Humanoid unveils KinetIQ AI system to control multiple robot fleets under single digital brain
2 Sources
2 Sources
[1]
Humanoid builds AI brain for fleet-level humanoid robot control
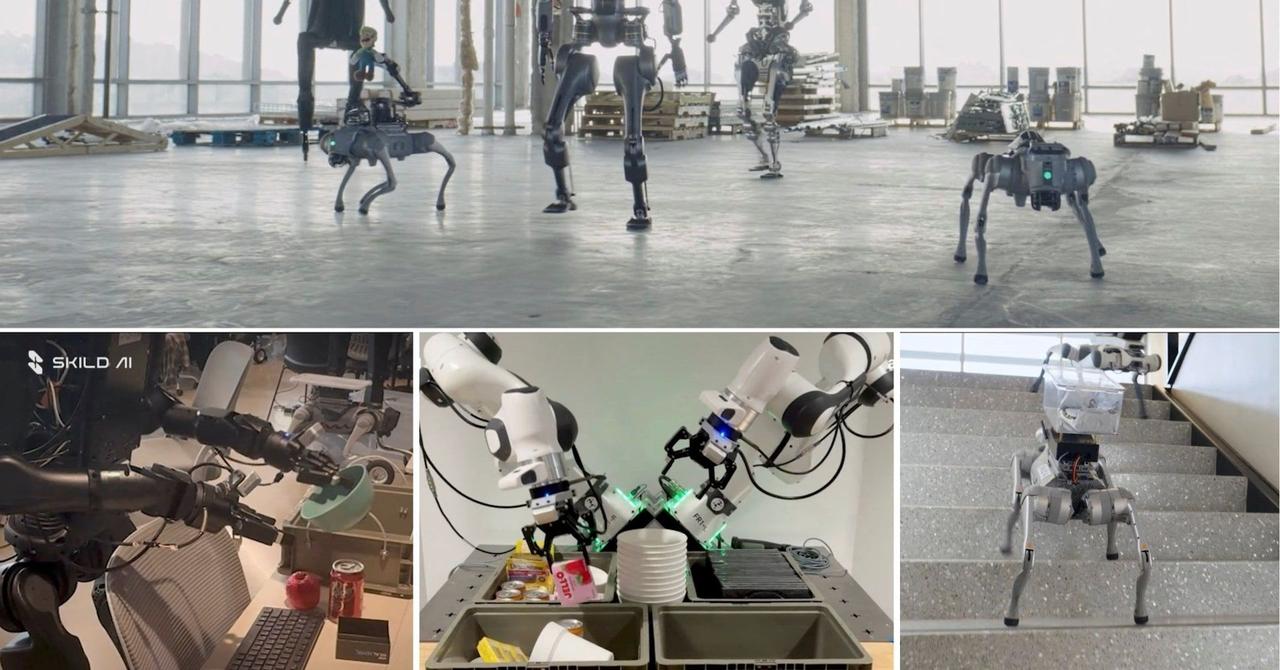
Humanoid has unveiled a new AI system designed to control and coordinate entire robot fleets under a single digital brain. The system, called KinetIQ, manages robots with different bodies, skills, and roles while allowing them to work together across industrial, service, and home environments. The company presented the platform through a demonstration video showing multiple robots operating at the same time. Wheeled robots handled industrial workflows such as grocery picking, container movement, and packing.
[2]
Watch: Humanoid robots work together using the same AI 'brain'
Until now, humanoid robots have largely worked on their own. A new AI system is designed to run them together. "Humanoid robots designed for different tasks can now share a single artificial intelligence 'brain' that coordinates their actions across multiple locations simultaneously." A UK-based company has unveiled an AI system that can virtually work as a "shared brain" for fleets of robots built for different purposes across factories, services, and homes simultaneously. Companies like Tesla, Boston Dynamics and XPeng have showcased humanoid robot prototypes in recent years, but these demonstrations typically feature robots operating on their own. The UK firm's approach is designed to manage multiple humanoid robots together under a single AI. Shared control systems are already common for industrial robots, however, applying the same approach to robots that rely on human-like movement and manipulation has been rare. The AI system, called KinetIQ, can assign tasks to entire robot fleets and control individual movements simultaneously in seconds, according to Humanoid, the robotics company behind the new system. Data from individual robots is shared across the system, helping improve performance fleet-wide. In a video released by Humanoid, a woman asks a bipedal humanoid robot to order cocoa powder and olive oil. In the next scene, wheeled robots in a warehouse-like environment use five-fingered hands to grasp a glass bottle and a soft paper bag, and then put them in a hard container box before packing them into a paper bag. Once the order reaches the home, the bipedal robot unpacks the bag and places the items as instructed by the woman's voice commands. According to Humanoid, the wheeled robots seen in the video are designed for industrial use, such as back-of-store grocery picking, container handling and packing, while the bipedal robots are intended for service roles and domestic use. The company describes the bipedal robot as an "intelligent assistant" capable of voice interaction, online ordering, and grocery handling. Humanoid has previously managed to have a 179 cm bipedal robot walk in just two days after its assembly, a process that typically takes weeks or months in humanoid robotics. The robot is designed to carry loads of up to 15 kilograms, with the company positioning it as a response to labour shortages, physically demanding work and unpaid domestic care. Humanoid said the capabilities shown in the video have already been tested in real-world pilot projects, and that a beta version of the wheeled robots will be available for sale early next year.
Share
Share
Copy Link
UK-based Humanoid has launched KinetIQ, an AI system that coordinates entire robot fleets under a shared digital brain. The platform manages robots with different bodies and skills across industrial, service, and home environments, marking a shift from individual robot operations to unified fleet-level control.
Humanoid Introduces KinetIQ for Fleet-Level Humanoid Robot Control
UK-based robotics company Humanoid has unveiled KinetIQ, an AI system designed to enable robots work together using same AI 'brain' across multiple locations simultaneously
2
. This single digital brain for controlling robots represents a departure from how companies like Tesla, Boston Dynamics, and XPeng have typically showcased humanoid robots—operating independently rather than as coordinated units2
. The platform manages robot fleets with different bodies, skills, and roles, allowing them to function cohesively across industrial environments, service roles, and home environments1
.Shared Brain for Multiple Humanoid Robots Enables Coordinated Operations
The unified AI system can assign tasks to entire robot fleets and control individual movements simultaneously in seconds, according to Humanoid
2
. While shared control systems are already common for industrial robots, applying this approach to humanoid robots that rely on human-like movement and manipulation has been rare2
. Data sharing across robot fleets forms a core component of the system, with information from individual robots shared across the platform to improve performance fleet-wide2
.AI System for Diverse Robots Handles Industrial and Domestic Tasks
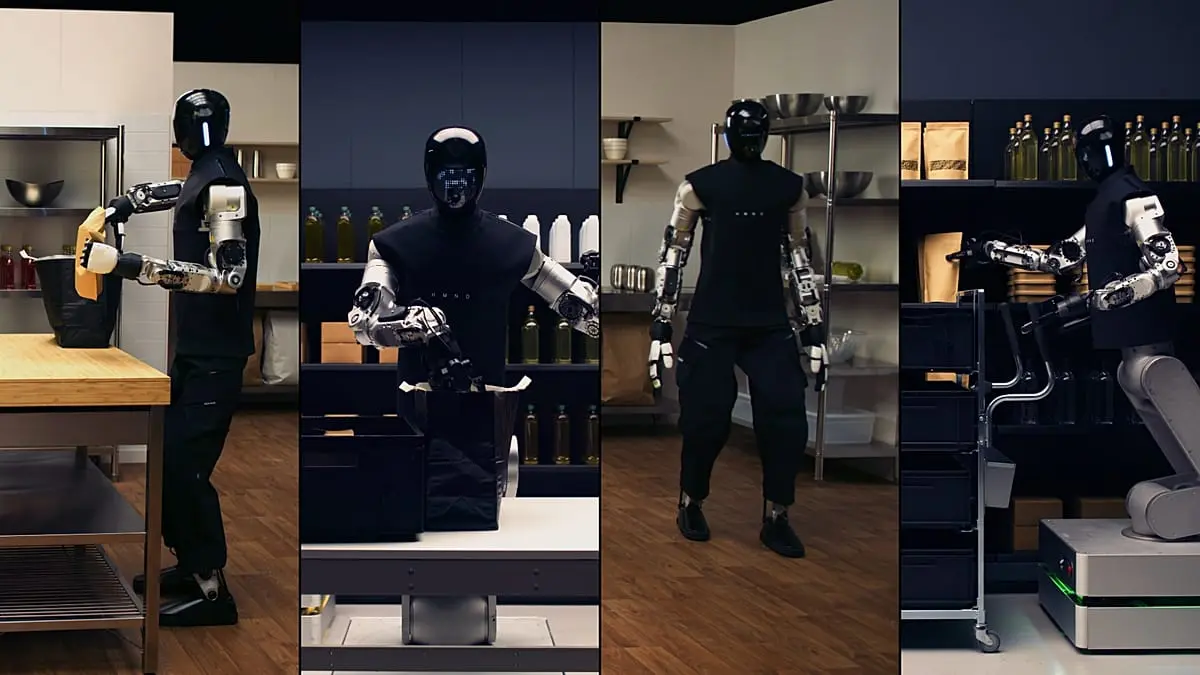
In a demonstration video, Humanoid showcased how the AI system coordinates different robot types for practical applications. Wheeled robots handled grocery picking and container movement in warehouse-like settings, using five-fingered hands to grasp items ranging from glass bottles to soft paper bags before packing them
2
. Bipedal robots, standing 179 cm tall and capable of carrying loads up to 15 kilograms, performed service roles including voice interaction, online ordering, and unpacking deliveries at home2
. The company achieved a notable milestone by having its bipedal robot walk just two days after assembly, a process that typically requires weeks or months in robotics2
.
Source: Euronews
Related Stories
Real-World Deployment and Response to Labor Shortages
Humanoid confirmed that the capabilities demonstrated have already been tested in pilot projects, with a beta version of the wheeled robots set for sale early next year
2
. The company positions its technology as a response to labor shortages, physically demanding work, and unpaid domestic care2
. This development signals a potential shift in how artificial intelligence and robotics address workforce challenges, particularly as industries face persistent staffing gaps. The ability to coordinate multiple robots through a centralized system could accelerate adoption across sectors where consistent, scalable automation has remained elusive.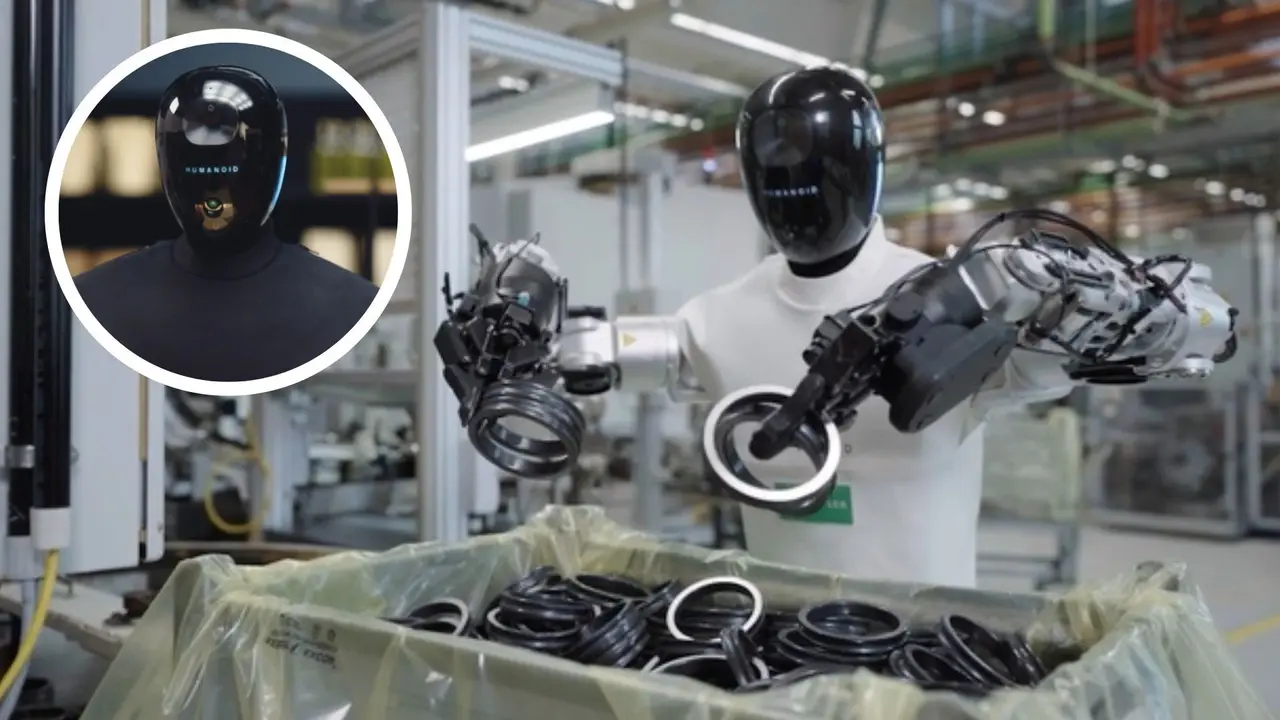
Source: Interesting Engineering
References
Summarized by
Navi
[1]
Related Stories
Recent Highlights
1
Pentagon threatens Anthropic with Defense Production Act over AI military use restrictions
Policy and Regulation

2
Google Gemini 3.1 Pro doubles reasoning score, beats rivals in key AI benchmarks
Technology

3
Anthropic accuses Chinese AI labs of stealing Claude through 24,000 fake accounts
Policy and Regulation