NVIDIA Accelerates Next-Gen 'Rubin' AI GPU Launch, Featuring Advanced 3nm Process and HBM4 Technology
4 Sources
4 Sources
[1]
Nvidia Blackwell chip successor "Rubin" moves forward by six months, uses 3nm manufacturing and HBM4
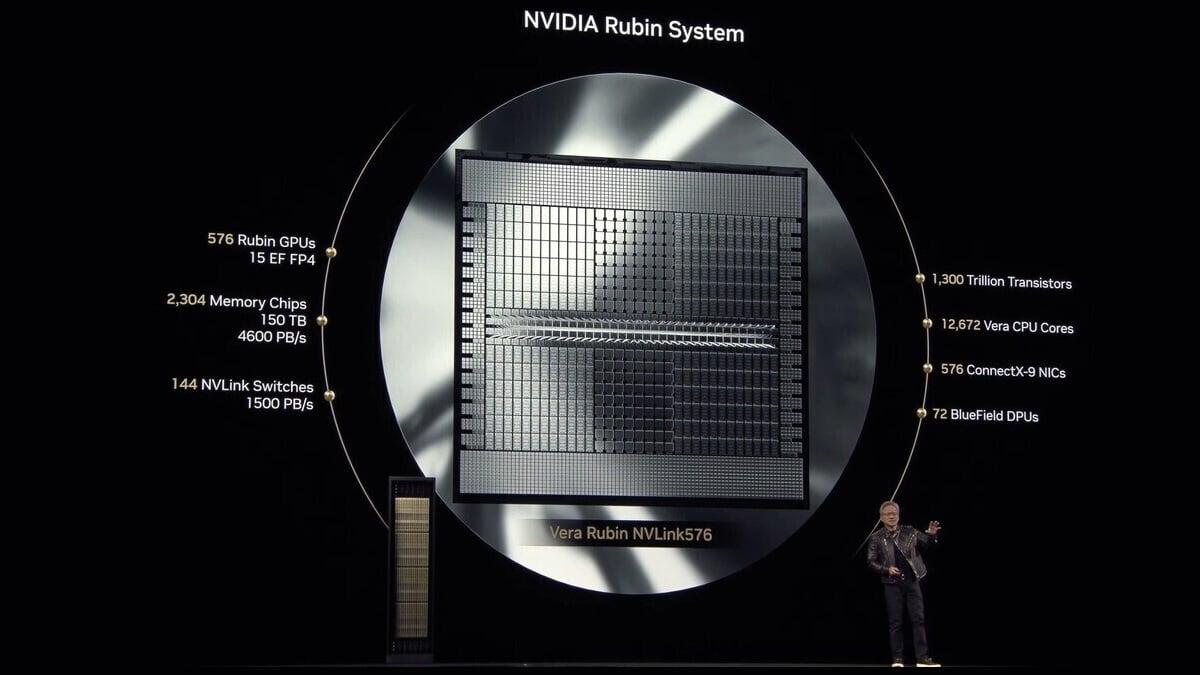
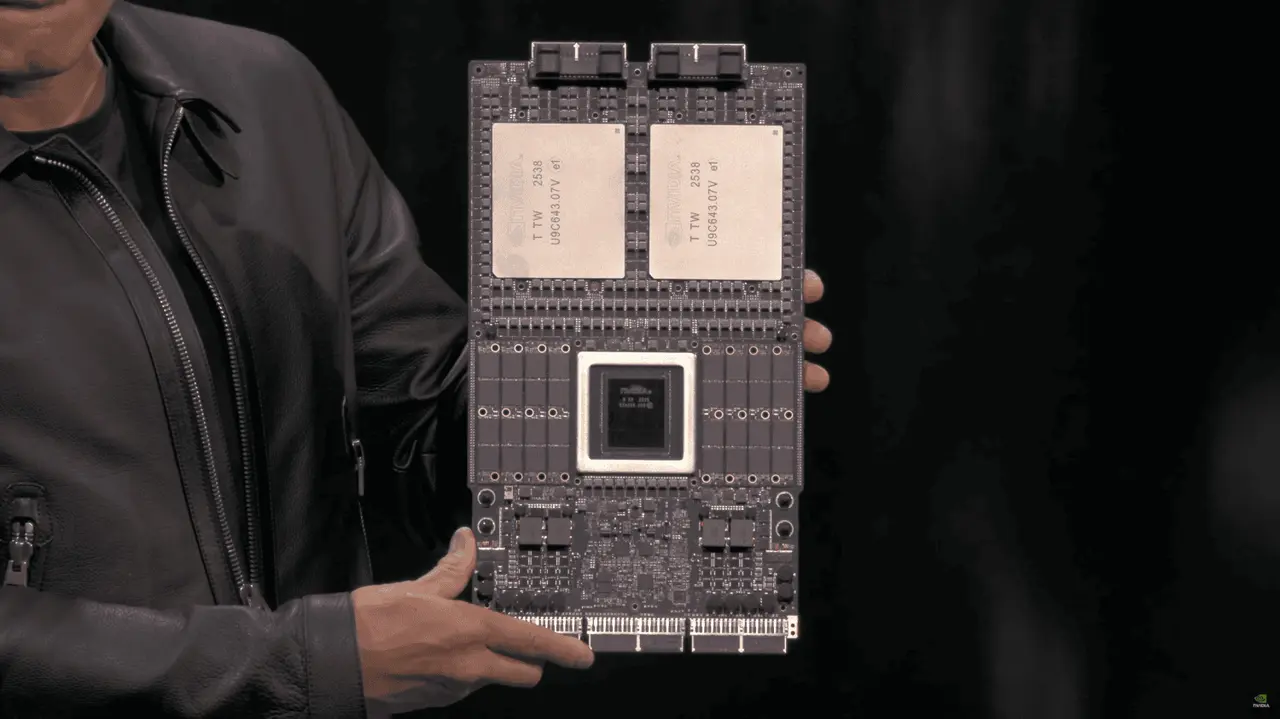
In brief: The immense demand for Nvidia's AI data center GPUs has sent the company into the stratosphere over the last few years, putting it in seesaw competition with Apple for the title of the most valuable firm on Earth. As Nvidia emerges from the production problems that delayed the Blackwell GPU launch, new reports indicate that its successor is significantly ahead of schedule. According to the Taiwan Economic Daily, Nvidia's Rubin series AI graphics chips will be available in the second half of 2025, half a year earlier than previously reported. Although details regarding performance improvements are slim, the new GPUs will feature more advanced memory and a newer semiconductor process node than Blackwell, which is set to launch soon. Prior roadmaps from Nvidia pegged the new architecture, named after American astronomer Vera Rubin, for release sometime in 2026. However, the chipmaker, manufacturing partner TSMC, and other supply chain participants have accelerated the lineup's development and implementation. A Morgan Stanley Semiconductor analyst told the Economic Daily that Rubin represents Nvidia's shift toward TSMC's 3nm N3 process node, which could significantly improve performance. The new chips will also upgrade to HBM4 memory, substantially boosting memory bandwidth. If the reports prove accurate, this could feel like a reversal of the delays that pushed Blackwell's implementation into the first quarter of 2025. The GB200 series, now entering mass production, encountered late-stage design flaws and currently suffers from overheating issues. Despite the setbacks, Blackwell chips are sold out through late 2025, as tech giants like Microsoft, Google, and Meta have spent billions to acquire them. The delays occurred partly due to challenges with TSMC's CoWoS-L packaging technology. The manufacturer is expected to significantly expand CoWoS production with Rubin, though its possible effects on the Blackwell successor's rollout remain unclear. The impact on GB300, previously called Blackwell Ultra, is another mystery. The upgraded lineup is set for a late 2025 debut, coinciding with Rubin's new release window. Prior reports indicate that Nvidia is considering moving to a socketed design for GB300, which might compromise performance in exchange for streamlining the production and upgrade pipelines. However, the lineup's introduction of FP4 is expected to boost demand considerably. Meanwhile, competitors like AMD and Intel are preparing to answer GB300 and Rubin with upcoming architectures like MI300 and Falcon Shores, also based on N3.
[2]
NVIDIA's next-gen Rubin AI GPU could be pushed up 6 months ahead of schedule with HBM4
NVIDIA's next-generation Rubin AI GPU architecture release rumored to be pulled up by 6 months, TSMC 3nm process expected, with ultra-fast next-gen HBM4 memory. The new Rubin AI GPU architecture is the successor to the Blackwell GPU architecture, which is being used in the current fleet of B200 and GB200 chips, as well as the future GB300 series AI GPU that we're hearing more and more about lately. In a new report from UDN, we're hearing that NVIDIA is already working with supply chain partners in Taiwan on the Rubin AI GPU architecture and its new R100-powered AI servers. Rubin was originally scheduled for 2026, but sources of UDN say that the company has launched the development of Rubin early, so that the AI boom can continue from one AI GPU chip to another (Blackwell to Rubin, and so on). TSMC is a key partner of the triangular alliance between NVIDIA + SK hynix + TSMC, with the company expected to expand its CoWoS advanced packaging capacity in 2026 to handle the large Rubin chip demand. TSMC plans to increase CoWoS production capacity to 80,000 pieces per month by Q4 2025 in preparation of Rubin.
[3]
NVIDIA's Next-Gen "Rubin" Architecture Is Now Rumored To Be Released By "Six Months" Ahead of Schedule
NVIDIA's "next-gen" Rubin architecture is now rumored to be available "six months" ahead of schedule as Team Green also looks to capture the upcoming AI markets. There's no stopping NVIDIA now, given that the firm is committed more than ever to maintaining dominance in the AI markets. Even though the Blackwell architecture has only seen a few weeks of the official launch, the industry is already talking about the next-gen Rubin AI lineup, which shows that NVIDIA is indeed more determined than ever to impact the industry. In a report by Taiwan Economic Daily, Team Green is now said to be releasing the Rubin architecture ahead of schedule, accelerating cadence between architectures. The Rubin lineup, initially scheduled for 2026, has now been pushed back to mid-2025. This gives NVIDIA the opportunity to advance much more quickly than its competitors, ultimately allowing the firm to maintain its dominance over the markets. For those unaware, NVIDIA is currently in a "one-year" cadence plan, which means that the company will release a new generation after each year, which is why Ampere, Hopper, and Blackwell are all separated by year intervals; however, Rubin, this might change. Reports don't mention a specific reason for why NVIDIA's Rubin will be launched early on, apart from categorizing it as a business move. However, if we look at the supply chain, Rubin is expected to feature TSMC's 3nm process, along with the cutting-edge HBM4 memory chips. Both of these components are either in their mass production stages or about to enter them. Given that NVIDIA has all the "tools" for Rubin available, the company may not feel it right to release Rubin in 2026. Previously, we reported on the debut of NVIDIA's "Blackwell Ultra" lineup or the "B300" series, where it was claimed that Team Green plans to release it by mid-2025. So, by this, we might expect Blackwell Ultra and Rubin to drop in similar timelines, although the release strategy isn't specific for now since, with Rubin, NVIDIA might potentially overshadow the B300 series. We expect further updates from the company soon, probably around CES 2025.
[4]
Nvidia Next gen Rubin GPU Release based on Enhanced TSMC 3nm Process and HBM4 Technology
Nvidia has moved up the release date for its Rubin GPU, now scheduled to launch in the latter half of 2025, six months earlier than the previously planned 2026. The Rubin architecture, succeeding Nvidia's Blackwell series, is engineered to provide advanced artificial intelligence (AI) computing performance. This GPU will feature Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company's (TSMC) latest 3-nanometer (nm) process technology and High Bandwidth Memory 4 (HBM4), which are expected to significantly improve computational efficiency and memory bandwidth necessary for complex AI tasks. To support the early launch, Nvidia is working closely with supply chain partners, including TSMC, to accelerate the development of the Rubin platform. This collaboration aims to meet the increasing demand for high-performance AI hardware and help Nvidia maintain its leadership position in the AI market. The use of TSMC's 3nm process technology is set to enhance the GPU's performance and energy efficiency, while the integration of HBM4 memory will provide the high data transfer rates required for demanding AI applications. In anticipation of the higher production requirements for the Rubin GPU, TSMC is expanding its Chip on Wafer on Substrate (CoWoS) advanced packaging facilities. The company plans to increase its monthly production capacity to 80,000 units by the fourth quarter of 2025. Source: ithome
Share
Share
Copy Link
NVIDIA is set to release its next-generation 'Rubin' AI GPU architecture six months ahead of schedule, leveraging TSMC's 3nm process and HBM4 memory technology. This move aims to maintain NVIDIA's dominance in the AI chip market amidst growing demand and competition.

NVIDIA Accelerates 'Rubin' GPU Development
NVIDIA, the leading AI chip manufacturer, is reportedly fast-tracking the development of its next-generation 'Rubin' GPU architecture. Originally slated for a 2026 release, the new AI chips are now expected to hit the market in the second half of 2025, a full six months ahead of schedule
1
2
. This acceleration comes as NVIDIA seeks to maintain its dominance in the rapidly evolving AI hardware market.Advanced Technology Integration
The Rubin architecture, named after American astronomer Vera Rubin, will incorporate cutting-edge technologies to push the boundaries of AI computing performance:
-
TSMC 3nm Process: Rubin will utilize Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company's (TSMC) advanced 3-nanometer (nm) process technology, promising significant improvements in performance and energy efficiency
3
4
. -
HBM4 Memory: The new GPUs will feature High Bandwidth Memory 4 (HBM4), substantially boosting memory bandwidth to meet the demands of complex AI tasks
1
3
.
Supply Chain Collaboration
To support the accelerated launch, NVIDIA is working closely with its supply chain partners:
- TSMC is expanding its Chip on Wafer on Substrate (CoWoS) advanced packaging facilities, aiming to increase monthly production capacity to 80,000 units by Q4 2025
2
4
. - SK hynix is part of the "triangular alliance" with NVIDIA and TSMC, likely contributing to the HBM4 memory production
2
.
Market Implications
The early release of Rubin has several potential impacts on the AI chip market:
-
Competitive Advantage: By accelerating its product cycle, NVIDIA aims to stay ahead of competitors like AMD and Intel, who are developing their own advanced AI architectures
1
. -
AI Boom Continuation: The faster release cycle could help sustain the ongoing AI boom by providing more powerful hardware to tech giants and researchers
2
. -
Blackwell and GB300 Overlap: The accelerated Rubin timeline may overlap with the release of NVIDIA's GB300 (Blackwell Ultra) series, scheduled for late 2025
1
3
.
Related Stories
Current Generation Challenges
While NVIDIA pushes forward with Rubin, its current Blackwell architecture faces some hurdles:
- The GB200 series encountered late-stage design flaws and overheating issues, delaying its mass production
1
. - Despite these setbacks, Blackwell chips are sold out through late 2025, with major tech companies investing billions in acquisitions
1
.
Industry Outlook
As NVIDIA accelerates its development cycle, the AI chip industry is poised for intense competition:
- AMD and Intel are preparing to challenge NVIDIA with their upcoming MI300 and Falcon Shores architectures, also based on TSMC's 3nm process
1
. - The rapid advancement in AI hardware is expected to drive further innovation in AI applications and research across various sectors.
With the Rubin architecture's early arrival, NVIDIA is sending a clear message about its commitment to maintaining leadership in the AI chip market, setting the stage for the next phase of AI hardware evolution.
References
Summarized by
Navi
[1]
[3]
Related Stories
Recent Highlights
1
Samsung unveils Galaxy S26 lineup with Privacy Display tech and expanded AI capabilities
Technology

2
Anthropic refuses Pentagon's ultimatum over AI use in mass surveillance and autonomous weapons
Policy and Regulation

3
AI models deploy nuclear weapons in 95% of war games, raising alarm over military use
Science and Research