JEDEC Unveils LPDDR6 Memory Standard: Boosting Performance and Efficiency for AI and Mobile Devices
5 Sources
5 Sources
[1]
The latest LPDDR6 certification could help your laptop battery last even longer
JEDEC has officially published the LPDDR6 specification, JESD209-6, which is the next generation in low-power memory design. While earlier LPDDR implementations were sometimes perceived as being mobile-centric, this latest generation shifts the focus elsewhere. LPDDR6 is not only a next-generation memory technology, but it is also intended to meet the increasing performance and efficiency demands of edge AI, embedded computing. It could help bring efficiency to high-end notebooks with low power targets, where memory bandwidth is a bottleneck. JEDEC unloads LPDDR6 specifications to the world Up to 14.4 GB/s of pure, unadulterated bandwidth For LPDDR5 and LPDDR5X, LPDDR6 brings a massive step up in data rates. JEDEC's new specification starts at 10.667 gigabits per second per pin and reaches a maximum of 14.4 GB/s, which is significantly higher than the maximum rate of LPDDR5X at 8.533 GB/s. That translates to a maximum bandwidth of as high as 38.4 GB/s on a 64-bit bus, roughly twice the bandwidth of LPDDR5 when it first shipped. However, LPDDR6 is not just faster; it's built with a different architecture, a move towards supporting increased speeds with increased efficiencies. Another significant structural transition is going to four 24-bit channels per die, further divided into two 12-bit sub-channels per die. This two-sub-channel design enhances memory concurrency while minimizing access latency, both of which are crucial in workloads such as local AI inference or graphics in ultra-thin notebooks. LPDDR5X, in contrast, has four 16-bit channels, which limits sub-channel granularity and concurrency in general under demanding mixed workloads. LPDDR5 vs. DDR5 RAM: What's the difference? Making sense of modern memory's jargon Posts LPDDR6 further introduces a new dynamic burst control feature. Devices can dynamically switch between 32-byte and 64-byte burst modes, enabling them to adjust bandwidth and power consumption in real-time. LPD only supports burst modes, which are sufficient in most applications but are not suitable for variable workloads, such as general AI or real-time applications, where access patterns shift rapidly. LPDDDR6 memory promises leading power efficiency VDD2 is a new parameter for better efficiency Another area where LPDDR6 takes the lead is in power efficiency. LPDDR6 incorporates a new voltage domain, VDD2, allowing memory devices to operate at a lower active voltage than LPDDR5X. LPDDR6 also features more efficient power management in its idle modes, with dynamic frequency/voltage scaling in low-activity modes. There are several static and partial refresh modes available, which significantly reduce background power consumption; a feature of increasing relevance in automotive and edge systems, where devices are often maintained powered up but idle for extended periods. Reliability features have also been significantly improved. LPDDR6 adds on-die ECC, command/address parity, row activation counters, and self-test routines, all of them absent or optional in LPDDR5. In use cases like the automotive industry, where data corruption is not just a throughput issue but a life safety concern, such improvements are necessary foundations. LPDDR6 can also have "carve-out" areas, wherein some of the DRAM is kept aside for high-integrity operations; a further indication of its readiness to deploy in both mission-critical applications as well as in embedded systems. 3 things I wish I knew before upgrading to 64GB of RAM More RAM isn't always better Posts 100 Even though JEDEC has solidified the specification, you will not see LPDDR6 in products tomorrow. You can already see vendors like Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron sampling devices with capacities ranging from 4 GB to 64 GB. Production on a large scale is likely to commence in the second quarter of 2025, with most analysts predicting a period of initial product adoption in late 2025 or early 2026. Early adoption is expected to occur in automotive compute boxes, edge inference accelerators, and high-end thin-and-light notebooks. Consider systems wherein DRAM is binned in place with unilaterally non-negotiable battery life. Still, workloads will only increase in burden. Intel's Arrow Lake processors, as well as the next-generation mobility platform under the unreleased name "Sarlak," will both appear internally as LPDDR6-capable, contingent on DRAM availability. Apple's M-series silicon, as well as newer next-gen Qualcomm Snapdragon X series processors, would likewise be targets once the ecosystem is mature enough. All would welcome increased bandwidth with reduced power consumption, of course, contingent on system integrators being able to order LPDDR6 in large enough quantities. LPDDR6 brings much-needed power efficiency Moving into a new era of low-profile and power-efficient memory Phones, despite the LPD, won't necessarily have priority. Whereas LPDDR4 and LPDDR5 were initially launched for mobile devices as the primary platform, LPDDR6 will initially be launched in specialized sub-segments. Phones will adopt it on board, sooner or later, but only after notebooks, auto, and AI boxes have proven their value. The arrival of JEDEC LPDDR6 is more than just a spec release. It is a harbinger of the new calculus of computing in which performance-per-watt is worth as much as raw throughput. As AI workloads permeate every corner of consumer and professional hardware, memory is the new battleground for balancing scalability and efficiency. One area where manufacturers can leverage power-saving and bandwidth improvements is in laptops, where power constraints due to battery life make this a plausible product segment that will greatly benefit from LPDDR6 memory. LPDDR6 does not arrive as a mere faster alternative, but as a wiser one, planned with an eye on the future, in which phone-refresh cycles have as much worth as edge computing and embedded smarts. Only OEMs will be able to keep pace with the spec integration roadmaps versus DRAM build quantities and manufacturing entering into play; however, LPDDR6 undoubtedly sets next-gen devices up with expectations for memory.
[2]
JEDEC publishes LPDDR6 memory standard with support from Qualcomm, Samsung and SK Hynix
Desktop systems expected to follow mobile and embedded device rollouts The next generation of low-power memory is on its way. LPDDR6, recently announced by the JEDEC Solid State Technology Association, is expected to begin appearing in products around 2026. The group has officially published the JESD209-6 specification, which outlines improvements aimed at mobile devices, AI workloads, and other power-sensitive environments. While workstations and desktop PCs will eventually benefit from the new standard, early adoption is focused elsewhere. LPDDR6 introduces a dual sub-channel architecture, with each sub-channel using 12 data lines and four command/address lines. This setup is designed to handle high-bandwidth tasks while staying efficient in compact system designs. Static efficiency mode allows for smarter use of bank resources, and the memory can shift burst lengths between 32B and 64B on demand. Energy efficiency is a clear priority of the new standard. LPDDR6 uses a lower voltage than its predecessor and introduces Dynamic Voltage Frequency Scaling for Low Power, which reduces voltage during slower operation. It also includes a dynamic efficiency mode and refresh control methods meant to cut power usage in real time. Security and reliability features have been updated as well. These include per-row activation tracking, on-die ECC, memory self-tests, and a carve-out mode for critical data. Such capabilities aim to support demanding AI workloads and mobile environments where system integrity matters. "JEDEC is proud to introduce LPDDR6, the culmination of years of dedicated effort by members of the JC-42.6 Subcommittee for Low Power Memories," said Mian Quddus, JEDEC's Chairman of the Board of Directors. "By delivering a balance of power efficiency, robust security options and high performance, LPDDR6 is an ideal choice for next-generation mobile devices, AI and related applications to thrive in a power-conscious, high-performance world." The new standard is backed by the likes of Micron, Qualcomm, Samsung, SK Hynix, Synopsys, and others, all of whom have contributed in someway towards its development and standardization. While the standard is ready, the hardware ecosystem will take time to catch up. Mobile and embedded platforms are expected to lead, while broader computing use will follow later. "Beyond the mobile industry, Qualcomm Technologies envisions LPDDR6 as an essential technology poised to revolutionize computing, automotive, AI, and other sectors, paving the way for transformative advancements in years to come," said Durga Malladi, SVP and GM of Edge Solutions at Qualcomm.
[3]
JEDEC LPDDR6 Specification: Key Features and Benefits
LPDDR6 is the next iteration of low-power double-data-rate DRAM, developed under JEDEC's JC-42.6 Low Power Memory Subcommittee. It delivers a substantial increase in data rate and bandwidth compared to LPDDR5, while targeting a similar or reduced power envelope. The specification introduces improvements in I/O signaling, power-rail management, and command timing to optimize energy use in memory-constrained environments. The specification addresses the rising demands of AI inference at the network edge and in endpoint devices. By supporting higher clock frequencies and wider I/O interfaces, LPDDR6 provides the throughput required for complex neural-network workloads. It also incorporates enhanced error-correction and on-die ECC to maintain data integrity under variable operating conditions, making it suitable for client computing, data-center accelerators, and automotive control systems. LPDDR6 is the latest low-power memory standard defined by JEDEC, the global authority for microelectronics standards. It's designed to push data rates and bandwidth well beyond LPDDR5, yet operate within a similar power budget. If you're working on an SoC for smartphones, edge AI, or automotive systems, understanding LPDDR6's new features is key to maximizing performance without draining your power budget. Under the hood, LPDDR6 ramps up the clock frequency and widens the data bus, allowing more bits to move in and out of the memory each cycle. But it's not just about brute force. The spec refines I/O signaling techniques -- such as improved equalization and voltage margins -- to ensure signals remain clean at high speeds. You'll also find more granular power-rail sequencing, which lets a controller selectively enable only the parts of the DRAM that are active, further trimming energy use. On the reliability front, LPDDR6 introduces enhanced on-die error-correction (ECC). This feature automatically detects and corrects single-bit errors, and flags multi-bit errors for higher-level system handlers. That's crucial for AI inference, where corrupt data can lead to mispredictions, and for automotive applications that demand bulletproof operation. Learn more about JEDEC ECC standards here. Why LPDDR6 Matters for Edge AI AI models are becoming more complex, and inference engines need both high throughput and low latency. Edge devices -- think smart cameras, industrial sensors, or AR glasses -- don't have the luxury of large power supplies. LPDDR6's improved bandwidth helps feed data pools to AI accelerators faster, while the power-saving modes maintain battery life. Cadence's involvement in the standard ensures IP availability for seamless integration; see their LPDDR6 PHY and controller offerings here. Mobile and Consumer Electronics In smartphones and tablets, LPDDR6 supports higher-resolution camera pipelines, faster app loads, and richer gaming experiences. With data rates nearly doubling those of LPDDR5, OEMs can push 4K and 8K video editing workflows right on the device. MediaTek has already confirmed support in upcoming SoC platforms, which you can read about on their product roadmap here. Automotive and Data Center Automotive systems are trending toward domain controllers, infotainment units, and ADAS (Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems) that require real-time processing of sensor data. LPDDR6's balance of low latency, high bandwidth, and robust error handling makes it well-suited for these roles. On the data-center side, LPDDR6 can serve as a high-speed buffer for AI inference cards and client-compute nodes, offering performance gains without the power costs of server-class memory. Industry Collaboration and Timeline The LPDDR6 specification was ratified after contributions from major DRAM vendors (Micron, Samsung, SK hynix), IP suppliers (Synopsys, Cadence), test-equipment firms (Keysight, Advantest), and end-system developers (Qualcomm). Prototype silicon has been circulating since early 2025, and JEDEC expects volume production modules to be available by late 2025 or early 2026. For official JEDEC documents, visit their standardization page here. Design Considerations Integrating LPDDR6 requires careful PCB layout to handle the high-speed interfaces. Signal-integrity simulations are a must, and power-delivery networks need to support the dynamic on-die voltage sequencing. Memory-controller IP typically provides training algorithms for calibration at startup, but you should validate across temperature and voltage corners. Consider using SI-optimized board materials and refer to JEDEC's thermal guidelines here. Looking Ahead As AI workloads move deeper into the edge and devices demand richer multimedia capabilities, memory standards will continue to evolve. LPDDR6 lays the groundwork for future low-power, high-bandwidth DRAM solutions. If you're designing next-generation SoCs or system modules, getting familiar with LPDDR6 now will pay dividends when the first commercial parts hit production lines. Whether you're in mobile, automotive, or data-centre markets, LPDDR6 offers a technically balanced approach to scaling memory performance while keeping energy consumption in check. Keep an eye on leading IP vendors and module suppliers for evaluation kits and development boards that let you prototype with LPDDR6 in your next project. Source: JEDEC
[4]
JEDEC reveals new LPDDR6 memory standard: higher speeds for mobile devices and AI
As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases. TweakTown may also earn commissions from other affiliate partners at no extra cost to you. JEDEC has just announced the publication of its new LPDDR6 memory standard dubbed "JESD209-6" which has been designed to boost memory speeds and efficiency, for the future of mobile devices and AI. The new LPDDR6 memory standard represents a significant advancement in memory technology, increasing performance, power efficiency, and security. In order to enable AI applications and other high-performance workloads, the new LPDDR6 standard uses a dual sub-channel architecture that allows for flexible operation while maintaining a small access granularity of 32 bytes. Mian Quddus, JEDEC's Chairman of the Board of Directors, explains: "JEDEC is proud to introduce LPDDR6, the culmination of years of dedicated effort by members of the JC-42.6 Subcommittee for Low Power Memories. By delivering a balance of power efficiency, robust security options and high performance, LPDDR6 is an ideal choice for next-generation mobile devices, AI and related applications to thrive in a power-conscious, high-performance world". To enable AI applications and other high-performance workloads, LPDDR6 employs a dual sub-channel architecture that allows for flexible operation while maintaining a small access granularity of 32 bytes. In addition, LPDDR6 key features offer: Power Efficiency To help meet ever-increasing demands for power efficiency, LPDDR6 operates with a lower voltage and low power consumption capable VDD2 supply as compared to LPDDR5, and mandates two supplies for VDD2. Additional power-saving features include: Security and Reliability Security and reliability improvements over the previous version of the standard include:
[5]
JEDEC Introduces LPDDR6 For Improved Performance And Efficiency On Mobile Devices
The newly released LPDDR6 standard will offer enhanced performance, efficiency, security, and reliability for mobile systems and will be adopted by leading memory makers. LPDDR5 and LPDDR5X will now be succeeded by JEDEC's newest memory standard, LPDDR6. The company has introduced LPDDR6 memory for mobile platforms, aiming for high performance and power efficiency. The new memory standard will be deployed across various sectors, including AI edge computing, client systems, servers, and the automotive industry, to bring additional benefits to these devices. JEDEC is proud to introduce LPDDR6, the culmination of years of dedicated effort by members of the JC-42.6 Subcommittee for Low Power Memories, By delivering a balance of power efficiency, robust security options and high performance, LPDDR6 is an ideal choice for next-generation mobile devices, AI and related applications to thrive in a power-conscious, high-performance world. - Mian Quddus, JEDEC Chairman of the Board of Directors The LPDDR6 memory brings various improvements over the LPDDR5 and LPDDR5X by introducing Dual Sub-Channel Architecture, bringing two sub-channels per die, each with 12 DQs, and supports flexible 32B and 64B burst lengths. Compared to LPDDR5, which has 16 DQ (2x8) lines per channel, the LPDDR6 reduces it to 2x 12 for better latency and access speed optimizations. For power efficiency, the LPDDR6 will use lower voltage to reduce dynamic power consumption and brings features like DVFSL (Dynamic Voltage Frequency Scaling for Low Power) to adjust voltage during low-frequency operations. With Dynamic Efficiency Mode, LPDDR6 will allow a single sub-channel operation for low-power states, and this brings noticeable improvements over LPDDR5 when it comes to power efficiency. For Security and Reliability, LPDDR6 brings ECC (On-Die Error Correction), CA Parity + MBIST, PRAC (Per Row Activation Counting), and Meta Region Carve-out features, ensuring data integrity, catching memory errors, and various enhancements in reliability. New generation low-power memory LPDDR6 offers significant performance improvements, LPDDR6 will have a positive impact not only on mobile applications but on many other computing fields such as Edge AI computing, Client computer, data center and automotive. - Osamu Nagashima, Advantest Corporation The new LPDDR6 standard will be deployed in multiple sectors for improved performance and efficiency, and companies like MediaTek, Micron, Samsung, SK Hynix, and Qualcomm Technologies will be the first to adopt the newer memory standard.
Share
Share
Copy Link
JEDEC has officially published the LPDDR6 specification, promising significant improvements in performance, power efficiency, and security for mobile devices, AI applications, and other power-sensitive environments.
JEDEC Unveils LPDDR6 Specification
The JEDEC Solid State Technology Association has officially published the JESD209-6 specification, introducing the next generation of low-power memory design: LPDDR6
1
2
. This new standard represents a significant leap forward in memory technology, aimed at meeting the increasing performance and efficiency demands of edge AI, embedded computing, and high-end notebooks with low power targets1
.
Source: TweakTown
Key Features and Improvements
LPDDR6 brings substantial enhancements over its predecessors, LPDDR5 and LPDDR5X:
-
Increased Bandwidth: The new specification supports data rates from 10.6 gigabits per second per pin up to 14.9 Gb/s, a significant increase from LPDDR5X's maximum of 8.5 Gb/s
1
. This translates to a maximum bandwidth of 38.4 GB/s on a 64-bit bus, nearly doubling LPDDR5's initial bandwidth1
. -
Architectural Changes: LPDDR6 introduces a dual sub-channel architecture with four 24-bit channels per die, further divided into two 12-bit sub-channels
1
3
. This design enhances memory concurrency and minimizes access latency, crucial for AI inference and graphics processing in ultra-thin notebooks1
. -
Power Efficiency: The new standard incorporates a lower voltage domain (VDD2) and more efficient power management in idle modes
1
4
. It features dynamic frequency/voltage scaling and various static and partial refresh modes to reduce background power consumption1
. -
Security and Reliability: LPDDR6 adds on-die ECC, command/address parity, row activation counters, and self-test routines
1
3
. These improvements make it suitable for mission-critical applications and embedded systems, particularly in the automotive industry1
.
Applications and Industry Impact

Source: TechRadar
The LPDDR6 standard is expected to have a broad impact across various sectors:
-
Mobile and Consumer Electronics: LPDDR6 will support higher-resolution camera pipelines, faster app loads, and richer gaming experiences in smartphones and tablets
3
. -
Automotive Systems: The new standard's balance of low latency, high bandwidth, and robust error handling makes it well-suited for domain controllers, infotainment units, and Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
3
. -
AI and Edge Computing: LPDDR6's improved bandwidth and power efficiency will benefit AI inference at the network edge and in endpoint devices
3
5
. -
Data Centers: The standard can serve as a high-speed buffer for AI inference cards and client-compute nodes in data centers
3
.
Related Stories
Industry Adoption and Timeline
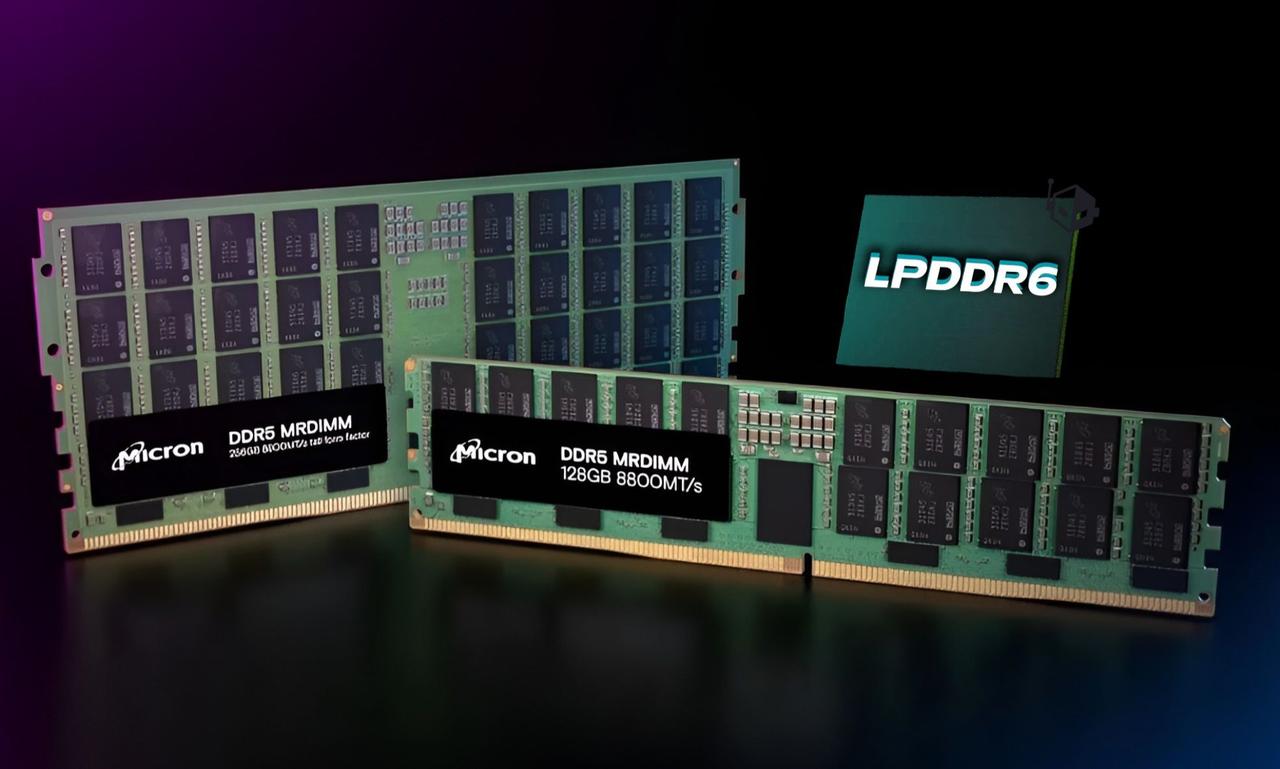
While JEDEC has solidified the specification, widespread adoption of LPDDR6 is not immediate. Major memory manufacturers like Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron are already sampling devices with capacities ranging from 4 GB to 64 GB
1
2
. Large-scale production is expected to commence in the second quarter of 2025, with initial product adoption likely in late 2025 or early 20261
2
.Early adoption is anticipated in automotive compute boxes, edge inference accelerators, and high-end thin-and-light notebooks
1
. Processors from Intel, Qualcomm, and potentially Apple's M-series silicon are expected to support LPDDR6, contingent on DRAM availability1
2
.
Source: Wccftech
Conclusion
The introduction of LPDDR6 marks a significant milestone in memory technology, promising to revolutionize computing, automotive, AI, and other sectors in the coming years
2
. As AI workloads become more prevalent and devices demand higher performance with lower power consumption, LPDDR6 is poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of computing and mobile technology.References
Summarized by
Navi
[2]
Related Stories
SK hynix validates LPDDR6 memory, 33% faster than LPDDR5X but AI devices get priority
10 Mar 2026•Technology

Micron Leads Memory Innovation with World's First 1γ LPDDR5X for AI-Driven Smartphones
05 Jun 2025•Technology

DDR6 Memory: Next-Gen Standard Set to Double DDR5 Speeds by 2027
24 Jul 2025•Technology
Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.4, New AI Model Built for Agents and Professional Work
Technology

2
Anthropic sues Pentagon over supply chain risk label after refusing autonomous weapons use
Policy and Regulation

3
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round as questions swirl around AI bubble and profitability
Business and Economy





