AI Revolutionizes Building Cooling: New Thermal Coating Promises Significant Energy Savings
2 Sources
2 Sources
[1]
AI-crafted coating cools buildings by 36°F, slashes AC use, bills
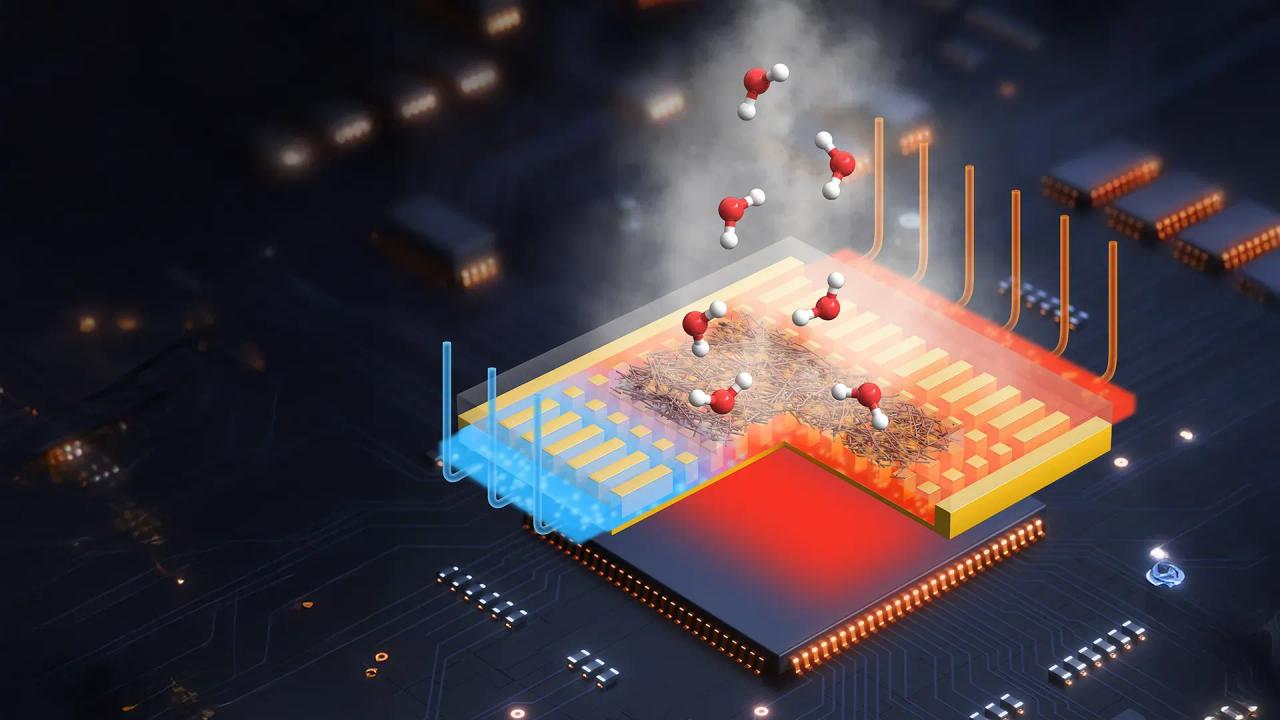
If you've ever complained about rising electricity bills, artificial intelligence is already coming to your rescue. Researchers from the University of Texas at Austin, the University of Shanghai Jiao Tong, the National University of Singapore, and Umea University in Sweden have designed a new machine learning-based approach for creating complex, three-dimensional thermal meta-emitters. The team has developed more than 1,500 different materials capable of emitting heat at various levels in different manners. These characteristics make them ideal for attaining energy efficiency through precise cooling and heating.
[2]
AI helps find formula for paint to keep buildings cooler
Research could help cut energy use and is latest example of AI being used for advances in materials science AI-engineered paint could reduce the sweltering urban heat island effect in cities and cut air-conditioning bills, scientists have claimed, as machine learning accelerates the creation of new materials for everything from electric motors to carbon capture. Materials experts have used artificial intelligence to formulate new coatings that can keep buildings between 5C and 20C cooler than normal paint after exposure to midday sun. They could also be applied to cars, trains, electrical equipment and other objects that will require more cooling in a world that is heating up. Using machine learning, researchers at universities in the US, China, Singapore and Sweden designed new paint formulas tuned to best reflect the sun's rays and emit heat, according to a peer-reviewed study published in the science journal Nature. It is the latest example of AI being used to leapfrog traditional trial-and-error approaches to scientific advances. Last year the British company MatNex used AI to create a new kind of permanent magnet used in electric vehicle motors to avoid the use of rare earth metals, whose mining is carbon-intensive. Microsoft has released AI tools to help researchers rapidly design new inorganic materials - often crystalline structures used in solar panels and medical implants. And there are hopes for new materials to better capture carbon in the atmosphere and to make more efficient batteries. The paint research was carried out by academics at the University of Texas in Austin, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, the National University of Singapore and Umeå University in Sweden. It found that applying one of several new AI-enabled paints to the roof of a four-storey apartment block could save electricity equivalent to 15,800 kilowatts a year in a hot climate such as Rio de Janeiro's or Bangkok's. If the paint were applied to 1,000 blocks, that could save enough electricity to power more than 10,000 air conditioning units for a year. Yuebing Zheng, a professor at the University of Texas and co-leader of the study, said: "Our machine learning framework represents a significant leap forward in the design of thermal meta-emitters. By automating the process and expanding the design space, we can create materials with superior performance that were previously unimaginable." He said a month's work designing a new material was being done in a few days using AI and that new materials that may never have been discovered through trial and error were being created. "Now, we follow the machine learning output, [its instructions for] the structure and what kind of materials we should use, and we can get it right without going through many, many design and fabrication testing cycles." Dr Alex Ganose, a chemistry lecturer at Imperial College London who also uses machine learning to design new materials, said: "Things are moving very fast in this space. In the last year or so there have been so many startups trying to use generative AI for materials." He said the process of designing a new material could require the calculation of millions of potential combinations. AI allows material scientists to push through previous restrictions in computational power. It also means the traditional process of creating a material and then testing its properties can be reversed, with scientists able to tell the AI what properties they want upfront.
Share
Share
Copy Link
Researchers use AI to develop a new thermal coating that can cool buildings by up to 20°C, potentially slashing air conditioning costs and energy consumption in urban areas.
AI-Powered Breakthrough in Thermal Coatings
Researchers from universities in the United States, China, Singapore, and Sweden have made a significant breakthrough in the field of thermal management using artificial intelligence. The team has developed a new machine learning-based approach for creating complex, three-dimensional thermal meta-emitters, resulting in a coating that can cool buildings by up to 20°C (36°F)
1
2
.The Power of AI in Materials Science
The study, published in the science journal Nature, showcases the potential of AI to revolutionize materials science. By leveraging machine learning, the researchers were able to design new paint formulas specifically tuned to reflect the sun's rays and emit heat effectively
2
. This approach has dramatically accelerated the material creation process, with Professor Yuebing Zheng of the University of Texas stating, "Now, we follow the machine learning output, [its instructions for] the structure and what kind of materials we should use, and we can get it right without going through many, many design and fabrication testing cycles"2
.Impressive Energy Savings
The potential energy savings from this AI-engineered paint are substantial. According to the research, applying the new coating to the roof of a four-story apartment block in hot climates like Rio de Janeiro or Bangkok could save electricity equivalent to 15,800 kilowatts a year
2
. Scaling this up, if the paint were applied to 1,000 such blocks, it could save enough electricity to power more than 10,000 air conditioning units for an entire year2
.
Source: Interesting Engineering
Broader Implications for Urban Heat Management
This innovation could have far-reaching implications for urban heat management. The new coating has the potential to mitigate the urban heat island effect in cities, a phenomenon where urban areas experience higher temperatures than their rural surroundings due to human activities and infrastructure
2
. By reducing the need for air conditioning, this technology could lead to significant reductions in energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.Related Stories
AI's Growing Role in Materials Science
The thermal coating breakthrough is just one example of AI's increasing importance in materials science. Dr. Alex Ganose, a chemistry lecturer at Imperial College London, notes that the field is moving rapidly, with numerous startups emerging to leverage generative AI for materials design
2
. AI allows scientists to overcome previous computational limitations, enabling them to explore millions of potential combinations in the search for new materials with desired properties.Future Applications and Potential
While the current focus is on building coatings, the researchers suggest that this technology could have broader applications. The AI-engineered paint could potentially be applied to cars, trains, electrical equipment, and other objects that require cooling in a warming world
2
. This versatility underscores the transformative potential of AI in addressing climate-related challenges and improving energy efficiency across various sectors.As climate change continues to drive up global temperatures, innovations like this AI-designed thermal coating could play a crucial role in our adaptation and mitigation strategies. By significantly reducing the energy demand for cooling, this technology represents a promising step towards more sustainable urban environments and reduced carbon emissions.
References
Summarized by
Navi
[1]
[2]
Related Stories
AI Breakthrough: Simulating Billions of Atoms to Create Carbon-Neutral, Long-Lasting Concrete
24 Jul 2025•Science and Research

AI's Energy Paradox: How Data Centers Are Reshaping Global Power Demand and Climate Goals
18 Nov 2025•Technology

Breakthrough in Evaporative Cooling Technology Could Revolutionize Data Center Energy Efficiency
14 Jun 2025•Technology
Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.4, New AI Model Built for Agents and Professional Work
Technology

2
Pentagon's Anthropic showdown exposes who controls AI guardrails in military contracts
Policy and Regulation

3
Anthropic challenges Pentagon supply chain risk label in court over AI usage restrictions
Policy and Regulation





