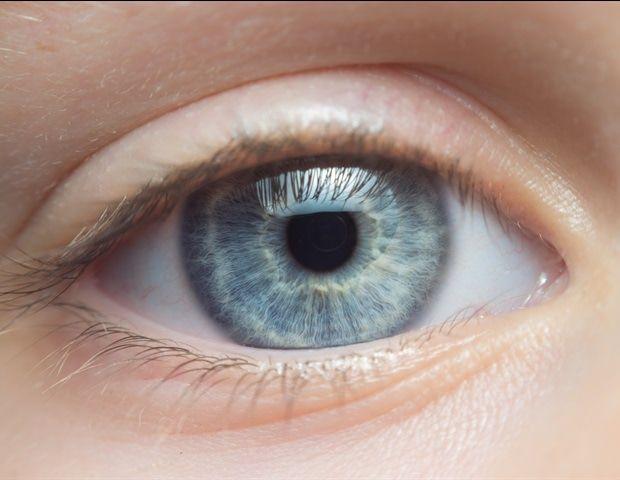
AI-Powered Retinal Mapping Breakthrough: A New Frontier in Disease Detection
2 Sources
2 Sources
[1]
Study could pave the way for routine eyecare imaging as a disease screening tool
Walter and Eliza Hall InstituteFeb 5 2025 Researchers have conducted one of the largest eye studies in the world to reveal new insights into retinal thickness, highlighting its potential in the early detection of diseases like type 2 diabetes, dementia and multiple sclerosis. The WEHI-led study, using cutting-edge artificial intelligence technology to analyze over 50,000 eyes, produced maps of the retina in unprecedented detail to better understand how retinal differences link to various diseases. The findings open up new possibilities for using routine eyecare imaging as a tool to screen for and manage diseases, much like mammograms have for breast cancer. At a glance Innovative AI-powered research has created the most detailed maps of the retina ever produced. WEHI researchers have used these maps to link retinal thinning to a range of diseases as well as identifying new genetic factors that influence retinal thickness. The findings could pave the way for routine eyecare imaging as a disease screening tool. Unlocking a window into the brain The retina is part of the central nervous system, which also comprises the brain and spinal cord. Many diseases are linked to degeneration or disruption of this critical system, including neurodegenerative conditions such as dementia and metabolic disorders like diabetes. Globally, neurological conditions alone are one of the leading causes of disability and illness, with over 3 billion people, or 43% of the world's population living with a brain related condition. Lead researcher, WEHI's Dr. Vicki Jackson, said the findings broaden the horizons for using retinal imaging as a doorway into the central nervous system, to help manage disease. "We've shown that retinal imaging can act as a window to the brain, by detecting associations with neurological disorders like multiple sclerosis and many other conditions. Our maps' fine-scale measurements reveal critical new details about connections between retinal thinning and a range of common conditions." Dr. Vicki Jackson, statistician and gene expert, lead researcher, WEHI The study also identified new genetic factors that influence retinal thickness, which are likely to play a role in the growth and development of a person's retina. "This research underscores the potential for retinal thickness to act as a diagnostic biomarker to aid in detecting and tracking the progression of numerous diseases. We can now pinpoint specific locations of the retina which show key changes in some diseases." The international research team, led by WEHI, applied AI methods to big population data of retinal imaging and compared information about each person's genetics and health to reveal unprecedented links to disease. The results created 50,000 maps with measurements at over 29,000 locations across the retina, identifying retinal thinning relating to 294 genes that play an important role in disease. AI fast-tracking the diagnostic future Study lead and bioinformatician, Professor Melanie Bahlo AM, said past studies had indicated correlations between retinal thickness and disease, but her team's AI-powered discoveries shed deeper light on the complex spatial anatomy of the retina and its role in disease. "Technologies like AI fuel discovery, and when fused with brilliant minds, there is an extraordinary ability to transform big population data into far-reaching insights," Prof Bahlo, a lab head at WEHI, said. "There has never been a time in history where this powerful combination - technology, big data and brilliant minds - has come together to advance human health." The research reinforces the growing field of oculomics (using the eye to diagnose health conditions) as an emerging, powerful and non-invasive approach for predicting and diagnosing diseases. Many collaborators were involved in the study, including the UK Biobank (retinal images), University of Washington (AI processing of imaging data); the Lowy Medical Research Institute (disease association analysis); as well as the Moorfields Eye Hospital and the University College London (clinical expertise). The research has been generously funded by the Lowy Medical Research Institute. Walter and Eliza Hall Institute Journal reference: Jackson, V. E., et al. (2025). Multi-omic spatial effects on high-resolution AI-derived retinal thickness. Nature Communications. doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-55635-7.
[2]
All in the eyes: High resolution retinal maps aid disease diagnoses
The WEHI-led study, using cutting-edge artificial intelligence technology to analyse over 50,000 eyes, produced maps of the retina in unprecedented detail to better understand how retinal differences link to various diseases. The findings open up new possibilities for using routine eyecare imaging as a tool to screen for and manage diseases, much like mammograms have for breast cancer. The retina is part of the central nervous system, which also comprises the brain and spinal cord. Many diseases are linked to degeneration or disruption of this critical system, including neurodegenerative conditions such as dementia and metabolic disorders like diabetes. Globally, neurological conditions alone are one of the leading causes of disability and illness, with over 3 billion people, or 43% of the world's population living with a brain related condition. Lead researcher, WEHI's Dr Vicki Jackson, said the findings broaden the horizons for using retinal imaging as a doorway into the central nervous system, to help manage disease. "We've shown that retinal imaging can act as a window to the brain, by detecting associations with neurological disorders like multiple sclerosis and many other conditions," said Dr Jackson, a statistician and gene expert. "Our maps' fine-scale measurements reveal critical new details about connections between retinal thinning and a range of common conditions." The study also identified new genetic factors that influence retinal thickness, which are likely to play a role in the growth and development of a person's retina. "This research underscores the potential for retinal thickness to act as a diagnostic biomarker to aid in detecting and tracking the progression of numerous diseases. We can now pinpoint specific locations of the retina which show key changes in some diseases." The international research team, led by WEHI, applied AI methods to big population data of retinal imaging and compared information about each person's genetics and health to reveal unprecedented links to disease. The results created 50,000 maps with measurements at over 29,000 locations across the retina, identifying retinal thinning relating to 294 genes that play an important role in disease. AI fast-tracking the diagnostic future Study lead and bioinformatician, Professor Melanie Bahlo AM, said past studies had indicated correlations between retinal thickness and disease, but her team's AI-powered discoveries shed deeper light on the complex spatial anatomy of the retina and its role in disease. "Technologies like AI fuel discovery, and when fused with brilliant minds, there is an extraordinary ability to transform big population data into far-reaching insights," Prof Bahlo, a lab head at WEHI, said. "There has never been a time in history where this powerful combination -- technology, big data and brilliant minds -- has come together to advance human health." The research reinforces the growing field of oculomics (using the eye to diagnose health conditions) as an emerging, powerful and non-invasive approach for predicting and diagnosing diseases. Many collaborators were involved in the study, including the UK Biobank (retinal images), University of Washington (AI processing of imaging data); the Lowy Medical Research Institute (disease association analysis); as well as the Moorfields Eye Hospital and the University College London (clinical expertise). The research has been generously funded by the Lowy Medical Research Institute.
Share
Share
Copy Link
Researchers at WEHI have used AI to create detailed retinal maps from over 50,000 eyes, potentially revolutionizing disease screening and management through routine eye care imaging.

AI-Powered Retinal Mapping: A Window to the Brain
In a groundbreaking study, researchers at the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute (WEHI) have harnessed the power of artificial intelligence to create the most detailed maps of the human retina ever produced. This innovative research, analyzing over 50,000 eyes, has unveiled new insights into retinal thickness and its potential as a diagnostic tool for various diseases, including type 2 diabetes, dementia, and multiple sclerosis
1
2
.Unprecedented Detail in Retinal Imaging
The WEHI-led international team employed cutting-edge AI technology to process and analyze a vast dataset of retinal images. The result was the creation of 50,000 high-resolution retinal maps, each containing measurements from over 29,000 locations across the retina. This level of detail has allowed researchers to identify specific areas of retinal thinning associated with 294 genes that play crucial roles in various diseases
1
.Retina as a Window to the Brain
Dr. Vicki Jackson, the lead researcher at WEHI, emphasized the significance of these findings: "We've shown that retinal imaging can act as a window to the brain, by detecting associations with neurological disorders like multiple sclerosis and many other conditions"
1
. The retina, being part of the central nervous system, provides a unique opportunity to observe changes that may be indicative of broader neurological issues.AI's Role in Advancing Medical Diagnostics
Professor Melanie Bahlo, the study lead and bioinformatician at WEHI, highlighted the transformative power of AI in medical research: "Technologies like AI fuel discovery, and when fused with brilliant minds, there is an extraordinary ability to transform big population data into far-reaching insights"
2
. This fusion of AI, big data, and expert analysis has opened new avenues for understanding the complex relationship between retinal anatomy and disease.Potential for Routine Disease Screening
The study's findings suggest that routine eye care imaging could become a powerful tool for disease screening and management, similar to how mammograms are used for breast cancer detection. This non-invasive approach, known as oculomics, could revolutionize the early detection and monitoring of various conditions, particularly neurological disorders
1
2
.Related Stories
Global Impact and Collaboration
With over 3 billion people worldwide living with brain-related conditions, the potential impact of this research is immense. The study involved collaborations with several institutions, including the UK Biobank, University of Washington, Lowy Medical Research Institute, Moorfields Eye Hospital, and University College London
1
2
.Future Implications
As this research progresses, it could lead to the development of new diagnostic tools and strategies for managing a wide range of diseases. The ability to detect early signs of neurological and metabolic disorders through routine eye examinations could significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce the burden on healthcare systems globally.
References
Summarized by
Navi
Related Stories
Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round from Amazon, Nvidia, and SoftBank at $730B valuation
Business and Economy

2
Pentagon accepts OpenAI's autonomous weapons restrictions after blacklisting Anthropic
Policy and Regulation

3
Trump orders federal agencies to ban Anthropic after Pentagon dispute over AI surveillance
Policy and Regulation