OpenAI reveals how AI agents protect users from malicious links as automated browsing expands
2 Sources
2 Sources
[1]
OpenAI explains how its AI agents avoid malicious links
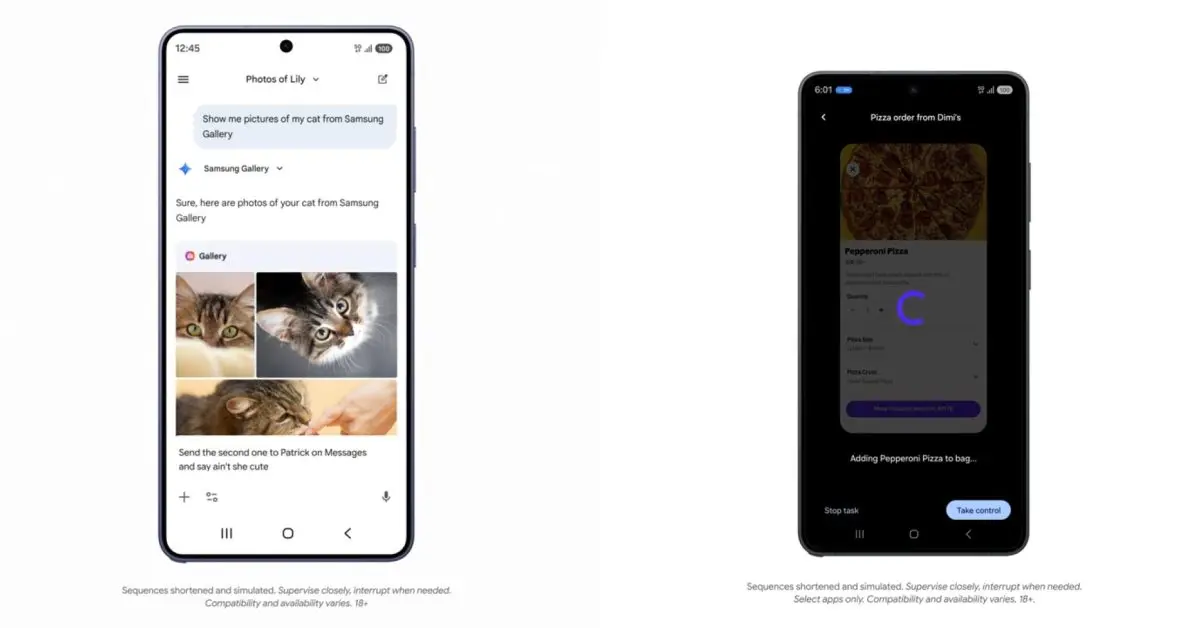
AI agents can perform tasks on behalf of the user, and this often involves controlling a web browser, sorting through emails, and interacting with the internet at large. And since there are lots of places on the internet that can steal your personal data or otherwise cause harm, it's important that these agents know what they're doing. So, as users migrate away from web browsers and Google Search to AI browsers and agents, AI companies like OpenAI need to make sure these tools don't fall straight into a phishing attempt or click on malicious links. In a new blog post, OpenAI explains exactly how its AI agents protect users. One possible solution to this problem would be for OpenAI to simply adopt a curated list of trusted websites its agents are allowed to access. However, as the company explained in the blog post, that would probably be too limiting and would harm the user experience. Instead, OpenAI uses something called an independent web index, which records public URLs that are already known to exist on the internet, independent of any user data. So, if a URL is on the index, then the AI agent can open it without a problem. If not, the user will see a warning asking for their permission to move forward. As OpenAI explains in its blog post, "This shifts the safety question from 'Do we trust this site?' to 'Has this specific address appeared publicly on the open web in a way that doesn't depend on user data?'" You can see a more technical explainer in a lengthy research paper OpenAI published last year, but the main thing to know is that it's possible for web pages to manipulate AI agents into doing things they shouldn't do. A common form of this is prompt injection, which gives clandestine instructions to the AI model, asking it to retrieve sensitive data or otherwise compromise your cybersecurity. To be clear, as OpenAI states in the blog post, this is just one layer of security that doesn't necessarily guarantee that what you're about to click on is entirely safe. Websites can contain social engineering or other bad-faith constructs that an AI agent wouldn't necessarily be able to notice.
[2]
OpenAI Warns Malicious Links Could Undermine Agentic AI | PYMNTS.com
In new guidance on artificial intelligence (AI) agent link safety, the company said on Wednesday (Jan. 29) that malicious links are emerging as one of the most exploitable surfaces as agents move beyond conversation into action. The concern is not abstract. As AI agents increasingly browse the web, retrieve information and complete tasks on behalf of users, links become gateways that can expose sensitive data or manipulate behavior if left unchecked. The warning comes at a moment when AI usage is becoming habitual. PYMNTS Intelligence data shows that more than 60% of consumers now start at least one daily task with AI. As autonomy increases, so does the cost of failure. OpenAI's position is that links should be treated as a core security risk for agentic systems, on par with prompts and permissions. That framing reflects a broader shift in how AI safety is being operationalized as these systems move closer to commerce, payments and enterprise workflows. In traditional browsing, humans decide whether to click a link and implicitly accept the risk. In agentic AI, that decision can be automated. An AI agent researching a product, managing a workflow or completing a transaction may encounter dozens of links in a single task. If even one of those links is malicious, the system can be manipulated into revealing information or taking actions the user never intended. OpenAI highlights the risk of malicious links that embed hidden instructions or deceptive redirects inside web content. When an AI agent consumes that content, it may treat those instructions as legitimate context rather than as an attack. This is especially dangerous when agents have access to tools, credentials or downstream systems. The problem scales with adoption. PYMNTS research shows that consumer trust in AI handling transactions is uneven, with a majority of shoppers saying they trust banks more than retailers to let AI buy on their behalf. That trust is fragile. A single high-profile failure tied to unsafe automation could slow adoption across entire categories. To address the risk, OpenAI outlines a layered approach designed to reduce exposure without undermining usability. One core safeguard is link transparency. AI agents are trained to distinguish between links that already exist publicly on the open web and links that are introduced or modified within a conversation. If a link cannot be independently verified as preexisting, the system treats it as higher risk. This verification step helps prevent attackers from injecting custom URLs designed to capture sensitive data or trigger unintended behavior. Instead of silently following such links, the agent pauses and surfaces the decision to the user. OpenAI also applies constrained browsing, limiting what agents are allowed to do automatically when interacting with external content. Rather than granting blanket permission to fetch or execute actions from any link, the system narrows the scope of autonomous behavior. This reduces the chance that a single malicious page can cascade into broader compromise. For actions that involve elevated risk, OpenAI requires explicit human approval. If an agent encounters ambiguity or a task that could expose private information or initiate a meaningful action, it does not proceed on its own. This introduces friction by design, reinforcing the idea that autonomy should expand only where confidence is high. The company is transparent that these safeguards do not eliminate risk entirely. Instead, they are meant to make attacks harder, more visible and easier to interrupt. That tradeoff is intentional.
Share
Share
Copy Link
OpenAI has detailed its security approach for AI agents that browse the web and complete tasks autonomously. As more than 60% of consumers now start at least one daily task with AI, the company warns that malicious links pose serious risks. OpenAI uses link transparency, constrained browsing, and human approval to protect users from phishing attempts and data exposure.
OpenAI Addresses Growing Security Risks from Malicious Links
As AI agents move beyond simple conversation into autonomous action, OpenAI has outlined how it protects users from one of the most exploitable vulnerabilities: malicious links. In guidance released Wednesday, the company explained that AI agents increasingly browse the web, retrieve information, and complete tasks on behalf of users, making URLs potential gateways for data exposure and behavioral manipulation
2
. The warning arrives as PYMNTS Intelligence data shows more than 60% of consumers now start at least one daily task with AI, signaling that autonomy is becoming habitual and the cost of failure is rising2
.
Source: PYMNTS
How AI Agents Safeguard Users Through Link Transparency
Rather than limiting AI agents to a curated list of trusted websites, which would harm user experience, OpenAI employs an independent web index that records public URLs already known to exist on the internet, independent of user data
1
. If a URL appears on the index, the AI agent can access it without issue. If not, the system triggers a warning that requires user permission for URLs before proceeding1
. This approach shifts the security question from "Do we trust this site?" to "Has this specific address appeared publicly on the open web in a way that doesn't depend on user data?"1
. AI agents are trained to distinguish between links that already exist publicly and those introduced or modified within a conversation, treating unverifiable links as higher risk2
.Prompt Injection and Automated Web Browsing Threats
OpenAI highlights specific dangers facing agentic AI systems, particularly prompt injection attacks where web pages embed hidden instructions that manipulate AI models into retrieving sensitive data or compromising cybersecurity
1
. In traditional browsing, humans decide whether to click a link and accept the risk. With automated web browsing, that decision can be automated, and an AI agent researching a product or managing a workflow may encounter dozens of links in a single task2
. If even one link is malicious, the system can be manipulated into revealing information or taking unintended actions. This risk scales with adoption, especially as agents gain access to tools, credentials, and downstream systems.Related Stories
Multi-Layered Security Approach With Constrained Browsing
OpenAI has implemented constrained browsing that limits what agents can do automatically when interacting with external content
2
. Rather than granting blanket permission to fetch or execute actions from any link, the system narrows the scope of autonomous behavior, reducing the chance that a single malicious page cascades into broader compromise. For actions involving elevated risk, OpenAI requires explicit human approval2
. If an agent encounters ambiguity or a task that could expose private information or initiate meaningful action, it does not proceed independently. This introduces friction by design, reinforcing that autonomy should expand only where confidence is high.Consumer Trust and Remaining Vulnerabilities
The stakes are significant as consumer trust in AI handling transactions remains uneven. PYMNTS research shows a majority of shoppers trust banks more than retailers to let AI buy on their behalf, and that trust is fragile
2
. A single high-profile failure tied to unsafe automation could slow adoption across entire categories. OpenAI acknowledges that these safeguards represent just one layer of security and do not guarantee complete safety1
. Websites can still contain social engineering or other bad-faith constructs that an AI agent might not notice1
. The company is transparent that these measures are meant to make attacks harder, more visible, and easier to interrupt rather than eliminate risk entirely2
. As users migrate from traditional web browsers to AI browsers and agents, OpenAI positions links as a core security risk for agentic systems, on par with prompts and permissions, reflecting how AI safety is being operationalized as these systems move closer to commerce, payments, and enterprise workflows.References
Summarized by
Navi
Related Stories
AI Browsers Face Critical Security Crisis as Prompt Injection Attacks Expose User Data
30 Oct 2025•Technology

AI Agents Under Siege: New Era of Cybersecurity Threats Emerges as Autonomous Systems Face Sophisticated Attacks
11 Nov 2025•Technology

Microsoft warns AI agents with excessive privileges can become insider threats to enterprises
12 Feb 2026•Technology

Recent Highlights
1
Pentagon threatens Anthropic with Defense Production Act over AI military use restrictions
Policy and Regulation

2
Google Gemini 3.1 Pro doubles reasoning score, beats rivals in key AI benchmarks
Technology

3
Anthropic accuses Chinese AI labs of stealing Claude through 24,000 fake accounts
Policy and Regulation