Stanford AI Tool Predicts Cancer Gene Activity from Biopsy Images, Potentially Revolutionizing Cancer Diagnosis
3 Sources
3 Sources
[1]
AI tool reads biopsy images
To determine the type and severity of a cancer, pathologists typically analyze thin slices of a tumor biopsy under a microscope. But to figure out what genomic changes are driving the tumor's growth - information that can guide how it is treated - scientists must perform genetic sequencing of the RNA isolated from the tumor, a process that can take weeks and costs thousands of dollars. Now, Stanford Medicine researchers have developed an artificial intelligence-powered computational program that can predict the activity of thousands of genes within tumor cells based only on standard microscopy images of the biopsy. The tool, described online in Nature Communications Nov. 14, was created using data from more than 7,000 diverse tumor samples. The team showed that it could use routinely collected biopsy images to predict genetic variations in breast cancers and to predict patient outcomes. "This kind of software could be used to quickly identify gene signatures in patients' tumors, speeding up clinical decision-making and saving the health care system thousands of dollars," said Olivier Gevaert, PhD, a professor of biomedical data science and the senior author of the paper. The work was also led by Stanford graduate student Marija Pizuria and postdoctoral fellows Yuanning Zheng, PhD, and Francisco Perez, PhD. Clinicians have increasingly guided the selection of which cancer treatments - including chemotherapies, immunotherapies, and hormone-based therapies - to recommend to their patients based on not only which organ a patient's cancer affects, but which genes a tumor is using to fuel its growth and spread. Turning on or off certain genes could make a tumor more aggressive, more likely to metastasize, or more or less likely to respond to certain drugs. However, accessing this information often requires costly and time-consuming genomic sequencing. Gevaert and his colleagues knew that the gene activity within individual cells can alter the appearance of those cells in ways that are often imperceptible to a human eye. They turned to artificial intelligence to find these patterns. The researchers began with 7,584 cancer biopsies from 16 different cancer types. Each biopsy had been sliced into thin sections and prepared using a method known as hematoxylin and eosin staining, which is standard for visualizing the overall appearance of cancer cells. Information on the cancers' transcriptomes - which genes the cells are actively using - was also available.
[2]
AI tool predicts cancer gene activity from biopsy images
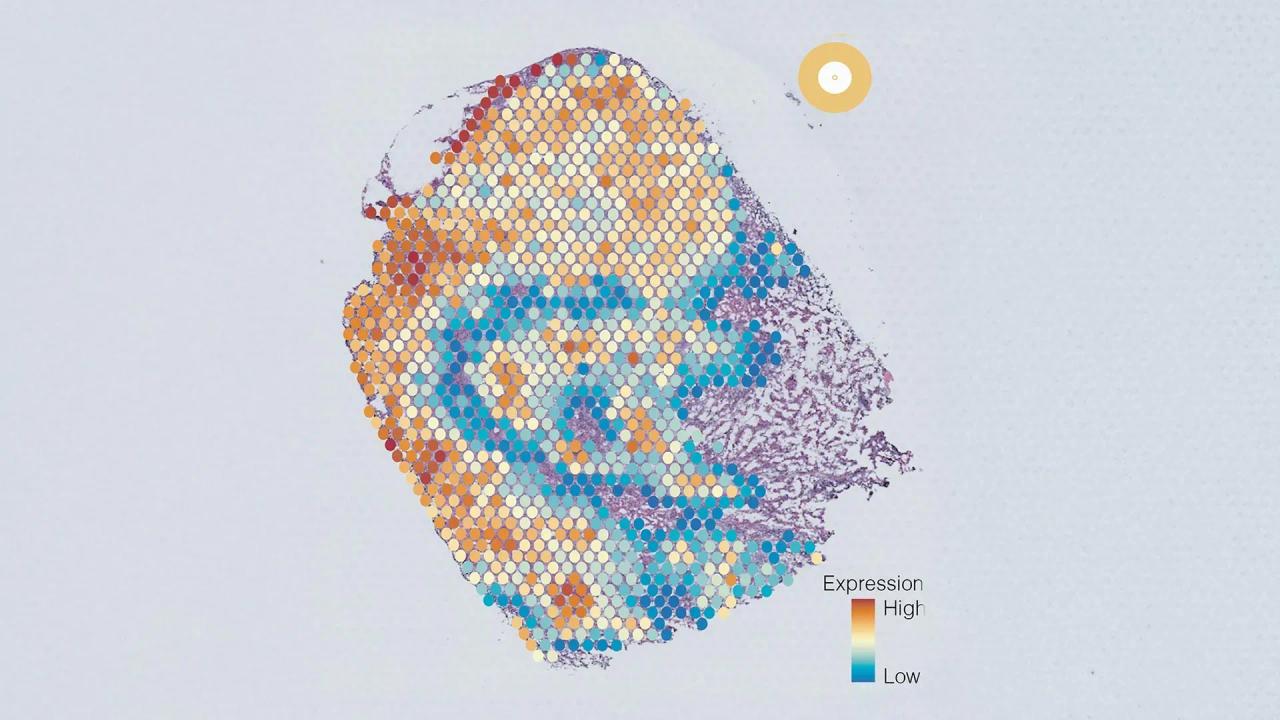
To determine the type and severity of a cancer, pathologists typically analyze thin slices of a tumor biopsy under a microscope. But to figure out what genomic changes are driving the tumor's growth -- information that can guide how it is treated -- scientists must perform genetic sequencing of the RNA isolated from the tumor, a process that can take weeks and costs thousands of dollars. Now, Stanford Medicine researchers have developed an artificial intelligence-powered computational program that can predict the activity of thousands of genes within tumor cells based only on standard microscopy images of the biopsy. The tool, described online in Nature Communications Nov. 14, was created using data from more than 7,000 diverse tumor samples. The team showed that it could use routinely collected biopsy images to predict genetic variations in breast cancers and to predict patient outcomes. "This kind of software could be used to quickly identify gene signatures in patients' tumors, speeding up clinical decision-making and saving the health care system thousands of dollars," said Olivier Gevaert, Ph.D., a professor of biomedical data science and the senior author of the paper. The work was also led by Stanford graduate student Marija Pizuria and postdoctoral fellows Yuanning Zheng, Ph.D., and Francisco Perez, Ph.D. Driven by genomics Clinicians have increasingly guided the selection of which cancer treatments -- including chemotherapies, immunotherapies and hormone-based therapies -- to recommend to their patients based on not only which organ a patient's cancer affects, but which genes a tumor is using to fuel its growth and spread. Turning on or off certain genes could make a tumor more aggressive, more likely to metastasize, or more or less likely to respond to certain drugs. However, accessing this information often requires costly and time-consuming genomic sequencing. Gevaert and his colleagues knew that the gene activity within individual cells can alter the appearance of those cells in ways that are often imperceptible to a human eye. They turned to artificial intelligence to find these patterns. The researchers began with 7,584 cancer biopsies from 16 different of cancer types. Each biopsy had been sliced into thin sections and prepared using a method known as hematoxylin and eosin staining, which is standard for visualizing the overall appearance of cancer cells. Information on the cancers' transcriptomes -- which genes the cells are actively using -- was also available. A working model After the researchers integrated their new cancer biopsies as well as other datasets, including transcriptomic data and images from thousands of healthy cells, the AI program -- which they named SEQUOIA (slide-based expression quantification using linearized attention) -- was able to predict the expression patterns of more than 15,000 different genes from the stained images. For some cancer types, the AI-predicted gene activity had a more than 80% correlation with the real gene activity data. In general, the more samples of any given cancer type that were included in the initial data, the better the model performed on that cancer type. "It took a number of iterations of the model for it to get to the point where we were happy with the performance," Gevaert said. "But ultimately for some tumor types, it got to a level that it can be useful in the clinic." Gevaert pointed out that doctors are often not looking at genes one at a time to make clinical decisions, but at gene signatures that include hundreds of different genes. For instance, many cancer cells activate the same groups of hundreds of genes related to inflammation, or hundreds of genes related to cell growth. Compared with its performance at predicting individual gene expression, SEQUOIA was even more accurate at predicting whether such large genomic programs were activated. To make the data accessible and easy to interpret, the researchers programmed SEQUOIA to display the genetic findings as a visual map of the tumor biopsy, letting scientists and clinicians see how genetic variations might be distinct in different areas of a tumor. Predicting patient outcomes To test the utility of SEQUOIA for clinical decision making, Gevaert and his colleagues identified breast cancer genes that the model could accurately predict the expression of and that are already used in commercial breast cancer genomic tests. (The Food and Drug Administration-approved MammaPrint test, for instance, analyzes the levels of 70 breast-cancer-related genes to provide patients with a score of the risk their cancer is likely to recur.) "Breast cancer has a number of very well-studied gene signatures that have been shown over the past decade to be highly correlated with treatment responses and patient outcomes," Gevaert said. "This made it an ideal test case for our model." SEQUOIA, the team showed, could provide the same type of genomic risk score as MammaPrint using only stained images of tumor biopsies. The results were repeated on multiple different groups of breast cancer patients. In each case, patients identified as high risk by SEQUOIA had worse outcomes, with higher rates of cancer recurrence and a shorter time before their cancer recurred. The AI model can't yet be used in a clinical setting -- it needs to be tested in clinical trials and be approved by the FDA before it's used in guiding treatment decisions -- but Gevaert said his team is improving the algorithm and studying its potential applications. In the future, he said, SEQUOIA could reduce the need for expensive gene expression tests. "We've shown how useful this could be for breast cancer, and we can now use it for all cancers and look at any gene signature that is out there," he said. "It's a whole new source of data that we didn't have before." Scientists from Roche Diagnostics were also authors of the paper.
[3]
AI-powered tool predicts gene activity in cancer cells from biopsy images
Stanford MedicineNov 14 2024 To determine the type and severity of a cancer, pathologists typically analyze thin slices of a tumor biopsy under a microscope. But to figure out what genomic changes are driving the tumor's growth -; information that can guide how it is treated -; scientists must perform genetic sequencing of the RNA isolated from the tumor, a process that can take weeks and costs thousands of dollars. Now, Stanford Medicine researchers have developed an artificial intelligence-powered computational program that can predict the activity of thousands of genes within tumor cells based only on standard microscopy images of the biopsy. The tool, described online in Nature Communications Nov. 14, was created using data from more than 7,000 diverse tumor samples. The team showed that it could use routinely collected biopsy images to predict genetic variations in breast cancers and to predict patient outcomes. This kind of software could be used to quickly identify gene signatures in patients' tumors, speeding up clinical decision-making and saving the health care system thousands of dollars." Olivier Gevaert, PhD, professor of biomedical data science and senior author of the paper The work was also led by Stanford graduate student Marija Pizuria and postdoctoral fellows Yuanning Zheng, PhD, and Francisco Perez, PhD. Driven by genomics Clinicians have increasingly guided the selection of which cancer treatments -; including chemotherapies, immunotherapies and hormone-based therapies -; to recommend to their patients based on not only which organ a patient's cancer affects, but which genes a tumor is using to fuel its growth and spread. Turning on or off certain genes could make a tumor more aggressive, more likely to metastasize, or more or less likely to respond to certain drugs. However, accessing this information often requires costly and time-consuming genomic sequencing. Gevaert and his colleagues knew that the gene activity within individual cells can alter the appearance of those cells in ways that are often imperceptible to a human eye. They turned to artificial intelligence to find these patterns. The researchers began with 7,584 cancer biopsies from 16 different of cancer types. Each biopsy had been sliced into thin sections and prepared using a method known as hematoxylin and eosin staining, which is standard for visualizing the overall appearance of cancer cells. Information on the cancers' transcriptomes -; which genes the cells are actively using -; was also available. A working model After the researchers integrated their new cancer biopsies as well as other datasets, including transcriptomic data and images from thousands of healthy cells, the AI program -; which they named SEQUOIA (slide-based expression quantification using linearized attention) -; was able to predict the expression patterns of more than 15,000 different genes from the stained images. For some cancer types, the AI-predicted gene activity had a more than 80% correlation with the real gene activity data. In general, the more samples of any given cancer type that were included in the initial data, the better the model performed on that cancer type. "It took a number of iterations of the model for it to get to the point where we were happy with the performance," Gevaert said. "But ultimately for some tumor types, it got to a level that it can be useful in the clinic." Gevaert pointed out that doctors are often not looking at genes one at a time to make clinical decisions, but at gene signatures that include hundreds of different genes. For instance, many cancer cells activate the same groups of hundreds of genes related to inflammation, or hundreds of genes related to cell growth. Compared with its performance at predicting individual gene expression, SEQUOIA was even more accurate at predicting whether such large genomic programs were activated. To make the data accessible and easy to interpret, the researchers programmed SEQUOIA to display the genetic findings as a visual map of the tumor biopsy, letting scientists and clinicians see how genetic variations might be distinct in different areas of a tumor. Predicting patient outcomes To test the utility of SEQUOIA for clinical decision making, Gevaert and his colleagues identified breast cancer genes that the model could accurately predict the expression of and that are already used in commercial breast cancer genomic tests. (The Food and Drug Administration-approved MammaPrint test, for instance, analyzes the levels of 70 breast-cancer-related genes to provide patients with a score of the risk their cancer is likely to recur.) "Breast cancer has a number of very well-studied gene signatures that have been shown over the past decade to be highly correlated with treatment responses and patient outcomes," Gevaert said. "This made it an ideal test case for our model." SEQUOIA, the team showed, could provide the same type of genomic risk score as MammaPrint using only stained images of tumor biopsies. The results were repeated on multiple different groups of breast cancer patients. In each case, patients identified as high risk by SEQUOIA had worse outcomes, with higher rates of cancer recurrence and a shorter time before their cancer recurred. The AI model can't yet be used in a clinical setting -; it needs to be tested in clinical trials and be approved by the FDA before it's used in guiding treatment decisions -; but Gevaert said his team is improving the algorithm and studying its potential applications. In the future, he said, SEQUOIA could reduce the need for expensive gene expression tests. "We've shown how useful this could be for breast cancer, and we can now use it for all cancers and look at any gene signature that is out there," he said. "It's a whole new source of data that we didn't have before." Scientists from Roche Diagnostics were also authors of the paper. Funding for this research was provided by the National Cancer Institute (grant R01 CA260271), a fellowship of the Belgian American Educational Foundation, a grant from Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek-Vlaanderen, the Fulbright Spanish Commission and Ghent University. Stanford Medicine Journal reference: Pizurica, M., et al. (2024). Digital profiling of gene expression from histology images with linearized attention. Nature Communications. doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-54182-5.
Share
Share
Copy Link
Stanford Medicine researchers have developed an AI-powered tool called SEQUOIA that can predict gene activity in cancer cells using only biopsy images, potentially speeding up diagnosis and treatment decisions while reducing costs.

Stanford Researchers Develop AI Tool to Predict Cancer Gene Activity
Stanford Medicine researchers have developed an innovative artificial intelligence (AI) tool that could revolutionize cancer diagnosis and treatment planning. The computational program, named SEQUOIA (slide-based expression quantification using linearized attention), can predict the activity of thousands of genes within tumor cells based solely on standard microscopy images of biopsy samples
1
.How SEQUOIA Works
SEQUOIA was developed using data from 7,584 cancer biopsies across 16 different cancer types. The AI model analyzes thin sections of tumor biopsies prepared with hematoxylin and eosin staining, a standard method for visualizing cancer cells
2
.By integrating this data with transcriptomic information and images from thousands of healthy cells, SEQUOIA can predict the expression patterns of more than 15,000 different genes from the stained images. For some cancer types, the AI-predicted gene activity showed over 80% correlation with actual gene activity data
3
.Potential Impact on Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Traditional methods of determining genomic changes driving tumor growth require genetic sequencing of RNA isolated from the tumor, a process that can take weeks and cost thousands of dollars. SEQUOIA could potentially bypass this need, offering several advantages:
- Speed: The AI tool can quickly identify gene signatures in patients' tumors, accelerating clinical decision-making.
- Cost-effectiveness: By reducing the need for expensive genetic sequencing, SEQUOIA could save the healthcare system significant amounts of money.
- Comprehensive analysis: The tool can predict the activation of large genomic programs, which is often more clinically relevant than individual gene expression.
Related Stories
Promising Results in Breast Cancer
To test SEQUOIA's clinical utility, the researchers focused on breast cancer, a well-studied cancer type with established gene signatures correlated to treatment responses and patient outcomes
1
.The team demonstrated that SEQUOIA could provide genomic risk scores comparable to the FDA-approved MammaPrint test, which analyzes 70 breast-cancer-related genes. Patients identified as high-risk by SEQUOIA showed worse outcomes, including higher rates of cancer recurrence and shorter time before recurrence
2
.Future Prospects and Limitations
While SEQUOIA shows great promise, it is not yet ready for clinical use. The tool needs to undergo clinical trials and receive FDA approval before it can be used to guide treatment decisions. However, the research team, led by Olivier Gevaert, PhD, a professor of biomedical data science at Stanford, is continually improving the algorithm and exploring its potential applications
3
.The development of SEQUOIA represents a significant step forward in the integration of AI and genomics in cancer research and treatment. As the tool continues to evolve, it could potentially be applied to all cancer types, offering a new source of valuable data for oncologists and researchers alike.
References
Summarized by
Navi
[1]
[2]
Related Stories
AI Model Predicts Gene Activity in Human Cells, Transforming Biological Research
09 Jan 2025•Science and Research

AI Tool Uncovers Five Distinct Cancer Cell Groups, Revolutionizing Tumor Characterization and Treatment
25 Jun 2025•Health
ChatGPT Like AI Model Shows Promise in Cancer Treatment Decision-Making
05 Sept 2024

Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round from Amazon, Nvidia, and SoftBank at $730B valuation
Business and Economy

2
Trump orders federal agencies to ban Anthropic after Pentagon dispute over AI surveillance
Policy and Regulation

3
Google releases Nano Banana 2 AI image model with Pro quality at Flash speed
Technology





