Google Unveils AI-Powered Environmental Conservation Platform to Support Global 30x30 Initiative
2 Sources
2 Sources
[1]
How we're using AI to help nature and people flourish together
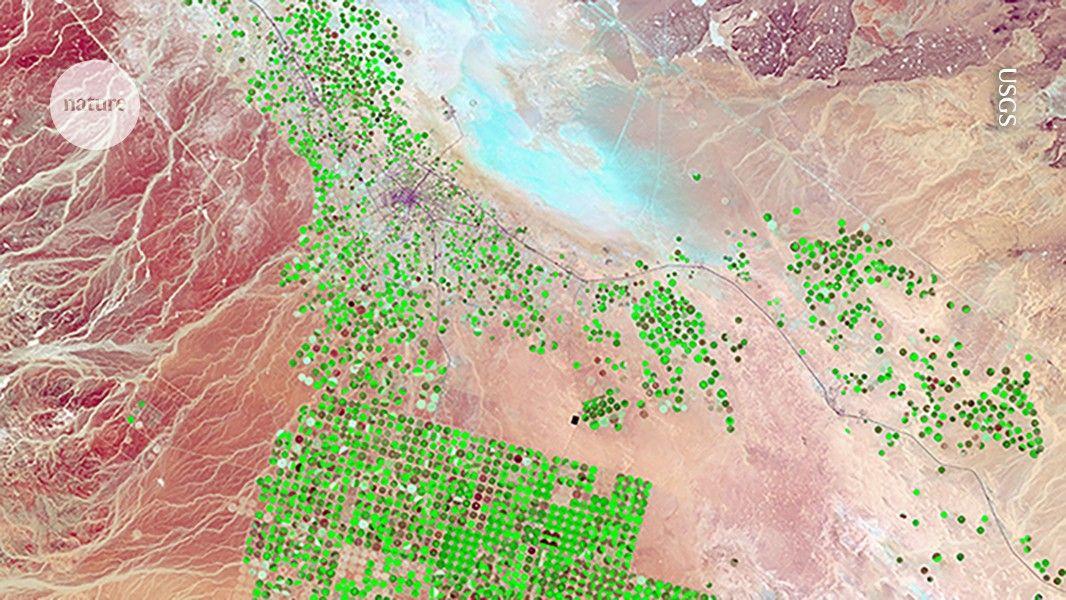
Thriving ecosystems power thriving communities. From the food we eat to the future of our economies, human wellbeing and opportunity are deeply tied to the health of our planet. But these vital natural systems are at risk. The World Wildlife Fund estimates that wildlife populations have declined by 73% since 1970, and the World Economic Forum ranks biodiversity loss as one of the greatest risks to global stability over the next ten years. For more than two decades, we've been providing a clearer view of our changing planet with tools like Google Earth and Google Earth Engine. Building on that foundation, we're working harder than ever to help support the worldwide initiative to protect and conserve 30% of the planet's land and oceans by 2030 (30x30), leveraging environmental data and AI technologies to help nature and people flourish together. We believe AI offers a tremendous opportunity to empower people everywhere to protect and restore nature. Here are three ways we're helping. You can't protect what you can't see. We're building technologies that can give everyone an unprecedented view of our planet by turning petabytes of satellite, climate and ecosystem data into a single, consistent picture of change. Our recently-launched Google Earth AI is built on decades modeling the world, combined with state of the art predictive models and Gemini's advanced reasoning capabilities, enabling enterprises, cities and nonprofits to achieve deeper understanding of our planet. In minutes, users can create powerful insights that previously required complex analytics and years of research. For example, EarthAI's Geospatial Reasoning capability can automatically connect different models -- like weather forecasts, population maps and satellite imagery -- to tackle complex analyses like spotting where a river has dried up to help communities predict the risk of dust storms during a drought and take action to prepare in advance. Our researchers are using cutting-edge AI approaches to synthesize complex data and reveal new insights into the past, present and future of our planet. Our Species Distribution Modeling project, for example, uses AI to create high-resolution maps of where species live, helping conservationists make critical decisions like how to best protect endangered wildlife and their habitats. In addition to helping us better understand the natural world in real-time, AI is also enabling us to forecast its future. For example, we just released a new paper and the first dataset dedicated to training deep learning models to predict deforestation risk, opening the door to opportunities to prevent deforestation before it happens. We believe technology's greatest potential is realized when it empowers local communities and puts powerful tools in the hands of those who can drive on-the-ground impact. That's why we partner with people on the front lines to help accelerate their work. Through Google Arts & Culture's Forest Listeners experiment, we're inviting everyone to help scientists identify hidden species by listening to sounds from Brazil's rainforests and classifying the data they hear to help train Google DeepMind's AI model. This helps enable measurement, preservation and restoration of the rainforests' biodiversity. And through Google.org, we're supporting eight Brazilian organizations who are using AI to do everything from predicting Amazonian wildfires to mapping biodiversity with eDNA. These efforts build on our commitment to deliver the benefits of AI for people and the planet while managing its environmental footprint responsibly -- by continuing to improve efficiency across our AI systems, investing in next-generation clean energy sources, and supporting carbon removal projects that push the frontier of science and technology to help restore the atmosphere while creating co-benefits for local communities and ecosystems. AI is not just a tool, it's a catalyst -- and it's the partnership between AI technology and human passion that will drive real change. We invite you to dive deeper into this work:
[2]
Alphabet : How we're using AI to help nature and people flourish together
Thriving ecosystems power thriving communities. From the food we eat to the future of our economies, human wellbeing and opportunity are deeply tied to the health of our planet. But these vital natural systems are at risk. The World Wildlife Fund estimates that wildlife populations have declined by 73% since 1970, and the World Economic Forum ranks biodiversity loss as one of the greatest risks to global stability over the next ten years. For more than two decades, we've been providing a clearer view of our changing planet with tools like Google Earth and Google Earth Engine. Building on that foundation, we're working harder than ever to help support the worldwide initiative to protect and conserve 30% of the planet's land and oceans by 2030 (30x30), leveraging environmental data and AI technologies to help nature and people flourish together. We believe AI offers a tremendous opportunity to empower people everywhere to protect and restore nature. Here are three ways we're helping. You can't protect what you can't see. We're building technologies that can give everyone an unprecedented view of our planet by turning petabytes of satellite, climate and ecosystem data into a single, consistent picture of change. Our recently-launched Google Earth AI is built on decades modeling the world, combined with state of the art predictive models and Gemini's advanced reasoning capabilities, enabling enterprises, cities and nonprofits to achieve deeper understanding of our planet. In minutes, users can create powerful insights that previously required complex analytics and years of research. For example, EarthAI's Geospatial Reasoning capability can automatically connect different models - like weather forecasts, population maps and satellite imagery - to tackle complex analyses like spotting where a river has dried up to help communities predict the risk of dust storms during a drought and take action to prepare in advance. Our researchers are using cutting-edge AI approaches to synthesize complex data and reveal new insights into the past, present and future of our planet. Our Species Distribution Modeling project, for example, uses AI to create high-resolution maps of where species live, helping conservationists make critical decisions like how to best protect endangered wildlife and their habitats. In addition to helping us better understand the natural world in real-time, AI is also enabling us to forecast its future. For example, we just released a new paper and the first dataset dedicated to training deep learning models to predict deforestation risk, opening the door to opportunities to prevent deforestation before it happens. We believe technology's greatest potential is realized when it empowers local communities and puts powerful tools in the hands of those who can drive on-the-ground impact. That's why we partner with people on the front lines to help accelerate their work. Through Google Arts & Culture's Forest Listeners experiment, we're inviting everyone to help scientists identify hidden species by listening to sounds from Brazil's rainforests and classifying the data they hear to help train Google DeepMind's AI model. This helps enable measurement, preservation and restoration of the rainforests' biodiversity. And through Google.org, we're supporting eight Brazilian organizations who are using AI to do everything from predicting Amazonian wildfires to mapping biodiversity with eDNA. These efforts build on our commitment to deliver the benefits of AI for people and the planet while managing its environmental footprint responsibly - by continuing to improve efficiency across our AI systems, investing in next-generation clean energy sources, and supporting carbon removal projects that push the frontier of science and technology to help restore the atmosphere while creating co-benefits for local communities and ecosystems. AI is not just a tool, it's a catalyst - and it's the partnership between AI technology and human passion that will drive real change. We invite you to dive deeper into this work:
Share
Share
Copy Link
Google launches Google Earth AI, leveraging Gemini's advanced reasoning capabilities and decades of environmental data to help protect 30% of Earth's land and oceans by 2030. The platform enables real-time ecosystem monitoring, species distribution mapping, and deforestation prediction.

Google Launches AI-Powered Environmental Platform
Google has unveiled a comprehensive AI-driven environmental conservation initiative centered around Google Earth AI, designed to support the global 30x30 commitment to protect and conserve 30% of the planet's land and oceans by 2030. The platform leverages decades of environmental modeling combined with Gemini's advanced reasoning capabilities to provide unprecedented insights into planetary health
1
.The announcement comes at a critical time for global biodiversity, with the World Wildlife Fund reporting a 73% decline in wildlife populations since 1970, and the World Economic Forum identifying biodiversity loss as one of the greatest risks to global stability over the next decade
1
.Advanced Geospatial Intelligence and Predictive Modeling
Google Earth AI represents a significant advancement in environmental monitoring technology, transforming petabytes of satellite, climate, and ecosystem data into a unified, consistent picture of planetary change. The platform's Geospatial Reasoning capability can automatically integrate multiple data sources including weather forecasts, population maps, and satellite imagery to perform complex analyses that previously required years of research
1
.One practical application demonstrates the system's ability to identify dried riverbeds and predict dust storm risks during droughts, enabling communities to prepare proactively for environmental hazards. This real-time analysis capability marks a substantial improvement over traditional environmental monitoring methods
2
.Species Conservation and Habitat Mapping
The Species Distribution Modeling project utilizes cutting-edge AI approaches to create high-resolution maps showing where species live, providing conservationists with critical data for protecting endangered wildlife and their habitats. This technology synthesizes complex environmental data to reveal new insights into past, present, and future planetary conditions
1
.Google researchers have also released the first dataset specifically designed for training deep learning models to predict deforestation risk, potentially enabling preventive measures before forest destruction occurs. This predictive capability represents a shift from reactive to proactive environmental protection strategies
2
.Related Stories
Community Engagement and Global Partnerships
The Forest Listeners experiment through Google Arts & Culture demonstrates an innovative approach to citizen science, inviting global participants to help identify hidden species by listening to and classifying sounds from Brazil's rainforests. This crowdsourced data helps train Google DeepMind's AI models for biodiversity measurement, preservation, and restoration efforts
1
.Through Google.org, the company supports eight Brazilian organizations using AI for various conservation applications, from predicting Amazonian wildfires to mapping biodiversity through environmental DNA analysis. These partnerships emphasize Google's commitment to empowering local communities with advanced technological tools
2
.References
Summarized by
Navi
[2]
Related Stories
Google Earth AI Evolves: Gemini-Powered Geospatial Reasoning Tackles Climate Crises
23 Oct 2025•Technology

Google Unveils Methodology for Measuring AI's Environmental Impact, Highlighting Significant Efficiency Gains
21 Aug 2025•Technology

Google's AlphaEarth Foundations: AI Model Maps Earth in Unprecedented Detail
31 Jul 2025•Technology
Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round from Amazon, Nvidia, and SoftBank at $730B valuation
Business and Economy

2
Anthropic stands firm against Pentagon's demand for unrestricted military AI access
Policy and Regulation

3
Pentagon Clashes With AI Firms Over Autonomous Weapons and Mass Surveillance Red Lines
Policy and Regulation





