Quantum Computing Shows Promise for Kidney Disease Detection Despite Current Limitations
2 Sources
2 Sources
[1]
Engineering study takes 'quantum leap' to detect kidney disease
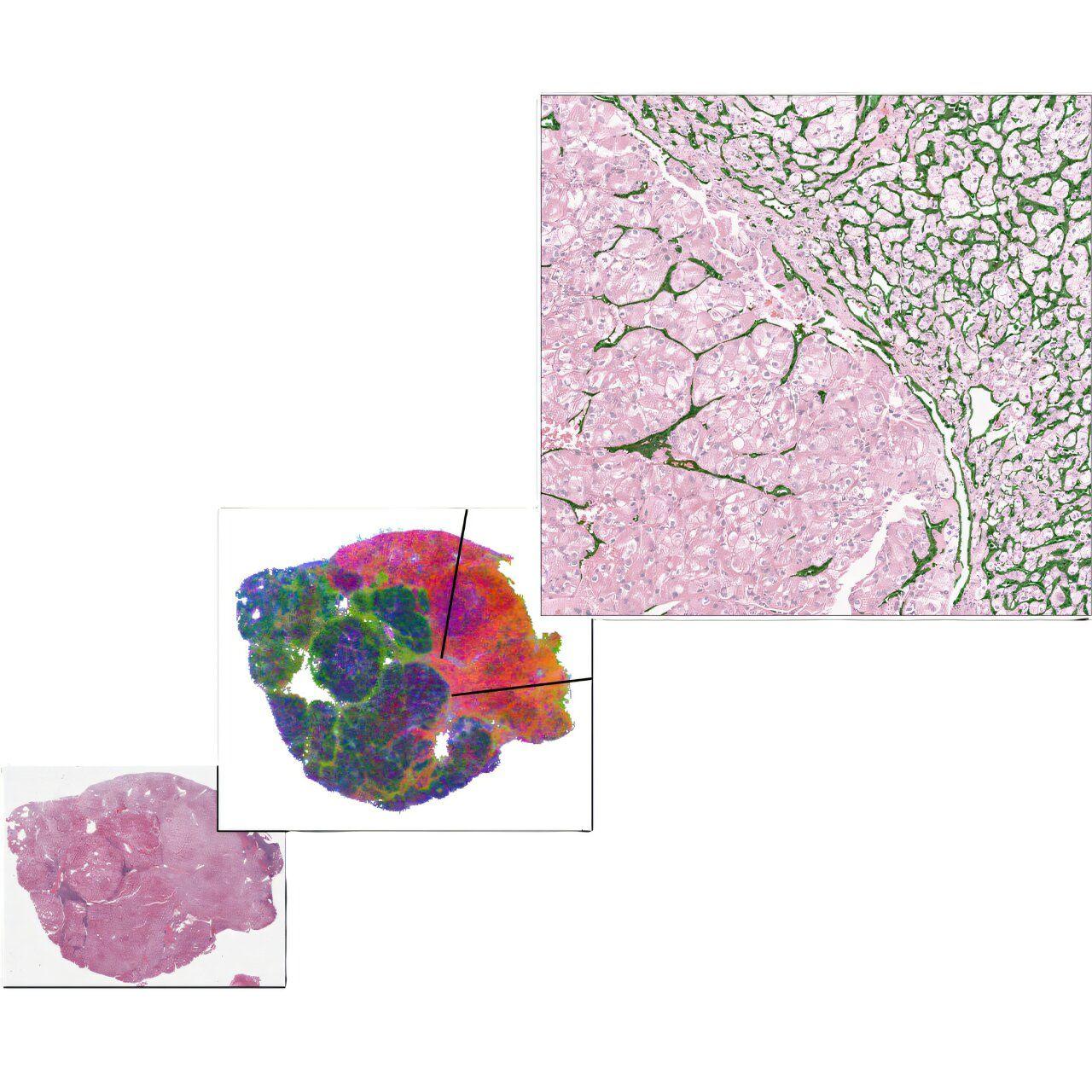
The kidney is one of the body's most vital organs, responsible for filtering waste, balancing electrolytes and maintaining overall health. Any impairment to its function can lead to serious and often irreversible consequences. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is one such condition -- a progressive illness that damages the kidneys over time, eventually leading to kidney failure if left untreated. Because CKD develops gradually and often shows few symptoms in its early stages, timely diagnosis is a major clinical challenge. Globally, an estimated 850 million people are living with some form of kidney disease. Among them, as many as 10 million require dialysis or kidney transplantation to survive. Despite the scale of this problem, CKD frequently goes undetected until it reaches an advanced stage. Early diagnosis is essential not only to slow disease progression but also to improve quality of life and survival rates. To help address this widespread issue, researchers are increasingly turning to artificial intelligence and machine learning (ML) to build automated tools that can detect CKD more efficiently and accurately. ML algorithms can recognize subtle patterns in complex medical data -- patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed by clinicians. Research from the College of Engineering and Computer Science at Florida Atlantic University is taking this concept further by exploring how quantum computing could enhance the accuracy and performance of ML-driven CKD diagnosis systems. Arslan Munir, Ph.D., senior author and an associate professor in the FAU Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, and his colleagues from Bangladesh, developed and compared two automated systems for CKD diagnosis: the Classical Support Vector Machine (CSVM) and the Quantum Support Vector Machine (QSVM). The goal of their study was to evaluate the efficiency and diagnostic accuracy of both approaches, and to better understand how emerging quantum machine learning techniques could eventually revolutionize real-world medical diagnostics. The team began by preparing and refining a CKD dataset, applying comprehensive data preprocessing to ensure the reliability of results. They then used two advanced data optimization methods: Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) to reduce noise and improve computational efficiency. Each optimized dataset was subsequently analyzed using both CSVM and QSVM algorithms, allowing for a detailed comparison of the two methods' predictive capabilities. The results of the study, published in the journal Informatics and Health, revealed clear differences. When paired with PCA, CSVM achieved a remarkable 98.75% accuracy, while QSVM reached 87.5%. Using SVD, the CSVM achieved 96.25%, compared to 60% for the QSVM. The classical SVM also proved far faster: up to 42 times quicker than the QSVM in certain experimental settings. The outcome indicates that, under current hardware conditions, the classical approach remains superior in both accuracy and time efficiency. However, Munir and his colleagues emphasized that QSVM's underperformance is primarily a reflection of today's computational limitations rather than the potential of quantum algorithms themselves. Even within the constraints of classical hardware, the QSVM still achieved competitive performance -- its 87.5% accuracy using PCA surpasses that of several existing classical SVM methods reported in prior studies. This suggests that hybrid quantum-classical systems could play an increasingly important role in the near term, combining the strengths of both paradigms to improve diagnostic precision while managing current technological challenges. "What makes our work unique is that we didn't just apply classical machine learning to detect chronic kidney disease -- we also tested a quantum version under the same conditions," said Munir. "By directly comparing classical and quantum models, and using two different optimization methods, we gained valuable insight into where the technology stands today and how quantum computing could help shape the future of health care analytics." Looking ahead, the research team plans to extend their work by exploring additional quantum ML algorithms beyond QSVM and testing their methods on larger, more diverse medical datasets. They also intend to focus on optimizing feature selection techniques to ensure scalability and adaptability across a wide range of diagnostic applications. Ultimately, the goal is to create more reliable, efficient and accessible AI-driven diagnostic tools that can assist clinicians in making faster, more accurate medical decisions. "This research is an important leap toward bringing quantum computing into health care -- an emerging field with the power to transform how we detect and treat complex diseases," said Stella Batalama, Ph.D., dean of the College of Engineering and Computer Science. "By combining machine learning with next-generation quantum technologies, this work offers real hope for earlier, faster and more accurate diagnosis of chronic kidney disease, ultimately improving outcomes and saving lives."
[2]
FAU Engineering Study Takes a 'Quantum Leap' to Detect Kidney Disease | Newswise
Newswise -- The kidney is one of the body's most vital organs, responsible for filtering waste, balancing electrolytes and maintaining overall health. Any impairment to its function can lead to serious and often irreversible consequences. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is one such condition - a progressive illness that damages the kidneys over time, eventually leading to kidney failure if left untreated. Because CKD develops gradually and often shows few symptoms in its early stages, timely diagnosis is a major clinical challenge. Globally, an estimated 850 million people are living with some form of kidney disease. Among them, as many as 10 million require dialysis or kidney transplantation to survive. Despite the scale of this problem, CKD frequently goes undetected until it reaches an advanced stage. Early diagnosis is essential not only to slow disease progression but also to improve quality of life and survival rates. To help address this widespread issue, researchers are increasingly turning to artificial intelligence and machine learning (ML) to build automated tools that can detect CKD more efficiently and accurately. ML algorithms can recognize subtle patterns in complex medical data - patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed by clinicians. Research from the College of Engineering and Computer Science at Florida Atlantic University is taking this concept further by exploring how quantum computing could enhance the accuracy and performance of ML-driven CKD diagnosis systems. Arslan Munir, Ph.D., senior author and an associate professor in the FAU Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, and his colleagues from Bangladesh, developed and compared two automated systems for CKD diagnosis: the Classical Support Vector Machine (CSVM) and the Quantum Support Vector Machine (QSVM). The goal of their study was to evaluate the efficiency and diagnostic accuracy of both approaches, and to better understand how emerging quantum machine learning techniques could eventually revolutionize real-world medical diagnostics. The team began by preparing and refining a CKD dataset, applying comprehensive data preprocessing to ensure the reliability of results. They then used two advanced data optimization methods: Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) to reduce noise and improve computational efficiency. Each optimized dataset was subsequently analyzed using both CSVM and QSVM algorithms, allowing for a detailed comparison of the two methods' predictive capabilities. The results of the study, published in the journal Informatics and Health, revealed clear differences. When paired with PCA, CSVM achieved a remarkable 98.75% accuracy, while QSVM reached 87.5%. Using SVD, the CSVM achieved 96.25%, compared to 60% for the QSVM. The classical SVM also proved far faster: up to 42 times quicker than the QSVM in certain experimental settings. The outcome indicates that, under current hardware conditions, the classical approach remains superior in both accuracy and time efficiency. However, Munir and his colleagues emphasized that QSVM's underperformance is primarily a reflection of today's computational limitations rather than the potential of quantum algorithms themselves. Even within the constraints of classical hardware, the QSVM still achieved competitive performance - its 87.5% accuracy using PCA surpasses that of several existing classical SVM methods reported in prior studies. This suggests that hybrid quantum-classical systems could play an increasingly important role in the near term, combining the strengths of both paradigms to improve diagnostic precision while managing current technological challenges. "What makes our work unique is that we didn't just apply classical machine learning to detect chronic kidney disease - we also tested a quantum version under the same conditions," said Munir. "By directly comparing classical and quantum models, and using two different optimization methods, we gained valuable insight into where the technology stands today and how quantum computing could help shape the future of health care analytics." Looking ahead, the research team plans to extend their work by exploring additional quantum ML algorithms beyond QSVM and testing their methods on larger, more diverse medical datasets. They also intend to focus on optimizing feature selection techniques to ensure scalability and adaptability across a wide range of diagnostic applications. Ultimately, the goal is to create more reliable, efficient and accessible AI-driven diagnostic tools that can assist clinicians in making faster, more accurate medical decisions. "This research is an important leap toward bringing quantum computing into health care - an emerging field with the power to transform how we detect and treat complex diseases," said Stella Batalama, Ph.D., dean of the College of Engineering and Computer Science. "By combining machine learning with next-generation quantum technologies, this work offers real hope for earlier, faster and more accurate diagnosis of chronic kidney disease, ultimately improving outcomes and saving lives." - FAU - About FAU's College of Engineering and Computer Science: The FAU College of Engineering and Computer Science is internationally recognized for innovative research and education in the areas of computer science and artificial intelligence (AI), computer engineering, electrical engineering, biomedical engineering, civil, environmental and geomatics engineering, mechanical engineering, and ocean engineering. Research conducted by the faculty and their teams expose students to technology innovations that push the current state-of-the art of the disciplines. The College research efforts are supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF), the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the Department of Defense (DOD), the Department of Transportation (DOT), the Department of Education (DOEd), the State of Florida, and industry. The FAU College of Engineering and Computer Science offers degrees with a modern twist that bear specializations in areas of national priority such as AI, cybersecurity, internet-of-things, transportation and supply chain management, and data science. New degree programs include Master of Science in AI (first in Florida), Master of Science and Bachelor in Data Science and Analytics, and the new Professional Master of Science and Ph.D. in computer science for working professionals. For more information about the College, please visit eng.fau.edu.
Share
Share
Copy Link
Florida Atlantic University researchers compared classical and quantum machine learning approaches for detecting chronic kidney disease, finding that while classical methods currently outperform quantum algorithms, quantum computing holds significant potential for future healthcare diagnostics.
Breakthrough Research Compares AI Approaches for Medical Diagnosis
Researchers at Florida Atlantic University have conducted a groundbreaking study comparing classical and quantum machine learning approaches for detecting chronic kidney disease (CKD), offering new insights into the potential of quantum computing in healthcare diagnostics. The research, led by Dr. Arslan Munir from the FAU Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, represents one of the first direct comparisons between classical and quantum algorithms under identical experimental conditions for medical diagnosis
1
.
Source: Newswise
The study addresses a critical healthcare challenge, as chronic kidney disease affects an estimated 850 million people globally, with 10 million requiring dialysis or kidney transplantation to survive. The progressive nature of CKD, combined with its often asymptomatic early stages, makes timely diagnosis a significant clinical challenge that could benefit from advanced AI-driven detection systems
2
.Methodology and Experimental Design
The research team developed and compared two automated diagnostic systems: the Classical Support Vector Machine (CSVM) and the Quantum Support Vector Machine (QSVM). To ensure robust results, researchers applied comprehensive data preprocessing to a CKD dataset and employed two advanced optimization methods - Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) - to reduce noise and improve computational efficiency
1
.Each optimized dataset underwent analysis using both CSVM and QSVM algorithms, enabling detailed performance comparisons across multiple metrics including diagnostic accuracy and computational speed. This methodical approach provided valuable insights into the current capabilities and limitations of quantum machine learning in medical applications
2
.Performance Results Reveal Current Limitations
The study results, published in the journal Informatics and Health, demonstrated clear performance differences between classical and quantum approaches. When paired with PCA optimization, CSVM achieved remarkable 98.75% accuracy compared to QSVM's 87.5%. Using SVD optimization, the performance gap widened further, with CSVM reaching 96.25% accuracy while QSVM achieved only 60%
1
.Beyond accuracy metrics, computational speed presented an even more dramatic contrast. Classical SVM algorithms proved up to 42 times faster than their quantum counterparts in certain experimental settings, highlighting significant efficiency advantages under current hardware conditions. These results indicate that classical approaches maintain superiority in both diagnostic precision and time efficiency for immediate practical applications
2
.Related Stories
Future Potential Despite Current Constraints
Despite quantum algorithms' underperformance, researchers emphasized that these limitations primarily reflect current computational constraints rather than inherent algorithmic weaknesses. Dr. Munir noted that the QSVM's 87.5% accuracy using PCA optimization actually surpasses several existing classical SVM methods reported in previous studies, suggesting significant untapped potential
1
.The findings point toward hybrid quantum-classical systems as a promising near-term solution, potentially combining the strengths of both paradigms to improve diagnostic precision while managing current technological challenges. As quantum hardware continues advancing, these hybrid approaches could bridge the gap between current limitations and future quantum advantages in healthcare analytics
2
.Research Implications and Next Steps
The research team plans to expand their work by exploring additional quantum machine learning algorithms beyond QSVM and testing methods on larger, more diverse medical datasets. Future efforts will focus on optimizing feature selection techniques to ensure scalability and adaptability across various diagnostic applications, ultimately aiming to create more reliable and accessible AI-driven diagnostic tools for clinical use
1
.Dr. Stella Batalama, dean of the College of Engineering and Computer Science, emphasized the research's significance in bringing quantum computing into healthcare, describing it as "an emerging field with the power to transform how we detect and treat complex diseases." This work represents an important step toward understanding quantum computing's role in future medical diagnostics and establishing foundations for next-generation healthcare AI systems
2
.References
Summarized by
Navi
[1]
Related Stories
AI and Nanomedicine Breakthrough: Detecting Rare Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer and Atherosclerosis
24 Jun 2025•Science and Research

AI Model Predicts Kidney Cancer Therapy Response with High Accuracy
25 Apr 2025•Health
Revolutionary AI System InfEHR Transforms Medical Diagnosis Through Advanced Pattern Recognition
16 Oct 2025•Health

Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round from Amazon, Nvidia, and SoftBank at $730B valuation
Business and Economy

2
Anthropic stands firm against Pentagon's demand for unrestricted military AI access
Policy and Regulation

3
Pentagon Clashes With AI Firms Over Autonomous Weapons and Mass Surveillance Red Lines
Policy and Regulation





