AI Slop Floods Social Media as Platforms Introduce Filters Amid Growing User Backlash
6 Sources
6 Sources
[1]
AI 'slop' is transforming social media - and there's a backlash
Théodore remembers the AI slop that tipped him over the edge. The image was of two emaciated, impoverished South Asian children. For some reason, despite their boyish features they have thick beards. One of them had no hands and only one foot. The other was holding a sign saying it's his birthday and asking for likes. Inexplicably they are sat in the middle of a busy road in the pouring rain with a birthday cake. The image is full of tell-tale signs that it was made with AI. But on Facebook it went viral with nearly one million likes and heart emojis. Something snapped in Théodore. "It boggled my mind. The absurd AI made images were all over Facebook and getting [a] huge amount of traction without any scrutiny at all - it was insane to me," says the 20-year-old student from Paris. So Théodore started an account on X, formerly known as Twitter, called "Insane AI Slop" and started calling out and poking fun at the content he came across that was fooling people. Others took notice and his inbox soon became flooded with people sending submissions for popular so-called AI slop. Common themes started becoming apparent - religion, military or poor children doing heartwarming things. "Kids in the third world doing impressive stuff is always popular - like a poor kid in Africa making an insane statue out of trash. I think people find it wholesome so the creators think, 'Great, let's make more of this stuff up,'" Théodore says. Théodore's account soon swelled to over 133,000 followers. The onslaught of AI slop - which he defines as fake, unconvincing videos and pictures, made quickly - is now unstoppable. Tech companies have embraced AI. Some of the firms say they are starting to crack down on some forms of AI 'slop' - though many social media feeds still appear to be full of the content. Over just a couple of years, the experience of using social media has changed profoundly. How did it happen, and what effect will it have on society? And, perhaps most pressingly of all, how much do the billions of social media users actually care? In October, during another jubilant earnings call, Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg happily declared that social media had entered a third phase, which is now centred around AI. "First was when all content was from friends, family, and accounts that you followed directly. "The second was when we added all of the creator content. Now as AI makes it easier to create and remix content, we're going to add yet another huge corpus of content," he told shareholders. Meta, which runs social media sites Facebook, Instagram and Threads, is not only allowing people to post AI generated content - it's launched products to enable more of it to be made. Image and video generators and increasingly powerful filters are now being offered across the board. When approached for comment, Meta pointed the BBC to January's earnings call. In that call, the billionaire said the firm was leaning even more into AI, and made no mention of any clampdown on slop. "Soon we'll see an explosion of new media formats that are more immersive and interactive, and only possible because of advances in AI," Zuckerberg said. YouTube's CEO, Neal Mohan, wrote in his 2026 look-ahead blog that in December alone more than one million YouTube channels used the platform's AI tools to make content. "Just as the synthesizer, Photoshop and CGI revolutionized sound and visuals, AI will be a boon to the creatives who are ready to lean in," he wrote. The CEO also acknowledged that there are growing concerns about "low-quality content, aka AI slop". He said his team is working on ways to improve systems to find and remove "low quality, repetitive content". But he also ruled out making any judgements on what should and shouldn't be allowed to flourish. He pointed out that once-niche content like ASMR (soothing sounds designed to make your scalp tingle) and live video game-playing is now mainstream. According to research from AI company Kapwing, 20% of content shown to a freshly opened YouTube account is now "low-quality AI video". Short-form video in particular was a hotspot, with Kapwing finding it featured in 104 of the first 500 YouTube Shorts clips shown to a new account created by the researchers. The creator economy seems to be a big driver as people and channels can earn money from engagement and views. Judging by the views on some AI channels and videos, people are indeed drawn to the content - or the algorithms that dictate what we see are, anyway. According to Kapwing, the AI slop channel with the most views is India's Bandar Apna Dost, which has 2.07 billion views, netting the creators an estimated annual earnings of $4m (£2.9 million). But there is something of a backlash taking place too. Under many viral AI videos, it's now common to see a furious flurry of comments decrying the content. Théodore, the student from Paris, helped to drive this backlash. Using his newfound influence on X he complained to YouTube moderators about the flood of weird AI cartoons that got huge numbers of views. In his view the were disturbing and harmful, and in some cases appeared to him to be aimed at children. The videos were called things like "Mum cat saves kitten from deadly belly parasites", and showed gory scenes. Another short clip showed a woman in a night dress who eats a parasite and then turns into a giant angry monster that is eventually healed by Jesus. YouTube removed the channels, telling us they did so because they violated their community guidelines. They said they are "focused on connecting our users with high-quality content, regardless of how it was made", and said they are working to "reduce the spread of low quality AI content". But that experience, plus many others like it, have ground Théodore down. Even seemingly cosy lifestyle sites like Pinterest - the forum for recipes and interior design ideas - have been affected. Users have become so frustrated by the deluge of AI slop that the company introduced a new opt-out system for AI-generated content - but this relies on users admitting that their perfect-house imagery is AI made. On my feed (and I'm aware that everyone's feed is different - including the comments) - the backlash to AI slop has become incessant. Whether it's TikTok, Threads, Instagram or X - there seems to be a people-power movement against this content. Sometimes the number of likes for the AI backlash comments far exceed the original post. Such is the case with a recent video showing a snowboarder rescuing a wolf from a bear. The video itself had 932 likes - versus 2,400 likes for a commenter who wrote, "Raise your hand if you're tired of this AI s**t". But of course it all feeds the beast. All engagement is good engagement for social media platforms where keeping us scrolling is key. So does it actually matter if the amazing, heartwarming or shocking video on your social feed is real or not? Emily Thorson, associate professor at Syracuse University in the US, who specialises in politics, misinformation and misperceptions, says it depends on what people are doing on the social media platform. "If a person is on a short-video platform solely for entertainment, then their standard for whether something is worthwhile is simply 'is it entertaining?'," she says. "But if someone is on the platform to learn about a topic or to connect with community members, then they might perceive AI-generated content as more problematic." How people feel about AI slop also depends on how it is communicated. If something is made clearly as a joke, it seems to be taken as such. But when AI slop has been created specifically to deceive, it can anger people. One AI-generated video I saw recently is emblematic: an incredibly realistic, natural-history-style video of an astonishing leopard hunt. In the comments, some viewers were fooled; others were unsure. "What documentary is it from?," one commenter asked. "Please - it is the only way to [prove] no AI." Alessandro Galeazzi, from the University of Padova in Italy, researches social media behaviour and echo chambers. He says that verifying whether or not a video is AI takes mental effort, and over the long run, he fears people will simply stop checking. "My feeling is that the flood of nonsense, low-quality content generated using AI might further reduce people's attention span," he says. He distinguishes content that is intended to deceive with the more comical and obviously-fake AI slop, like fish with shoes, or gorillas lifting weights at the gym. But even that more whimsical content might also have a damaging impact. He talks of the risk of "brain rot" - the idea that our constant exposure to social media is harming our intellectual abilities. "I would say AI slop increases the brain rot effect, making people quickly consume content that they know is not only unlikely to be real, but probably not meaningful or interesting," he says. Beyond the slop, some AI-made content can have far worse implications. Elon Musk's companies xAI and social platform X were recently forced to change their rules after the chatbot Grok was being used to digitally undress women and children on X. And in the aftermath of the US attack on Venezuela, fake videos were spread of people crying in the streets and thanking the US. Content like this can shape public opinion and give the impression that the US raid was more popular that it might have really been. This is especially concerning as so many people use social media as their only source of news, analysts say. Dr Manny Ahmed, CEO of OpenOrigins, a company that distinguishes between AI and real images, says we need a new way for real content posters to be able to prove their clips and pictures are genuine. "We are already at the point where you cannot confidently tell what is real by inspection alone," he says. "Instead of trying to detect what is fake, we need infrastructure that allows real content to publicly prove its origin." You might think this is something that social media companies could take on. But many, including Meta and X, have cut their moderation teams down and embraced a more collective approach. They now lean towards relying on users to label things as fake or misleading. So if the existing tech giants are broadly happy to let the slop flow, could a new social media platform rise up, promising a slop-free alternative, and eventually challenge the incumbents? It seems unlikely because detection of AI is becoming harder and harder. Machines are no longer able to accurately detect if a video or image is definitively fake, and machines would struggle even more on the subjective judgement of whether or not content counts as 'slop'. However, if a new social media does come along and people vote with their feet (or eyeballs and thumbs, more accurately), it just might move the dial. I'm reminded of the rise of social media challenger BeReal, a French app that gained popularity during the pandemic, which encourages users to show their authentic selves via non-filtered selfies at random times. BeReal hasn't yet reached the same heights as the Facebooks and Snapchats of the world, and probably never will. But it did make the other platforms sit up and in some cases, they copied the idea. Perhaps that could happen again if an anti AI slop challenger makes a move. As for Théodore, he feels that the battle is lost and that AI slop is here to stay. In spite of the submissions still coming into his mailbox from his now 130,000 followers, he doesn't post as much anymore and has largely resigned himself to the new normal of life online. "Unlike a lot of my followers, I'm not dogmatically against AI," he says. "I'm against the pollution online of AI slop that's made for quick entertainment and views." Top image credit: BBC; AI image generated with Adobe Firefly. BBC InDepth is the home on the website and app for the best analysis, with fresh perspectives that challenge assumptions and deep reporting on the biggest issues of the day. Emma Barnett and John Simpson bring their pick of the most thought-provoking deep reads and analysis, every Saturday. Sign up for the newsletter here
[2]
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop
New York (AFP) - As "AI slop" floods the internet, efforts are mounting to stem an online deluge of shoddy images and videos made using increasingly advanced tech tools. Easily accessible generative artificial intelligence tools, such as Google's Veo and OpenAI's Sora, enable the creation of realistic imagery using just a few descriptive words. Images of cats painting, celebrities in compromising situations, and cartoon characters endorsing products are among the AI-generated detritus proliferating on social networks and video-sharing platforms. "The rise of AI has raised concerns about low-quality content -- also known as AI slop," YouTube chief executive Neal Mohan said of the irksome phenomenon. Such content is "cheap, bland and mass-produced," Swiss engineer Yves, who declined to give his last name, told AFP, echoing discussions on social media website Reddit. Brands like Equinox gyms and Almond Breeze almond milk have played off AI slop frustration in recent ad campaigns, offering themselves as authentic, real alternatives. Meanwhile, Microsoft chief executive Satya Nadella has urged people to move beyond the debate over whether AI creations are slop or sophistication to embracing the technology as a way to amplify creativity and productivity. Microsoft is among the tech giants investing heavily in AI. "At its core, the criticism of AI slop is the criticism of some individual's creative expression," argued Bob Doyle, a YouTube personality specializing in AI-driven media creation. "You may think it's useless, but to them it's the beginning of an idea; a seed." -- Machine made -- However, online bulletin board Pinterest saw fit late last year to begin allowing users to filter out some AI-generated content. Pinterest told AFP that it added the filter after hearing from people who wanted to see fewer synthetic images. TikTok introduced a similar filter on its globally popular video platform late last year. YouTube, along with Meta-owned Instagram and Facebook, also offers ways to reduce the amount of synthetic imagery their users encounter, but gives no clear-cut filter. Major social media platforms had previously focused primarily on labeling AI-created videos so viewers would not mistake them for showing real scenes, but ample synthetic content seemed to avoid the labels. Some smaller tech players, such as streaming platform Coda Music, have introduced measures such as having users report AI creations. Once confirmed, accounts get labeled as AI artists so listeners know what they are getting, according to Coda founder and chief executive Randy Fusee. "There has been a lot of participation in the identification of AI artists so far," Fusee told AFP. "By and large, (Coda users) just don't want AI music." Coda, which reports having some 2,500 users, offers the option of completely blocking AI content from suggested playlists. Cara, a social network for artists and designers with more than a million users, relies on a combination of algorithms and human moderation to filter AI-generated content. "People want the human connection," said Cara founder Jingna Zhang. "I could like a child's drawing because I'm charmed by it, as opposed to (something made by) a machine with no intention."
[3]
How to dial down the AI slop on platforms
If you want fewer cartoonish videos of dead celebrities, creepy or absurd images or fake bands playing synthetic tunes, a few platforms have rolled out settings and features to help minimize AI-generated content. Here is a guide on how to use them. But first, a caveat from Henry Ajder, who advises businesses and governments on AI and has been studying deepfakes since 2018. He warned that it's "incredibly difficult" to entirely remove AI slop content entirely from all your feeds. He compared AI slop to the smog generated from the industrial revolution, when there weren't any pollution controls in place.
[4]
Fed Up With AI Slop? These Platforms Will Let You Dial it Down
If you want fewer cartoonish videos of dead celebrities, creepy or absurd images or fake bands playing synthetic tunes, a few platforms have rolled out settings and features to help minimize AI-generated content. Here is a guide on how to use them. But first, a caveat from Henry Ajder, who advises businesses and governments on AI and has been studying deepfakes since 2018. He warned that it's "incredibly difficult" to entirely remove AI slop content entirely from all your feeds. He compared AI slop to the smog generated from the industrial revolution, when there weren't any pollution controls in place.
[5]
One Tech Tip: Fed up With AI Slop? A Few Platforms Will Let You Dial It Down
AI slop seems to be everywhere. Low-quality digital content made with artificial intelligence has flooded our feeds, screens and speakers. Is there anything we can do about it? If you want fewer cartoonish videos of dead celebrities, creepy or absurd images or fake bands playing synthetic tunes, a few platforms have rolled out settings and features to help minimize AI-generated content. Here is a guide on how to use them. But first, a caveat from Henry Ajder, who advises businesses and governments on AI and has been studying deepfakes since 2018. He warned that it's "incredibly difficult" to entirely remove AI slop content entirely from all your feeds. He compared AI slop to the smog generated from the industrial revolution, when there weren't any pollution controls in place. "It's going to be very, very hard for people to avoid inhaling, in this analogy." Pinterest Pinterest's move to lean into the AI boom made it something of a poster child for the AI slop problem, as user complained that the online moodboard for pinning inspirational material by themes has become overrun with AI content. So Pinterest recently rolled out a "tuner" that lets users adjust the amount of AI content they see in their feeds. It rolled out first on Android and desktop operating systems, before starting on a more gradual roll out on iOS. "Now, users can dial down the AI and add more of a human touch," Pinterest said, adding that it would initially cover some categories that are "highly prone to AI modification or generation" such as beauty, art, fashion and home decor. More categories have since been added, including architecture, art, beauty, entertainment, men's, women's and children's fashion, health, home décor, and sport, food and drink. To use the tuner, go to Settings and then to "refine your recommendations." and then tap on GenAI interests, where you can use toggles to indicate the categories you'd like to see less AI-content. TikTok It's no surprise that AI-generated videos proliferate on TikTok, the short-video sharing app. The company says there are at least 1.3 billion video clips on its platform it has labeled as AI-generated. TikTok said in November it was testing an update to give users more control of the AI-generated content in their For You feeds. It's not clear when it will be widely available. TikTok did not respond to requests for comment. To see if you have it on the TikTok mobile app, go to Settings, then Content Preferences, then to Manage Topics where you'll see a set of sliders to control various types of content, such as dance, humor, lifestyle and nature. You can also access the controls from the For You feed, by tapping the Share button on the side of a post, then tap Why this Video, then Adjust your For You, and then Manage topics. There should be a new slider that allows you to dial down -- or turn up -- the amount of AI-generated content that you receive. If you don't see it yet, it might be because you haven't received the update yet. TikTok said late last year that it would start testing the feature in coming weeks. These controls are not available on the desktop browser interface. You won't be able to get red of AI content altogether -- TikTok says the controls are used to tailor the content rather than removing or replacing it entirely from feeds. "This means that people who love AI-generated history content can see more of this content, while those who'd rather see less can choose to dial things down," it said. Deezer Song generation tools like Suno and Udio let users create music merely by typing some ideas into a chatbot window. Anyone can use them to spit out polished pop songs, but it also means streaming services have been flooded with AI tunes, often by accounts masquerading as real artists. Among the music streaming platforms, only Deezer, a smaller European-based player, gives listeners a way to tell them apart by labeling songs as AI. "Deezer has been really, really pushing the anti-AI generation music narrative," said Henry Ajder. Deezer says 60,000 fully AI-generated tracks, or more than 39% of the daily total, are uploaded to its platform every day and last year it detected and labeled more than 13.4 million AI tracks. The company says the people doing it are trying to make money by fraudulent streams. Change your platform If you can tear yourself away from Big Tech platforms, there are a new generation of apps targeting users who want to avoid AI. Cara is a portfolio-sharing platform for artists that bans AI-generated work. Pixelfed is an ad-free Instagram rival where users can join different servers, or communities, including one for art that does not allow AI-generated content. Spread is a new social media platform with content for people who want to "access human ideas" and "escape the flood of AI slop." Watch out for the upcoming launch of diVine, a reboot of Twitter founder Jack Dorsey's defunct short form video app Vine. The app has only been available as a limited prerelease for Apple iOS. It promises "No AI Slop" and uses multiple approaches to detect AI. An Android beta app is expected soon. The company plans to launch it in app stores soon but needs more time to get ready for unexpectedly high demand. ___ Is there a tech topic that you think needs explaining? Write to us at [email protected] with your suggestions for future editions of One Tech Tip.
[6]
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop
As "AI slop" floods the internet, efforts are mounting to stem an online deluge of shoddy images and videos made using increasingly advanced tech tools. Easily accessible generative artificial intelligence tools, such as Google's Veo and OpenAI's Sora, enable the creation of realistic imagery using just a few descriptive words. Images of cats painting, celebrities in compromising situations, and cartoon characters endorsing products are among the AI-generated detritus proliferating on social networks and video-sharing platforms. "The rise of AI has raised concerns about low-quality content - also known as AI slop," YouTube chief executive Neal Mohan said of the irksome phenomenon. Such content is "cheap, bland and mass-produced," Swiss engineer Yves, who declined to give his last name, told AFP, echoing discussions on social media website Reddit. Brands like Equinox gyms and Almond Breeze almond milk have played off AI slop frustration in recent ad campaigns, offering themselves as authentic, real alternatives. Meanwhile, Microsoft chief executive Satya Nadella has urged people to move beyond the debate over whether AI creations are slop or sophistication to embracing the technology as a way to amplify creativity and productivity. Microsoft is among the tech giants investing heavily in AI. "At its core, the criticism of AI slop is the criticism of some individual's creative expression," argued Bob Doyle, a YouTube personality specializing in AI-driven media creation. "You may think it's useless, but to them it's the beginning of an idea; a seed." Machine made However, online bulletin board Pinterest saw fit late last year to begin allowing users to filter out some AI-generated content. Pinterest told AFP that it added the filter after hearing from people who wanted to see fewer synthetic images. TikTok introduced a similar filter on its globally popular video platform late last year. YouTube, along with Meta-owned Instagram and Facebook, also offers ways to reduce the amount of synthetic imagery their users encounter, but gives no clear-cut filter. Major social media platforms had previously focused primarily on labeling AI-created videos so viewers would not mistake them for showing real scenes, but ample synthetic content seemed to avoid the labels. Some smaller tech players, such as streaming platform Coda Music, have introduced measures such as having users report AI creations. Once confirmed, accounts get labeled as AI artists so listeners know what they are getting, according to Coda founder and chief executive Randy Fusee. "There has been a lot of participation in the identification of AI artists so far," Fusee told AFP. "By and large, (Coda users) just don't want AI music." Coda, which reports having some 2,500 users, offers the option of completely blocking AI content from suggested playlists. Cara, a social network for artists and designers with more than a million users, relies on a combination of algorithms and human moderation to filter AI-generated content. "People want the human connection," said Cara founder Jingna Zhang. "I could like a child's drawing because I'm charmed by it, as opposed to (something made by) a machine with no intention."
Share
Share
Copy Link
Low-quality AI-generated content is overwhelming social media platforms, prompting user backlash and forcing companies to respond. While Pinterest and TikTok introduce filters to dial down synthetic content, Meta doubles down on AI creation tools. The shift marks a fundamental transformation in how we experience social media.
Social Media Platforms Face AI Slop Crisis
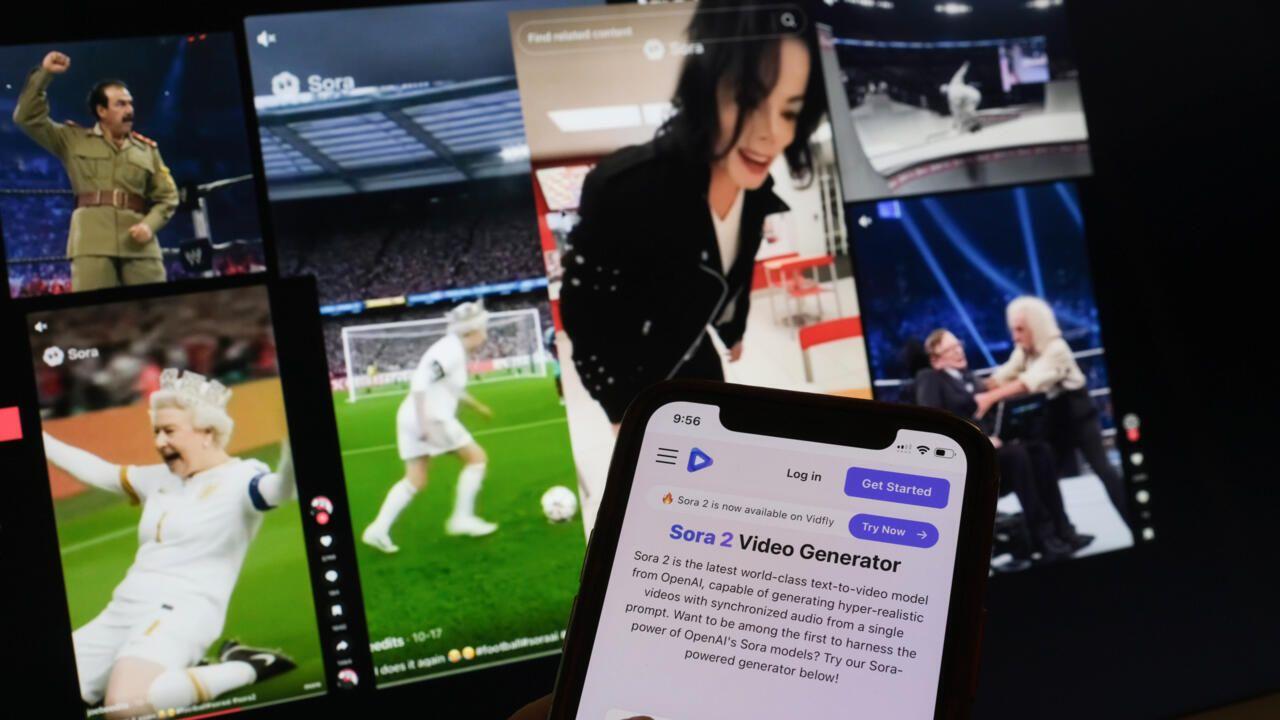
AI slop has become an unavoidable reality across social media platforms, fundamentally altering how billions of users experience online content. The term describes cheap, mass-produced synthetic content flooding feeds with fake images, videos, and music created using increasingly accessible generative AI tools from companies like Google and OpenAI
2
. From emaciated children with beards holding birthday signs to cartoonish videos of dead celebrities, this low-quality content has sparked intense user backlash1
.
Source: Inc.
The scale of the problem is staggering. Research from AI company Kapwing reveals that 20% of content shown to a freshly opened YouTube account is now low-quality AI video, with 104 of the first 500 YouTube Shorts containing AI-generated material
1
. One viral Facebook image of impoverished children garnered nearly one million likes despite obvious AI artifacts. The creator economy drives much of this proliferation, with India's Bandar Apna Dost channel accumulating 2.07 billion views and estimated annual earnings of $4m1
.
Source: France 24
Meta Embraces AI While Others Introduce Controls
Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg declared in October that social media has entered a third phase centered around AI-generated content. "As AI makes it easier to create and remix content, we're going to add yet another huge corpus of content," he told shareholders
1
. Meta, which operates Facebook, Instagram and Threads, has launched image and video generators to enable more synthetic content creation rather than restricting it.In contrast, Pinterest and TikTok have responded to user concerns by introducing ways to filter AI content. Pinterest recently rolled out a "tuner" allowing users to adjust the amount of AI-generated content in their feeds across categories including beauty, art, fashion, home decor, architecture, and food
5
. TikTok began testing slider controls in November to help users manage AI-generated content in their For You feeds, though complete removal remains impossible5
.Expert Warns of Digital Pollution
Henry Ajder, who advises businesses and governments on AI and has studied deepfakes since 2018, compared AI slop to industrial revolution smog before pollution controls existed. "It's incredibly difficult to entirely remove AI slop content entirely from all your feeds," he warned, adding that "it's going to be very, very hard for people to avoid inhaling, in this analogy"
5
. This digital pollution metaphor captures the pervasive nature of unwanted AI-generated content.Related Stories
Growing Movement for Authenticity
A grassroots movement against AI slop is gaining momentum. Théodore, a 20-year-old Paris student, started the "Insane AI Slop" account on X after seeing absurd AI images go viral without scrutiny. His account swelled to over 133,000 followers as users submitted examples of deceptive content featuring common themes like religion, military imagery, or impoverished children
1
. Brands like Equinox gyms and Almond Breeze have capitalized on this frustration in ad campaigns positioning themselves as authentic alternatives2
.Alternative platforms prioritizing human-created content are emerging. Cara, a social network for artists with over one million users, bans AI-generated work using algorithms and human moderation. "People want the human connection," said founder Jingna Zhang
2
. Music streaming service Deezer reports that 60,000 fully AI-generated tracks are uploaded daily, representing 39% of daily uploads, and has labeled more than 13.4 million AI tracks .Platform Responses Reveal Divided Approach
YouTube CEO Neal Mohan acknowledged growing concerns about AI slop while defending creative freedom. He revealed that over one million YouTube channels used the platform's AI tools in December alone, comparing AI to synthesizers and Photoshop as creative tools
1
. His team is working on content moderation systems to find and remove repetitive content, though he ruled out making judgments about what should flourish1
.The divide between platforms embracing AI generation and those offering controls reflects deeper questions about authenticity, misinformation, and the future of online spaces. Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella has urged moving beyond the slop debate to embrace AI as amplifying creativity, while critics argue that mass-produced synthetic content degrades the online experience
2
. As tools from Sora to Google's Veo become more sophisticated, the tension between innovation and quality control will shape how we interact with social media for years to come.References
Summarized by
Navi
[2]
[3]
Related Stories
The Rise of 'AI Slop': How Artificial Intelligence is Flooding Social Media with Fake Content
29 May 2025•Technology

AI Slop: The Rise of Low-Quality AI-Generated Content Flooding the Internet
03 Sept 2025•Technology

Over 21% of YouTube Shorts is AI slop, with creators earning millions farming views
27 Dec 2025•Entertainment and Society

Recent Highlights
1
Google Maps unveils Ask Maps with Gemini AI and 3D Immersive Navigation in biggest update
Technology

2
AI chatbots help plan violent attacks as safety guardrails fail, new investigation reveals
Technology

3
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round as questions swirl around AI bubble and profitability
Business and Economy





