AI System Identifies 3D Printers by Their Unique 'Fingerprints' on Printed Parts
3 Sources
3 Sources
[1]
AI can track 3D printed parts back to specific machine that made them
Researchers have developed an AI-driven system which can pinpoint "the specific machine" following an inspection of the 3D printed parts it has produced. A Grainger College of Engineering team from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign say that the system could be used for managing supply chains, "detecting early problems and verifying that suppliers are following agreed upon processes." However, talk of the "hidden fingerprints" of 3D printers have got this Sherlock, Columbo, Monk, and Fargo fan more interested in the criminal investigatory implications of the new AI. Only a photograph of a part printed by a certain 3D printer is needed to verify its "unique signature... or fingerprint" says the Grainger blog. "We are still amazed that this works: we can print the same part design on two identical machines - same model, same process settings, same material - and each machine leaves a unique fingerprint that the AI model can trace back to the machine," said Bill King, a professor of mechanical science and engineering, and the research project leader. "It's possible to determine exactly where and how something was made. You don't have to take your supplier's word on anything." The researchers looked most closely at the (major) implications for supplier management and quality control. They described how this was important to 3D printer vendors to ensure users "adhere to a specific set of machines, processes, and factory procedures" to deliver the expected quality levels throughout the printing / production process. In tests, smartphone photographs of 9,192 parts made on 21 3D printing machines from six companies, and with four different fabrication processes, could be fingerprinted "with 98% accuracy from just 1 square millimeter of the part's surface." It would be interesting to see how much more accurate the Ai could be, given a larger area to anaylze. Despite what sounds like a rather narrow focus on 3D printers used in factory production environments, the AI can work its magic on a far broader pool of devices. "These manufacturing fingerprints have been hiding in plain sight," King said. "There are thousands of 3D printers in the world, and tens of millions of 3D printed parts used in airplanes, automobiles, medical devices, consumer products, and a host of other applications. Each one of these parts has a unique signature that can be detected using AI." We assume King's assertion includes all the printers listed in the regularly updated Tom's Hardware's best 3D printers article. Beyond its touted use for supply chain management, the researchers say the tech could be applied to "track the origins of illicit goods." Other than that, they don't discuss any implications for criminal investigations. However, we'd like to see the technology used to trace the origin of a 3D printed gun discovered at a crime scene, for example.
[2]
3D printers leave hidden 'fingerprints' that reveal part origins
A new artificial intelligence system pinpoints the origin of 3D printed parts down to the specific machine that made them. The technology could allow manufacturers to monitor their suppliers and manage their supply chains, detecting early problems and verifying that suppliers are following agreed upon processes. A team of researchers led by Bill King, a professor of mechanical science and engineering at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, has discovered that parts made by additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, carry a unique signature from the specific machine that fabricated them. This inspired the development of an AI system which detects the signature, or "fingerprint," from a photograph of the part and identifies its origin. "We are still amazed that this works: we can print the same part design on two identical machines -same model, same process settings, same material -- and each machine leaves a unique fingerprint that the AI model can trace back to the machine," King said. "It's possible to determine exactly where and how something was made. You don't have to take your supplier's word on anything." The results of this study were recently published in the Nature partner journal Advanced Manufacturing. The technology has major implications for supplier management and quality control, according to King. When a manufacturer contracts a supplier to produce parts for a product, the supplier typically agrees to adhere to a specific set of machines, processes, and factory procedures and not to make any changes without permission. However, this provision is difficult to enforce. Suppliers often make changes without notice, from the fabrication process to the materials used. They are normally benign, but they can also cause major issues in the final product. "Modern supply chains are based on trust," King said. "There's due diligence in the form of audits and site tours at the start of the relationship. But, for most companies, it's not feasible to continuously monitor their suppliers. Changes to the manufacturing process can go unnoticed for a long time, and you don't find out until a bad batch of products is made. Everyone who works in manufacturing has a story about a supplier that changed something without permission and caused a serious problem." While studying the repeatability of 3D printers, King's research group noticed that the tolerances of part dimensions were correlated with individual machines. This inspired the researchers to examine photographs of the parts. It turned out that it is possible to determine the specific machine made the part, the fabrication process, and the materials used -- the production "fingerprint." "These manufacturing fingerprints have been hiding in plain sight," King said. "There are thousands of 3D printers in the world, and tens of millions of 3D printed parts used in airplanes, automobiles, medical devices, consumer products, and a host of other applications. Each one of these parts has a unique signature that can be detected using AI." King's research group developed an AI model to identify production fingerprints from photographs taken with smartphone cameras. The AI model was developed on a large data set, comprising photographs of 9,192 parts made on 21 machines from six companies and with four different fabrication processes. When calibrating their model, the researchers found that a fingerprint could be obtained with 98% accuracy from just 1 square millimeter of the part's surface. "Our results suggest that the AI model can make accurate predictions when trained with as few as 10 parts," King said. "Using just a few samples from a supplier, it's possible to verify everything that they deliver after." King believes that this technology has the potential to overhaul supply chain management. With it, manufacturers can detect problems at early stages of production, and they save the time and resources needed to pinpoint the origins of errors. The technology could also be used to track the origins of illicit goods.
[3]
Researchers discover that every 3D printer leaves a unique "fingerprint" on prints, and they can be tracked back pretty accurately
Summary 3D prints have unique "fingerprints" that allow the identification of individual machines, even those of the same model. University of Illinois researchers, led by Bill King, created an AI system that can identify machine prints with 98% accuracy. There's the potential to trace poor quality products back to the machine that printed them, improving larger-scale manufacturing processes. If someone 3D printed an object and handed it to you, how confident would you be in your ability to tell exactly what model of 3D printer made it? I don't know about you, but I would have zero chance at identifying what machine made it without random guessing. Well, it turns out that every print has a unique "fingerprint" that allows someone to trace it back to the machine that made it. And we're not just talking about which model made it; we're talking about which exact individual machine made which individual prints, even if each machine was the same printer model. Related I can finally 3D print remotely thanks to this self-hosted slicer 3D printing remotely is finally a possibility Posts University of Illinois researchers discover 3D printer "fingerprints" that can identify a specific machine As Notebook Check spotted, University of Illinois researchers found a reliable way to match a 3D print to the exact machine that made it. The researcher team was headed by Bill King, aprofessor of mechanical science and engineering at the University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign. Once King made the discovery, they created an AI system that could analyze and identify which machine made which component. To create the AI model, the team fed it 9,192 photographs of parts. These parts were printed on 21 machines, which were collectively built by six brands and with four different fabrication processes. The team then gave the AI an image of a square millimeter of a printed part, and it managed to pin the print to the machine with 98% accuracy. Surprised? You have every right to be. In fact, even King themselves can't quite believe it: "We are still amazed that this works: we can print the same part design on two identical machines -same model, same process settings, same material - and each machine leaves a unique fingerprint that the AI model can trace back to the machine," King said. "It's possible to determine exactly where and how something was made. You don't have to take your supplier's word on anything." King believes the tech could be pushed even further, with the AI developing an accurate reading after just 10 scans of parts printed from a machine. King believes this research would make it a lot easier for people to figure out where something went wrong in larger-scale product manufacturing processes. If a particular product's build quality is poor, people can quickly trace the 3D print back to the very machine that made it, making it easy to report "bad eggs" in the production chain.
Share
Share
Copy Link
Researchers have developed an AI-driven system that can identify the specific 3D printer that produced a part, opening new possibilities for supply chain management and quality control in manufacturing.
AI System Detects Unique 3D Printer Signatures
Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed an innovative AI-driven system capable of identifying the specific 3D printer that produced a given part. This groundbreaking technology, led by Professor Bill King from the Grainger College of Engineering, has demonstrated an impressive 98% accuracy rate in tracing parts back to their origin machines
1
2
.The Hidden Fingerprints of 3D Printers
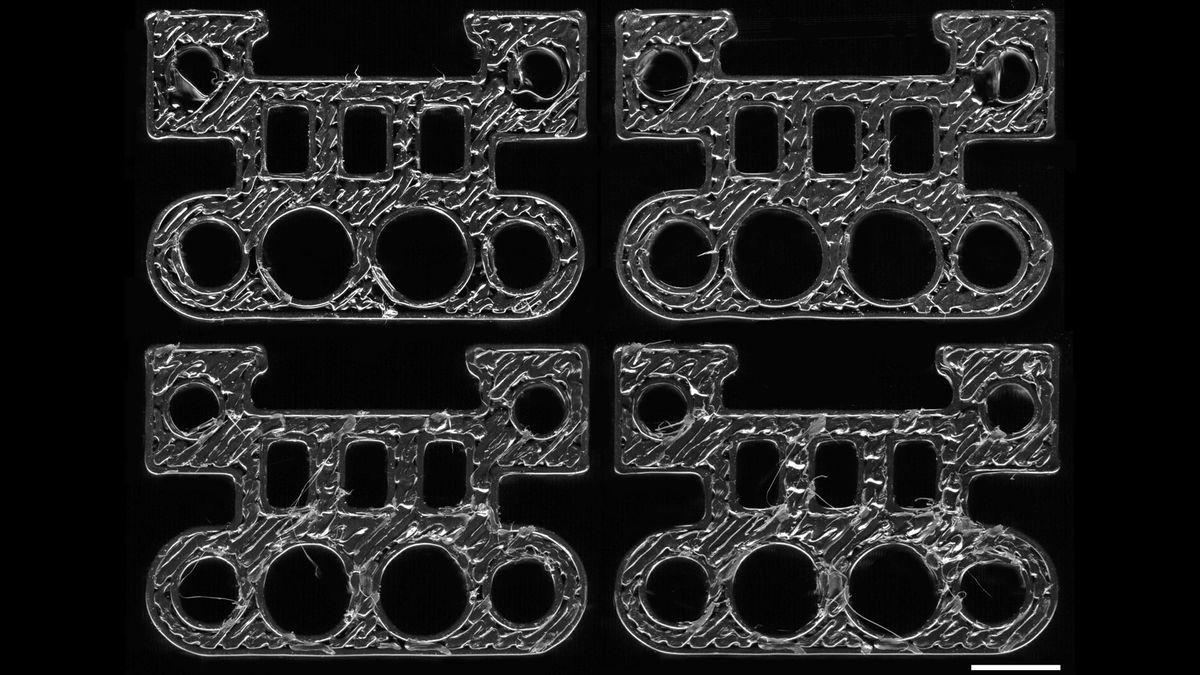
Source: Tom's Hardware
The research team discovered that each 3D printer leaves a unique "fingerprint" on the parts it produces, even when using identical machines, settings, and materials. This signature is so distinct that the AI model can differentiate between parts made by different printers of the same model
3
."We are still amazed that this works," said Professor King. "We can print the same part design on two identical machines - same model, same process settings, same material - and each machine leaves a unique fingerprint that the AI model can trace back to the machine"
1
.AI Model Development and Accuracy
To create this highly accurate AI model, the researchers utilized a large dataset comprising:
- 9,192 parts
- 21 different 3D printing machines
- 6 manufacturing companies
- 4 distinct fabrication processes
The system's ability to identify a printer's unique signature from just 1 square millimeter of a part's surface is particularly noteworthy. Professor King suggests that the AI model can make accurate predictions with as few as 10 sample parts from a supplier
2
.Related Stories
Implications for Manufacturing and Supply Chain Management
This technology has significant implications for various industries:
-
Quality Control: Manufacturers can easily trace problematic parts back to specific machines, enabling swift identification and resolution of issues
1
2
. -
Supply Chain Verification: Companies can ensure that suppliers adhere to agreed-upon processes and materials without relying solely on trust
2
. -
Early Problem Detection: The system allows for the early identification of manufacturing discrepancies, potentially saving time and resources
2
. -
Tracking Illicit Goods: The technology could be applied to trace the origins of unauthorized or illegally manufactured items
1
3
.

Source: XDA-Developers
Broader Applications and Future Potential
While the research focused primarily on 3D printers used in factory production environments, the technology's potential extends far beyond this scope. Professor King noted, "There are thousands of 3D printers in the world, and tens of millions of 3D printed parts used in airplanes, automobiles, medical devices, consumer products, and a host of other applications. Each one of these parts has a unique signature that can be detected using AI"
1
.As this technology continues to develop, it could revolutionize supply chain management, enhance product authenticity verification, and provide new tools for law enforcement in tracking the origins of 3D-printed contraband.
References
Summarized by
Navi
[1]
[2]
Related Stories
AI Takes Center Stage in Combating 3D-Printed Ghost Guns
26 Jul 2025•Technology

MIT's MechStyle uses generative AI to create 3D printed objects strong enough for daily use
15 Jan 2026•Science and Research

AI Breakthrough Accelerates and Strengthens Titanium Alloy Production
08 Mar 2025•Science and Research

Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.4, New AI Model Built for Agents and Professional Work
Technology

2
Anthropic sues Pentagon over supply chain risk label after refusing autonomous weapons use
Policy and Regulation

3
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round as questions swirl around AI bubble and profitability
Business and Economy





