AI Doctors: Personalization and Privacy Key to Patient Satisfaction
3 Sources
3 Sources
[1]
Personal info and privacy control may be key to better visits with AI doctors
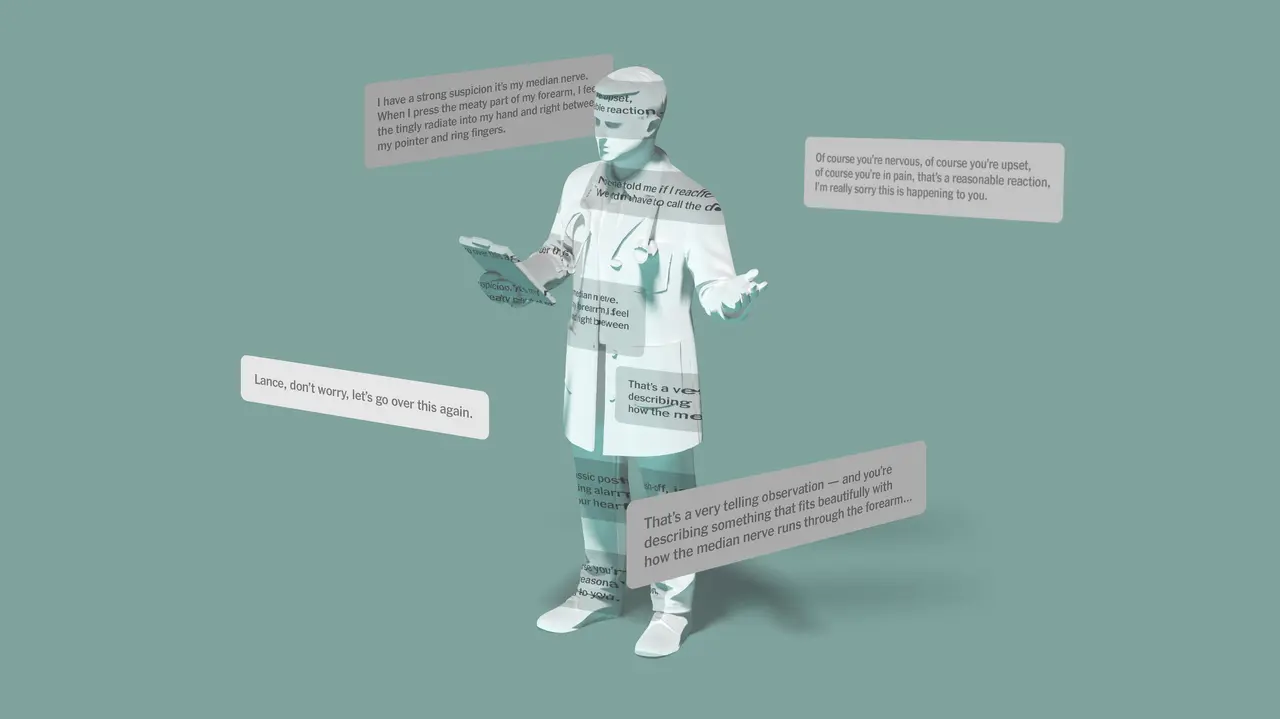
Artificial intelligence (AI) may one day play a larger role in medicine than the online symptom checkers available today. But these "AI doctors" may need to get more personal than human doctors to increase patient satisfaction, according to a study led by researchers at Penn State. They found that the more social information an AI doctor recalls about patients, the higher the patients' satisfaction, but only if they were offered privacy control. The research team published their findings in the journal Communication Research. "We tend to think of AI doctors as machines that are antiseptic and generic," said S. Shyam Sundar, Evan Pugh University Professor and the James P. Jimirro Professor of Media Effects at Penn State. "What we show in this study is that it's important for these AI systems to not just talk about a patient's medical history but also to individuate them socially by recalling certain non-medical information about them, such as their occupation and hobbies. At the end of the day, AI doctors may guide patients through telehealth visits just as well as human doctors." To see whether a doctor's knowledge of a patient's social or medical history increases patient satisfaction, the researchers asked 382 online participants to interact with a medical chatbot over two visits spaced about two weeks apart. Participants were told that they were interacting with a human doctor, an AI doctor or an AI-assisted human doctor. During the first visit the "doctor" -- in reality, a pre-compiled script that the researchers created for consistency -- chatted with patients about topics related to diet, fitness, lifestyle, sleep and mental health, and asked personal information about their occupation, relationship with their family, dietary habits and favorite activities. Then the doctor offered general recommendations for diet, exercise and mental health management. During the second visit, the doctor either recalled the patient's medical or personal information or asked the patient to remind them of this information. Then the doctor gave similar health advice as they did in the first visit and offered half the patients the option to put their visit on the record and save their information to the online platform at the conclusion of the final session. Participants then completed an online questionnaire to assess their satisfaction with the service. The researchers found that patients gave higher scores to AI doctors that recalled the patient's social information as long as the doctor offered privacy control before concluding the visit. The human doctor, on the other hand, did not need to recall either social or medical information for patients to feel that they had a close relationship with the doctor. "When an AI doctor recalls a patient's social information, it is perceived as putting more effort into individuation, which leads to higher patient satisfaction, but only when the patient has privacy control," said Cheng "Chris" Chen, lead author and assistant professor of communication design at Elon University who graduated from the doctoral program of mass communications at Penn State. "This was surprising because AI systems treat all data the same, but patients see it differently. They perceived it as the doctor putting in more effort to recall the patient's social information." The process still requires effort on the patient's part, Sundar added. "Patients still want the AI system to provide them privacy control," he said. "It's like, as long as you give me control over my data, I appreciate you knowing about my social life and appreciate the effort you put in." The study has implications for the design of AI systems in the medical field, according to the researchers. "Recalling patient social information may lead to better satisfaction and patient compliance and more positive health outcomes," Cheng said. According to co-author Joe Walther, Bertelsen Presidential Chair in Technology and Society and distinguished professor of communication at the University of California, Santa Barbara, the research also addresses larger questions about what it means to know someone, or rather to feel known by someone or something. "When I tell a student her homework was better than many other students', it's just a numerical comparison," Walther said. "When I tell her that her homework is better than she did earlier in the semester, she knows I know her, that she's not just a number. The same goes for doctors: Am I just the latest lab tests, or am I unique?" Other contributors to the study include Mengqi Liao, University of Georgia.
[2]
Personal info and privacy control may be key to better visits with AI doctors
Artificial intelligence (AI) may one day play a larger role in medicine than the online symptom checkers available today. But these "AI doctors" may need to get more personal than human doctors to increase patient satisfaction, according to a study led by researchers at Penn State. They found that the more social information an AI doctor recalls about patients, the higher the patients' satisfaction, but only if they were offered privacy control. The research team published their findings in the journal Communication Research. "We tend to think of AI doctors as machines that are antiseptic and generic," said S. Shyam Sundar, Evan Pugh University Professor and the James P. Jimirro Professor of Media Effects at Penn State. "What we show in this study is that it's important for these AI systems to not just talk about a patient's medical history but also to individuate them socially by recalling certain non-medical information about them, such as their occupation and hobbies. At the end of the day, AI doctors may guide patients through telehealth visits just as well as human doctors." To see whether a doctor's knowledge of a patient's social or medical history increases patient satisfaction, the researchers asked 382 online participants to interact with a medical chatbot over two visits spaced about two weeks apart. Participants were told that they were interacting with a human doctor, an AI doctor or an AI-assisted human doctor. During the first visit, the "doctor" -- in reality, a pre-compiled script that the researchers created for consistency -- chatted with patients about topics related to diet, fitness, lifestyle, sleep and mental health, and asked personal information about their occupation, relationship with their family, dietary habits and favorite activities. Then the doctor offered general recommendations for diet, exercise and mental health management. During the second visit, the doctor either recalled the patient's medical or personal information or asked the patient to remind them of this information. Then the doctor gave similar health advice as they did in the first visit and offered half the patients the option to put their visit on the record and save their information to the online platform at the conclusion of the final session. Participants then completed an online questionnaire to assess their satisfaction with the service. The researchers found that patients gave higher scores to AI doctors that recalled the patient's social information as long as the doctor offered privacy control before concluding the visit. The human doctor, on the other hand, did not need to recall either social or medical information for patients to feel that they had a close relationship with the doctor. "When an AI doctor recalls a patient's social information, it is perceived as putting more effort into individuation, which leads to higher patient satisfaction, but only when the patient has privacy control," said Cheng "Chris" Chen, lead author and assistant professor of communication design at Elon University who graduated from the doctoral program of mass communications at Penn State. "This was surprising because AI systems treat all data the same, but patients see it differently. They perceived it as the doctor putting in more effort to recall the patient's social information." The process still requires effort on the patient's part, Sundar added. "Patients still want the AI system to provide them privacy control," he said. "It's like, as long as you give me control over my data, I appreciate you knowing about my social life and appreciate the effort you put in." The study has implications for the design of AI systems in the medical field, according to the researchers. "Recalling patient social information may lead to better satisfaction and patient compliance and more positive health outcomes," Cheng said. According to co-author Joe Walther, Bertelsen Presidential Chair in Technology and Society and distinguished professor of communication at the University of California, Santa Barbara, the research also addresses larger questions about what it means to know someone, or rather to feel known by someone or something. "When I tell a student her homework was better than many other students," it's just a numerical comparison," Walther said. "When I tell her that her homework is better than she did earlier in the semester, she knows I know her, that she's not just a number. The same goes for doctors: Am I just the latest lab tests, or am I unique?" Other contributors to the study include Mengqi Liao, University of Georgia.
[3]
Personalization key to patient satisfaction with AI doctors
The Pennsylvania State UniversityNov 1 2024 Artificial intelligence (AI) may one day play a larger role in medicine than the online symptom checkers available today. But these "AI doctors" may need to get more personal than human doctors to increase patient satisfaction, according to a study led by researchers at Penn State. They found that the more social information an AI doctor recalls about patients, the higher the patients' satisfaction, but only if they were offered privacy control. The research team published their findings in the journal Communication Research. "We tend to think of AI doctors as machines that are antiseptic and generic," said S. Shyam Sundar, Evan Pugh University Professor and the James P. Jimirro Professor of Media Effects at Penn State. What we show in this study is that it's important for these AI systems to not just talk about a patient's medical history but also to individuate them socially by recalling certain non-medical information about them, such as their occupation and hobbies. At the end of the day, AI doctors may guide patients through telehealth visits just as well as human doctors." Shyam Sundar, James P. Jimirro Professor of Media Effects, The Pennsylvania State University To see whether a doctor's knowledge of a patient's social or medical history increases patient satisfaction, the researchers asked 382 online participants to interact with a medical chatbot over two visits spaced about two weeks apart. Participants were told that they were interacting with a human doctor, an AI doctor or an AI-assisted human doctor. During the first visit the "doctor" -; in reality, a pre-compiled script that the researchers created for consistency -; chatted with patients about topics related to diet, fitness, lifestyle, sleep and mental health, and asked personal information about their occupation, relationship with their family, dietary habits and favorite activities. Then the doctor offered general recommendations for diet, exercise and mental health management. During the second visit, the doctor either recalled the patient's medical or personal information or asked the patient to remind them of this information. Then the doctor gave similar health advice as they did in the first visit and offered half the patients the option to put their visit on the record and save their information to the online platform at the conclusion of the final session. Participants then completed an online questionnaire to assess their satisfaction with the service. The researchers found that patients gave higher scores to AI doctors that recalled the patient's social information as long as the doctor offered privacy control before concluding the visit. The human doctor, on the other hand, did not need to recall either social or medical information for patients to feel that they had a close relationship with the doctor. "When an AI doctor recalls a patient's social information, it is perceived as putting more effort into individuation, which leads to higher patient satisfaction, but only when the patient has privacy control," said Cheng "Chris" Chen, lead author and assistant professor of communication design at Elon University who graduated from the doctoral program of mass communications at Penn State. "This was surprising because AI systems treat all data the same, but patients see it differently. They perceived it as the doctor putting in more effort to recall the patient's social information." The process still requires effort on the patient's part, Sundar added. "Patients still want the AI system to provide them privacy control," he said. "It's like, as long as you give me control over my data, I appreciate you knowing about my social life and appreciate the effort you put in." The study has implications for the design of AI systems in the medical field, according to the researchers. "Recalling patient social information may lead to better satisfaction and patient compliance and more positive health outcomes," Cheng said. According to co-author Joe Walther, Bertelsen Presidential Chair in Technology and Society and distinguished professor of communication at the University of California, Santa Barbara, the research also addresses larger questions about what it means to know someone, or rather to feel known by someone or something. "When I tell a student her homework was better than many other students', it's just a numerical comparison," Walther said. "When I tell her that her homework is better than she did earlier in the semester, she knows I know her, that she's not just a number. The same goes for doctors: Am I just the latest lab tests, or am I unique?" Other contributors to the study include Mengqi Liao, University of Georgia. The Pennsylvania State University Journal reference: Chen, C., et al. (2024) When an AI Doctor Gets Personal: The Effects of Social and Medical Individuation in Encounters With Human and AI Doctors. Communication Research. doi.org/10.1177/00936502241263482.
Share
Share
Copy Link
A Penn State study reveals that AI doctors recalling patients' social information, combined with privacy control, leads to higher patient satisfaction. This finding has implications for the future of AI in healthcare and telehealth visits.

AI Doctors: Balancing Personalization and Privacy in Healthcare
A groundbreaking study led by researchers at Penn State has shed light on the potential future of AI in medicine, revealing that AI doctors may need to adopt a more personalized approach than their human counterparts to enhance patient satisfaction. The research, published in the journal Communication Research, explores the delicate balance between personalization and privacy in AI-driven healthcare interactions
1
.Study Design and Methodology
The research team, led by S. Shyam Sundar and Cheng "Chris" Chen, conducted an experiment involving 382 online participants. These individuals interacted with a medical chatbot over two visits, spaced about two weeks apart. Participants were told they were communicating with either a human doctor, an AI doctor, or an AI-assisted human doctor
2
.During the initial visit, the "doctor" (a pre-compiled script) discussed various health-related topics and collected personal information. In the follow-up visit, the doctor either recalled the patient's information or asked for a reminder. Half of the participants were offered privacy control options at the end of the session
3
.Key Findings
The study revealed several important insights:
- AI doctors that recalled patients' social information received higher satisfaction scores, but only when privacy control was offered.
- Human doctors did not need to recall either social or medical information for patients to feel a close relationship.
- Patients perceived the AI's recall of social information as an effort towards individuation, leading to higher satisfaction.
The Importance of Privacy Control
A crucial finding was the role of privacy control in patient satisfaction. Sundar explained, "Patients still want the AI system to provide them privacy control. It's like, as long as you give me control over my data, I appreciate you knowing about my social life and appreciate the effort you put in"
1
.Related Stories
Implications for AI in Healthcare
The study's findings have significant implications for the design of AI systems in the medical field. Chen suggested that "Recalling patient social information may lead to better satisfaction and patient compliance and more positive health outcomes"
2
.Joe Walther, a co-author of the study, highlighted the broader implications of the research, stating, "The same goes for doctors: Am I just the latest lab tests, or am I unique?" This perspective underscores the importance of personalization in healthcare interactions, whether with human or AI doctors
3
.Future of AI in Telehealth
The research suggests that AI doctors may eventually guide patients through telehealth visits as effectively as human doctors. However, this potential relies on striking the right balance between personalization and privacy. As AI continues to advance in the medical field, these findings will likely shape the development of more patient-centered AI healthcare systems.
References
Summarized by
Navi
[3]
Related Stories
AI in Healthcare: Patients Trust AI Medical Advice Over Doctors, Raising Concerns and Challenges
18 Aug 2025•Health

AI Chatbots Enhance Physician Decision-Making in Clinical Management, Study Finds
08 Feb 2025•Health

AI Outperforms Physicians in Virtual Urgent Care Study, Highlighting Potential for Improved Patient Care
05 Apr 2025•Health

Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.4, New AI Model Built for Agents and Professional Work
Technology

2
Anthropic sues Pentagon over supply chain risk label after refusing autonomous weapons use
Policy and Regulation

3
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round as questions swirl around AI bubble and profitability
Business and Economy