NASA's Perseverance Rover Completes First AI-Planned Drive on Mars Using Claude AI Models
11 Sources
11 Sources
[1]
NASA's Perseverance Rover Completes First AI-Planned Drive on Mars - NASA
The team for the six-wheeled scientist used a vision-capable AI to create a safe route over the Red Planet's surface without the input of human route planners. NASA's Perseverance Mars rover has completed the first drives on another world that were planned by artificial intelligence. Executed on Dec. 8 and 10, and led by the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, the demonstration used generative AI to create waypoints for Perseverance, a complex decision-making task typically performed manually by the mission's human rover planners. "This demonstration shows how far our capabilities have advanced and broadens how we will explore other worlds," said NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman. "Autonomous technologies like this can help missions to operate more efficiently, respond to challenging terrain, and increase science return as distance from Earth grows. It's a strong example of teams applying new technology carefully and responsibly in real operations." During the demonstration, the team leveraged a type of generative AI called vision-language models to analyze existing data from JPL's surface mission dataset. The AI used the same imagery and data that human planners rely on to generate waypoints -- fixed locations where the rover takes up a new set of instructions -- so that Perseverance could safely navigate the challenging Martian terrain. The initiative was led out of JPL's Rover Operations Center (ROC) in collaboration with Anthropic, using the company's Claude AI models. Mars is on average about 140 million miles (225 million kilometers) away from Earth. This vast distance creates a significant communication lag, making real-time remote operation -- or "joy-sticking" -- of a rover impossible. Instead, for the past 28 years, over several missions, rover routes have been planned and executed by human "drivers," who analyze the terrain and status data to sketch a route using waypoints, which are usually spaced no more than 330 feet (100 meters) apart to avoid any potential hazards. Then they send the plans via NASA's Deep Space Network to the rover, which executes them. But for Perseverance's drives on the 1,707 and 1,709 Martian days, or sols, of the mission, the team did something different: Generative AI provided the analysis of the high-resolution orbital imagery from the HiRISE (High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and terrain-slope data from digital elevation models. After identifying critical terrain features -- bedrock, outcrops, hazardous boulder fields, sand ripples, and the like -- it generated a continuous path complete with waypoints. To ensure the AI's instructions were fully compatible with the rover's flight software, the engineering team also processed the drive commands through JPL's "digital twin" (virtual replica of the rover), verifying over 500,000 telemetry variables before sending commands to Mars. On Dec. 8, with generative AI waypoints in its memory, Perseverance drove 689 feet (210 meters). Two days later, it drove 807 feet (246 meters). "The fundamental elements of generative AI are showing a lot of promise in streamlining the pillars of autonomous navigation for off-planet driving: perception (seeing the rocks and ripples), localization (knowing where we are), and planning and control (deciding and executing the safest path)," said Vandi Verma, a space roboticist at JPL and a member of the Perseverance engineering team. "We are moving towards a day where generative AI and other smart tools will help our surface rovers handle kilometer-scale drives while minimizing operator workload, and flag interesting surface features for our science team by scouring huge volumes of rover images." "Imagine intelligent systems not only on the ground at Earth, but also in edge applications in our rovers, helicopters, drones, and other surface elements trained with the collective wisdom of our NASA engineers, scientists, and astronauts," said Matt Wallace, manager of JPL's Exploration Systems Office. "That is the game-changing technology we need to establish the infrastructure and systems required for a permanent human presence on the Moon and take the U.S. to Mars and beyond." Managed for NASA by Caltech, JPL is home to the Rover Operations Center (ROC). It also manages operations of the Perseverance rover on behalf of the agency's Science Mission Directorate as part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program portfolio.
[2]
NASA Used AI to Drive Its Perseverance Mars Rover for the First Time
NASA used Anthropic's Claude for an experiment in plotting the rover's course, which the agency deemed successful. Plotting a course for NASA's Perseverance rover, 140 million miles away on Mars, is significantly more difficult than setting a driving route here on Earth, where we can punch an address into Google Maps and be on our way in seconds. The rover's course is usually plotted by a team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Lab to account for terrain, obstacles and potential hazards, lest the rover tip over or get damaged. For the first time, NASA's JPL used AI to plot a course for Perseverance, and it seems to have worked out. The two demonstrations, which took place on Dec. 8 and 10, were plotted by Anthropic's Claude AI models and double-checked by JPL to ensure that the AI didn't accidentally drive the rover into a ditch. Perseverance drove just under 1,500 feet across the two drives with no documented issues. NASA took a similar approach with plotting the waypoints as it would with human operators. Claude was fed the same satellite imagery and data from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter that JPL scientists would use, and then asked to plot waypoints that Perseverance could handle safely. The resulting path was slightly modified by NASA and then shipped to Perseverance, which then drove the path autonomously. "This demonstration shows how far our capabilities have advanced and broadens how we will explore other worlds," said NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman. "Autonomous technologies like this can help missions to operate more efficiently, respond to challenging terrain and increase science return as distance from Earth grows. It's a strong example of teams applying new technology carefully and responsibly in real operations." You can watch the Dec. 10 drive on NASA's YouTube channel, which has been condensed into a 52-second video. While AI is largely known as a provider of slop, which has been blamed for rapidly degrading people's internet experience, it can be useful in some scientific pursuits. It takes time to parse years of imagery and data, plot the Perseverance waypoints, and then execute them. Per NASA, waypoints are usually set no more than 330 feet apart, which means Perseverance is exploring the red planet one football field at a time. Take its epic climb out of the Jezero Crater in 2024. The journey took Perseverance 3.5 months and, all told, the rover climbed a total of 1,640 vertical feet. As of December 2025, the rover has driven a total of just 25 miles in roughly four years. The goal, according to JPL space roboticist Vandi Verma, is to let Perseverance (and other Mars rovers) travel much farther while "minimizing operator workload." Verma also notes that AI could be used to flag interesting features on the planet, saving the human science teams time by eliminating the need to manually check "huge volumes of rover images." "This demonstration shows how far our capabilities have advanced and broadens how we will explore other worlds," said Isaacman. "Autonomous technologies like this can help missions to operate more efficiently, respond to challenging terrain and increase science return as distance from Earth grows. It's a strong example of teams applying new technology carefully and responsibly in real operations."
[3]
NASA's Perseverance rover completes the first AI-planned drive on Mars
The team behind NASA's six-wheeled Mars explorer tested a vision-enabled artificial intelligence system to map a safe route across the Martian surface without relying on human route planners. NASA's Perseverance rover has now completed the first drives on another planet that were planned by artificial intelligence. The milestone demonstration took place on Dec. 8 and 10 and was led by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. During the test, generative AI was used to select waypoints for the rover, a complex planning task that is normally handled by human experts on Earth. "This demonstration shows how far our capabilities have advanced and broadens how we will explore other worlds," said NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman. "Autonomous technologies like this can help missions to operate more efficiently, respond to challenging terrain, and increase science return as distance from Earth grows. It's a strong example of teams applying new technology carefully and responsibly in real operations." How Vision AI Helped Navigate the Martian Surface For the demonstration, engineers used a form of generative AI known as vision-language models to examine existing data from JPL's surface mission dataset. The system analyzed the same images and information that human planners typically use, then identified waypoint locations so Perseverance could travel safely across difficult Martian terrain. The work was coordinated from JPL's Rover Operations Center (ROC) and carried out in collaboration with Anthropic, using the company's Claude AI models. Why Mars Rover Routes Are Hard to Plan Mars sits an average of about 140 million miles (225 million kilometers) from Earth. That distance creates long communication delays, making real-time control of a rover impossible. For nearly three decades, rover navigation has depended on human drivers who carefully study terrain data and plan routes in advance. These planners design paths made up of waypoints, usually spaced no more than 330 feet (100 meters) apart, to reduce the risk of encountering hazards. The completed plans are sent through NASA's Deep Space Network, and the rover carries out the instructions on its own. AI Takes Over Route Planning for Perseverance During Perseverance's drives on the 1,707 and 1,709 Martian days, known as sols, the mission team shifted that responsibility to generative AI. The system examined high-resolution orbital images captured by the HiRISE (High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, along with terrain slope data from digital elevation models. Using this information, the AI identified important surface features such as bedrock, outcrops, boulder fields, and sand ripples. It then produced a continuous driving path that included all necessary waypoints. Before sending the commands to Mars, engineers ran the AI-generated instructions through JPL's digital twin (virtual replica of the rover). This step checked more than 500,000 telemetry variables to ensure the plan would work safely with Perseverance's flight software. On Dec. 8, Perseverance traveled 689 feet (210 meters) using the AI-generated plan. Two days later, it drove another 807 feet (246 meters). What This Means for Future Space Exploration "The fundamental elements of generative AI are showing a lot of promise in streamlining the pillars of autonomous navigation for off-planet driving: perception (seeing the rocks and ripples), localization (knowing where we are), and planning and control (deciding and executing the safest path)," said Vandi Verma, a space roboticist at JPL and a member of the Perseverance engineering team. "We are moving towards a day where generative AI and other smart tools will help our surface rovers handle kilometer-scale drives while minimizing operator workload, and flag interesting surface features for our science team by scouring huge volumes of rover images." "Imagine intelligent systems not only on the ground at Earth, but also in edge applications in our rovers, helicopters, drones, and other surface elements trained with the collective wisdom of our NASA engineers, scientists, and astronauts," said Matt Wallace, manager of JPL's Exploration Systems Office. "That is the game-changing technology we need to establish the infrastructure and systems required for a permanent human presence on the Moon and take the U.S. to Mars and beyond." More About Perseverance Managed for NASA by Caltech, JPL is home to the Rover Operations Center (ROC). The laboratory also oversees daily operations of the Perseverance rover for NASA's Science Mission Directorate as part of the agency's Mars Exploration Program portfolio.
[4]
NASA's Perseverance Mars rover completes its 1st drive planned by AI
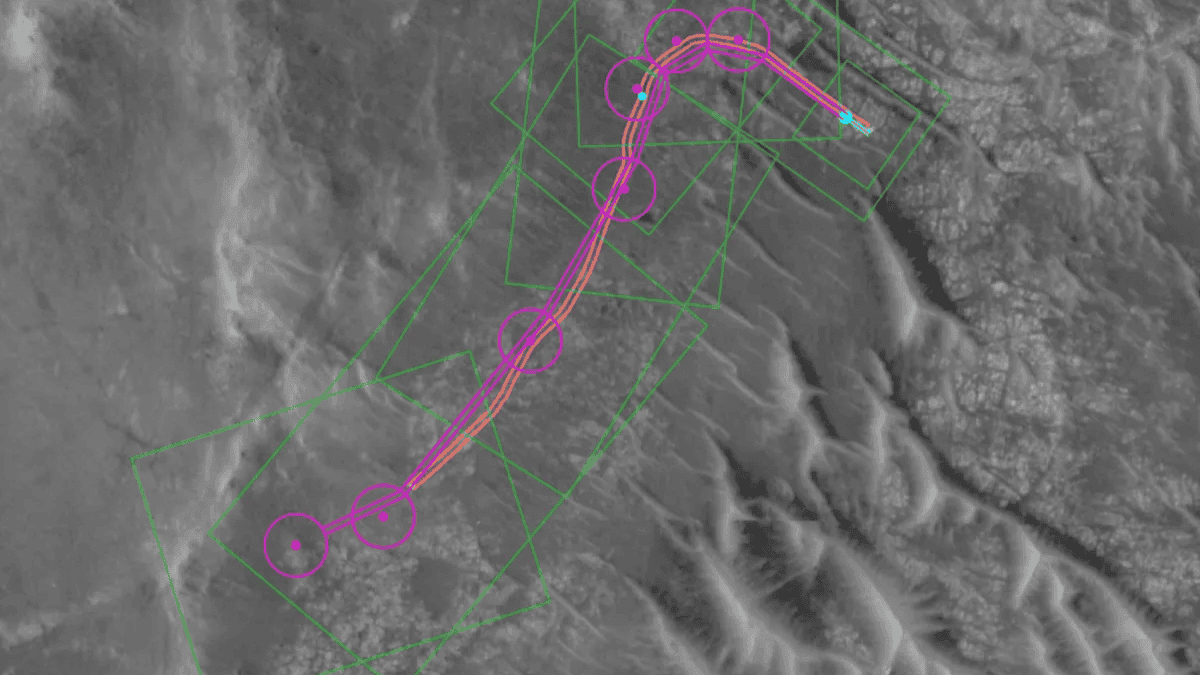
"The fundamental elements of generative AI are showing a lot of promise in streamlining the pillars of autonomous navigation for off-planet driving." NASA's Perseverance rover has completed its first-ever drive on Mars fully planned by artificial intelligence, the space agency announced. The demonstration, carried out on Dec. 8 and Dec. 10 of 2025, showed that generative AI could safely plan rover routes across Mars' rugged terrain without manual input, automating a labor-intensive decision-making process typically performed by human planners on Earth. "This demonstration shows how far our capabilities have advanced and broadens how we will explore other worlds," NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman said in a statement. Autonomous technologies like this, he added, could help future missions operate more efficiently, respond to hazardous terrain, and "increase science return" as spacecraft venture farther from Earth. "It's a strong example of teams applying new technology carefully and responsibly in real operations." Because Mars is an average of 140 million miles (225 million kilometers) from Earth, communication delays make real-time control impossible. For decades, mission teams have instead planned daily routes by hand; human "drivers" analyze terrain and rover status data, then map out paths using waypoints typically spaced no more than about 330 feet (100 meters) apart to avoid hazards. Those plans are sent to Mars via NASA's Deep Space Network, where the rover executes them, according to NASA. Perseverance's recent AI-driven test drive was led by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California, which built and operates the car-sized rover, in collaboration with Anthropic using the company's Claude AI models. To plan the routes, the AI analyzed the same images and data used by human planners. According to NASA, this included images captured by a camera aboard the agency's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter as well as terrain-slope data from computer models. From this information, the AI identified key surface features such as rocks, steep slopes and boulder fields, then mapped out a route for the rover to follow. That route included navigation waypoints, which are fixed surface coordinates that the rover is instructed to reach in sequence. In the video above from the rover's Dec. 10 drive along the rim of Jezero Crater, a waypoint appears as a blue circle. Pale blue lines trace the rover's wheel tracks, while black lines show the alternate route options the rover evaluated, NASA said. During the two test drives, Perseverance traveled nearly 1,500 feet (456 meters), the space agency said. Before sending commands to Mars, the mission team extensively tested the instructions using a detailed "digital twin" of Perseverance to confirm the rover could safely carry out the plan, according to the statement. "The fundamental elements of generative AI are showing a lot of promise in streamlining the pillars of autonomous navigation for off-planet driving," Vandi Verma, a space roboticist at JPL and a member of the Perseverance engineering team, said in the statement. "We are moving towards a day where generative AI and other smart tools will help our surface rovers handle kilometer-scale drives while minimizing operator workload," she added, "and flag interesting surface features for our science team by scouring huge volumes of rover images."
[5]
NASA taps Claude to conjure Mars rover's travel plan
Anthropic's Claude machine learning model has boldly planned what no Claude has planned before - a path across Mars for NASA's Perseverance rover. Perseverance traveled about 400 meters on the Martian surface last month based on an AI-generated path. It did so with the blessing of engineers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), who decided to delegate the meticulous work of route planning to Anthropic's AI model. As Anthropic explains in its writeup of the milestone, the surface of Mars can be treacherous for rovers. No one wants to be responsible for getting pricey space kit stuck in the sand, as happened with the Spirit rover in 2009. So the Perseverance team spends a fair amount of time on route planning. This involves consulting orbital and surface imagery of Mars in order to set a series of waypoints to guide the rover's movements. Once plotted, this data gets transmitted about 140 million miles or 225 million kilometers - the average distance from Earth to Mars - where it's received by Perseverance as a navigational plan. Live-driving via joystick isn't feasible given the distance involved. Perseverance has an AutoNav system that handles real-time decision making. "AutoNav allows the rover to autonomously re-plan its route around rocks or other obstacles on its way to a pre-established destination," NASA explains. The re-planning may not be needed if the pre-planning went well. The pre-planning is "time-consuming" and "laborious," as Anthropic puts it, so JPL researchers decided to let Claude - using its vision capabilities - have a go. "Generative AI provided the analysis of the high-resolution orbital imagery from the HiRISE (High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and terrain-slope data from digital elevation models," JPL said in an online post. "After identifying critical terrain features - bedrock, outcrops, hazardous boulder fields, sand ripples, and the like - it generated a continuous path complete with waypoints." Claude generated Rover commands in Rover Markup Language (RML), which is based on XML. The version of Claude available on the web could not emit RML when asked and initially denied any knowledge of RML. When pointed to Anthropic's statement on the matter, Claude responded, "You're absolutely right, and I apologize for my initial response!" Nonetheless, Claude could not provide an example of RML, a shortcoming that the model attributed to the lack of a publicly documented standard. But Claude evidently did generate RML when it had access to NASA's data. And that's when the humans took the opportunity to check the route plan. AI models make mistakes and, even if that weren't a concern, that's just the sort of thing one does when programming rovers on other planets. Using a simulator representing a virtual replica of the rover, JPL engineers checked more than 500,000 telemetry variables about the rover's projected position and potential obstacles. And they made corrections. "When the JPL engineers reviewed Claude's plans, they found that only minor changes were needed," Anthropic said. "For instance, ground-level camera images (which Claude hadn't seen) gave a clearer view of sand ripples on either side of a narrow corridor; the rover drivers elected to split the route more precisely than Claude had at this point. But otherwise, the route held up well. The plans were sent to Mars, and the rover successfully traversed the planned path." On Martian days (sols) 1,707 and 1,709 (starting from the landing date 18 February 2021 at 08.55pm GMT), which corresponded to December 8 and December 10, 2025, Perseverance executed routes planned by AI instead of humans. The rover didn't follow the set route exactly. NASA's image of the December 10 path shows that the pre-planned route and the actual route differ slightly, presumably based on decisions made by the AutoNav system. But AI played a role, one many models can be expected to reprise as vision-language-actions models become more capable and get stuffed into robots. "This demonstration shows how far our capabilities have advanced and broadens how we will explore other worlds," said NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman in a statement. "Autonomous technologies like this can help missions to operate more efficiently, respond to challenging terrain, and increase science return as distance from Earth grows. It's a strong example of teams applying new technology carefully and responsibly in real operations." Anthropic reports that JPL engineers say Claude can cut the time required for route planning in half. The AI biz however failed specify the amount of time being halved. Representatives of Anthropic and JPL couldn't immediately be reached to quantify that fraction. ®
[6]
NASA used Claude to plot a route for its Perseverance rover on Mars
Since 2021, NASA's Perseverance rover has achieved a number of historic milestones, including sending back the first audio recordings from Mars. Now, nearly five years after landing on the Red Planet, it just achieved another feat. This past December, Perseverance successfully completed a route through a section of the Jezero crater plotted by Anthropic's Claude chatbot, marking the first time NASA has used a large language model to pilot the car-sized robot. Between December 8 and 10, Perseverance drove approximately 400 meters (about 437 yards) through a field of rocks on the Martian surface mapped out by Claude. As you might imagine, using an AI model to plot a course for Perseverance wasn't as simple as inputting a single prompt. As NASA explains, routing Perseverance is no easy task, even for a human. "Every rover drive needs to be carefully planned, lest the machine slide, tip, spin its wheels, or get beached," NASA said. "So ever since the rover landed, its human operators have painstakingly laid out waypoints -- they call it a 'breadcrumb trail' -- for it to follow, using a combination of images taken from space and the rover's onboard cameras." To get Claude to complete the task, NASA had to first provide Claude Code, Anthropic's programming agent, with the "years" of contextual data from the rover before the model could begin writing a route for Perseverance. Claude then went about the mapping process methodically, stringing together waypoints from ten-meter segments it would later critique and iterate on. This being NASA we're talking about, engineers from the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) made sure to double check the model's work before sending it to Perseverance. The JPL team ran Claude's waypoints through a simulation they use every day to confirm the accuracy of commands sent to the rover. In the end, NASA says it only had to make "minor changes" to Claude's route, with one tweak coming as a result of the fact the team had access to ground-level images Claude hadn't seen in its planning process. "The engineers estimate that using Claude in this way will cut the route-planning time in half, and make the journeys more consistent," NASA said. "Less time spent doing tedious manual planning -- and less time spent training -- allows the rover's operators to fit in even more drives, collect even more scientific data, and do even more analysis. It means, in short, that we'll learn much more about Mars." While the productivity gains offered by AI are often overstated, in the case of NASA, any tool that could allow its scientists to be more efficient is sure to be welcome. Over the summer, the agency lost about 4,000 employees - accounting for about 20 percent of its workforce - due to Trump administration cuts. Going into 2026, the president had proposed gutting the agency's science budget by nearly half before Congress ultimately rejected that plan in early January. Still, even with its funding preserved just below 2025 levels, the agency has a tough road ahead. It's being asked to return to the Moon with less than half the workforce it had during the height of the Apollo program. For Anthropic, meanwhile, this is a major feat. You may recall last spring Claude couldn't even beat Pokémon Red. In less than a year, the company's models have gone from struggling to navigate a simple 8-bit Game Boy game to successfully plotting a course for a rover on a distant planet. NASA is excited about the possibility of future collaborations, saying "autonomous AI systems could help probes explore ever more distant parts of the solar system."
[7]
NASA Let AI Drive a Rover on Marsâ€"and It Somehow Survived
February marks the five-year anniversary of Perseverance's time on Mars. But when it comes to trying out new things, NASA's rover seems to be as active as it was on the day it first arrived on the Martian regolith. According to NASA JPL, Perseverance completed two driving stints using an itinerary created by Claude, a generative AI model developed by California-based firm Anthropic. To create the rover's travel plan, the AI program referred to the same datasets used by human engineers in creating waypointsâ€"a "breadcrumb trail" for the rover to follow, Anthropic explained in a statement. These drives took place on the 1,707th and 1,709th Martian days of the mission, during which Perseverance traveled 689 feet (210 meters) and 807 feet (246 meters), respectively. “This demonstration shows how far our capabilities have advanced and broadens how we will explore other worlds,†NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman said in JPL’s statement. “It’s a strong example of teams applying new technology carefully and responsibly in real operations.†Suffice to say, operating a rover on Mars is a lot different from driving a car on Earth. On average, Mars lies around 140 million miles (225 million kilometers) from Earth. The distance between Earthbound drivers and the actual rovers creates a sizable communication lag, leaving the rover unprepared for unexpected environmental barriers on the Martian surface. “This is high-stakes work,†Anthropic noted in its statement. For instance, Perseverance’s predecessor, Spirit, drove into a sand trap and “never moved again,†it added. To prevent such travesties, researchers will meticulously study images of the Martian terrain taken both from space and by the rover. Based on the images, engineers devise a travel plan that hopefully evades natural obstacles such as bedrock, outcrops, bumpy boulder fields, and sand ripples. This is a process that takes a lot of time and effort. And so, NASA and collaborators wondered if AI could help alleviate the intensity of manually planning rover routes. Before the demonstration, JPL engineers fed Claude data on how to operate the rover, which the AI used to generate its commands. The commands were then checked for accuracy through simulations verifying over 500,000 variables, NASA said. The engineers found Claude’s commands to be surprisingly unproblematic, only requiring minor fixes to account for certain images Claude hadn’t seen, Anthropic explained. Once the team was satisfied with the results, the AI-written plan was transmitted to Perseverance and executed in December. “The fundamental elements of generative AI are showing a lot of promise in streamlining the pillars of autonomous navigation for off-planet driving,†Vandi Verma, an engineer at JPL’s Perseverance team, said in the NASA release. “It means, in short, that we’ll learn much more about Mars,†Anthropic added, as engineers anticipate the program could help cut the route-planning time by half. Although Perseverance has only driven a few hundred feet so far, AI could soon start planning mile-long routes across the Martian terrain, Verma said.
[8]
For the first time on Mars, a rover planned its own drive
Planning a Mars rover drive is usually a slow, careful chess game played from Earth. But in a new test, NASA let an AI system do one of the hardest parts - picking the route. The result? NASA's Perseverance rover completed the first drives on another planet whose waypoint plans were generated by AI, not human route planners. The demonstration ran on December 8 and 10 and was led by NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Southern California. The team used a vision-enabled, generative AI approach to choose waypoints - those "go here next" markers that guide a rover safely across hazardous terrain. The experts tested the plan in simulation before uplinking it to Mars. "This demonstration shows how far our capabilities have advanced and broadens how we will explore other worlds," said NASA administrator Jared Isaacman. "Autonomous technologies like this can help missions to operate more efficiently, respond to challenging terrain, and increase science return as distance from Earth grows. It's a strong example of teams applying new technology carefully and responsibly in real operations." For this trial, engineers leaned on a type of generative system often described as a vision-language model. In plain terms, it "looked" at the same mission imagery and supporting data that human planners use, and then suggested a set of waypoint locations that would let the rover thread through rough ground without getting itself into trouble. The work was coordinated from JPL's Rover Operations Center, and the team partnered with Anthropic, using its Claude models to help with the waypoint-selection task. The goal wasn't to let an algorithm freestyle. It was to see whether AI could reliably handle a specific, high-stakes planning job that normally demands a lot of human time and expertise. Mars is far enough away that you can't "drive" a rover with a joystick. Signals take too long, and even small delays make real-time control impossible. That's why rover teams plan in advance. They study the landscape, pick a cautious route, and break it into short segments so the rover always has a safe next step to aim for. Traditionally those routes are built from waypoints spaced relatively close together - often around 100 meters or less - because the terrain can change fast. A patch that looks flat from above can hide sand that traps wheels, rocks that threaten the chassis, or slopes that could tilt the rover into a bad day. Once the plan is ready, it's sent to the rover through NASA Deep Space Network, and the rover carries out the commands on its own. During two drives - on sols 1,707 and 1,709 - the mission team handed the waypoint planning to the AI system. The system analyzed high-resolution orbital images from the HiRISE camera aboard Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, along with slope information from digital elevation models. Using that input, the system identified features that matter for rover safety such as bedrock, outcrops, boulder fields, and sand ripples. Then, a continuous route was generated that included the waypoint markers the rover would follow. On December 8, Perseverance drove 689 feet on the AI-generated plan. Two days later, it traveled another 807 feet. In rover terms, that's not a cross-country road trip, but it's long enough for a serious operational test, especially when the point is proving the planning method is trustworthy. Before the commands left Earth, engineers ran the AI-produced route through JPL's digital twin - a virtual replica of the rover used to test whether planned activities will behave properly with flight software and hardware constraints. In this case, the check wasn't superficial. The verification step evaluated more than 500,000 telemetry variables, essentially stress-testing the plan against an enormous list of "what could go wrong" details. After the plan passed those tests, it was sent to the rover. This kind of automation is attractive for a simple reason: rover teams have limited time, and Mars is big. If you can safely reduce the human workload for routine driving plans, you can either drive farther, drive more often, or spend more of the team's attention on the science decisions that really need human judgment. "Imagine intelligent systems not only on the ground at Earth, but also in edge applications in our rovers, helicopters, drones, and other surface elements trained with the collective wisdom of our NASA engineers, scientists, and astronauts," noted Matt Wallace, the manager of JPL's Exploration Systems Office. "That is the game-changing technology we need to establish the infrastructure and systems required for a permanent human presence on the Moon and take the U.S. to Mars and beyond." -- - Like what you read? Subscribe to our newsletter for engaging articles, exclusive content, and the latest updates.
[9]
NASA and Anthropic complete first AI-planned drive on Mars
Image taken by the Perseverance Mars Rover whilst driving. Image: NASA/Anthropic The organisation used GenAI to create waypoints for NASA's rover, a task that is typically undertaken by a mission's human planners. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and artificial intelligence (AI) platform Anthropic have "made history" by using GenAI technology Claude to perform the first AI-assisted drive on Mars. In December of last year NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) led by the Rover Operations Centre (ROC) team used Claude to plan the Perseverance Mars rover's journey, a task that is typically delegated to human rover planners. "This demonstration shows how far our capabilities have advanced and broadens how we will explore other worlds," said NASA administrator Jared Isaacman. He added, "Autonomous technologies like this can help missions to operate more efficiently, respond to challenging terrain and increase science return as distance from Earth grows. It's a strong example of teams applying new technology carefully and responsibly in real operations." To create a safe and efficient route to explore, NASA explained Claude analysed territory and identified obstacles using decades of rover data and mission constraints. Additionally, the rover could traverse specific Mars locations previously buried in 30 years of mission imagery logs. The organisation said this is work that previously took hours or days, but with advanced technologies was completed in minutes. After identifying critical terrain features, for example bedrock, outcrops, hazardous boulder fields and sand ripples, Claude generated a continuous path complete with waypoints. To ensure the AI's instructions were fully compatible with the rover's flight software, the engineering team also processed the drive commands through JPL's digital twin, before sending the commands to the Mars-based rover. Vandi Verma, a space roboticist at JPL and a member of the Perseverance engineering team said, "The fundamental elements of GenAI are showing a lot of promise in streamlining the pillars of autonomous navigation for off-planet driving: perception (seeing the rocks and ripples), localisation (knowing where we are), and planning and control (deciding and executing the safest path). "We are moving towards a day where generative AI and other smart tools will help our surface rovers handle kilometer-scale drives while minimising operator workload, and flag interesting surface features for our science team by scouring huge volumes of rover images." Also in December of last year, NASA JPL was reconsigned alongside Ubotica Technologies and Open Cosmos at the SpaceNews Icon Award for Space AI Partnership event, for their joint work on Dynamic Targeting. This is a technology that uses artificial intelligence to allow spacecraft to decide autonomously and within seconds where to make science observations from orbit. Don't miss out on the knowledge you need to succeed. Sign up for the Daily Brief, Silicon Republic's digest of need-to-know sci-tech news.
[10]
AI Takes the Wheel as Perseverance Rover Navigates Mars on Its Own
Breakthrough could enable faster, long-distance rover missions on Mars The Perseverance rover, which landed in Jezero Crater on Mars in 2021 to investigate evidence of ancient life and sample the rocks and another milestone has been achieved by NASA. In December 2025, the six-wheeled rover made its maiden drives on Mars entirely using artificial intelligence laid-out routes. A vision-capable AI examined high-resolution images and terrain data in order to map safe waypoints, enabling Perseverance to travel across Martian terrain on its own. AI-Powered Navigation According to reports, during an experiment by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, engineers had to plan the Dec. 8 and Dec. 10 drives of Perseverance using generative AI. The vision-language model performed the analysis of orbital images and terrain data to detect hazards (rocks, sand ripples, steep slopes) and generate a path with safe station points to the rover. Perseverance then ran the two AI-planned routes, covering 210 meters (246) each. Engineers tested the AI-generated commands in a simulated digital twin of the rover to confirm more than 500,000 variables were correct, and that is why it was safe to deploy commands to Mars. Implications and Future Exploration According to NASA, Mars is 225 million kilometers away, which means that real-time joystick control is not feasible; in practice, the planning of rover missions is done by hand using a sequence of waypoints. Administrator Jared Isaacman stated that AI-based planning could help make missions more efficient and increase the returns of science over such distances. JPL engineers say that generative AI can reduce the planning process and ultimately allow rovers to drive at kilometer scales with minimal operator intervention. The development opens the door to smarter robotic systems on the Moon and Mars that will help in future exploration and human missions.
[11]
NASA's Perseverance Makes History on Mars with Claude AI at the Helm
NASA's Mars rover, Perseverance, recently completed its first drive using commands shared by Anthropic's artificial intelligence (AI) chatbot, Claude. The milestone marks the first time a generative AI model has played a direct role in planning a rover's movement on another planet. The drive took place on January 27, with Claude delivering high-level navigation instructions that were translated into precise waypoints before transmission to Mars. Typically, these complex instructions are shared manually after long calculations and planning. Claude AI Commands NASA's Perseverance Rover on Mars In a newsroom post, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) announced this milestone. The process began with a human mission planner providing a terrain map and scientific goals to Claude. The AI chatbot then generated a sequence of waypoints, or intermediate coordinates the rover should aim for, based on the desired route, slope constraints, and safety considerations. These waypoints were reviewed and refined by mission engineers before being uplinked to Perseverance across 362 million kilometres between Earth and Mars, Anthropic said in a post. Perseverance drove approximately 23 metres (75 feet) on the Martian surface following the AI-generated plan, traversing rocky terrain inside Jezero Crater, where it is conducting geological and astrobiological investigations. The rover's successful movement confirmed that the AI-assisted planning produced a safe route, NASA said. The drive was monitored by the mission's navigation and engineering teams, who verified the rover's status and telemetry after execution. For this project, Anthropic equipped Claude with vision-language models to analyse existing data from JPL's mission dataset. NASA said that the chatbot used the same imagery and data that human planners rely on to create these waypoints. NASA highlighted that Claude did not control the rover directly or autonomously. Instead, the chatbot's role was to assist with planning and suggest waypoints for engineers to evaluate. Before this experiment, Mars rover drives were typically planned by human teams who selected traverse paths based on orbital imagery, 3D terrain models and defined mission constraints. "The fundamental elements of generative AI are showing a lot of promise in streamlining the pillars of autonomous navigation for off-planet driving. We are moving towards a day where generative AI and other smart tools will help our surface rovers handle kilometre-scale drives while minimising operator workload, and flag interesting surface features for our science team by scouring huge volumes of rover images," said Vandi Verma, a space roboticist at JPL and a member of the Perseverance engineering team.
Share
Share
Copy Link
NASA's Perseverance rover achieved a milestone by completing the first drives on another planet planned entirely by artificial intelligence. On December 8 and 10, the rover traveled nearly 1,500 feet across Mars using routes generated by Anthropic's Claude AI models, marking a shift from decades of manual route planning by human drivers at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
NASA Achieves Milestone in Autonomous Space Exploration
NASA's Perseverance rover has completed the first AI-planned drive on Mars, marking a significant advance in autonomous space exploration. Executed on December 8 and 10, 2025, the demonstration used generative AI to plan routes across the Martian terrain without manual input from human route planners
1
. Led by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, the initiative leveraged Anthropic's Claude AI models to generate waypoints—a complex decision-making task that has traditionally consumed significant time and resources2
.
Source: Gadgets 360
During the two test drives on sols 1,707 and 1,709 of the mission, the Perseverance rover traveled 689 feet (210 meters) and 807 feet (246 meters) respectively, totaling nearly 1,500 feet across the challenging surface of Mars
4
. NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman emphasized the significance: "This demonstration shows how far our capabilities have advanced and broadens how we will explore other worlds. Autonomous technologies like this can help missions to operate more efficiently, respond to challenging terrain, and increase science return as distance from Earth grows"1
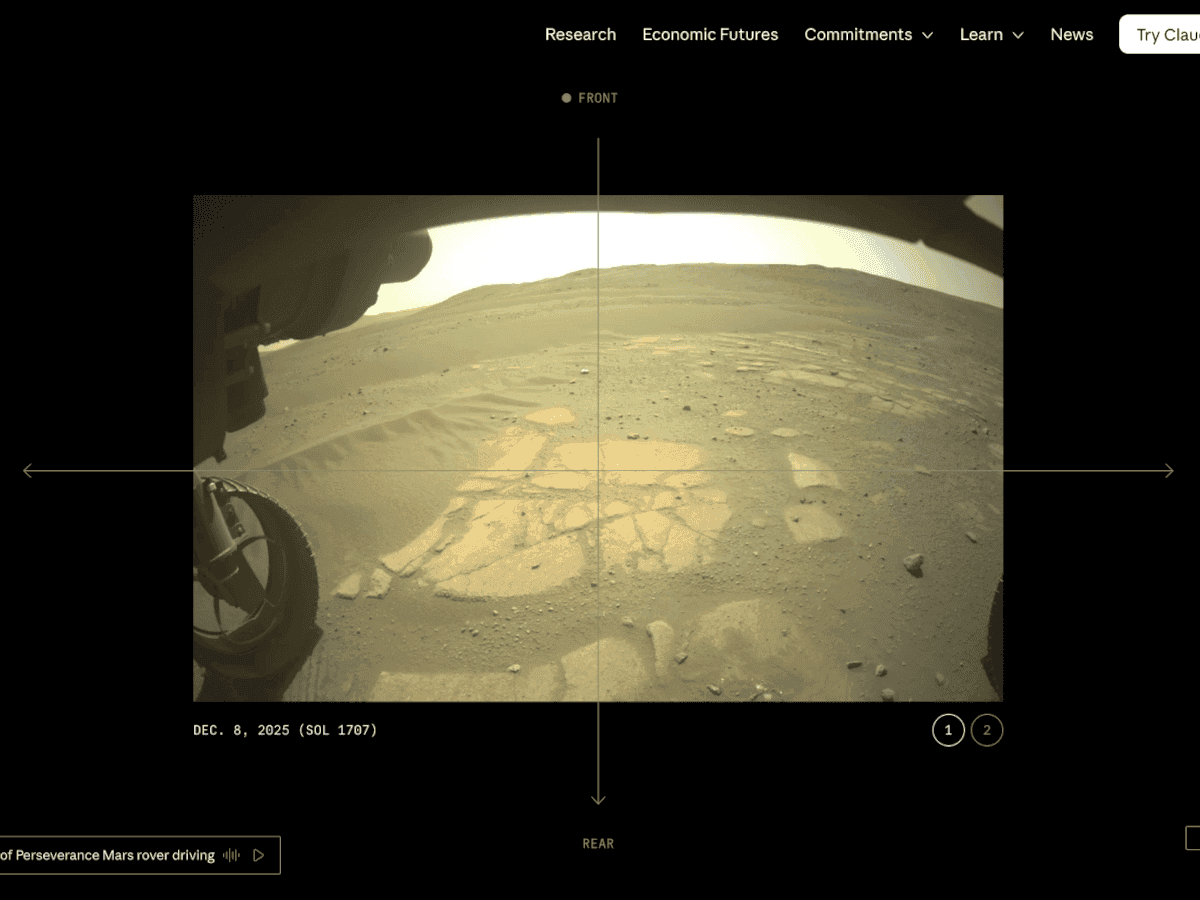
.
Source: Silicon Republic
How Generative AI Transformed Route Planning
The team at the Rover Operations Center used vision-language models to analyze the same data that human planners typically rely on for route planning. The AI examined high-resolution orbital imagery from the HiRISE (High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, along with terrain-slope data from digital elevation models
3
. After identifying critical terrain features—bedrock, outcrops, hazardous boulder fields, and sand ripples—the Claude AI models generated a continuous path complete with waypoints1
.
Source: Gadgets 360
Before transmission to Mars via the Deep Space Network, engineers processed the AI-generated commands through JPL's digital twin, a virtual replica of the rover. This verification step checked more than 500,000 telemetry variables to ensure full compatibility with the rover's flight software
1
. According to Anthropic, JPL engineers found that only minor changes were needed when reviewing Claude's plans, and the route planning time could be cut in half5
.Overcoming Communication Delays and Operator Workload
Mars sits an average of 140 million miles (225 million kilometers) from Earth, creating significant communication delays that make real-time remote operation impossible
1
. For nearly 28 years across several missions, rover routes have been planned by human planners who analyze terrain and status data to sketch routes using waypoints, typically spaced no more than 330 feet (100 meters) apart to avoid potential hazards3
.Vandi Verma, a space roboticist at JPL and member of the Perseverance engineering team, explained the broader implications: "The fundamental elements of generative AI are showing a lot of promise in streamlining the pillars of autonomous navigation for off-planet driving: perception (seeing the rocks and ripples), localization (knowing where we are), and planning and control (deciding and executing the safest path). We are moving towards a day where generative AI and other smart tools will help our surface rovers handle kilometer-scale drives while minimizing operator workload, and flag interesting surface features for our science team by scouring huge volumes of rover images"
1
.Related Stories
Implications for Future Missions to Enhance Mission Efficiency
The successful demonstration carries substantial implications for future autonomous technologies in space exploration. As of December 2025, the Perseverance rover has driven a total of just 25 miles in roughly four years, with waypoints typically set no more than 330 feet apart—exploring Mars one football field at a time
2
. AI-assisted navigation could dramatically accelerate this pace while reducing the burden on mission teams.Matt Wallace, manager of JPL's Exploration Systems Office, outlined the vision: "Imagine intelligent systems not only on the ground at Earth, but also in edge applications in our rovers, helicopters, drones, and other surface elements trained with the collective wisdom of our NASA engineers, scientists, and astronauts. That is the game-changing technology we need to establish the infrastructure and systems required for a permanent human presence on the Moon and take the U.S. to Mars and beyond"
1
.The AI-generated routes work in tandem with Perseverance's existing AutoNav system, which handles real-time decision making and allows the rover to autonomously re-plan its route around rocks or other obstacles on its way to pre-established destinations
5
. While the rover didn't follow the AI-planned route exactly—making slight adjustments based on AutoNav decisions—the demonstration proved that AI can safely handle the time-consuming and laborious task of pre-planning5
. This careful and responsible application of new technology in real operations sets a precedent for how AI might enhance mission efficiency and increase scientific return as NASA ventures farther into the solar system.References
Summarized by
Navi
[5]
Related Stories
Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.4, New AI Model Built for Agents and Professional Work
Technology

2
Anthropic sues Pentagon over supply chain risk label after refusing autonomous weapons use
Policy and Regulation

3
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round as questions swirl around AI bubble and profitability
Business and Economy








