AI-Powered NextBrain Atlas Creates Most Detailed 3D Map of Human Brain for Medical Imaging
4 Sources
4 Sources
[1]
A probabilistic histological atlas of the human brain for MRI segmentation - Nature
The Bayesian segmentation tool in NextBrain is compatible with 1-mm isotropic scans, as illustrated by the Alzheimer's and ageing experiments. As with other probabilistic atlases, Bayesian segmentation can be augmented with models of pathology to automatically segment pathology, such as tumours55 or white matter hyperintensities56. Importantly, NextBrain's high level of detail enables us to fully take advantage of high-resolution data, such as ex vivo MRI, ultra-high-field MRI (for example, 7 T) and exciting new modalities like HiP-CT57. As high-quality 3D brain images become increasingly available, NextBrain's ability to analyse them with high granularity holds great promise to advance knowledge on the human brain in health and in disease. Hemispheres from five individuals (including half of the cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem), were used in this study, following informed consent to use the tissue for research and the ethical approval for research by the National Research Ethics Service Committee London - Central. All hemispheres were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin (Fig. 1a). The laterality and demographics are summarized in Supplementary Table 1; the donors were neurologically normal, but one case had an undiagnosed, asymptomatic tumour (diameter roughly 10 mm) in the white matter, adjacent to the pars opercularis. This tumour did not pose issues in any of the processing steps described below. Our data acquisition pipeline largely leverages our previous work. We summarize it here for completeness; the reader is referred to the corresponding publication for further details. Before dissection, the hemispheres were scanned on a 3-T Siemens MAGNETOM Prisma scanner. The specimens were placed in a container filled with Fluorinert (perfluorocarbon), a proton-free fluid with no MRI signal that yields excellent ex vivo MRI contrast and does not affect downstream histological analysis. The MRI scans were acquired with a T2-weighted sequence (optimized long echo train 3D fast spin echo) with the following parameters: TR = 500 ms, TEeff = 69 ms, BW = 558 hertz per pixel, echo spacing = 4.96 ms, echo train length = 58, 10 averages, with 400-μm isotropic resolution, acquisition time for each average = 547 s, total scanning time = 91 min. These scans were processed with a combination of SAMSEG and the FreeSurfer 7.0 cortical stream to bias-field-correct the images, generate rough subcortical segmentations and obtain white matter and pial surfaces with corresponding parcellations according to the Desikan-Killiany atlas (Fig. 1b). After MRI scanning, each hemisphere is dissected to fit into standard 74 mm × 52 mm cassettes. First, each hemisphere was split into cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem. Using a metal frame as a guide, these were subsequently cut into 10-mm-thick slices in coronal, sagittal and axial orientation, respectively. These slices were photographed inside a rectangular frame of known dimensions for pixel size and perspective correction; we refer to these images as 'whole slice photographs'. Although the brainstem and cerebellum slices all fit into the cassettes, the cerebrum slices were further cut into as many blocks as needed. 'Blocked slice photographs' were also taken for these blocks (Fig. 1c, left). After standard tissue processing steps, each tissue block was embedded in paraffin wax and sectioned with a sledge microtome at 25-μm thickness. Before each cut, a photograph was taken with a 24 MPx Nikon D5100 camera (ISO = 100, aperture = f/20, shutter speed = automatic) mounted right above the microtome, pointed perpendicularly to the sectioning plane. These photographs (henceforth 'blockface photographs') were corrected for pixel size and perspective using fiducial markers. The blockface photographs have poor contrast between grey and white matter (Fig. 1c, right) but also negligible nonlinear geometric distortion, so they can be readily stacked into 3D volumes. A two-dimensional convolutional neural network (CNN) pretrained on the ImageNet dataset and fine-tuned on 50 manually labelled examples was used to automatically produce binary tissue masks for the blockface images. We mounted on glass slides and stained two consecutive sections every N (see below), one with H&E and one with LFB (Fig. 1d). The sampling interval was N = 10 (that is, 250 μm) for blocks that included subcortical structures in the cerebrum, medial structures of the cerebellum or brainstem structures. The interval was N = 20 (500 μm) for all other blocks. All stained sections were digitized with a flatbed scanner at 6,400 DPI resolution (pixel size 3.97 μm). Tissue masks were generated using a two-dimensional CNN similar to the one used for blockface photographs (pretrained on ImageNet and fine-tuned on 100 manually labelled examples). The in vivo ADNI dataset used in the preparation of this article were obtained from the ADNI database (https://adni.loni.usc.edu/). The ADNI was launched in 2003 as a public-private partnership, led by Principal Investigator M. W. Weiner. The primary goal of ADNI has been to test whether serial MRI, positron emission tomography, other biological markers and clinical and neuropsychological assessments can be combined to measure the progression of mild cognitive impairment and early Alzheimer's disease. For up-to-date information, see www.adni-info.org. Segmentations of 333 ROIs (34 cortical, 299 subcortical) were made by authors E.R., J.A. and E.B. (with guidance from D.K., M.B., Z.J. and J.C.A.) for all the LFB sections, using a combination of manual and automated techniques (Fig. 1e). The general procedure to label each block was (1) produce an accurate segmentation for one of every four sections, (2) run SmartInterpol to automatically segment the sections in between and (3) manually correct these automatically segmented sections when needed. SmartInterpol is a dedicated artificial intelligence technique that we have developed specifically to speed up segmentation of histological stacks in this project. To obtain accurate segmentations on sparse sections, we used two different strategies depending on the brain region. For the blocks containing subcortical or brainstem structures, ROIs were manually traced from scratch using a combination of ITK-SNAP and FreeSurfer's viewer 'Freeview'. For cerebellum blocks, we first trained a two-dimensional CNN (a U-Net) on 20 sections on which we had manually labelled the white matter and the molecular and granular layers of the cortex. The CNN was then run on the (sparse) sections and the outputs manually corrected. This procedure saves a substantial amount of time, because manually tracing the convoluted shape of the arbor vitae is extremely time consuming. For the cortical cerebrum blocks, we used a similar strategy as for the cerebellum, labelling the tissue as either white or grey matter. The subdivision of the cortical grey matter into parcels was achieved by taking the nearest neighbouring cortical label from the aligned MRI scan (details on the alignment below). The manual labelling followed neuroanatomical protocols based on different brain atlases, depending on the brain region. Further details on the specific delineation protocols are provided in the Supplementary Information. The general ontology of the 333 ROIs is based on the Allen reference brain and is provide in a spreadsheet as part of the Supplementary Information. 3D histology reconstruction is the inverse problem of reversing all the distortion that brain tissue undergoes during acquisition, to reassemble a 3D shape that accurately follows the original anatomy. For this purpose, we used a framework with four modules. To roughly initialize the 3D reconstruction, we relied on the stacks of blockface photographs. Specifically, we used our previously presented hierarchical joint registration framework that seeks to (1) align each block to the MRI with a similarity transform, by maximizing the normalized cross-correlation of their intensities while (2) discouraging overlap between blocks or gaps in between, by means of a differentiable regularizer. The similarity transforms allowed for rigid deformation (rotation, translation), as well as isotropic scaling to model the shrinking due to tissue processing. The registration algorithm was initialized with transforms derived from the whole slice, blocked slice and blockface photographs (see details in ref. ). The registration was hierarchical in the sense that groups of transforms were forced to share the same parameters in the earlier iterations of the optimization, to reflect our knowledge of the cutting procedure. In the first iterations, we clustered the blocks into three groups: cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem. In the following iterations, we clustered the cerebral blocks that were cut from the same slice and allowed translations in all directions, in-plane rotation and global scaling. In the final iterations, each block alignment was optimized independently. The numerical optimization used the LBFGS algorithm. The approximate average error after this procedure was about 2 mm (ref. ). A sample 3D reconstruction is shown in Fig. 1f. Once a good initial alignment is available, we can use the LFB sections to refine the registration. These LFB images have exquisite contrast (Fig. 1d) but suffer from nonlinear distortion -- rendering the good initialization from the blockface images crucial. The registration procedure was nearly identical to that of the blockface, with two main differences. First, the similarity term used the local (rather than global) normalized cross-correlation function to handle uneven staining across sections. Second, the deformation model and optimization hierarchy were slightly different because nonlinear registration benefits from more robust methods. Specifically, the first two levels of optimization were the same, with blocks grouped into cerebrum/cerebellum/brainstem (first level) or cerebral slices (second level) and optimization of similarity transforms. The third level (that is, each block independently) was subdivided into four stages in which we optimized transforms with increasing complexity, such that the solution of every level of complexity served as initialization to the next. In the first and simplest stage, we allowed for translations in all directions, in-plane rotation and global scaling (five parameters per block). In the second stage, we added a different scaling parameter in the normal direction of the block (six parameters per block). In the third stage, we allowed for rotation in all directions (eight parameters per block). In the fourth and final stage, we added to every section in every block a nonlinear field modelled with a grid of control points (10-mm spacing) and interpolating B-splines. This final deformation model has about 100,000 parameters per case (about 100 parameters per section, times about 1,000 LFB sections). We seek to produce final nonlinear registrations that are accurate, consistent with each other and robust against tears and folds in the sections. We capitalize on Synth-by-Reg (SbR), an artificial intelligence tool for multimodal registration that we have recently developed, to register histological sections to MRI slices resampled to the plane of the histology (as estimated by the linear alignment). SbR exploits the facts that (1) intramodality registration is more accurate than intermodality registration with generic metrics like mutual information and (2) there is a correspondence between histological sections and MRI slices: that is, they represent the same anatomy. In short, SbR trains a CNN to make histological sections look like MRI slices (a task known as style transfer), using a second CNN that has been previously trained to register MRI slices to each other. The style transfer relies on the fact that only good MRI synthesis will yield a good match when used as input to the second CNN, which enables SbR to outperform unpaired approaches such as CycleGAN. SbR also includes a contrastive loss that prevents blurring and content shift due to overfitting. SbR produces highly accurate deformations parameterized as stationary velocity fields (SVFs). Running SbR for each stain and section independently (that is, LFB to resampled MRI and H&E to resampled MRI) yields a reconstruction that is jagged and sensitive to folds and tears. One alternative is to register each histological section to each neighbour directly, which achieves smooth reconstructions but incurs the so-called 'banana effect': that is, a straightening of curved structures. We have proposed a Bayesian method that yields smooth reconstructions without the banana effect. This method follows an overconstrained strategy by computing registrations between LFB and MRI, H&E and MRI, H&E and LFB, each LFB section and the two nearest neighbours in either direction across the stack, each H&E section and its neighbours, and each MRI slice and its neighbours. For a stack with S sections, this procedure yields 15xS-18 registrations, whereas the underlying dimensionality of the spanning tree connecting all the images is just 3xS-1. We use a probabilistic model of SVFs to infer the most likely spanning tree given the computed registrations, which are seen as noisy measurements of combinations of transforms in the spanning tree. The probabilistic model uses a Laplace distribution, which relies on L1 norms and is thus robust to outliers. Moreover, the properties of SVFs enable us to write the optimization problem as a linear program, which we solve with a standard simplex algorithm. The result of this procedure was a 3D reconstruction that is accurate (it is informed by many registrations), robust and smooth (Figs. 1g and 2). The transforms for the LFB sections produced by the 3D reconstructions were applied to the segmentations to bring them into 3D space. Despite the regularizer from ref. , minor overlaps and gaps between blocks still occur. The former were resolved by selecting the label that is furthest inside the corresponding ROI. For the latter, we used our previously developed smoothing approach. Given the low number of available cases, we combined the left (2) and right (3) hemispheres into a single atlas. This was achieved by flipping the right hemispheres and computing a probabilistic atlas of the left hemisphere using an iterative technique. To initialize the procedure, we registered the MRI scans to the MNI atlas with the right hemisphere masked out and averaged the deformed segmentations to obtain an initial estimate of the probabilistic atlas. This first registration was based on intensities, using a local normalized cross-correlation loss. From that point on, the algorithm operates exclusively on the segmentations. Every iteration of the atlas construction process comprises two steps. First, the current estimate of the atlas and the segmentations are coregistered one at a time using (1) a diffeomorphic deformation model based on SVFs parameterized by grids of control points and B-splines (as implemented in NiftyReg), which preserves the topology of the segmentations; (2) a data term, which is the log-likelihood of the label at each voxel according to the probabilities given by the deformed atlas (with a weak Dirichlet prior to prevent logs of zero); and (3) a regularizer based on the bending energy of the field, which encourages regularity in the deformations. The second step of each iteration updates the atlas by averaging the segmentations. The procedure converged (negligible change in the atlas) after five iterations. Slices of the atlas are shown in Figs. 1h and 3. Our Bayesian segmentation algorithm builds on well-established methods in the neuroimaging literature. In short, the algorithm jointly estimates a set of parameters that best explain the observed image in light of the probabilistic atlas, according to a generative model based on a Gaussian mixture model (GMM) conditioned on the segmentation, combined with a model of bias field. The parameters include the deformation of the probabilistic atlas; a set of coefficients describing the bias field; and the means, variances and weights of the GMM. The atlas deformation is regularized in the same way as the atlas construction (bending energy, in our case) and is estimated by means of numerical optimization with LBFGS. The bias field and GMM parameters are estimated with the Expectation Maximization algorithm. Compared with classical Bayesian segmentation methods operating at 1-mm resolution with just a few classes (for example, SAMSEG, SPM), our proposed method has several distinct features: Sample segmentations with this method can be found in Fig. 1h (in vivo) and Fig. 4 (ex vivo). To quantitatively assess the accuracy of our segmentation method on the ultra-high-resolution ex vivo scan, we produced a gold standard segmentation of the publicly available 100-μm scan as follows. First, we downsampled the data to 200-μm resolution and discarded the left hemisphere, to alleviate the manual labelling requirements. Next, we used Freeview to manually label from scratch one coronal slice of every ten; we labelled as many regions from the histological protocol as the MRI contrast allowed -- without subdividing the cortex. Then, we used SmartInterpol to complete the segmentation of the missing slices. Next, we manually corrected the SmartInterpol output as needed, until we were satisfied with the 200-μm isotropic segmentation. The cortex was subdivided using standard FreeSurfer routines. This labelling scheme led to a ground truth segmentation with 98 ROIs, which we have made publicly available. Supplementary Videos 3 and 4 fly over the coronal and axial slices of the labelled scan, respectively. We used a simplified version of the NextBrain atlas when segmenting the 100-μm scan, to better match the ROIs of the automated segmentation and the ground truth (especially in the brainstem). This version was created by replacing the brainstem labels in the histological 3D reconstruction (Fig. 1g, right) by new segmentations made directly in the underlying MRI scan. These segmentations were made with the same methods as for the 100-μm isotropic scan. The new combined segmentations were used to rebuild the atlas. Automated labelling with the Allen MNI template relied on registration-based segmentation with the NiftyReg package, which yields state-of-the-art performance in brain MRI registration. We used the same deformation model and parameters as the NiftyReg authors used in their own registration-based segmentation work: (1) symmetric registration with a deformation model parameterized by a grid of control points (spacing 2.5 mm = 5 voxels) and B-spline interpolation; (2) local normalized cross-correlation as objective function (s.d. 2.5 mm); and (3) bending energy regularization (weight 0.001). We performed linear classification of Alzheimer's disease versus controls based on ROI volumes as follows. Leaving out one subject at a time, we used all other subjects to (1) compute linear regression coefficients to correct for sex and age (intracranial volume was corrected by division); (2) estimate mean vectors for the two classes , as well as a pooled covariance matrix (Σ); and (3) use the means and covariance to compute an unbiased log-likehood criterion L for the left-out subject: where x is the vector with ICV-, sex- and age-corrected volumes for the left-out subject. Once the criterion L has been computed for all subjects, it can be globally thresholded for accuracy and ROC analysis. We note that, for NextBrain, the high number of ROIs renders the covariance matrix singular. We prevent this by using regularized LDA: we normalize all the ROIs to unit variance and then compute the covariance as where S is the sample covariance, I is the identity matrix and is a constant. We note that normalizing to unit variance enables us to use a fixed, unit λ -- rather than having to estimate λ for every left-out subject. To compute the B-spline fits in Extended Data Fig. 8, we first corrected the ROI volumes by sex (using regression) and intracranial volume (by division). Next, we modelled the data with a Laplace distribution, which is robust against outliers which may be caused by potential segmentation mistakes. Specifically, we used an age-dependent Laplacian where the location μ and scale b are both B-splines with four evenly space control points at 30, 51.6, 73.3 and 95 years. The fit is optimized with gradient ascent over the log-likelihood function: where is the Laplace distribution with location μ and scale b; v is the volume of ROI for subject n; a is the age of subject n; is a B-spline describing the location, parameterized by θ; and is a B-spline describing the scale, parameterized by θ. The 95% confidence interval of the Laplace distribution is given by μ ± 3b. The brain donation programme and protocols have received ethical approval for research by the National Research Ethics Service Committee London - Central, and tissue is stored for research under a license issued by the Human Tissue Authority (no. 12198). Further information on research design is available in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this article.
[2]
New AI-assisted atlas tcan help visualize the human brain in unprecedented detail
University College LondonNov 5 2025 A new AI-assisted brain atlas that can help visualize the human brain in unprecedented detail has been developed by UCL researchers, in a major step forward for neuroscience and neuroimaging. The human brain comprises hundreds of interconnected regions that drive our thoughts, emotions, and behaviours. Existing brain atlases can identify major structures in MRI scans - such as the hippocampus, which supports memory and learning - but their finer sub-regions remain hard to detect. These distinctions matter because sub-regions of areas like the hippocampus, for example, are affected differently during Alzheimer's disease progression. Examining the brain at the cellular level is achievable using microscopy (histology), but cannot be done in living individuals, limiting its potential for understanding how the human brain changes during development, ageing and disease. Published in Nature, the new study introduces NextBrain, an atlas of the entire adult human brain that can be used to analyze MRI scans of living patients in a matter of minutes and at a level of detail not possible until now. The creators of the atlas, which is freely available, hope it will ultimately help to accelerate discovery in brain science and its translation into better diagnosis and treatment of conditions such as Alzheimer's. How the AI-assisted brain atlas was developed The atlas took the research team six years to build through a painstaking process akin to completing a jigsaw puzzle - albeit one made using post-mortem tissue from five human brains. Each brain was painstakingly dissected and sectioned into 10,000 pieces, stained to help identify brain structures, photographed under a microscope, then reassembled into a 3D digital model. Before they began this process, the team conducted MRI scans of the brains so they would know how to put them back together, not unlike the picture on the front of a jigsaw box. AI was used to help align the microscope images and the MRI scans, accounting for the differences between the two techniques and ensuring that the pieces did not overlap or have gaps in between them. A total of 333 brain regions were then labelled on the digital 3D models of each of the five brains, a process greatly accelerated by AI. Done manually, the researchers say it would've taken decades. NextBrain is the culmination of years of effort to bridge the gap between microscope imaging and MRI. By combining high-resolution tissue data with advanced AI techniques, we've created a tool that allows researchers to analyze brain scans in a level of detail that was previously unattainable. This opens up new possibilities for studying neurodegenerative diseases and aging." Dr. Juan Eugenio Iglesias, senior author of the study from UCL Medical Physics & Biomedical Engineering and Massachusetts General Hospital/Harvard Medical School The resulting atlas, which is an 'average' of the five brain models, is generalizable to all adult humans - meaning it can be used to automatically infer detail from MRI scans of living or deceased subjects. Brain atlas accuracy tested on thousands of scans NextBrain was successfully tested on thousands of MRI datasets, demonstrating the ability to reliably identify brain regions across diverse imaging conditions and scanner types. In one experiment, the team used the atlas to automatically label brain regions in a publicly available ultra-high-resolution MRI scan, which closely matched the manually labelled regions, even for small areas such as subregions of the hippocampus. In another experiment, the researchers applied NextBrain to over 3,000 MRI scans of living individuals to investigate age-related changes in brain volume. The atlas enabled more detailed analysis of aging patterns than could be achieved using existing tools. Dr Zane Jaunmuktane, an author of the study from UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology and the Queen Square Brain Bank for Neurological Disorders, said: "Our goal by building this atlas was to enable researchers to identify hundreds of brain regions in living patients quickly and consistently, while maintaining the fine-grained anatomical accuracy of microscope data. The level of anatomical detail in NextBrain is remarkable, and its public availability means that researchers worldwide can benefit from it immediately. "NextBrain provides an unparalleled map of the brain's cellular architecture. The foundation built into the atlas now enables rapid, accurate and accessible analysis of brain images in living individuals, opening the door to detecting the earliest signs of neurological diseases such as Alzheimer's, long before symptoms appear, and advancing our ability to understand, monitor and ultimately prevent these devastating diseases." All underlying data, tools, and annotations used in NextBrain have been released openly through the FreeSurfer neuroimaging platform, along with visualization tools and educational resources. The study was supported by the European Research Council, Alzheimer's Society, the Lundbeck Foundation, and the National Institutes of Health (US). University College London Journal reference: Casamitjana, A., et al. (2025). A probabilistic histological atlas of the human brain for MRI segmentation. Nature. doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09708-2
[3]
AI Creates the Most Detailed 3D Map of the Human Brain Ever Made - Neuroscience News
Summary: A new AI-powered atlas called NextBrain allows researchers to visualize the human brain in unprecedented detail, down to hundreds of tiny subregions previously invisible on MRI scans. Built from 10,000 microscopic slices of post-mortem brains and aligned with AI, the atlas precisely maps 333 brain regions in 3D. When tested on thousands of MRI scans, it identified intricate brain structures quickly and consistently, outperforming previous tools. The open-access atlas will accelerate global research on ageing, neurodegenerative diseases, and brain development, paving the way for earlier diagnosis and new therapies. A new AI-assisted brain atlas that can help visualise the human brain in unprecedented detail has been developed by UCL researchers, in a major step forward for neuroscience and neuroimaging. The human brain comprises hundreds of interconnected regions that drive our thoughts, emotions, and behaviours. Existing brain atlases can identify major structures in MRI scans - such as the hippocampus, which supports memory and learning - but their finer sub-regions remain hard to detect. These distinctions matter because sub-regions of areas like the hippocampus, for example, are affected differently during Alzheimer's disease progression. Examining the brain at the cellular level is achievable using microscopy (histology), but cannot be done in living individuals, limiting its potential for understanding how the human brain changes during development, ageing and disease. Published in Nature, the new study introduces NextBrain, an atlas of the entire adult human brain that can be used to analyse MRI scans of living patients in a matter of minutes and at a level of detail not possible until now. The creators of the atlas, which is freely available, hope it will ultimately help to accelerate discovery in brain science and its translation into better diagnosis and treatment of conditions such as Alzheimer's. How the AI-assisted brain atlas was developed The atlas took the research team six years to build through a painstaking process akin to completing a jigsaw puzzle - albeit one made using post-mortem tissue from five human brains. Each brain was painstakingly dissected and sectioned into 10,000 pieces, stained to help identify brain structures, photographed under a microscope, then reassembled into a 3D digital model. Before they began this process, the team conducted MRI scans of the brains so they would know how to put them back together, not unlike the picture on the front of a jigsaw box. AI was used to help align the microscope images and the MRI scans, accounting for the differences between the two techniques and ensuring that the pieces did not overlap or have gaps in between them. A total of 333 brain regions were then labelled on the digital 3D models of each of the five brains, a process greatly accelerated by AI. Done manually, the researchers say it would've taken decades. Dr Juan Eugenio Iglesias, senior author of the study from UCL Medical Physics & Biomedical Engineering and Massachusetts General Hospital/Harvard Medical School, said: "NextBrain is the culmination of years of effort to bridge the gap between microscope imaging and MRI. By combining high-resolution tissue data with advanced AI techniques, we've created a tool that allows researchers to analyse brain scans in a level of detail that was previously unattainable. This opens up new possibilities for studying neurodegenerative diseases and ageing." The resulting atlas, which is an 'average' of the five brain models, is generalisable to all adult humans - meaning it can be used to automatically infer detail from MRI scans of living or deceased subjects. Brain atlas accuracy tested on thousands of scans NextBrain was successfully tested on thousands of MRI datasets, demonstrating the ability to reliably identify brain regions across diverse imaging conditions and scanner types. In one experiment, the team used the atlas to automatically label brain regions in a publicly available ultra-high-resolution MRI scan, which closely matched the manually labelled regions, even for small areas such as subregions of the hippocampus. In another experiment, the researchers applied NextBrain to over 3,000 MRI scans of living individuals to investigate age-related changes in brain volume. The atlas enabled more detailed analysis of ageing patterns than could be achieved using existing tools. Dr Zane Jaunmuktane, an author of the study from UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology and the Queen Square Brain Bank for Neurological Disorders, said: "Our goal by building this atlas was to enable researchers to identify hundreds of brain regions in living patients quickly and consistently, while maintaining the fine-grained anatomical accuracy of microscope data. The level of anatomical detail in NextBrain is remarkable, and its public availability means that researchers worldwide can benefit from it immediately. "NextBrain provides an unparalleled map of the brain's cellular architecture. The foundation built into the atlas now enables rapid, accurate and accessible analysis of brain images in living individuals, opening the door to detecting the earliest signs of neurological diseases such as Alzheimer's, long before symptoms appear, and advancing our ability to understand, monitor and ultimately prevent these devastating diseases." All underlying data, tools, and annotations used in NextBrain have been released openly through the FreeSurfer neuroimaging platform, along with visualisation tools and educational resources. Funding: The study was supported by the European Research Council, Alzheimer's Society, the Lundbeck Foundation, and the National Institutes of Health (US). A probabilistic histological atlas of the human brain for MRI segmentation In human neuroimaging, brain atlases are essential for segmenting regions of interest (ROIs) and comparing subjects in a common coordinate frame. State-of-the-art atlases derived from histology provide exquisite three-dimensional cytoarchitectural maps but lack probabilistic labels throughout the whole brain: that is, the likelihood of each location belonging to a given ROI. Here we present NextBrain, a probabilistic histological atlas of the whole human brain. We developed artificial intelligence-enabled methods to align roughly 10,000 histological sections from five whole brain hemispheres into three-dimensional volumes and to produce delineations for 333 ROIs on these sections. We also created a companion Bayesian tool for automatic segmentation of these ROIs in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. We showcase two applications of the atlas: segmentation of ultra-high-resolution ex vivo MRI and volumetric analysis of Alzheimer's disease using in vivo MRI. We publicly release raw and aligned data, an online visualization tool, the atlas, the segmentation tool, and ground truth delineations for a high-resolution ex vivo hemisphere used in validation. By enabling researchers worldwide to automatically analyse brain MRIs at a higher level of granularity, NextBrain holds promise to increase the specificity of findings and accelerate our quest to understand the human brain in health and disease.
[4]
New brain atlas offers unprecedented detail in MRI scans
A new AI-assisted brain atlas that can help visualize the human brain in unprecedented detail has been developed by UCL researchers, in a major step forward for neuroscience and neuroimaging. The human brain comprises hundreds of interconnected regions that drive our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. Existing brain atlases can identify major structures in MRI scans -- such as the hippocampus, which supports memory and learning -- but their finer sub-regions remain hard to detect. These distinctions matter because sub-regions of areas like the hippocampus, for example, are affected differently during Alzheimer's disease progression. Examining the brain at the cellular level is achievable using microscopy (histology), but cannot be done in living individuals, limiting its potential for understanding how the human brain changes during development, aging and disease. Published in Nature, the new study introduces NextBrain, an atlas of the entire adult human brain that can be used to analyze MRI scans of living patients in a matter of minutes and at a level of detail not possible until now. The creators of the atlas, which is freely available, hope it will ultimately help to accelerate discovery in brain science and its translation into better diagnosis and treatment of conditions such as Alzheimer's. How the AI-assisted brain atlas was developed The atlas took the research team six years to build through a painstaking process akin to completing a jigsaw puzzle -- albeit one made using post-mortem tissue from five human brains. Each brain was painstakingly dissected and sectioned into 10,000 pieces, stained to help identify brain structures, photographed under a microscope, then reassembled into a 3D digital model. Before they began this process, the team conducted MRI scans of the brains so they would know how to put them back together, not unlike the picture on the front of a jigsaw box. AI was used to help align the microscope images and the MRI scans, accounting for the differences between the two techniques and ensuring that the pieces did not overlap or have gaps in between them. A total of 333 brain regions were then labeled on the digital 3D models of each of the five brains, a process greatly accelerated by AI. Done manually, the researchers say it would've taken decades. Dr. Juan Eugenio Iglesias, senior author of the study from UCL Medical Physics & Biomedical Engineering and Massachusetts General Hospital/Harvard Medical School, said, "NextBrain is the culmination of years of effort to bridge the gap between microscope imaging and MRI. "By combining high-resolution tissue data with advanced AI techniques, we've created a tool that allows researchers to analyze brain scans at a level of detail that was previously unattainable. This opens up new possibilities for studying neurodegenerative diseases and aging." The resulting atlas, which is an "average" of the five brain models, is generalizable to all adult humans -- meaning it can be used to automatically infer detail from MRI scans of living or deceased subjects. Brain atlas accuracy tested on thousands of scans NextBrain was successfully tested on thousands of MRI datasets, demonstrating the ability to reliably identify brain regions across diverse imaging conditions and scanner types. In one experiment, the team used the atlas to automatically label brain regions in a publicly available ultra-high-resolution MRI scan, which closely matched the manually labeled regions, even for small areas such as subregions of the hippocampus. In another experiment, the researchers applied NextBrain to over 3,000 MRI scans of living individuals to investigate age-related changes in brain volume. The atlas enabled more detailed analysis of aging patterns than could be achieved using existing tools. Dr. Zane Jaunmuktane, an author of the study from UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology and the Queen Square Brain Bank for Neurological Disorders, said, "Our goal by building this atlas was to enable researchers to identify hundreds of brain regions in living patients quickly and consistently, while maintaining the fine-grained anatomical accuracy of microscope data. "The level of anatomical detail in NextBrain is remarkable, and its public availability means that researchers worldwide can benefit from it immediately. "NextBrain provides an unparalleled map of the brain's cellular architecture. The foundation built into the atlas now enables rapid, accurate and accessible analysis of brain images in living individuals, opening the door to detecting the earliest signs of neurological diseases such as Alzheimer's, long before symptoms appear, and advancing our ability to understand, monitor and ultimately prevent these devastating diseases." All underlying data, tools, and annotations used in NextBrain have been released openly through the FreeSurfer neuroimaging platform, along with visualization tools and educational resources.
Share
Share
Copy Link
UCL researchers have developed NextBrain, an AI-assisted brain atlas that provides unprecedented detail in MRI scan analysis. The atlas maps 333 brain regions from microscopic tissue data and can analyze living patients' brain scans in minutes, potentially revolutionizing diagnosis of neurological diseases like Alzheimer's.
Revolutionary Brain Mapping Technology
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have developed NextBrain, a groundbreaking AI-assisted brain atlas that represents the most detailed 3D map of the human brain ever created. Published in Nature, this innovative tool enables scientists to analyze MRI scans of living patients with unprecedented precision, identifying hundreds of brain subregions that were previously invisible to conventional imaging techniques
1
2
.
Source: Neuroscience News
The human brain contains hundreds of interconnected regions that control thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. While existing brain atlases can identify major structures like the hippocampus, their finer subregions remain difficult to detect in standard MRI scans. This limitation has significant implications for understanding neurological diseases, as different subregions of brain areas like the hippocampus are affected differently during Alzheimer's disease progression
3
.Six-Year Development Process
The creation of NextBrain required an extraordinary six-year effort that researchers describe as akin to completing a massive jigsaw puzzle. The team used post-mortem tissue from five human brains, each painstakingly dissected and sectioned into approximately 10,000 pieces. These tissue samples were stained to help identify brain structures, photographed under microscopes, and then digitally reassembled into comprehensive 3D models
4
.Before beginning the dissection process, researchers conducted MRI scans of the intact brains to serve as reference images, similar to the picture on a jigsaw puzzle box. AI algorithms played a crucial role in aligning the microscopic images with the MRI scans, accounting for differences between the two imaging techniques while ensuring that reconstructed pieces did not overlap or contain gaps
2
.AI-Accelerated Brain Region Mapping
A total of 333 distinct brain regions were labeled on the digital 3D models of each brain, a process that was significantly accelerated by artificial intelligence. According to the researchers, completing this labeling manually would have required decades of work. The resulting atlas represents an average of the five brain models and is generalizable to all adult humans, meaning it can automatically infer detailed information from MRI scans of both living and deceased subjects
3
.
Source: News-Medical
Dr. Juan Eugenio Iglesias, senior author of the study from UCL Medical Physics & Biomedical Engineering and Massachusetts General Hospital/Harvard Medical School, explained that "NextBrain is the culmination of years of effort to bridge the gap between microscope imaging and MRI. By combining high-resolution tissue data with advanced AI techniques, we've created a tool that allows researchers to analyze brain scans at a level of detail that was previously unattainable"
4
.Related Stories
Extensive Validation and Testing
NextBrain underwent rigorous testing on thousands of MRI datasets, demonstrating its ability to reliably identify brain regions across diverse imaging conditions and scanner types. In one validation experiment, the team used the atlas to automatically label brain regions in a publicly available ultra-high-resolution MRI scan, achieving results that closely matched manually labeled regions, even for small areas such as hippocampal subregions
1
.In another significant test, researchers applied NextBrain to over 3,000 MRI scans of living individuals to investigate age-related changes in brain volume. The atlas enabled more detailed analysis of aging patterns than could be achieved using existing neuroimaging tools, demonstrating its superior analytical capabilities
2
.Clinical Applications and Future Impact
The atlas shows particular promise for advancing the diagnosis and treatment of neurological conditions. Dr. Zane Jaunmuktane from UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology emphasized that NextBrain "provides an unparalleled map of the brain's cellular architecture" that enables "rapid, accurate and accessible analysis of brain images in living individuals, opening the door to detecting the earliest signs of neurological diseases such as Alzheimer's, long before symptoms appear"
4
.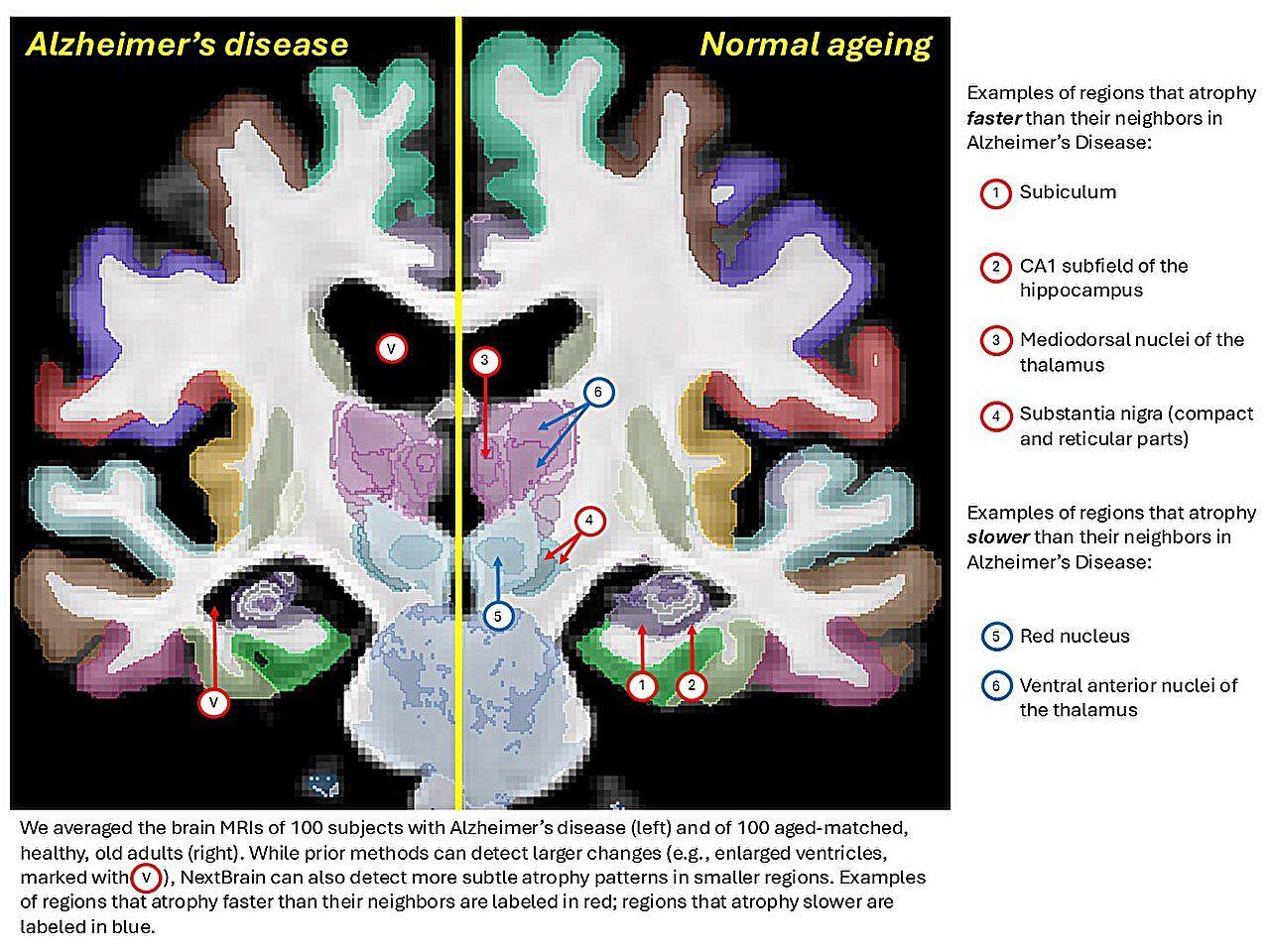
Source: Medical Xpress
The tool's compatibility with various imaging modalities, including 1-mm isotropic scans and ultra-high-field MRI systems, makes it particularly valuable for analyzing high-quality 3D brain images. As advanced imaging technologies become more widely available, NextBrain's ability to extract detailed information from these scans holds significant promise for advancing understanding of the human brain in both health and disease states
1
.All underlying data, tools, and annotations used in NextBrain have been released as open-access resources through the FreeSurfer neuroimaging platform, along with visualization tools and educational materials, ensuring that researchers worldwide can immediately benefit from this breakthrough technology
3
.References
Summarized by
Navi
[3]
[4]
Related Stories
AI-Powered CellTransformer Creates Most Detailed Mouse Brain Map to Date
07 Oct 2025•Science and Research
AI-Powered 3D Brain Mapping Tool Revolutionizes Neurodegenerative Disease Research
20 Mar 2025•Science and Research

LICONN: Revolutionary Light Microscopy Technique Maps Brain Networks in Unprecedented Detail
08 May 2025•Science and Research

Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round from Amazon, Nvidia, and SoftBank at $730B valuation
Business and Economy

2
Pentagon accepts OpenAI's autonomous weapons restrictions after blacklisting Anthropic
Policy and Regulation

3
Trump orders federal agencies to ban Anthropic after Pentagon dispute over AI surveillance
Policy and Regulation