused more directly on consumers, like those from AI-powered app-building startup, Wabi.
[2]
Gemini web app just got Opal where you can build mini apps with no code
Google Labs' Opal is now in Gemini's Gems manager, letting you chain prompts, models, and tools into shareable workflows. Opal is now inside the Gemini web app, which means you can build reusable AI mini-apps right where you already manage Gems. If you've been waiting for an easier way to create custom Gemini tools without writing code, this is Google's latest experiment to try. Google Labs describes Opal as a visual, natural-language builder for multi-step workflows, the kind that chain prompts, model calls, and tools into a single mini app. Google also says Opal handles hosting, so once an app's ready, you can share it without setting up servers or deploying anything yourself. Go to Gems manager and try it now To find Opal in the Gemini web app, head to your Gems manager and look for the Opal option to create experimental Gems. From there, you can type what you want the mini app to do in plain language, then edit the generated workflow and reuse it later for the same task. Recommended Videos Google's pitch is speed-to-prototype. Instead of rebuilding the same prompt chain every time, you can turn it into something you can run again and again. A new step list view Opal's editor is also getting a clearer way to understand what you've built. Google says you'll see a view that converts your prompt into a step-by-step list, so it's easier to spot what each part does and where a change should go. That's a practical upgrade because "no code" only works if editing stays approachable. If a single step is off, you can tweak that step instead of rewriting the whole thing. If you need more control, Google points builders to the Advanced Editor at opal.google for finer-grained edits. Think of Gemini's Opal entry point as the quick build path, and the Advanced Editor as the place you go when workflows get complex. Both are available today: Opal in the Gemini web app via Gems manager and the standalone Advanced Editor at opal.google. Try it out now and compare it to the best AI tools out today.
[3]
Google's Opal explained: How Gemini now lets you build apps by describing ideas
Build AI mini apps without coding using Google Opal in Gemini For years, building even a simple app meant choosing a programming language, setting up frameworks, and wrestling with logic flows. Google's new tool, Opal, takes a radically different approach. Integrated directly into the Gemini web app, Opal allows users to create functional AI-powered mini apps simply by describing what they want in plain language. No traditional coding required. This shift places Google firmly in the growing "vibe coding" movement, where intent matters more than syntax. Instead of writing lines of code, users explain said intent and let AI handle the structure. Also read: AI won't replace humans: Google to OpenAI, big tech CEOs agree Opal is Google's visual, natural-language app builder designed for Gemini. At its core, it converts a user's description into a workflow that connects prompts, logic steps, and AI model calls. Google refers to the finished outputs as mini apps or reusable AI tools that live inside Gemini. A user might say something like, "Create a tool that summarizes meeting notes and emails them to my team," and Opal builds a working flow to do exactly that. The app can then be saved, reused, or modified later. Unlike standard chat interactions, Opal focuses on repeatable actions. It turns one-off prompts into structured tools that can be triggered again and again. Opal's biggest strength is its visual editor. Once Gemini generates an app from a description, users can see how it works step by step. Each block represents a part of the logic, such as input, processing, or output. These blocks can be edited, reordered, or refined without touching code. This transparency is crucial. Rather than treating AI as a black box, Opal shows how prompts and decisions are chained together. For beginners, this makes experimentation less intimidating. For advanced users, it provides control without complexity. Because Opal lives inside Gemini, it can easily tap into the assistant's strengths, including text generation, summarization, reasoning, and context awareness from emails or documents, depending on permissions. Opal is clearly not aimed at professional software engineers building large-scale products. Instead, it targets creators, analysts, students, and everyday users who want custom AI tools without technical barriers. Also read: World's smallest programmable robot: 5 crazy things it can do For example, a journalist could build a research assistant that summarizes articles and highlights contradictions. A marketer could create a content ideation tool tuned to brand guidelines. A student could design a study helper that quizzes them based on uploaded notes. By lowering the barrier to entry, Google is positioning Gemini as more than just a chatbot. It becomes a platform for personal productivity tools. Opal reflects a broader shift in how AI tools are evolving. The industry is moving away from single-prompt chat experiences toward systems that act, repeat, and automate. Google's decision to embed Opal directly into Gemini signals that it sees app creation as a core AI use case, not a niche experiment. It also intensifies competition with other no-code and AI agent platforms. By keeping everything inside Gemini, Google removes friction and keeps users within its ecosystem. In simple terms, Opal turns ideas into usable tools. If it works as smoothly as promised, it could change how people think about building software at the smallest scale, not as something you code, but something you describe.
Share
Share
Copy Link
Google has integrated Opal, its vibe-coding tool, directly into the Gemini web app. Users can now build custom AI-powered mini-apps by describing what they want in plain language, without writing any code. The tool features a visual editor that shows workflow steps, making app development accessible to creators, analysts, and students.
Google Opal Brings No-Code App Building to Gemini
Google has integrated its vibe-coding tool, Google Opal, directly into the Gemini web app, marking a significant shift in how users can create custom AI-powered mini-apps
1
. The integration allows anyone to build mini apps with no code by simply describing their ideas in natural language prompts, effectively removing traditional programming barriers from app development2
.
Source: Digit
Users can now access Opal through the Gems manager within Gemini, where these custom creations are called Gems—customized versions of Gemini designed for specific tasks or scenarios
1
. Introduced in 2024, Gems already include pre-made options like learning coaches, brainstorming assistants, career guides, coding partners, and editors. Opal expands this ecosystem by enabling users to create their own custom Gemini tools tailored to unique workflows.How the No-Code Visual Builder Works
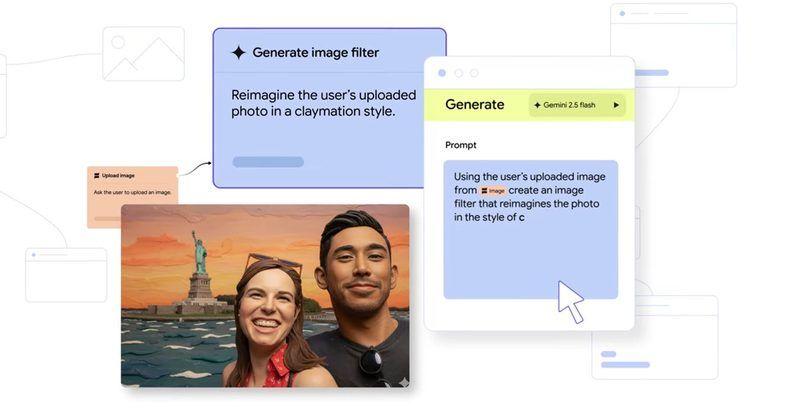
The integration centers on Opal's visual editor, which lays out the steps required to create an application in a transparent, editable format
1
. Users describe what they want their mini app to do in plain language, and Opal uses different Gemini models to generate a working flow. Google Labs describes Opal as a natural-language builder for multi-step workflows that chain prompts, model calls, and tools into a single functional unit2
.
Source: Digital Trends
The editor includes a new step list view that converts written prompts into a clear breakdown of each action, making it easier to understand how the app works and where adjustments should be made
1
. Users can rearrange steps and link them together without writing code, and these reusable AI workflows can be saved and triggered repeatedly for the same task2
.For more complex needs, users can transition from Gemini to the Advanced Editor at opal.google.com, which offers finer-grained control over workflows
2
. Google also handles hosting, eliminating the need for users to set up servers or deploy anything themselves.Who Benefits from Building Apps by Describing Ideas
Google Opal targets creators, analysts, students, and non-technical users who want custom AI tools without technical barriers
3
. A journalist could build a research assistant that summarizes articles and highlights contradictions. A marketer might create a content ideation tool aligned with brand guidelines. A student could design a study helper that quizzes them based on uploaded notes3
.
Source: TechCrunch
Because Opal lives inside Gemini, it taps into the assistant's existing capabilities, including text generation, summarization, reasoning, and context awareness from emails or documents
3
. This integration positions Gemini as more than just a chatbot—it becomes a platform for personal productivity tools that act, repeat, and automate.Related Stories
The Vibe-Coding Movement Intensifies
The move reflects the growing "vibe coding" trend, where intent matters more than syntax
1
. Using AI to program and make apps has skyrocketed in popularity over the past couple of years, with competition now including startups like Lovable and Cursor, as well as offerings from OpenAI and Anthropic1
.Google's decision to embed Opal directly into Gemini signals that it sees app creation as a core AI use case, not a niche experiment
3
. By keeping everything inside Gemini, Google removes friction and keeps users within its ecosystem, intensifying competition with other no-code and AI agent platforms. The industry is moving away from single-prompt chat experiences toward systems that can chain prompts into repeatable, structured actions.Both entry points are available now: Opal in the Gemini web app via the Gems manager and the standalone Advanced Editor at opal.google
2
. If Opal works as smoothly as promised, it could reshape how people approach software creation at the smallest scale—not as something you code, but something you describe.References
Summarized by
Navi
[2]
Related Stories
Recent Highlights
1
Samsung unveils Galaxy S26 lineup with Privacy Display tech and expanded AI capabilities
Technology

2
Anthropic refuses Pentagon's ultimatum over AI use in mass surveillance and autonomous weapons
Policy and Regulation

3
AI models deploy nuclear weapons in 95% of war games, raising alarm over military use
Science and Research