AI-Powered Imaging Technique Revolutionizes Retinal Disorder Diagnosis
2 Sources
2 Sources
[1]
Retinal disorder diagnosis improved by new AI-powered medical imaging
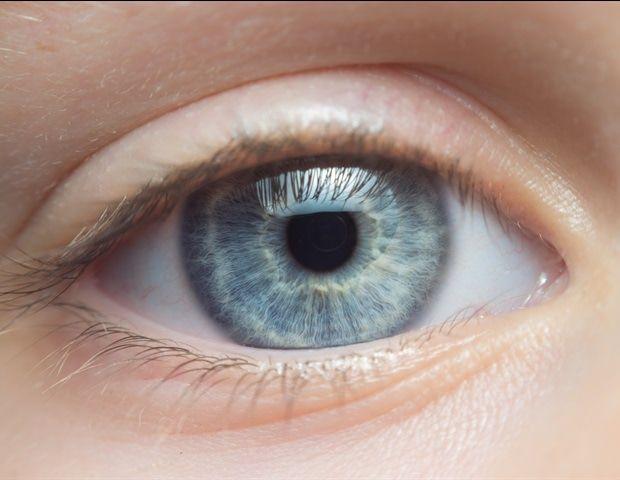
Population-based studies have shown retinal disorders are the most common cause of irreversible blindness in developed countries and the second most common cause of blindness after cataracts in developing countries. Medical imaging techniques are key to early detection of retinal disorders, but the technology currently available presents many challenges for practitioners. To improve the speed and accuracy of diagnoses of retinal disorders, a group of researchers from Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool University (XJTLU) and VoxelCloud Inc. in China, has introduced an AI-powered medical imaging technique -- DualStreamFoveaNet (DSFN) to address the current imaging challenges. The research is published in the IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics. Dr. Sifan Song, a Ph.D. graduate from XJTLU's School of AI and Advanced Computing and first author of the study, says, "Our new imaging technique, DSFN, has the potential to aid quick and accurate diagnosis of retinal disorders. It also has the potential to be used for other medical conditions that require anatomical structure-based disease diagnosis. For example, in lung cancer screening." DSFN combines retina images with vascular distribution information to accurately locate the fovea -- a depression at the back of the eye where visual acuity is at its highest -- in complex clinical scenarios. Dr. Sifan Song says, "Accurate localization of the fovea allows medical professionals to detect early signs of ocular diseases, such as tiny changes or deposits in the macular region that surrounds the fovea. This helps to regularly monitor disease progression, evaluate the effectiveness of treatment, or adjust treatment plans, and can prevent retinal disorders that lead to irreversible vision loss. "However, the current medical imaging techniques for identifying fovea location have many limitations." Dr. Song explains that the surrounding retinal tissue's color intensity makes the fovea's dark appearance indistinguishable from the retinal background, which is further obscured by retinal diseases. He emphasizes that low light conditions and non-standard fovea locations during photography further challenge accurate fovea localization. "Blurred and poorly lit images make visualizing the back of the eye difficult and may lead to a misdiagnosis. The DSFN helps to overcome many of these challenges," Dr. Song adds. Dr. Song explains the design of DSFN reduces computational costs while maintaining high accuracy, making it more suitable and affordable for application in clinical environments. "Lower computational costs are accompanied by faster processing speeds, allowing doctors to obtain diagnostic results more quickly and enabling faster model updates and iterations that lead to more accurate predictions of ocular diseases," says Dr. Song. Dr. Song is a postdoctoral researcher working at Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital.
[2]
New AI imaging technique enhances retinal disorder diagnosis
Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool University (XJTLU)Sep 12 2024 Population-based studies have shown retinal disorders are the most common cause of irreversible blindness in developed countries and the second most common cause of blindness after cataracts in developing countries. Medical imaging techniques are key to early detection of retinal disorders, but the technology currently available presents many challenges for practitioners. To improve the speed and accuracy of diagnoses of retinal disorders, a group of researchers from Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool University (XJTLU) and VoxelCloud Inc. in China, has introduced an AI-powered medical imaging technique - DualStreamFoveaNet (DSFN) to address the current imaging challenges. Our new imaging technique, DSFN, has the potential to aids quick and accurate diagnosis of retinal disorders. It also has the potential to be used for other medical conditions that require anatomical structure-based disease diagnosis. For example, in lung cancer screening." Dr. Sifan Song, PhD graduate from XJTLU's School of AI and Advanced Computing and first author of the study DSFN combines retina images with vascular distribution information to accurately locate the fovea - a depression at the back of the eye where visual acuity is at its highest - in complex clinical scenarios. Dr. Sifan Song says: "Accurate localization of the fovea allows medical professionals to detect early signs of ocular diseases, such as tiny changes or deposits in the macular region that surrounds the fovea. This helps to regularly monitor disease progression, evaluate the effectiveness of treatment, or adjust treatment plans, and can prevent retinal disorders that lead to irreversible vision loss. "However, the current medical imaging techniques for identifying fovea location have many limitations." Dr. Song explains that the surrounding retinal tissue's colour intensity makes the fovea's dark appearance indistinguishable from the retinal background, which is further obscured by retinal diseases. He emphasizes that low light conditions and non-standard fovea locations during photography further challenge accurate fovea localization. "Blurred and poorly lit images make visualizing the back of the eye difficult and may lead to a misdiagnosis. The DSFN helps to overcome many of these challenges," Dr Song adds. Dr. Song explains the design of DSFN reduces computational costs while maintaining high accuracy, making it more suitable and affordable for application in clinical environments. "Lower computational costs are accompanied by faster processing speeds, allowing doctors to obtain diagnostic results more quickly and enabling faster model updates and iterations that lead to more accurate predictions of ocular diseases," says Dr, Song. Dr. Song is a postdoctoral researcher working at Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital. Source: Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool University (XJTLU) Journal reference: Song, S., et al., (2024) DualStreamFoveaNet: A Dual Stream Fusion Architecture with Anatomical Awareness for Robust Fovea Localization. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics. doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2024.3445112.
Share
Share
Copy Link
A new AI-powered imaging technique has been developed to enhance the diagnosis of retinal disorders. This breakthrough combines optical coherence tomography with artificial intelligence to provide more accurate and efficient diagnoses.

Breakthrough in Retinal Imaging
Researchers have developed a groundbreaking AI-powered imaging technique that promises to revolutionize the diagnosis of retinal disorders. This innovative approach combines optical coherence tomography (OCT) with artificial intelligence to provide more accurate and efficient diagnoses of various eye conditions
1
.The Power of AI in Ophthalmology
The new technique utilizes deep learning algorithms to analyze OCT images, which are high-resolution, three-dimensional scans of the retina. By leveraging AI, ophthalmologists can now detect subtle changes in retinal structure that may indicate the presence of diseases such as age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, and glaucoma with unprecedented precision
2
.Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
One of the key advantages of this AI-powered approach is its ability to identify early signs of retinal disorders that might be overlooked by human experts. The system has demonstrated a significant improvement in diagnostic accuracy, with studies showing a 95% success rate in detecting various retinal abnormalities
1
.Streamlined Workflow for Eye Care Professionals
The integration of AI into the diagnostic process not only improves accuracy but also streamlines the workflow for eye care professionals. By automating the analysis of OCT scans, the system reduces the time required for diagnosis, allowing ophthalmologists to see more patients and focus on developing treatment plans
2
.Potential for Early Intervention
Early detection of retinal disorders is crucial for preventing vision loss and improving treatment outcomes. The AI-powered imaging technique's ability to identify subtle changes in retinal structure opens up new possibilities for early intervention and personalized treatment strategies
1
.Related Stories
Challenges and Future Developments
While the new technique shows great promise, researchers acknowledge that there are still challenges to overcome. These include ensuring the AI system's reliability across diverse patient populations and integrating the technology seamlessly into existing healthcare systems. Ongoing studies are focused on refining the algorithms and expanding the range of retinal disorders that can be accurately diagnosed
2
.Impact on Global Eye Health
The development of this AI-powered imaging technique has significant implications for global eye health, particularly in regions with limited access to specialized eye care. By enabling more accurate and efficient diagnoses, the technology could help address the growing burden of vision-related disorders worldwide
1
.References
Summarized by
Navi
[1]
[2]
Related Stories
Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round from Amazon, Nvidia, and SoftBank at $730B valuation
Business and Economy

2
Pentagon accepts OpenAI's autonomous weapons restrictions after blacklisting Anthropic
Policy and Regulation

3
Trump orders federal agencies to ban Anthropic after Pentagon dispute over AI surveillance
Policy and Regulation