Anthropic Unveils 'Skills for Claude': A Leap Towards Customizable AI Assistants
12 Sources
12 Sources
[1]
Skills for Claude will let you customize tasks with pre-set instructions - here's how
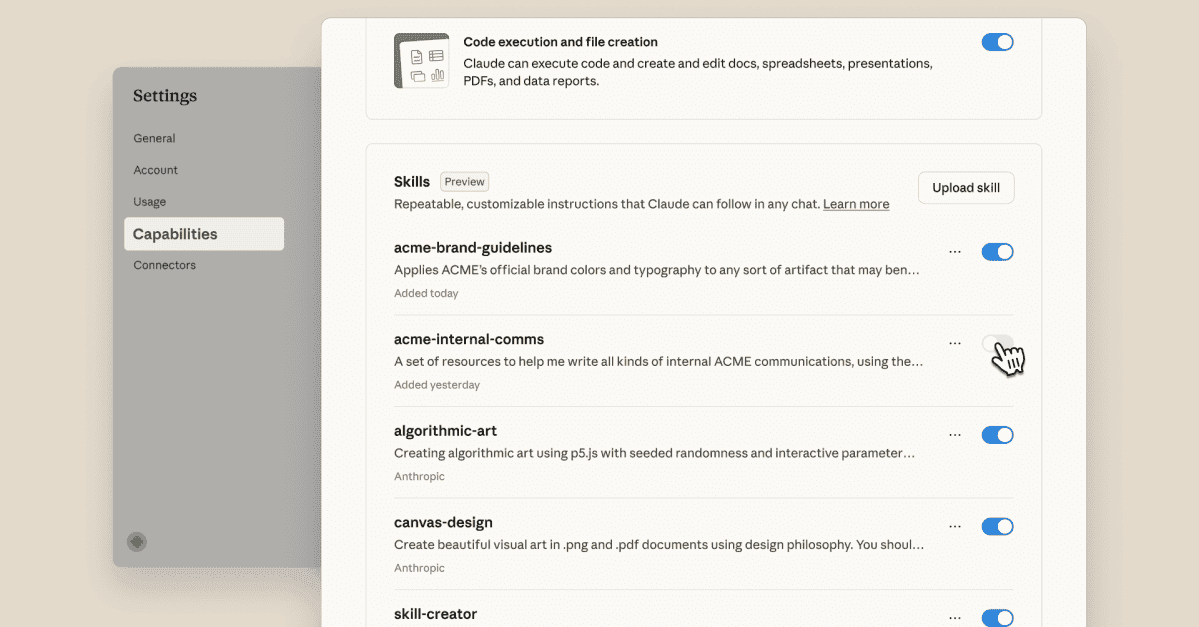
Bear in mind that more access to personal data means more risk. Anthropic launched Skills for Claude on Wednesday, a new feature aimed at making the company's flagship AI chatbot more customizable for individual users and businesses. You can think of Skills as little digital instruction manuals, each of which can be used by Claude to guide its behavior on a given task. Anthropic described them in a blog post as "custom onboarding materials that let you package expertise, making Claude a specialist on what matters most to you." Anthropic has developed its own, one-size-fits-all skills -- including those to help generate Word docs, Excel spreadsheets, and PowerPoint docs -- but users can also create and upload their own, custom skills. Claude can automatically determine which Skills it should use based on the prompt it's been given by a user. The core idea behind Skills is to make Claude more customizable: individuals and businesses all have their own unique preferences when it comes to using AI chatbots, and Skills are essentially a shortcut towards ensuring you receive the outputs you're looking for as quickly as possible. Also: Claude's latest model is cheaper and faster than Sonnet 4 - and free For example, say you're turning to Claude for help creating a pitch deck for a prospective new client. Rather than having to meticulously explain the subtleties of your brand's voice and approach to sales, Claude can automatically reference the "Brand guidelines" Skill you've previously uploaded, and from there, infer everything it needs to know to generate a PowerPoint presentation that's tailor-made for your company. (You can learn more about creating custom Skills here.) The launch of Skills, therefore, also marks a step towards making Claude more agentic, or able to carry out complex tasks with minimal user oversight, based on its growing ability to analyze the context and goals of particular users. Skills are available now for Pro, Max, Team, and Enterprise users, and can be viewed via Settings > Capabilities. Account admins for Team and Enterprise accounts must first enable organization-wide access before Skills can be used by individual employees. Skills work across the Claude app, Claude Code, and the Claude API, meaning developers only need to build them once before they can be deployed across their organizations. AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini were designed to be general-purpose tools, trained effectively on the entirety of the internet and able to respond to prompts covering virtually any topic. Increasingly, however, tech developers have been transforming their AI systems into more specialized tools. A predominant, burgeoning vision of AI that's started to flower across Silicon Valley is a future in which each of us has a personal AI assistant (or a collection of assistants), which knows us at an intimate level and is customized to execute tasks according to our particular preferences. Anthropic's Wednesday launch of Skills for Claude is just the latest in a long string of similar efforts throughout the AI industry. Just last week, for example, Microsoft debuted new connectors for Copilot, which allow the chatbot to pull user information from Gmail, Google Drive, and other apps. The previous week, Anthropic announced a new Slack integration for Claude. All of these personalization features also present new risks. The more personal data you elect to share with AI tools, the more rigorous your security protocols should be. Also: Claude now integrates directly with Microsoft 365 While every AI developer has their own data privacy policies, it's generally wise to operate under the assumption that any information you share with a chatbot will be stored by the system and added to its training data, thus presenting the possibility that it will be unintentionally surfaced by some other user in the future. The fact that Skills for Claude can enable the chatbot to auto-run code carries dangers of its own. "While powerful," Anthropic wrote in its blog post, "it means being mindful about which Skills you use -- stick to trusted sources to keep your data safe."
[2]
Anthropic turns to 'skills' to make Claude more useful at work
AI agents spent years as a concept and then as an experiment. Now, AI companies are devoting even more time and resources than before to make their agents actually useful for end users, whether they're consumers or professionals. Anthropic on Thursday announced its next step toward that goal: Skills for Claude. The tool is made up of "folders that include instructions, scripts, and resources that Claude can load when needed to make it smarter at specific work tasks -- from working with Excel [to] following your organization's brand guidelines," per a release. People can also build their own Skills for Claude relative to their specific jobs and use them across Claude.ai, Claude Code, Anthropic's API, and the Claude Agent SDK. Box, Rakuten, and Canva have already used the tool, according to the release. Essentially, the feature is designed to improve Claude's AI agent capabilities for your work specifically, so you don't have to spend as much time writing the perfect prompt or referring to past context every time you're trying to accomplish a task. It's available to Pro, Max, Team, and Enterprise users. Brad Abrams, a product lead at Anthropic, told The Verge that "the thing that's interesting to me about Skills is basically about agents." He said that Skills as a feature essentially provides organizations building agents a way to teach Claude to do a good job "in their specific context." He emphasized that it's not about meeting arbitrary benchmarks -- it's about being able to do the task you need at your own company. Using an Anthropic layer on top of Claude's PowerPoint Skill, "I had Claude create me a presentation about how Haiku 4.5 is doing in the market," Abrams said, adding that Claude created "well-formatted slides that are easy to digest." OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Microsoft, and others have been working toward the goal of actually useful AI agents for years, with executives regularly bringing up agentic AI on earnings calls and redirecting internal resources toward building the tools. To date, though, progress has been largely incremental, with companies fighting to release new feature updates or iterations of agents. (Think: Anthropic's Computer Use -- or OpenAI's Operator, then Deep Research, and then ChatGPT Agent, which essentially combined the two.) Anthropic's news also follows an OpenAI announcement in the same realm earlier this month at the company's annual DevDay event. At the event, OpenAI unveiled AgentKit, a group of tools executives said were "designed to help you take agents from prototype to production" and targeted both big companies and individual developers. The example use case OpenAI demonstrated was Albertsons, which runs more than 2,000 US grocery stores, using a custom agent with custom data to create a plan to improve ice cream sales if they were down more than 30 percent. Box, Canva, Evernote, and Ramp were also mentioned as having tried the tool. OpenAI also announced a consumer-facing tool that allows people to work with apps inside ChatGPT, like Zillow and Uber Eats.
[3]
Anthropic brings mad Skills to Claude
Paying Anthropic customers can now teach their Claude new tricks, which the company calls Skills. Despite much talk about superintelligence, AI models can be clueless when it comes to interacting with specific applications. Sure, they can parse PDF text, but they probably don't know how to fill in a PDF form. Skills, or Agent Skills for jargon maximalists, offer a way to instill Claude with specific knowledge that it may not possess in its distillation of training data. Anthropic has already deployed a few of them within Claude to handle common tasks like creating spreadsheets or presentations. Now, paying Claude customers - not the freeloader tier - can create Skills that suit their specific needs. Just make sure to subtract the labor that went into creating them when tabulating time saved by AI. A Skill consists of a directory with a SKILL.md file - a mix of YAML and Markdown - and possibly other resources such as text, scripts, and data. This turducken of instructions and executable code can be stored locally (~/.claude/skills/) or uploaded to the cloud for use with the Claude API. Claude's context window when loaded appends metadata from available Skills in the system prompt. Thereafter, when Claude is asked to carry out a relevant task, it will launch the appropriate skill by invoking the Bash tool to read the SKILL.md file. Once done, the model should have the data necessary to perform the desired task, such as interacting with content in a third-party application like Box or creating a PowerPoint presentation. The AI model will do so through a process Anthropic calls progressive disclosure. "Progressive disclosure is the core design principle that makes Agent Skills flexible and scalable," the company explains in its engineering blog post on the subject. "Like a well-organized manual that starts with a table of contents, then specific chapters, and finally a detailed appendix, skills let Claude load information only as needed." The result is that Claude doesn't process tokens unnecessarily for Skills that won't be used, which helps keep operating costs down. Skills also provide a way to revert to programmatic code execution when a large language model would be the wrong tool for the job. As an example, Anthropic cites the inefficiency of sorting a list via token generation - a coded sorting algorithm will complete the task much faster and at less cost, and will produce the same output every time. Creating Skills can be complicated for those who want to create the relevant files manually, but they're less burdensome with Claude's help. Claude incorporates a "skill-creator" that enables the creation of new Skills through interactive chatbot banter. There's also a Claude Skills Cookbook for those who want to understand the creation process. Speaking of malware, Anthropic warns that Skills present some risk (not unlike giving Claude access to Bash). Malicious Skills, the company cautions, may introduce vulnerabilities or allow the exfiltration of data. "We recommend installing skills only from trusted sources," the company says. "When installing a skill from a less-trusted source, thoroughly audit it before use. Start by reading the contents of the files bundled in the skill to understand what it does, paying particular attention to code dependencies and bundled resources like images or scripts. Similarly, pay attention to instructions or code within the skill that instruct Claude to connect to potentially untrusted external network sources." With that in mind, we note that Anthropic says it hopes to enable AI agents to create their own Skills. ®
[4]
Claude just got customizable 'Skills' -- here's how they could supercharge your workflow
A day after launching Haiku 4.5, Anthropic is giving users even more ways to level up their workflow. A new feature called Claude Skills allows users to teach Claude a new specialty on the fly, without code. This could mean everything from formatting Excel formulas to applying your company's branding within PowerPoint decks or even following a legal policy when reviewing contracts. These Skills are small, task-specific modules made up of folders, scripts and instructions that Claude can "load" when they're relevant. It's a way to give you a hand on demand without needing an extensive training program to make it happen. Claude Skills are now live across Claude apps, Claude Code, and API integrations, available to Pro, Max, Team and Enterprise users. Claude Skills are customizable workflows that teach Claude how to perform specific tasks exactly in the way you want them done. For example, you can build a Skill that makes Claude follow your team's design language when generating decks, or one that includes formatting rules for financial spreadsheets. Anthropic describes them as: If you've seen Claude generate Excel spreadsheets or PDFs in-app, you've already experienced built-in Skills. But now Anthropic is taking it a bit further. Claude will automatically detect and apply the right Skills without manual toggling; you'll even see which ones were used in its "chain of thought." There's also a "skill-creator" Skill that walks you through building your first one. It asks about your workflow, generates the folder structure and builds out the required files. No coding needed. integratewhileEnterprise teams, developers and creative professionals are the first to benefit. Canva, for example, is using Skills to plug Claude into their design workflows, and Box is using them to transform stored content into on-brand presentations and documents. For developers, Skills can be installed via plugins or version-controlled through Claude Code. You can also manage Skills through the Claude Console or via API with full version control, just know you'll need access to the Code Execution Tool beta, since some Skills run executable code. Anthropic cautions users to stick to trusted Skills, especially when using code execution features. Giving an AI access to run code always comes with privacy risks, but Claude is only as safe as the instructions it's following. Still, if you've been waiting for an AI assistant that actually understands how you work, Claude Skills might be the upgrade that finally delivers. Claude Skills move us one step closer to personalization with an AI assistant equipped with the knowledge and formatting preferences you need with very little training. This rollout is also a big step in the agentic direction, giving Claude more structured capabilities to support long-running workflows, multi-step planning and contextual awareness.
[5]
How Anthropic's 'Skills' make Claude faster, cheaper, and more consistent for business workflows
Anthropic launched a new capability on Thursday that allows its Claude AI assistant to tap into specialized expertise on demand, marking the company's latest effort to make artificial intelligence more practical for enterprise workflows as it chases rival OpenAI in the intensifying competition over AI-powered software development. The feature, called Skills, enables users to create folders containing instructions, code scripts, and reference materials that Claude can automatically load when relevant to a task. The system marks a fundamental shift in how organizations can customize AI assistants, moving beyond one-off prompts to reusable packages of domain expertise that work consistently across an entire company. "Skills are based on our belief and vision that as model intelligence continues to improve, we'll continue moving towards general-purpose agents that often have access to their own filesystem and computing environment," said Mahesh Murag, a member of Anthropic's technical staff, in an exclusive interview with VentureBeat. "The agent is initially made aware only of the names and descriptions of each available skill and can choose to load more information about a particular skill when relevant to the task at hand." The launch comes as Anthropic, valued at $183 billion after a recent $13 billion funding round, projects its annual revenue could nearly triple to as much as $26 billion in 2026, according to a recent Reuters report. The company is currently approaching a $7 billion annual revenue run rate, up from $5 billion in August, fueled largely by enterprise adoption of its AI coding tools -- a market where it faces fierce competition from OpenAI's recently upgraded Codex platform. How 'progressive disclosure' solves the context window problem Skills differ fundamentally from existing approaches to customizing AI assistants, such as prompt engineering or retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), Murag explained. The architecture relies on what Anthropic calls "progressive disclosure" -- Claude initially sees only skill names and brief descriptions, then autonomously decides which skills to load based on the task at hand, accessing only the specific files and information needed at that moment. "Unlike RAG, this relies on simple tools that let Claude manage and read files from a filesystem," Murag told VentureBeat. "Skills can contain an unbounded amount of context to teach Claude how to complete a task or series of tasks. This is because Skills are based on the premise of an agent being able to autonomously and intelligently navigate a filesystem and execute code." This approach allows organizations to bundle far more information than traditional context windows permit, while maintaining the speed and efficiency that enterprise users demand. A single skill can include step-by-step procedures, code templates, reference documents, brand guidelines, compliance checklists, and executable scripts -- all organized in a folder structure that Claude navigates intelligently. The system's composability provides another technical advantage. Multiple skills automatically stack together when needed for complex workflows. For instance, Claude might simultaneously invoke a company's brand guidelines skill, a financial reporting skill, and a presentation formatting skill to generate a quarterly investor deck -- coordinating between all three without manual intervention. What makes Skills different from OpenAI's Custom GPTs and Microsoft's Copilot Anthropic is positioning Skills as distinct from competing offerings like OpenAI's Custom GPTs and Microsoft's Copilot Studio, though the features address similar enterprise needs around AI customization and consistency. "Skills' combination of progressive disclosure, composability, and executable code bundling is unique in the market," Murag said. "While other platforms require developers to build custom scaffolding, Skills let anyone -- technical or not -- create specialized agents by organizing procedural knowledge into files." The cross-platform portability also sets Skills apart. The same skill works identically across Claude.ai, Claude Code (Anthropic's AI coding environment), the company's API, and the Claude Agent SDK for building custom AI agents. Organizations can develop a skill once and deploy it everywhere their teams use Claude, a significant advantage for enterprises seeking consistency. The feature supports any programming language compatible with the underlying container environment, and Anthropic provides sandboxing for security -- though the company acknowledges that allowing AI to execute code requires users to carefully vet which skills they trust. Early customers report 8x productivity gains on finance workflows Early customer implementations reveal how organizations are applying Skills to automate complex knowledge work. At Japanese e-commerce giant Rakuten, the AI team is using Skills to transform finance operations that previously required manual coordination across multiple departments. "Skills streamline our management accounting and finance workflows," said Yusuke Kaji, general manager of AI at Rakuten in a statement. "Claude processes multiple spreadsheets, catches critical anomalies, and generates reports using our procedures. What once took a day, we can now accomplish in an hour." That's an 8x improvement in productivity for specific workflows -- the kind of measurable return on investment that enterprises increasingly demand from AI implementations. Mike Krieger, Anthropic's chief product officer and Instagram co-founder, recently noted that companies have moved past "AI FOMO" to requiring concrete success metrics. Design platform Canva plans to integrate Skills into its own AI agent workflows. "Canva plans to leverage Skills to customize agents and expand what they can do," said Anwar Haneef, general manager and head of ecosystem at Canva in a statement. "This unlocks new ways to bring Canva deeper into agentic workflows -- helping teams capture their unique context and create stunning, high-quality designs effortlessly." Cloud storage provider Box sees Skills as a way to make corporate content repositories more actionable. "Skills teaches Claude how to work with Box content," said Yashodha Bhavnani, head of AI at Box. "Users can transform stored files into PowerPoint presentations, Excel spreadsheets, and Word documents that follow their organization's standards -- saving hours of effort." The enterprise security question: Who controls which AI skills employees can use? For enterprise IT departments, Skills raise important questions about governance and control -- particularly since the feature allows AI to execute arbitrary code in sandboxed environments. Anthropic has built administrative controls that allow enterprise customers to manage access at the organizational level. "Enterprise admins control access to the Skills capability via admin settings, where they can enable or disable access and monitor usage patterns," Murag said. "Once enabled at the organizational level, individual users still need to opt in." That two-layer consent model -- organizational enablement plus individual opt-in -- reflects lessons learned from previous enterprise AI deployments where blanket rollouts created compliance concerns. However, Anthropic's governance tools appear more limited than some enterprise customers might expect. The company doesn't currently offer granular controls over which specific skills employees can use, or detailed audit trails of custom skill content. Organizations concerned about data security should note that Skills require Claude's code execution environment, which runs in isolated containers. Anthropic advises users to "stick to trusted sources" when installing skills and provides security documentation, but the company acknowledges this is an inherently higher-risk capability than traditional AI interactions. From API to no-code: How Anthropic is making Skills accessible to everyone Anthropic is taking several approaches to make Skills accessible to users with varying technical sophistication. For non-technical users on Claude.ai, the company provides a "skill-creator" skill that interactively guides users through building new skills by asking questions about their workflow, then automatically generating the folder structure and documentation. Developers working with Anthropic's API get programmatic control through a new /skills endpoint and can manage skill versions through the Claude Console web interface. The feature requires enabling the Code Execution Tool beta in API requests. For Claude Code users, skills can be installed via plugins from the anthropics/skills GitHub marketplace, and teams can share skills through version control systems. "Skills are included in Max, Pro, Teams, and Enterprise plans at no additional cost," Murag confirmed. "API usage follows standard API pricing," meaning organizations pay only for the tokens consumed during skill execution, not for the skills themselves. Anthropic provides several pre-built skills for common business tasks, including professional generation of Excel spreadsheets with formulas, PowerPoint presentations, Word documents, and fillable PDFs. These Anthropic-created skills will remain free. Why the Skills launch matters in the AI coding wars with OpenAI The Skills announcement arrives during a pivotal moment in Anthropic's competition with OpenAI, particularly around AI-assisted software development. Just one day before releasing Skills, Anthropic launched Claude Haiku 4.5, a smaller and cheaper model that nonetheless matches the coding performance of Claude Sonnet 4 -- which was state-of-the-art when released just five months ago. That rapid improvement curve reflects the breakneck pace of AI development, where today's frontier capabilities become tomorrow's commodity offerings. OpenAI has been pushing hard on coding tools as well, recently upgrading its Codex platform with GPT-5 and expanding GitHub Copilot's capabilities. Anthropic's revenue trajectory -- potentially reaching $26 billion in 2026 from an estimated $9 billion by year-end 2025 -- suggests the company is successfully converting enterprise interest into paying customers. The timing also follows Salesforce's announcement this week that it's deepening AI partnerships with both OpenAI and Anthropic to power its Agentforce platform, signaling that enterprises are adopting a multi-vendor approach rather than standardizing on a single provider. Skills addresses a real pain point: the "prompt engineering" problem where effective AI usage depends on individual employees crafting elaborate instructions for routine tasks, with no way to share that expertise across teams. Skills transforms implicit knowledge into explicit, shareable assets. For startups and developers, the feature could accelerate product development significantly -- adding sophisticated document generation capabilities that previously required dedicated engineering teams and weeks of development. The composability aspect hints at a future where organizations build libraries of specialized skills that can be mixed and matched for increasingly complex workflows. A pharmaceutical company might develop skills for regulatory compliance, clinical trial analysis, molecular modeling, and patient data privacy that work together seamlessly -- creating a customized AI assistant with deep domain expertise across multiple specialties. Anthropic indicates it's working on simplified skill creation workflows and enterprise-wide deployment capabilities to make it easier for organizations to distribute skills across large teams. As the feature rolls out to Anthropic's more than 300,000 business customers, the true test will be whether organizations find Skills substantively more useful than existing customization approaches. For now, Skills offers Anthropic's clearest articulation yet of its vision for AI agents: not generalists that try to do everything reasonably well, but intelligent systems that know when to access specialized expertise and can coordinate multiple domains of knowledge to accomplish complex tasks. If that vision catches on, the question won't be whether your company uses AI -- it will be whether your AI knows how your company actually works.
[6]
Anthropic's Claude gets new Skills system to help you work smarter
What's happened? Anthropic has just rolled out a major upgrade called 'Skills,' a new toolkit designed to enhance the capabilities and ease of customization of its AI assistant, Claude, for real-world applications. Skills are essentially folders containing instructions, scripts, and resources that teach Claude to handle specific tasks Each Skill acts like a 'preset' that gives Claude context before you even start typing. You can build your own custom Skills if you want the AI assistant to follow certain rules or workflows automatically. They'll be available across all versions of Claude, from the web app to the API and even the developer tools. This follows the launch of Anthropic's hybrid reasoning model, highlighting the company's steady push to make Claude more intelligent, adaptable, and ready for complex work. Recommended Videos This is important because: You no longer have to repeat instructions; teach Claude once, and it remembers. Thanks to Skills and Claude's powerful file tools, Anthropic's chatbot is turning into a teammate rather than just another chat window. Think of it as Claude finally learning the ropes -- your brand style, tools, and how you like things done. Breaking things into simple, reusable pieces helps teams save time and get more consistent results across prompts. It also powers scalability: once a Skill is built, many users or teams can reuse it, rather than reinventing from scratch. Compared to pure 'prompt engineering,' Skills represent a more structured, maintainable layer on top of AI. Why should I care? If you're a user, developer, or working in a team that uses AI, using Skills will make Claude smarter, faster, and tailored to what you actually need. You won't have to repeat the same prompts every day. Small teams can get big-company-level AI efficiency with minimal setup. Developers can use Skills to create smarter, reusable setups for their apps or clients. If you are a beginner, here's a guide on how to use Claude to get the most out of it.
[7]
Anthropic's Skills for Claude helps AI agents perform certain tasks better than before - SiliconANGLE
Anthropic's Skills for Claude helps AI agents perform certain tasks better than before Anthropic PBC wants to make artificial intelligence agents more effective when it comes to doing real work, and its latest idea is to provide them with additional "skills" that can help them when assigned a very specific task. The company announced Skills for Claude today, explaining that it's a tool that comes with various folders that include "instructions, scripts and resources for Claude" that can be loaded up when necessary. For instance, if Claude is told to create an Excel spreadsheet or a PowerPoint presentation, it can access a special skill for those tools and use them more effectively. Users will also be able to create their own Skills for Claude and make the large language model better able to perform specific work that might have to take into account things like brand guidelines, the company said. The Skills can be used with Claude.ai, Claude Code, the Claude Agent software development kit and the Anthropic application programming interface. In a deep dive blog post, Anthropic explained that Claude will only access the Skills when they're relevant to whatever task it has been instructed to perform. The Skills are meant to help it perform more specialized work using specific tools or guidelines, and will be ignored when not needed. In other words, they help make Claude "better" at doing something. The idea is that by giving Claude special Skills, users won't have to be so specific when it comes to prompting the agent, or refer to previous context each time they're trying to tell it what they need it to do. Anthropic said that Skills, which are available now to Pro, Team, Max and Enterprise subscribers, can be thought of as "custom onboarding materials that let you package expertise", so as to transform Claude into an expert at the tasks that matter most to users. Anthropic Product Lead Brad Abrams told The Verge in an interview that he loaded up Claude's PowerPoint skill and instructed it to create a presentation that shows how the company's Haiku 4.5 model is performing in the market compared to competing models. He said it created a number of "well-formatted slides that are easy to digest". Other kinds of Skills pertain to creating PDF files, Word files, canvas design, image editing and writing code in specific programming languages. The company hopes that Skills for Claude will help to make AI agents more powerful and useful, and encourage businesses to use them more often, so they ultimately become more reliant on them over time. It's a goal that's shared by other AI companies, including Google LLC and OpenAI, which are also focused on agentic AI productivity. OpenAI made a similar move recently with the launch of its AgentKit earlier this month, saying that it's a group of tools that will help enterprises "take agents from prototype to production". The company showed how the U.S. grocery chain Albertsons Companies Inc. was able to build a custom agent based on its corporate data that was able to develop a marketing plan to improve ice cream sales at its more than 2,000 stores.
[8]
These New AI Features Could Cut Hours of Work From Your Marketing and Presentations
In a blog post, Anthropic wrote that Claude can now use a feature called skills. These skills operate like a folder that contains instructions for how Claude should perform a specific task and any relevant resources needed to help it do that task. Here's how it works in practice, according to a video demo posted by Anthropic. Say you need to make marketing materials for a new video game you're working on. By uploading a .ZIP file containing brand guidelines for your game and text instructions for how Claude should convert those guidelines, you create a skill that Claude can call upon whenever it needs to make documents or art assets in your brand's style. Skills are also how Claude connects to external apps, such as Google Drive and Microsoft 365. When Claude needs to create a PowerPoint presentation, for example, it calls upon the PowerPoint skill. That skill gives Claude the information and guidance it needs to create working presentations.
[9]
Claude Skills : Unlock the Secret to Building AI Experts Tailored to Your Needs
What if your AI could go beyond generic responses and become a true specialist in your field? Imagine an assistant that doesn't just answer questions but crafts a polished marketing plan, designs branded presentations, or even solves complex problems, all with precision and efficiency. With Claude AI's new "agent skills" feature, this vision is now a reality. By allowing you to build task-specific AI experts, Claude transforms from a general-purpose tool into a highly customized partner tailored to your unique needs. This isn't just an upgrade, it's a shift in how professionals across industries can approach productivity and problem-solving. Below Marketing Against the Grain explains how to harness the full potential of Claude's agent skills, from creating your own custom abilities to seamlessly integrating them into your workflow. Whether you're looking to automate repetitive tasks, tackle intricate challenges, or simply free up time for higher-value work, these skills offer a world of possibilities. Along the way, you'll explore practical examples, learn tips for fine-tuning your AI's performance, and discover how to overcome common challenges. By the end, you'll not only understand how to build your own AI experts but also rethink what's possible when technology aligns perfectly with your goals. What could you achieve with an AI that truly understands your work? Agent skills are specialized abilities you can assign to Claude AI, allowing it to perform specific tasks with precision and efficiency. These skills transform Claude from a general-purpose AI into a task-specific expert, capable of adapting to your unique requirements. For example, whether you need a comprehensive marketing plan or a branded presentation, Claude can select the appropriate skill and deliver tailored results. This feature is particularly valuable for professionals aiming to automate repetitive tasks or tackle complex challenges. By integrating agent skills into your workflow, you can enhance productivity, reduce manual effort, and focus on higher-value activities. The ability to customize Claude ensures that it aligns with your goals, making it a versatile and indispensable tool. Creating agent skills is a straightforward process that involves defining tasks, crafting detailed prompts, and uploading them to Claude's platform. Each skill is saved in a specific format called 'skill.md', making sure the AI can interpret and execute your instructions effectively. Once uploaded, Claude can autonomously select the appropriate skill whenever you issue a related command. This process allows you to build a library of customized skills tailored to your specific needs, allowing seamless task execution. Enhance your knowledge on Claude AI by exploring a selection of articles and guides on the subject. Agent skills can be applied across a wide range of tasks, making Claude an invaluable tool for professionals in various fields. Below are some examples of how these skills can be used: These examples highlight the versatility of agent skills, demonstrating how they can be customized to handle both creative and analytical tasks. By using these capabilities, you can enhance your efficiency and the quality of your output. Effective management and refinement of agent skills are essential for maximizing their potential. You can create multiple skills for different tasks, making sure Claude is equipped to handle a variety of scenarios. Additionally, Claude can assist in generating skill files based on your instructions, simplifying the creation process and reducing the time required to develop new skills. Fine-tuning is equally important. By testing and refining your prompts, you can improve the accuracy and effectiveness of each skill. This iterative process ensures that Claude consistently delivers results that align with your expectations and objectives. Regularly reviewing and updating your skills allows you to adapt to changing needs and maintain optimal performance. The versatility of agent skills makes Claude AI a powerful tool for professionals in diverse industries. Below are some practical applications that illustrate its potential: These applications demonstrate how agent skills can transform your work processes, allowing you to focus on high-priority tasks while delegating routine activities to the AI. By integrating Claude into your workflow, you can achieve greater efficiency and effectiveness in your professional endeavors. While agent skills offer significant benefits, there are some challenges to consider. Proper formatting and uploading of skills are critical for their functionality. Making sure that your 'skill.md' files are correctly structured and compatible with Claude's platform is essential for seamless integration. Additionally, crafting effective prompts requires careful thought and experimentation. The quality of your prompts directly impacts the AI's performance, making it important to invest time in refining them. Addressing these challenges ensures you can fully use Claude AI's capabilities. By dedicating effort to skill creation and management, you can unlock the full potential of this feature and achieve your desired outcomes. The introduction of agent skills represents a significant advancement in AI customization, empowering you to tailor Claude AI to your specific needs. By creating, managing, and fine-tuning these skills, you can transform Claude into a task-specific expert capable of handling a wide range of challenges autonomously. Whether you're optimizing marketing efforts, automating workflows, or solving everyday problems, agent skills provide the tools you need to enhance productivity and achieve your goals.
[10]
Unlock the Secret to Simpler, Smarter AI Automation with Claude Skills
What if the secret to unlocking your AI agent's full potential wasn't about adding more complexity, but stripping it away? Imagine a framework so intuitive and efficient that it not only reduces token usage but also eliminates the need for bloated configurations. Enter Claude Skills, a innovative approach that's poised to outshine the once-dominant Modular Command Packages (MCPs). With its focus on clarity, precision, and reusability, Claude Skills redefine how we think about task automation, making it simpler, faster, and more impactful. If you've ever felt bogged down by the inefficiencies of traditional AI frameworks, this might just be the solution you've been waiting for. In this exploration of Claude Skills, AI Jason explains how this streamlined framework transforms AI agents into hyper-efficient taskmasters. From its core blueprint, the 'skill.md' file, to its ability to handle intricate workflows with minimal overhead, Claude Skills offer a fresh perspective on AI-driven automation. We'll unpack why they outperform MCPs, not just in terms of resource consumption but also in adaptability and ease of use. Whether you're curious about real-world applications like algorithmic art generation or intrigued by how these skills foster consistency across projects, this deep dive promises to challenge your assumptions about what AI agents can achieve. Because sometimes, less really is more. Claude Skills are a systematic approach to defining and guiding AI agents in performing specific tasks. They integrate clear, actionable prompts with optional resources, such as templates, tools, or predefined functions, to deliver precise instructions. These skills can range from simple, single-step tasks to more intricate setups that reuse resources across multiple operations. The primary objective is to provide clarity and efficiency while avoiding unnecessary complexity. For example, a Claude Skill might guide an AI agent to generate a report by combining predefined templates with specific data inputs. This approach ensures that the task is completed accurately and consistently, regardless of its complexity. At the heart of every Claude Skill is the 'skill.md' file, which serves as a blueprint for the task. This file outlines the skill's purpose, context, and usage instructions, acting as a centralized guide for the AI agent. When loaded into the agent's context, the 'skill.md' file ensures that the task is executed effectively and consistently. The 'skill.md' file consolidates all relevant information, eliminating the need for repetitive instructions. This not only saves time but also reduces resource consumption, making it an essential component of the Claude Skills framework. By providing a single source of truth for task execution, the 'skill.md' file enhances both efficiency and reliability. Stay informed about the latest in Claude Code by exploring our other resources and articles. Claude Skills offer several distinct advantages over Modular Command Packages (MCPs), making them a more efficient and versatile choice for many applications: For instance, while an MCP might require extensive configuration to generate algorithmic art, a Claude Skill can achieve the same result using predefined templates and clear prompts. This streamlined approach reduces setup time and simplifies task execution. The versatility of Claude Skills is evident in their wide range of applications. Here are a few examples that highlight their practical utility: These examples demonstrate how Claude Skills can be tailored to meet specific needs, offering both flexibility and efficiency in diverse scenarios. Claude Skills provide several advantages for developers and organizations looking to optimize their workflows and enhance AI agent functionality: These benefits make Claude Skills an invaluable tool for developers and organizations aiming to streamline their processes and maximize the potential of their AI agents. Claude Skills can be customized to fit specific projects, making them a versatile tool for developers. For example, you can create skills that enforce best practices in UI development. These skills can analyze existing design conventions and apply them to new components, making sure consistency and quality across your codebase. Additionally, Claude Skills can be used to automate repetitive tasks, such as generating reports, analyzing data, or creating visual content. This adaptability makes them an essential part of modern development workflows, allowing teams to focus on higher-value activities while delegating routine tasks to AI agents. The open repository for Claude Skills encourages collaboration among developers, fostering a community-driven approach to innovation. By sharing and refining skills, developers can contribute to a growing library of resources that enhance AI agent functionality. This collaborative environment not only accelerates the development of new skills but also ensures that existing ones remain relevant and effective as technology evolves. By participating in this ecosystem, you can help shape the future of AI-driven task automation while benefiting from the collective expertise of the community. Claude Skills represent a significant advancement in AI agent frameworks, offering a streamlined and scalable solution for task automation. By combining clear prompts with optional resources, these skills reduce complexity, improve efficiency, and enable AI agents to perform a wide range of tasks with accuracy and consistency. Whether you're automating workflows, generating creative content, or developing user interfaces, Claude Skills provide the tools you need to achieve your goals effectively. As the technology continues to evolve, the adaptability and efficiency of Claude Skills will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of AI-driven innovation.
[11]
Claude Skills to Redefine How AI Agents Do Specialized Tasks
Anthropic announced Claude Skills on October 15, 2025, its latest tool for customising AI agents to perform specialised task-based workflows. The technical documentation describes Skills as reusable, file-based, predefined prompt resources that give Claude domain-specific knowledge, workflows, and best practices, turning it from a general-purpose assistant into a task-specific expert. Unlike general user prompts, which may give out one-time tasks or a call-out for information, Skills performs the tasks on demand and removes the need to repeat the same instructions across conversations within Claude. So, this can enable Claude to maintain consistent, efficient performance in specialised areas without extra setup. Key benefits of these personalised preset prompts include the ability to specialise Claude for domain-specific tasks, reduce repetition by creating a Skill once and using it automatically, and compose multiple Skills to build more complex workflows. "Skills extend Claude's capabilities by packaging your expertise into composable resources for Claude, transforming general-purpose agents into specialised agents that fit your needs," reads Anthropic's blog. Claude Skills isn't the first system to let AI chatbots perform focused, task-oriented work through preset prompts or configurations. OpenAI's Custom GPTs allow users to create tailored versions of ChatGPT with custom instructions, knowledge bases, and API integrations. Google's Gemini Gems offers similar functionality, letting users build AI "experts" for tasks like writing or coding. Microsoft's Copilot Studio uses Skills to extend bots with reusable, multi-step workflows, while Salesforce's Agentforce also enables enterprises to build autonomous agents that integrate with Customer 360 data for operational tasks. By pre-packaging and task logic into reusable modules, companies reduce the need for repetitive prompt engineering and maintain quality control across teams. Anthropic's approach stands out through progressive disclosure, composability, and bundled code execution, signalling another step in the competitive race to make AI agents more specialised, efficient, and deployable at scale. AI systems and AI-driven semi-autonomous agents like Claude Skills are still vulnerable to security breaches and require very strict oversight, especially when dealing with sensitive and important information. Additionally, persistent long-memory and unspecified data retention policies can raise concerns about what information is stored and reused and for how long. Therefore, the users also face training data risks, as opting in to model improvement can unintentionally expose proprietary content. In a similar vein, prompt injection and data poisoning can manipulate agents or corrupt outputs. Third-party integrations widen the attack surface, while insider misuse remains a major source of breaches. Outdated or conflicting Skills can also cause operational errors and security gaps. Despite their advantages, AI agents remain insecure and unreliable without constant monitoring, access controls, and regular audits. This raises further questions: who takes the legal liability if the AI agent fails at the specified task, resulting in financial loss or real-life harm? During an interview with MediaNama for another story, Germaine Pereira, a Partner at Solomon & Co, highlighted a legal grey area, using a hypothetical example of a chatbot employed by an airline company. If an AI-powered system gives passengers false information, such as an incorrect flight delay, and a customer suffers financial loss as a result, she asked, who should be held accountable? The airline that employed an LLM-based chatbot or the AI service provider? For context, MakeMyTrip has already launched Myra, a generative AI travel assistant that lets users plan and book trips via voice, text, image, or video. Currently in beta in English and Hindi, with more languages coming, Myra supports bookings for flights, hotels, holidays, transport, visas, and forex. During MediaNama's roundtable discussion, Governing the AI Ecosystem, Independent consultant Varun Bahl suggested that the manufacturer or developer of the product of AI agents and chatbots can be held liable. However, another participant, Vishal Singhhal, the co-founder of CellStrat.ai, argued back, saying that customer negligence, like weak or imperfect prompting, can act in the manufacturer's defence in avoiding legal liability.
[12]
AI Tools That Work Like Pros: Discover the Future of Task Management
What if artificial intelligence could follow instructions as carefully as a seasoned professional, making sure precision, consistency, and efficiency every time? This isn't a far-off dream, it's the reality being shaped by tools like Anthropic's Claude Skills. By adapting the time-tested principles of standard operating procedures (SOPs) for AI agents, Claude Skills are redefining how tasks are executed in industries ranging from healthcare to finance. Imagine an AI agent that not only understands your goals but also executes them with the same clarity and reliability as a well-trained team member. This shift is more than just a technical upgrade; it's a bold reimagining of how humans and machines collaborate to tackle complex challenges. In this overview, Sam Witteveen explores how Claude Skills bring structured workflows to the forefront of AI functionality, offering a modular and customizable framework that's as versatile as it is powerful. You'll discover how these tools streamline repetitive tasks, enhance operational accuracy, and adapt to unique business needs. From pre-built solutions for everyday challenges to custom workflows tailored for niche applications, Claude Skills exemplify the potential of merging human ingenuity with machine efficiency. As we unpack the fantastic implications of SOPs in AI, consider this: could structured workflows be the key to unlocking the next era of intelligent systems? Standard operating procedures (SOPs) have long been a foundational element in business operations, making sure consistency, reducing errors, and maintaining quality. These structured workflows provide clear, repeatable instructions that allow teams to execute tasks efficiently and reliably. When applied to AI, SOPs serve a similar purpose: they guide AI agents through predefined workflows, making sure predictable and dependable outcomes. This structured approach is especially critical as AI systems are increasingly deployed in complex operational environments. By embedding SOPs into AI workflows, organizations can achieve greater accuracy, efficiency, and scalability. This is particularly valuable in industries where precision and consistency are non-negotiable, such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing. Anthropic's Claude Skills represent a significant step in adapting the principles of SOPs for AI agents. These skills are task-specific modules that include instructions, scripts, and resources designed to streamline execution. They are built to be flexible and modular, allowing users to compose, stack, and port them across various applications. Claude Skills can be accessed through the Claude chat interface or integrated via API, making them versatile tools for a wide range of use cases. By providing AI agents with structured workflows, these skills enable more precise and efficient task execution. Whether automating repetitive tasks or managing complex processes, Claude Skills are designed to enhance the functionality and reliability of AI systems. Check out more relevant guides from our extensive collection on Claude Code that you might find useful. To cater to a variety of use cases, Anthropic offers pre-built skills for common tasks such as working with Excel, creating presentations, and formatting documents. These pre-built options provide immediate solutions for frequently encountered challenges, saving time and effort for users. For more specialized requirements, the Skill Creator tool allows users to design custom workflows. This tool generates "Skill MD" files, which can include tailored prompts, coding, and instructions to meet specific operational demands. By allowing customization, Claude Skills can adapt to unique business needs, making them suitable for industries with specialized workflows or niche applications. Claude Skills are designed for seamless integration with Claude's API and backend tools. Each skill includes a name, description, and structured steps, making sure clarity and ease of use. A standout feature of this system is token conservation, which optimizes processing efficiency by managing context effectively. This is particularly advantageous in scenarios involving resource constraints or high-volume tasks, where efficiency is paramount. The structured nature of Claude Skills ensures that AI agents can execute tasks with minimal errors and maximum precision. By incorporating clear instructions and resource management, these skills enable AI systems to handle complex workflows with ease, making them a valuable asset in both small-scale and enterprise-level operations. Claude Skills are part of a broader ecosystem of AI tools, sharing similarities with features like Claude Code Plugins and Google's Gemini CLI Extensions. These tools enhance AI agent performance by providing contextual coding capabilities and command-line integrations. Additionally, plugin marketplaces offer repositories of tools that expand the functionality of AI platforms, allowing users to access a wide range of pre-built solutions. However, differences in API capabilities among providers such as OpenAI, Google, and Anthropic highlight the varied approaches to AI development. While some platforms focus on general-purpose tools, others prioritize specialized features like token conservation or modular workflows. These distinctions underscore the importance of selecting the right tools based on specific operational needs and objectives. Anthropic's skill repository includes both open source (Apache 2) and proprietary licenses, striking a balance between accessibility and intellectual property protection. This dual licensing model encourages community contributions while safeguarding proprietary innovations. Open source contributions, in particular, have the potential to accelerate innovation by fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing. The development of community-driven repositories featuring "awesome skills" could further expand the range of available workflows. Such collaborative efforts would not only benefit individual users but also contribute to the growth of the broader AI ecosystem, allowing the creation of more advanced and versatile tools. The introduction of Claude Skills reflects a broader trend toward integrated AI ecosystems. These platforms are evolving into comprehensive environments capable of hosting applications and performing agentic tasks. As this evolution continues, the need to protect proprietary skills and user-generated content will likely grow. At the same time, the application of SOPs in AI workflows opens new avenues for innovation. By allowing AI agents to tackle increasingly complex challenges, SOPs are helping to bridge the gap between human expertise and machine efficiency. This convergence of structured workflows and advanced AI capabilities is poised to redefine how organizations approach problem-solving and operational management. Claude Skills represent a significant advancement in applying structured workflows to AI agents. By adapting the principles of SOPs, Anthropic has created a tool that enhances efficiency, precision, and adaptability. As AI ecosystems continue to expand, tools like Claude Skills will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of intelligent systems. Whether through pre-built solutions or customized workflows, these innovations highlight the fantastic potential of AI across industries. By combining the reliability of SOPs with the flexibility of AI, Claude Skills are setting a new standard for operational excellence in the digital age.
Share
Share
Copy Link
Anthropic introduces Skills for Claude, a feature allowing users to create custom instruction sets for the AI chatbot. This development aims to make Claude more adaptable to specific user needs and workflows.
Anthropic Introduces Skills for Claude
Anthropic has unveiled a groundbreaking feature called 'Skills for Claude,' designed to enhance the customization and efficiency of its AI chatbot for individual users and businesses
1
2
. This new tool allows users to create and upload custom instruction sets, enabling Claude to become a specialist in specific tasks or domains1
.
Source: Digital Trends
How Skills Work
Skills are essentially digital instruction manuals that guide Claude's behavior for particular tasks
1
. They consist of folders containing instructions, scripts, and resources that Claude can load when needed4
. The AI automatically determines which Skills to use based on the user's prompt, streamlining the interaction process1
.Technical Implementation
Anthropic employs a 'progressive disclosure' approach, where Claude initially sees only skill names and brief descriptions, then autonomously decides which skills to load based on the task
5
. This method allows for efficient token usage and keeps operating costs down3
.
Source: The Verge
Applications and Benefits
Skills can be applied to various tasks, from generating Word documents and Excel spreadsheets to following specific brand guidelines
1
4
. This feature is particularly beneficial for businesses seeking to integrate AI into their workflows while maintaining consistency and efficiency5
.Related Stories
Availability and Security Considerations
Skills for Claude is available to Pro, Max, Team, and Enterprise users across various Claude platforms
2
4
. However, Anthropic warns users to be cautious about the Skills they implement, as malicious Skills could potentially introduce vulnerabilities or allow data exfiltration3
.Industry Impact
The introduction of Skills for Claude represents a significant step towards more personalized and efficient AI assistants in the workplace. It positions Anthropic competitively in the AI market, alongside developments from companies like OpenAI and Microsoft
2
5
.References
Summarized by
Navi
[3]
[4]
Related Stories
Recent Highlights
1
Google Gemini 3.1 Pro doubles reasoning score, beats rivals in key AI benchmarks
Technology

2
Meta strikes up to $100 billion AI chips deal with AMD, could acquire 10% stake in chipmaker
Technology

3
Pentagon threatens Anthropic with supply chain risk label over AI safeguards for military use
Policy and Regulation








