NVIDIA Unveils Vision for Next-Gen 'AI Factories' with Vera Rubin and Kyber Architectures
4 Sources
4 Sources
[1]
NVIDIA, Partners Drive Next-Gen Efficient Gigawatt AI Factories in Buildup for Vera Rubin
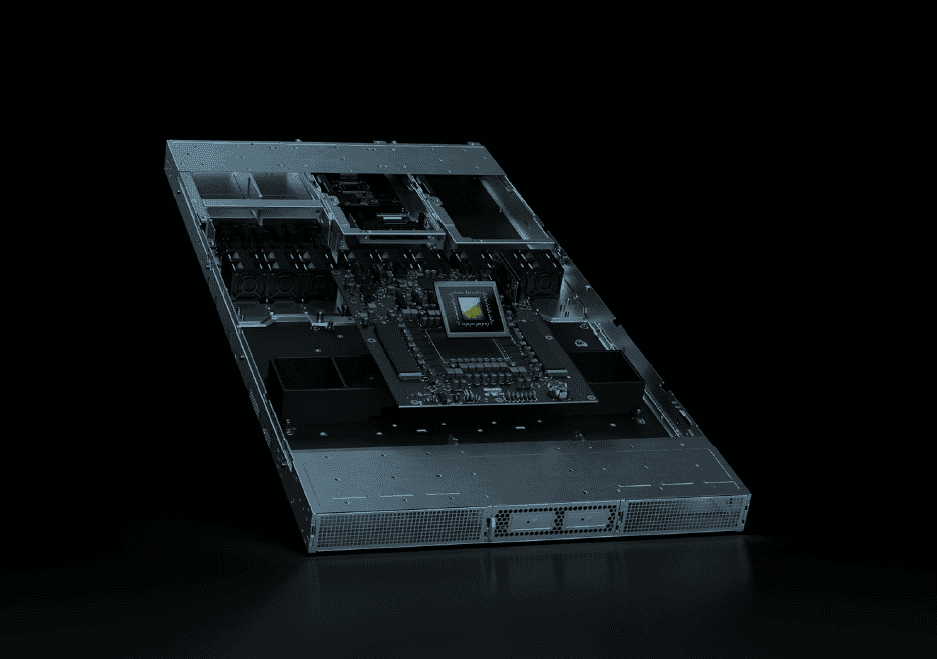
More than 50 NVIDIA MGX partners are gearing up for NVIDIA Vera Rubin NVL144; 20-plus companies will join NVIDIA's growing ecosystem of partners supporting 800 VDC data centers to enable future gigawatt AI factories. At the OCP Global Summit, NVIDIA is offering a glimpse into the future of gigawatt AI factories. NVIDIA will unveil specs of the NVIDIA Vera Rubin NVL144 MGX-generation open architecture rack servers, which more than 50 MGX partners are gearing up for along with ecosystem support for NVIDIA Kyber, which connects 576 Rubin Ultra GPUs, built to support increasing inference demands. Some 20-plus industry partners are showcasing new silicon, components, power systems and support for the next-generation, 800-volt direct current (VDC) data centers of the gigawatt era that will support the NVIDIA Kyber rack architecture. Foxconn provided details on its 40-megawatt Taiwan data center, Kaohsiung-1, being built for 800 VDC. CoreWeave, Lambda, Nebius, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and Together AI are among other industry pioneers designing for 800-volt data centers. In addition, Vertiv unveiled its space-, cost- and energy-efficient 800 VDC MGX reference architecture, a complete power and cooling infrastructure architecture. HPE is announcing product support for NVIDIA Kyber as well as NVIDIA Spectrum-XGS Ethernet scale-across technology, part of the Spectrum-X Ethernet platform. Moving to 800 VDC infrastructure from traditional 415 or 480 VAC three-phase systems offers increased scalability, improved energy efficiency, reduced materials usage and higher capacity for performance in data centers. The electric vehicle and solar industries have already adopted 800 VDC infrastructure for similar benefits. The Open Compute Project, founded by Meta, is an industry consortium of hundreds of computing and networking providers and more focused on redesigning hardware technology to efficiently support the growing demands on compute infrastructure. The Vera Rubin NVL144 MGX compute tray offers an energy-efficient, 100% liquid-cooled, modular design. Its central printed circuit board midplane replaces traditional cable-based connections for faster assembly and serviceability, with modular expansion bays for NVIDIA ConnectX-9 800GB/s networking and NVIDIA Rubin CPX for massive-context inference. The NVIDIA Vera Rubin NVL144 offers a major leap in accelerated computing architecture and AI performance. It's built for advanced reasoning engines and the demands of AI agents. Its fundamental design lives in the MGX rack architecture and will be supported by 50+ MGX system and component partners. NVIDIA plans to contribute the upgraded rack as well as the compute tray innovations as an open standard for the OCP consortium. Its standards for compute trays and racks enable partners to mix and match in modular fashion and scale faster with the architecture. The Vera Rubin NVL144 rack design features energy-efficient 45°C liquid cooling, a new liquid-cooled busbar for higher performance and 20x more energy storage to keep power steady. The MGX upgrades to compute tray and rack architecture boost AI factory performance while simplifying assembly, enabling a rapid ramp-up to gigawatt-scale AI infrastructure. NVIDIA is a leading contributor to OCP standards across multiple hardware generations, including key portions of the NVIDIA GB200 NVL72 system electro-mechanical design. The same MGX rack footprint supports GB300 NVL72 and will support Vera Rubin NVL144, Vera Rubin NVL144 CPX and Vera Rubin CPX for higher performance and fast deployments. The OCP ecosystem is also preparing for NVIDIA Kyber, featuring innovations in 800 VDC power delivery, liquid cooling and mechanical design. These innovations will support the move to rack server generation NVIDIA Kyber -- the successor to NVIDIA Oberon -- which will house a high-density platform of 576 NVIDIA Rubin Ultra GPUs by 2027. The most effective way to counter the challenges of high-power distribution is to increase the voltage. Transitioning from a traditional 415 or 480 VAC three-phase system to an 800 VDC architecture offers various benefits. The transition afoot enables rack server partners to move from 54 VDC in-rack components to 800 VDC for better results. An ecosystem of direct current infrastructure providers, power system and cooling partners, and silicon makers -- all aligned on open standards for the MGX rack server reference architecture -- attended the event. NVIDIA Kyber is engineered to boost rack GPU density, scale up network size and maximize performance for large-scale AI infrastructure. By rotating compute blades vertically, like books on a shelf, Kyber enables up to 18 compute blades per chassis, while purpose-built NVIDIA NVLink switch blades are integrated at the back via a cable-free midplane for seamless scale-up networking. Over 150% more power is transmitted through the same copper with 800 VDC, enabling eliminating the need for 200-kg copper busbars to feed a single rack. Kyber will become a foundational element of hyperscale AI data centers, enabling superior performance, efficiency and reliability for state-of-the-art generative AI workloads in the coming years. NVIDIA Kyber racks offer a way for customers to reduce the amount of copper they use by the tons, leading to millions of dollars in cost savings. In addition to hardware, NVIDIA NVLink Fusion is gaining momentum, enabling companies to seamlessly integrate their semi-custom silicon into highly optimized and widely deployed data center architecture, reducing complexity and accelerating time to market. Intel and Samsung Foundry are joining the NVLink Fusion ecosystem that includes custom silicon designers, CPU and IP partners, so that AI factories can scale up quickly to handle demanding workloads for model training and agentic AI inference. More than 20 NVIDIA partners are helping deliver rack servers with open standards, enabling the future gigawatt AI factories.
[2]
Nvidia unveils its vision for gigawatt 'AI factories' based on its Vera Rubin architecture - SiliconANGLE
Nvidia unveils its vision for gigawatt 'AI factories' based on its Vera Rubin architecture Nvidia Corp. took to the stage at the 2025 OCP Global Summit in San Jose today to talk about how it's collaborating with more than 70 partners on the design of more efficient "gigawatt AI factories" to support the next generation of artificial intelligence models. The gigawatt AI factories envisioned by Nvidia will utilize Vera Rubin NVL144, which is an open architecture rack server based on a 100% liquid-cooled design. It's designed to support the company's next-generation Vera Rubin graphics processing units, which are expected to launch in 2027. The architecture will enable companies to scale their data centers exponentially, with a central printed circuit board midplane that enables faster assembly, and modular expansion bays for networking and inference to be added as needed. Nvidia said it's donating the Vera Rubin NVL144 architecture to the Open Compute Project as an open standard, so that any company will be able to implement it in its own data centers. It also talked about how its ecosystem partners are ramping up support for the Nvidia Kyber server rack design, which will ultimately be able to connect 576 Rubin Ultra GPUs when they become available. In addition, Nvidia was boosted with the news that both Meta Platforms Inc. and Oracle Corp. have announced plans to standardize their data centers on the company's Spectrum-X Ethernet networking switches. The Vera Rubin NVL144 architecture is designed to support the roll-out of 800-volt direct current data centers for the gigawatt era, and Nvidia hopes it will become the foundation of new "AI factories," or data centers that are optimized for AI workloads. One of the main design innovations is the central printed circuit board midplane, which replaces the traditional cable-based connections in data centers to enable more rapid assembly, while making them easier to service and upgrade. The modular expansion bays help to future proof the architecture, allowing data center operators to add Nvidia ConnectX-9 800GB/s networking and Vera Rubin GPUs to scale up their AI factories to meet increasing demands for computational power and bandwidth. In addition, Vera Rubin NVL144 features an advanced 45°C liquid-cooled busbar to enable higher performance, with 20 times greater energy storage to ensure reliable power supply. Nvidia explained that Vera Rubin NVL144 is all about preparing for the future, with the flexible architecture designed to scale up over time to support advanced reasoning engines and the demands of autonomous AI agents. It's based on the existing Nvidia MGX modular architecture, which means it's compatible with numerous third-party components and systems from more than 50 ecosystem partners. With the new architecture, data center operators will be able to mix and match different components in a modular fashion in order to customize their AI factories. At the Summit, more than 50 ecosystem partners announced their support for the Vera Rubin NVL144 architecture. Nvidia also revealed the growing support for its Nvidia Kyber rack server architecture, which is designed to support the infrastructure that will power clusters of 576 Vera Rubin GPUs. Like Vera Rubin NVL144, Nvidia Kyber features several innovations in terms of 800 VDC power delivery, liquid cooling and mechanical design. The company explained that the increased power demands of the upcoming Vera Rubin GPUs necessitate a revamped energy distribution system. It said the most effective way to counter the challenges of higher power distribution is to increase the voltage, which means it's ditching the traditional 415 and 480 volt three-phase system in favor of a new 800 VDC architecture. With this system, Nvidia said it will be possible to transmit 150% more power through the same copper wires. Nvidia Kyber also supports increased rack GPU density to maximize the performance of AI infrastructure. It introduces a new design that rotates compute blades vertically like books on a shelf in order to fit 18 compute blades on a single chassis. At the same time, purpose-built Nvidia NVLink switch blades are integrated at the back through a cableless midplane to scale up the networking capabilities. Nvidia said Kyber will become a "foundational element" of future hyperscale data centers, with superior performance, greater reliability and enhanced energy efficiency, able to support the anticipated advances in AI over the coming years. The impact of Vera Rubin NVL144 and Kyber probably won't be felt for a couple of years yet, but Nvidia says Meta and Oracle will see more immediate gains following their decision to standardize on its Spectrum-X Ethernet switches (pictured) in their existing and future data centers. Spectrum-X Ethernet switches are more advanced networking switches that can deliver immediate performance gains for AI workloads by providing higher-speed connectivity and enhanced data throughput. They utilize adaptive routing to optimize the flow of data through the network, which makes them better able to handle the unique traffic patterns of AI applications, Nvidia said. In an earlier demonstration, Nvidia showed how the world's largest AI supercomputer was able to achieve 95% faster data throughput speeds using Spectrum-X. Meta plans to integrate Spectrum-X Ethernet switches within the Facebook Open Switching System, which is the software platform it uses to manage and control network switches at massive scales. Meta Vice President of Network Engineering Gaya Nagarajan said the company expects to unlock immediate gains in AI training efficiency. "Meta's next-generation AI infrastructure requires open and efficient networking at a scale the industry has never seen before," he said. "By integrating Nvidia Spectrum-X Ethernet into the Minipack3N switch and FBOSS, we can extend our open networking approach while unlocking the efficiency and predictability needed to train ever-larger models and bring generative AI applications to billions of people." Meanwhile, Oracle is looking further ahead. Not only will it integrate Spectrum-X Ethernet in its existing data centers, but also its future gigawatt-scale AI factories powered by Vera Rubin GPUs. "By adopting Spectrum-X Ethernet, we can interconnect millions of GPUs with breakthrough efficiency so our customers can more quickly train, deploy and benefit from the next wave of generative and reasoning AI," said Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Executive Vice President Mahesh Thiagarajan.
[3]
NVIDIA Unveils New Partners & Plans across AI Networking, Compute, OCP | AIM
The company confirmed new NVLink Fusion partnerships with Intel and Samsung Foundry, as well as the expansion of its partnership with Fujitsu. NVIDIA detailed new developments in AI infrastructure at the Open Compute Project (OCP), revealing advances in networking, compute platforms and power systems. The company also revealed new benchmarks for its Blackwell GPUs and plans to introduce 800-volt direct current (DC) power designs for future data centres. Speaking at a press briefing ahead of the OCP Summit, NVIDIA executives said the company aims to support the rapid growth of AI factories by coordinating "from chip to grid". Joe DeLaere, data centre product marketing manager at NVIDIA, said the surge in AI demand requires integrated solutions in networking, compute, power and cooling, and that NVIDIA's contributions will remain open to the OCP community. Meta will integrate NVIDIA's Spectrum-X Ethernet platforms into its AI infrastructure, while Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) will adopt the same technology for large-scale AI training clusters. NVIDIA said Spectrum-X is explicitly designed for AI workloads, claiming it achieves "95% throughput with zero latency degradation". On performance, NVIDIA highlighted new open-source benchmarks showing a 15-fold gain in inference throughput for its Blackwell GB200 GPUs compared to the previous Hopper generation. "A $5 million investment in Blackwell can generate $75 million in token revenue," the company said, linking performance efficiency directly to AI factory returns. NVIDIA also confirmed that the forthcoming Rubin and Rubin CPX systems will build on the MGX rack platform and are expected to launch in the second half of 2026. A significant focus was the industry move towards 800V DC power delivery, which NVIDIA presented as a way to cut energy losses and support higher rack densities. The company is working with infrastructure providers, including Schneider Electric and Siemens, to develop reference architectures. When asked by AIM about how OCP contributions and Spectrum-X adoption by Meta and Oracle may affect smaller enterprises, NVIDIA said the technology is designed for all scales. "Spectrum-X becomes the infrastructure for AI; it serves enterprise, cloud and the world's largest AI supercomputers," said Gilad Shainer, SVP of marketing at NVIDIA. The company confirmed new NVLink Fusion partnerships with Intel, Samsung Foundry and Fujitsu to expand custom silicon integration within MGX-compatible racks. NVIDIA will also publish a technical white paper on 800V DC design and present full architectural details during the OCP Summit.
[4]
NVIDIA Unveils Development On 'Kyber' Rack-Scale Generation, Scaling Up To 576 Rubin Ultra GPUs In One Platform By 2027 To Bring Immense AI Power
NVIDIA has announced several important updates to its AI compute portfolio at the OCP, including development around its Kyber rack-scale generation, a significant advancement. As the world increasingly demands more computing capabilities, NVIDIA has been making advances across its entire tech stack, leaving competitors with little room to catch up in the race. Now, at the OCP Global Summit, Team Green has showcased the future of 'AI factories' and while the firm reveals several interesting developments, one of the most optimistic ones includes the work around next-gen Kyber rack-scale technology, which will replace Oberon and potentially allow the firm to scale up to a massive NVL576 configuration. The OCP ecosystem is also preparing for NVIDIA Kyber, featuring innovations in 800 VDC power delivery, liquid cooling and mechanical design. These innovations will support the move to rack server generation NVIDIA Kyber -- the successor to NVIDIA Oberon -- which will house a high-density platform of 576 NVIDIA Rubin Ultra GPUs by 2027. - NVIDIA If you are still unfamiliar with the topic being discussed, Kyber and Oberon refer to rack generations, where the primary aspects addressed are chip arrangements, power ratings, and cooling solutions. Oberon has been NVIDIA's dominant design for the Blackwell generations (GB200/GB300), but with Rubin Ultra, Team Green plans to transition to the Kyber generation, which will bring several upgrades. One central improvement area is rack architecture, where NVIDIA will switch to stacking compute trays, mounted vertically, similar to books, called vertical blades. This technique will bring in higher GPU density and more efficient networking. Another interesting upgrade is the inclusion of built-in NVLink switch blades inside the same rack enclosure, which will enable higher scalability and easier rack maintenance. In terms of performance, one of the key benefits of Kyber is that NVIDIA will switch to an 800 VDC facility-to-rack power-delivery model, which is also an upgrade from the previous 415 or 480 VAC three-phase system. This will enable significantly improved power efficiency figures, and more importantly, a 150% increase in power transferred through the same copper wire, leading to 'millions saved' by reducing the amount of copper needed to deploy large-scale clusters. Overall, Kyber will pave the way for NVIDIA's Rubin Ultra NVL576 systems, bringing unprecedented computing power onboard and driving the race for cutting-edge AI infrastructure.
Share
Share
Copy Link
NVIDIA showcases plans for gigawatt-scale AI infrastructure, introducing Vera Rubin NVL144 and Kyber rack designs. The company collaborates with over 70 partners to revolutionize data center efficiency and performance for future AI demands.
NVIDIA's Vision for Next-Generation AI Infrastructure
NVIDIA has unveiled its ambitious plans for the future of AI computing at the 2025 OCP Global Summit, showcasing new architectures and collaborations aimed at creating gigawatt-scale 'AI factories'
1
2
. The company's vision centers around two key innovations: the Vera Rubin NVL144 open architecture rack server and the Kyber rack-scale generation.
Source: Wccftech
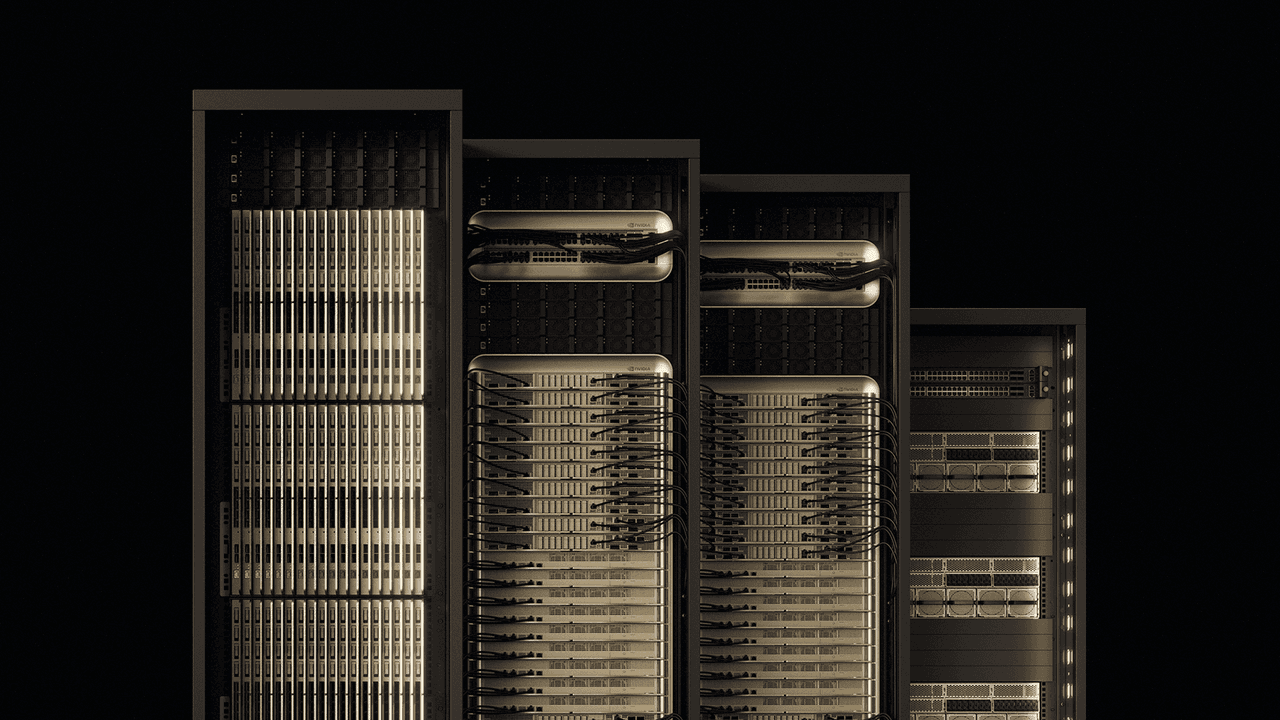
Vera Rubin NVL144: Powering the AI Factories of Tomorrow
The Vera Rubin NVL144 is designed as a 100% liquid-cooled, modular system that promises to revolutionize data center efficiency and performance
1
2
. Key features include:- A central printed circuit board midplane replacing traditional cable connections
- Modular expansion bays for NVIDIA ConnectX-9 800GB/s networking
- Support for NVIDIA Rubin CPX for massive-context inference
- 45°C liquid cooling and a new liquid-cooled busbar for higher performance
- 20x more energy storage for steady power delivery
NVIDIA is contributing the Vera Rubin NVL144 design to the Open Compute Project (OCP) as an open standard, allowing widespread adoption across the industry
2
.
Source: NVIDIA
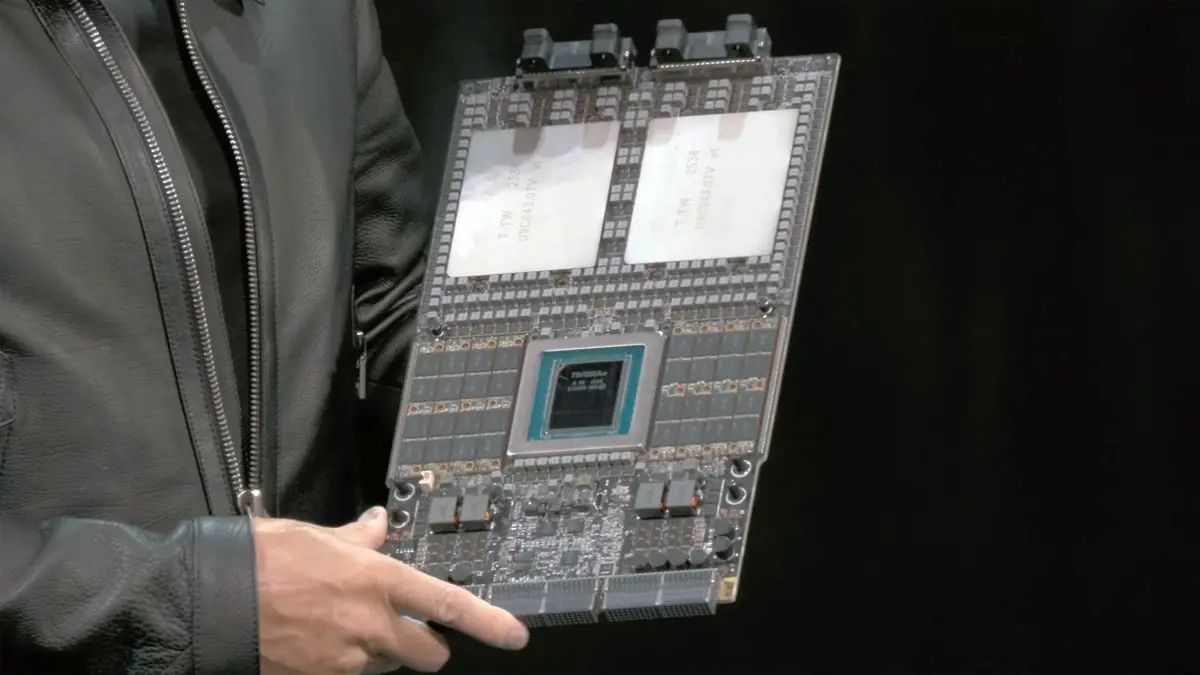
Kyber: Scaling to New Heights
The Kyber rack-scale generation represents NVIDIA's vision for the future of AI infrastructure, designed to support up to 576 NVIDIA Rubin Ultra GPUs by 2027
1
4
. Kyber introduces several innovations:- Vertical blade design, allowing up to 18 compute blades per chassis
- Purpose-built NVIDIA NVLink switch blades integrated at the back
- Cable-free midplane for seamless scale-up networking
- Support for 800-volt direct current (VDC) power delivery
Revolutionizing Power Delivery and Efficiency
A significant focus of NVIDIA's new designs is the transition to 800 VDC power delivery
1
2
3
. This shift from traditional 415 or 480 VAC three-phase systems offers several benefits:- 150% more power transmitted through the same copper
- Reduced material usage and costs
- Improved energy efficiency
- Higher capacity for performance in data centers
Industry Collaboration and Adoption
NVIDIA's vision is supported by a growing ecosystem of partners and early adopters:
- Over 50 NVIDIA MGX partners are preparing for the Vera Rubin NVL144
1
- 20-plus companies are joining NVIDIA's ecosystem supporting 800 VDC data centers
1
- Meta and Oracle have announced plans to standardize their data centers on NVIDIA's Spectrum-X Ethernet networking switches
2
- Foxconn is building a 40-megawatt data center in Taiwan designed for 800 VDC
1
Related Stories
Performance and Efficiency Gains
NVIDIA claims significant performance improvements with its new architectures:
- The Blackwell GB200 GPUs show a 15-fold gain in inference throughput compared to the previous Hopper generation
3
- The company suggests that a $5 million investment in Blackwell can generate $75 million in token revenue
3
Looking Ahead
As NVIDIA continues to push the boundaries of AI infrastructure, the company is positioning itself at the forefront of the AI revolution. With the Vera Rubin and Kyber architectures, NVIDIA is laying the groundwork for the next generation of AI applications and services, promising unprecedented computational power and efficiency for the AI-driven future
1
2
3
4
.References
Summarized by
Navi
[2]
Related Stories
NVIDIA Unveils Next-Gen AI Powerhouses: Rubin and Rubin Ultra GPUs with Vera CPUs
19 Mar 2025•Technology

Nvidia Vera Rubin architecture slashes AI costs by 10x with advanced networking at its core
06 Jan 2026•Technology

Nvidia ships first Vera Rubin AI system samples, promising 10x efficiency over Blackwell
25 Feb 2026•Technology
Recent Highlights
1
Samsung unveils Galaxy S26 lineup with Privacy Display tech and expanded AI capabilities
Technology

2
Anthropic refuses Pentagon's ultimatum over AI use in mass surveillance and autonomous weapons
Policy and Regulation

3
AI models deploy nuclear weapons in 95% of war games, raising alarm over military use
Science and Research