AI Tool Uncovers Five Distinct Cancer Cell Groups, Revolutionizing Tumor Characterization and Treatment
4 Sources
4 Sources
[1]
Inside the tumor: AI cracks five hidden cell types to stop cancer's comeback
A multinational team of researchers, co-led by the Garvan Institute of Medical Research, has developed and tested a new AI tool to better characterize the diversity of individual cells within tumors, opening doors for more targeted therapies for patients. Findings on the development and use of the AI tool, called AAnet, have today been published in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. Not all tumor cells the same Tumors aren't made up of just one cell type - they're a mix of different cells that grow and respond to treatment in different ways. This diversity, or heterogeneity, makes cancer harder to treat and can in turn lead to worse outcomes, especially in triple-negative breast cancer. "Heterogeneity is a problem because currently we treat tumors as if they are made up of the same cell. This means we give one therapy that kills most cells in the tumor by targeting a particular mechanism. But not all cancer cells may share that mechanism. As a result, while the patient may have an initial response, the remaining cells can grow and the cancer may come back," says Associate Professor Christine Chaffer, co-senior author of the study and Co-Director of the Cancer Plasticity and Dormancy Program at Garvan. But while heterogeneity is a problem, researchers don't know enough to characterize it: "So far researchers haven't been able to clearly explain how adjacent cells in a tumor differ from each other, and how to classify those differences into meaningful ways to better treat tumors. But this is exactly what we need to know so we can kill all cells within that tumor with the right therapies," Associate Professor Chaffer adds. A new tool characterizes five new cancer cell groups To solve this problem, the team developed and trained a powerful new AI tool called AAnet that can detect biological patterns in cells within tumors. They then used the AI tool to uncover patterns in the level of gene expression of individual cells within tumors, focusing on preclinical models of triple-negative breast cancer and human samples of ER positive, HER2 positive and triple-negative breast cancer. Through this, they identified five different cancer cell groups within a tumor, with distinct gene expression profiles that indicated vast differences in cell behaviour. "By using our AI tool, we were consistently able to discover five new groups of cell types within single tumors called 'archetypes'. Each group exhibited different biological pathways and propensities for growth, metastasis and markers of poor prognosis. Our next steps are to see how these groups may change over time, for example before and after chemotherapy," says Associate Professor Chaffer. This is a first for cancer research. Co-lead, Associate Professor Smita Krishnaswamy from Yale University who led the development of the AI tool states: "Thanks to technology advances, the last 20 years have seen an explosion of data at the single-cell level. With this data we have been finding out that not only is each patient's cancer different, but each cancer cell behaves differently from another. Our study is the first time that single-cell data have been able to simplify this continuum of cell states into a handful of meaningful archetypes through which diversity can be analyzed to find meaningful associations with spatial tumor growth and metabolomic signatures. This could be a game changer." New classification to drive better, targeted treatments The researchers say the use of AAnet to characterize the different groups of cells in a tumor according to their biology opens doors for a paradigm shift in how we treat cancer. "Currently the choice of cancer treatment for a patient is largely based on the organ that the cancer came from such as breast, lung or prostate and any molecular markers it may exhibit. But this assumes that all cells in that cancer are the same. Instead, now we have a tool to characterize the heterogeneity of a patient's tumor and really understand what each group of cells is doing at a biological level. With AAnet, we now hope to improve the rational design of combination therapies that we know will target each of those different groups through their biological pathways. This has the potential to vastly improve outcomes for that patient," says Associate Professor Chaffer. On the application of AAnet, co-senior author of the study and Chief Scientific Officer of Garvan Professor Sarah Kummerfeld states: "We envision a future where doctors combine this AI analysis with traditional cancer diagnoses to develop more personalized treatments that target all cell types within a person's unique tumor. These results represent a true melding of cutting-edge technology and biology that can improve patient care. Our study focused on breast cancer, but it could be applied to other cancers and illnesses such as autoimmune disorders. The technology is already there." This research was supported through the following sources. In Australia: The NELUNE Foundation, Tour de Cure, Estee Lauder, The Kinghorn Foundation, The Paramor Family Foundation, University of New South Wales Scientia Research Fellowship, Ramaciotti Biomedical Research Award, ARC Development Project grant and NHMRC Ideas Grants and Investigator Grant. In the US: Gruber Foundation Science Fellowship and the Eric and Wendy Schmidt Center at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, National Science Foundation, Yale Cancer Center Pilot grant and Sloan Fellowship. Christine Chaffer is a Conjoint Associate Professor at St Vincent's Clinical School, Faculty of Medicine and Health, UNSW Sydney, Director of the Cancer Plasticity and Dormancy Program, and Lab Head at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research. Smita Krishnaswamy is Associate Professor in Genetics and Computer Science, Yale School of Medicine.
[2]
New AI tool characterizes the diversity of individual cells within tumors
Garvan Institute of Medical ResearchJun 24 2025 A multinational team of researchers, co-led by the Garvan Institute of Medical Research, has developed and tested a new AI tool to better characterize the diversity of individual cells within tumors, opening doors for more targeted therapies for patients. Findings on the development and use of the AI tool, called AAnet, have today been published in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. Not all tumor cells the same Tumors aren't made up of just one cell type - they're a mix of different cells that grow and respond to treatment in different ways. This diversity, or heterogeneity, makes cancer harder to treat and can in turn lead to worse outcomes, especially in triple-negative breast cancer. Heterogeneity is a problem because currently we treat tumors as if they are made up of the same cell. This means we give one therapy that kills most cells in the tumor by targeting a particular mechanism. But not all cancer cells may share that mechanism. As a result, while the patient may have an initial response, the remaining cells can grow and the cancer may come back." Associate Professor Christine Chaffer, co-senior author of the study and Co-Director of the Cancer Plasticity and Dormancy Program at Garvan But while heterogeneity is a problem, researchers don't know enough to characterise it: "So far researchers haven't been able to clearly explain how adjacent cells in a tumor differ from each other, and how to classify those differences into meaningful ways to better treat tumors. But this is exactly what we need to know so we can kill all cells within that tumor with the right therapies," Associate Professor Chaffer adds. A new tool characterises five new cancer cell groups To solve this problem, the team developed and trained a powerful new AI tool called AAnet that can detect biological patterns in cells within tumors. They then used the AI tool to uncover patterns in the level of gene expression of individual cells within tumors, focusing on preclinical models of triple-negative breast cancer and human samples of ER positive, HER2 positive and triple-negative breast cancer. Through this, they identified five different cancer cell groups within a tumor, with distinct gene expression profiles that indicated vast differences in cell behaviour. "By using our AI tool, we were consistently able to discover five new groups of cell types within single tumors called 'archetypes'. Each group exhibited different biological pathways and propensities for growth, metastasis and markers of poor prognosis. Our next steps are to see how these groups may change over time, for example before and after chemotherapy," says Associate Professor Chaffer. This is a first for cancer research. Co-lead, Associate Professor Smita Krishnaswamy from Yale University who led the development of the AI tool states: "Thanks to technology advances, the last 20 years have seen an explosion of data at the single-cell level. With this data we have been finding out that not only is each patient's cancer different, but each cancer cell behaves differently from another. Our study is the first time that single-cell data have been able to simplify this continuum of cell states into a handful of meaningful archetypes through which diversity can be analysed to find meaningful associations with spatial tumor growth and metabolomic signatures. This could be a game changer." New classification to drive better, targeted treatments The researchers say the use of AAnet to characterise the different groups of cells in a tumor according to their biology opens doors for a paradigm shift in how we treat cancer. "Currently the choice of cancer treatment for a patient is largely based on the organ that the cancer came from such as breast, lung or prostate and any molecular markers it may exhibit. But this assumes that all cells in that cancer are the same. Instead, now we have a tool to characterise the heterogeneity of a patient's tumor and really understand what each group of cells is doing at a biological level. With AAnet, we now hope to improve the rational design of combination therapies that we know will target each of those different groups through their biological pathways. This has the potential to vastly improve outcomes for that patient," says Associate Professor Chaffer. On the application of AAnet, co-senior author of the study and Chief Scientific Officer of Garvan Professor Sarah Kummerfeld states: "We envision a future where doctors combine this AI analysis with traditional cancer diagnoses to develop more personalised treatments that target all cell types within a person's unique tumor. These results represent a true melding of cutting-edge technology and biology that can improve patient care. Our study focused on breast cancer, but it could be applied to other cancers and illnesses such as autoimmune disorders. The technology is already there." This research was supported through the following sources. In Australia: The NELUNE Foundation, Tour de Cure, Estee Lauder, The Kinghorn Foundation, The Paramor Family Foundation, University of New South Wales Scientia Research Fellowship, Ramaciotti Biomedical Research Award, ARC Development Project grant and NHMRC Ideas Grants and Investigator Grant. In the US: Gruber Foundation Science Fellowship and the Eric and Wendy Schmidt Center at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, National Science Foundation, Yale Cancer Center Pilot grant and Sloan Fellowship. Source: Garvan Institute of Medical Research Journal reference: Venkat, A., et al. (2025) AAnet resolves a continuum of spatially-localized cell states to unveil intratumoral heterogeneity. Cancer Discovery. doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-0684.
[3]
AI tool identifies five distinct cancer cell groups within individual tumors
A multinational team of researchers, co-led by the Garvan Institute of Medical Research, has developed and tested a new AI tool to better characterize the diversity of individual cells within tumors, opening doors for more targeted therapies for patients. Findings on the development and use of the AI tool, called AAnet, have been published in Cancer Discovery. Tumors aren't made up of just one cell type -- they're a mix of different cells that grow and respond to treatment in different ways. This diversity, or heterogeneity, makes cancer harder to treat and can in turn lead to worse outcomes, especially in triple-negative breast cancer. "Heterogeneity is a problem because currently we treat tumors as if they are made up of the same cell. This means we give one therapy that kills most cells in the tumor by targeting a particular mechanism. But not all cancer cells may share that mechanism. As a result, while the patient may have an initial response, the remaining cells can grow and the cancer may come back," says Associate Professor Christine Chaffer, co-senior author of the study and Co-Director of the Cancer Plasticity and Dormancy Program at Garvan. But while heterogeneity is a problem, researchers don't know enough to characterize it: "So far, researchers haven't been able to clearly explain how adjacent cells in a tumor differ from each other, and how to classify those differences into meaningful ways to better treat tumors. But this is exactly what we need to know so we can kill all cells within that tumor with the right therapies," Associate Professor Chaffer adds. A new tool characterizes five new cancer cell groups To solve this problem, the team developed and trained a powerful new AI tool called AAnet that can detect biological patterns in cells within tumors. They then used the AI tool to uncover patterns in the level of gene expression of individual cells within tumors, focusing on preclinical models of triple-negative breast cancer and human samples of ER positive, HER2 positive and triple-negative breast cancer. Through this, they identified five different cancer cell groups within a tumor, with distinct gene expression profiles that indicated vast differences in cell behavior. "By using our AI tool, we were consistently able to discover five new groups of cell types within single tumors called 'archetypes.' Each group exhibited different biological pathways and propensities for growth, metastasis and markers of poor prognosis. Our next steps are to see how these groups may change over time, for example before and after chemotherapy," says Associate Professor Chaffer. This is a first for cancer research. Co-lead, Associate Professor Smita Krishnaswamy from Yale University, who led the development of the AI tool, says, "Thanks to technology advances, the last 20 years have seen an explosion of data at the single-cell level. With these data, we have been finding out that not only is each patient's cancer different, but each cancer cell behaves differently from another. "Our study is the first time that single-cell data have been able to simplify this continuum of cell states into a handful of meaningful archetypes through which diversity can be analyzed to find meaningful associations with spatial tumor growth and metabolomic signatures. This could be a game-changer." New classification to drive better, targeted treatments The researchers say the use of AAnet to characterize the different groups of cells in a tumor according to their biology opens doors for a paradigm shift in how we treat cancer. "Currently, the choice of cancer treatment for a patient is largely based on the organ that the cancer came from, such as breast, lung or prostate, and any molecular markers it may exhibit. But this assumes that all cells in that cancer are the same," says Associate Professor Chaffer. "Instead, now we have a tool to characterize the heterogeneity of a patient's tumor and really understand what each group of cells is doing at a biological level. With AAnet, we now hope to improve the rational design of combination therapies that we know will target each of those different groups through their biological pathways. This has the potential to vastly improve outcomes for that patient." On the application of AAnet, co-senior author of the study and Chief Scientific Officer of Garvan Professor Sarah Kummerfeld said, "We envision a future where doctors combine this AI analysis with traditional cancer diagnoses to develop more personalized treatments that target all cell types within a person's unique tumor. "These results represent a true melding of cutting-edge technology and biology that can improve patient care. Our study focused on breast cancer, but it could be applied to other cancers and illnesses such as autoimmune disorders. The technology is already there."
[4]
AI Tool Set to Transform Characterization and Treatment of Cancers | Newswise
Tumor cross section showing five cell groups, each colored differently based on gene expression. Newswise -- A multinational team of researchers, co-led by Yale Prof. Smita Krishnaswamy, has developed and tested a new AI tool to better characterize the diversity of individual cells within tumors, opening doors for more targeted therapies for patients. "Our study is the first time that single cell data have been able to simplify this continuum of cell states into a handful of meaningful archetypes through which diversity can be analysed to find meaningful associations with spatial tumour growth and metabolomic signatures," says Krishnaswamy, associate professor of computer science and genetics at Yale School of Medicine and member of Yale Cancer Center. "This could be a game changer." Findings on the development and use of the AI tool, called AAnet, have today been published in Cancer Discovery. Not all tumor cells the same Tumors aren't made of just one cell type - they're a mix of different cells that grow and respond to treatment in different ways. This diversity, or heterogeneity, makes cancer harder to treat and can in turn lead to worse outcomes, especially in triple negative breast cancer. "Heterogeneity is a problem because currently we treat tumors as if they are made up of the same cell. This means we give one therapy that kills most cells in the tumor by targeting a particular mechanism. But not all cancer cells may share that mechanism. As a result, while the patient may have an initial response, the remaining cells can grow and the cancer may come back," says associate professor Christine Chaffer, co-senior author of the study and co-director of the Cancer Plasticity and Dormancy Program at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research. But while heterogeneity is a problem, researchers don't know enough to characterize it: "So far researchers haven't been able to clearly explain how adjacent cells in a tumor differ from each other, and how to classify those differences into meaningful ways to better treat tumors. But this is exactly what we need to know so we can kill all cells within that tumor with the right therapies," Chaffer adds. A new tool characterizes five new cancer cell groups To solve this problem, the team developed and trained a powerful new AI tool called AAnet that can detect patterns in data of individual cells within tumors. They used the AI tool to uncover patterns in the level of gene expression of individual cells within tumors to derive new groups. The team focused on human models of triple-negative breast cancer and human samples of ER positive, HER2 positive and triple-negative breast cancer. Through this, they identified five different cancer cell groups within a tumor, with distinct gene expression profiles that indicated vast differences in cell behavior. "By using our AI tool, we were consistently able to discover five new groups of cell types within single tumors called 'archetypes'. Each group exhibited different biological pathways and propensities for growth, metastasis and markers of poor prognosis. Our next steps are to see how these groups may change over time, for example before and after chemotherapy," says Chaffer. Having access to this level of detail is a major breakthrough for cancer research. "Thanks to technology advances, the last 20 years have seen an explosion of data at the single cell level," Krishnaswamy said. "With this data we have been finding out that not only is each patient's cancer different, but each cancer cell behaves differently from another." New classification to drive better, targeted treatments The researchers say the use of AAnet to characterize the different groups of cells in a tumour according to their biology opens doors for a paradigm shift in how we treat cancer. "Currently the choice of cancer treatment for a patient is largely based on the organ that the cancer came from such as breast, lung or prostate and any molecular markers it may exhibit. But this assumes that all cells in that cancer are the same. Instead, now we have a tool to characterize the heterogeneity of a patient's tumour and really understand what each group of cells is doing at a biological level. With AAnet, we now hope to improve the rational design of combination therapies that we know will target each of those different groups through their biological pathways. This has the potential to vastly improve outcomes for that patient," says Chaffer. On the application of AAnet, co-senior author of the study and Chief Scientific Officer of Garvan Professor Sarah Kummerfeld states: "We envision a future where doctors combine this AI analysis with traditional cancer diagnoses to develop more personalised treatments that target all cell types within a person's unique tumour. These results represent a true melding of cutting-edge technology and biology that can improve patient care. Our study focused on breast cancer, but it could be applied to other cancers and illnesses such as autoimmune disorders. The technology is already there."
Share
Share
Copy Link
A multinational research team has developed an AI tool called AAnet that identifies five distinct cancer cell groups within tumors, potentially transforming cancer treatment by enabling more targeted therapies.
Revolutionizing Cancer Research with AI
A groundbreaking artificial intelligence tool, AAnet, has been developed by a multinational research team co-led by the Garvan Institute of Medical Research and Yale University. This innovative AI system has the potential to transform cancer treatment by uncovering the hidden diversity within tumors
1
2
3
4
.The Challenge of Tumor Heterogeneity
Cancer treatment has long been hindered by the heterogeneous nature of tumors. Associate Professor Christine Chaffer, co-senior author of the study, explains, "Heterogeneity is a problem because currently we treat tumors as if they are made up of the same cell"
1
. This approach often leads to initial treatment responses followed by cancer recurrence, as not all cancer cells share the same vulnerabilities2
.AAnet: Unveiling Cancer's Hidden Complexity
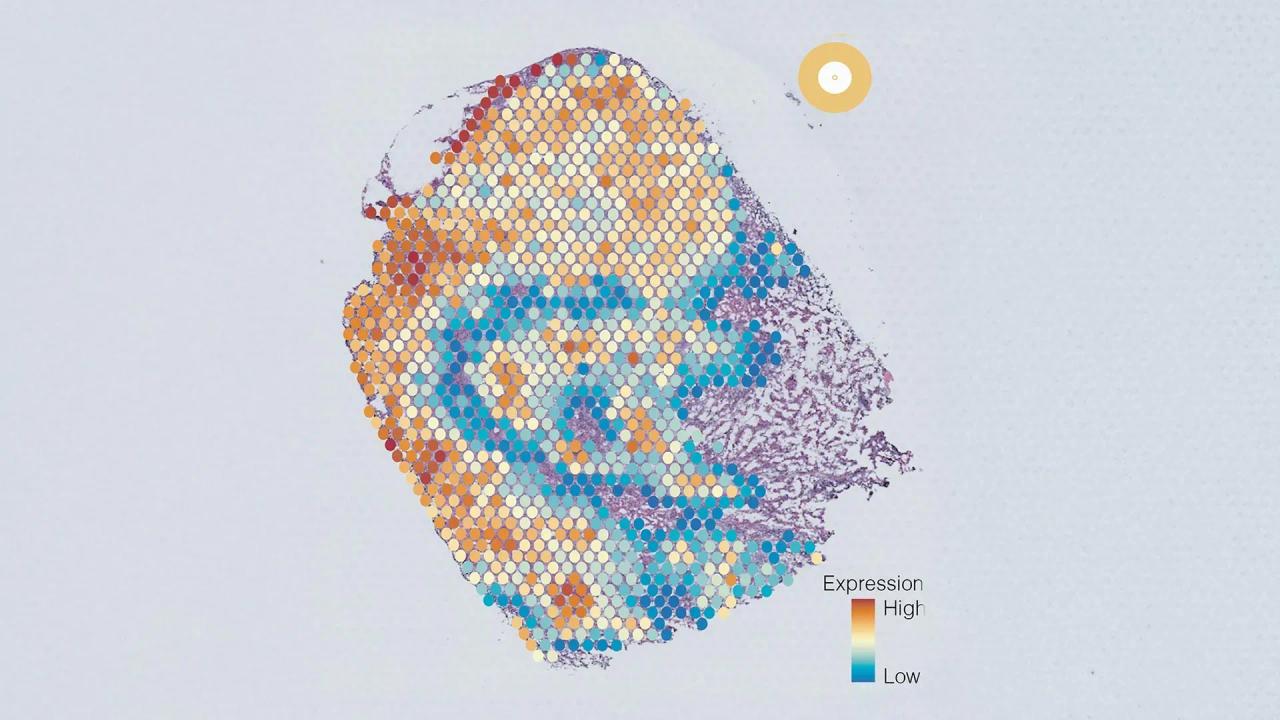
Source: ScienceDaily
The newly developed AI tool, AAnet, addresses this challenge by detecting biological patterns in individual cells within tumors. Through analysis of gene expression levels, AAnet consistently identified five distinct cancer cell groups, or "archetypes," within single tumors
1
2
3
.Associate Professor Smita Krishnaswamy from Yale University, who led the AI tool's development, states, "Our study is the first time that single-cell data have been able to simplify this continuum of cell states into a handful of meaningful archetypes"
4
. Each archetype exhibits unique biological pathways and tendencies for growth, metastasis, and poor prognosis markers3
.Implications for Personalized Cancer Treatment
The discovery of these distinct cell groups opens new avenues for targeted cancer therapies. "With AAnet, we now hope to improve the rational design of combination therapies that we know will target each of those different groups through their biological pathways," says Associate Professor Chaffer
2
.Professor Sarah Kummerfeld, Chief Scientific Officer of Garvan, envisions a future where "doctors combine this AI analysis with traditional cancer diagnoses to develop more personalized treatments that target all cell types within a person's unique tumor"
1
4
.Related Stories
Broader Applications and Future Directions

Source: News-Medical
While the study focused on breast cancer, including triple-negative, ER-positive, and HER2-positive types, the researchers believe AAnet could be applied to other cancers and even autoimmune disorders
1
2
3
4
. The team's next steps include investigating how these cell groups may change over time, particularly before and after chemotherapy3
.A Collaborative Effort
This research represents a significant collaboration between institutions and was supported by various funding sources in Australia and the United States, including the NELUNE Foundation, Tour de Cure, Estee Lauder, and the National Science Foundation
1
2
.The development of AAnet marks a crucial step forward in cancer research, offering the potential for more effective, personalized treatments that address the complex nature of tumors. As this technology continues to evolve, it may revolutionize our approach to cancer therapy and improve outcomes for patients worldwide.
References
Summarized by
Navi
Related Stories
NicheCompass: AI Tool Revolutionizes Cancer Treatment by Visualizing Cellular 'Social Networks'
19 Mar 2025•Science and Research

ChatGPT Like AI Model Shows Promise in Cancer Treatment Decision-Making
05 Sept 2024

AI-Powered scNET System Revolutionizes Understanding of Cellular Responses to Drug Treatments
02 Apr 2025•Science and Research

Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.4, New AI Model Built for Agents and Professional Work
Technology

2
Pentagon's Anthropic showdown exposes who controls AI guardrails in military contracts
Policy and Regulation

3
Anthropic challenges Pentagon supply chain risk label in court over AI usage restrictions
Policy and Regulation





