Self-Powered Artificial Synapse Mimics Human Color Vision for Edge AI Devices
5 Sources
5 Sources
[1]
Self-powered artificial synapse mimics human color vision
As artificial intelligence and smart devices continue to evolve, machine vision is taking an increasingly pivotal role as a key enabler of modern technologies. Unfortunately, despite much progress, machine vision systems still face a major problem: processing the enormous amounts of visual data generated every second requires substantial power, storage, and computational resources. This limitation makes it difficult to deploy visual recognition capabilities in edge devices -- such as smartphones, drones, or autonomous vehicles. Interestingly, the human visual system offers a compelling alternative model. Unlike conventional machine vision systems that have to capture and process every detail, our eyes and brain selectively filter information, allowing for higher efficiency in visual processing while consuming minimal power. Neuromorphic computing, which mimics the structure and function of biological neural systems, has thus emerged as a promising approach to overcome existing hurdles in computer vision. However, two major challenges have persisted. The first is achieving color recognition comparable to human vision, whereas the second is eliminating the need for external power sources to minimize energy consumption. Against this backdrop, a research team led by Associate Professor Takashi Ikuno from the School of Advanced Engineering, Department of Electronic Systems Engineering, Tokyo University of Science (TUS), Japan, has developed a groundbreaking solution. Their paper, published in Volume 15 of the journal Scientific Reports on May 12, 2025, introduces a self-powered artificial synapse capable of distinguishing colors with remarkable precision. The study was co-authored by Mr. Hiroaki Komatsu and Ms. Norika Hosoda, also from TUS. The researchers created their device by integrating two different dye-sensitized solar cells, which respond differently to various wavelengths of light. Unlike conventional optoelectronic artificial synapses that require external power sources, the proposed synapse generates its electricity via solar energy conversion. This self-powering capability makes it particularly suitable for edge computing applications, where energy efficiency is crucial. As evidenced through extensive experiments, the resulting system can distinguish between colors with a resolution of 10 nanometers across the visible spectrum -- a level of discrimination approaching that of the human eye. Moreover, the device also exhibited bipolar responses, producing positive voltage under blue light and negative voltage under red light. This makes it possible to perform complex logic operations that would typically require multiple conventional devices. "The results show great potential for the application of this next-generation optoelectronic device, which enables high-resolution color discrimination and logical operations simultaneously, to low-power artificial intelligence (AI) systems with visual recognition," notes Dr. Ikuno. To demonstrate a real-world application, the team used their device in a physical reservoir computing framework to recognize different human movements recorded in red, green, and blue. The system achieved an impressive 82% accuracy when classifying 18 different combinations of colors and movements using just a single device, rather than the multiple photodiodes needed in conventional systems. The implications of this research extend across multiple industries. In autonomous vehicles, these devices could enable more efficient recognition of traffic lights, road signs, and obstacles. In healthcare, they could power wearable devices that monitor vital signs like blood oxygen levels with minimal battery drain. For consumer electronics, this technology could lead to smartphones and augmented/virtual reality headsets with dramatically improved battery life while maintaining sophisticated visual recognition capabilities. "We believe this technology will contribute to the realization of low-power machine vision systems with color discrimination capabilities close to those of the human eye, with applications in optical sensors for self-driving cars, low-power biometric sensors for medical use, and portable recognition devices," remarks Dr. Ikuno. Overall, this work represents a significant step toward bringing the wonders of computer vision to edge devices, enabling our everyday devices to see the world more like we do.
[2]
Self-powered artificial synapse brings human-like color vision to edge devices
Tokyo University of ScienceJun 2 2025 As artificial intelligence and smart devices continue to evolve, machine vision is taking an increasingly pivotal role as a key enabler of modern technologies. Unfortunately, despite much progress, machine vision systems still face a major problem: processing the enormous amounts of visual data generated every second requires substantial power, storage, and computational resources. This limitation makes it difficult to deploy visual recognition capabilities in edge devices-such as smartphones, drones, or autonomous vehicles. Interestingly, the human visual system offers a compelling alternative model. Unlike conventional machine vision systems that have to capture and process every detail, our eyes and brain selectively filter information, allowing for higher efficiency in visual processing while consuming minimal power. Neuromorphic computing, which mimics the structure and function of biological neural systems, has thus emerged as a promising approach to overcome existing hurdles in computer vision. However, two major challenges have persisted. The first is achieving color recognition comparable to human vision, whereas the second is eliminating the need for external power sources to minimize energy consumption. Against this backdrop, a research team led by Associate Professor Takashi Ikuno from the School of Advanced Engineering, Department of Electronic Systems Engineering, Tokyo University of Science (TUS), Japan, has developed a groundbreaking solution. Their paper, published in Volume 15 of the journal Scientific Reports on May 12, 2025, introduces a self-powered artificial synapse capable of distinguishing colors with remarkable precision. The study was co-authored by Mr. Hiroaki Komatsu and Ms. Norika Hosoda, also from TUS. The researchers created their device by integrating two different dye-sensitized solar cells, which respond differently to various wavelengths of light. Unlike conventional optoelectronic artificial synapses that require external power sources, the proposed synapse generates its electricity via solar energy conversion. This self-powering capability makes it particularly suitable for edge computing applications, where energy efficiency is crucial. As evidenced through extensive experiments, the resulting system can distinguish between colors with a resolution of 10 nanometers across the visible spectrum-a level of discrimination approaching that of the human eye. Moreover, the device also exhibited bipolar responses, producing positive voltage under blue light and negative voltage under red light. This makes it possible to perform complex logic operations that would typically require multiple conventional devices. "The results show great potential for the application of this next-generation optoelectronic device, which enables high-resolution color discrimination and logical operations simultaneously, to low-power artificial intelligence (AI) systems with visual recognition," notes Dr. Ikuno. To demonstrate a real-world application, the team used their device in a physical reservoir computing framework to recognize different human movements recorded in red, green, and blue. The system achieved an impressive 82% accuracy when classifying 18 different combinations of colors and movements using just a single device, rather than the multiple photodiodes needed in conventional systems. The implications of this research extend across multiple industries. In autonomous vehicles, these devices could enable more efficient recognition of traffic lights, road signs, and obstacles. In healthcare, they could power wearable devices that monitor vital signs like blood oxygen levels with minimal battery drain. For consumer electronics, this technology could lead to smartphones and augmented/virtual reality headsets with dramatically improved battery life while maintaining sophisticated visual recognition capabilities. "We believe this technology will contribute to the realization of low-power machine vision systems with color discrimination capabilities close to those of the human eye, with applications in optical sensors for self-driving cars, low-power biometric sensors for medical use, and portable recognition devices," remarks Dr. Ikuno. Overall, this work represents a significant step toward bringing the wonders of computer vision to edge devices, enabling our everyday devices to see the world more like we do. Tokyo University of Science Journal reference: Komatsu, H., et al. (2025). Polarity-tunable dye-sensitized optoelectronic artificial synapses for physical reservoir computing-based machine vision. Scientific Reports. doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-00693-0.
[3]
Self-Powered Synapse Brings Human-Like Vision to AI Devices - Neuroscience News
Summary: Researchers have developed a self-powered artificial synapse capable of color recognition with near-human precision. Unlike traditional systems that demand external energy and massive data processing, this device mimics biological vision and generates its own electricity using solar cells. It can distinguish colors with 10-nanometer resolution and enables logic functions based on light wavelengths. The innovation paves the way for low-power, high-performance machine vision in edge devices like smartphones, wearables, and autonomous vehicles. As artificial intelligence and smart devices continue to evolve, machine vision is taking an increasingly pivotal role as a key enabler of modern technologies. Unfortunately, despite much progress, machine vision systems still face a major problem: processing the enormous amounts of visual data generated every second requires substantial power, storage, and computational resources. This limitation makes it difficult to deploy visual recognition capabilities in edge devices -- such as smartphones, drones, or autonomous vehicles. Interestingly, the human visual system offers a compelling alternative model. Unlike conventional machine vision systems that have to capture and process every detail, our eyes and brain selectively filter information, allowing for higher efficiency in visual processing while consuming minimal power. Neuromorphic computing, which mimics the structure and function of biological neural systems, has thus emerged as a promising approach to overcome existing hurdles in computer vision. However, two major challenges have persisted. The first is achieving color recognition comparable to human vision, whereas the second is eliminating the need for external power sources to minimize energy consumption. Against this backdrop, a research team led by Associate Professor Takashi Ikuno from the School of Advanced Engineering, Department of Electronic Systems Engineering, Tokyo University of Science (TUS), Japan, has developed a groundbreaking solution. Their paper, published in Volume 15 of the journal Scientific Reports on May 12, 2025, introduces a self-powered artificial synapse capable of distinguishing colors with remarkable precision. The study was co-authored by Mr. Hiroaki Komatsu and Ms. Norika Hosoda, also from TUS. The researchers created their device by integrating two different dye-sensitized solar cells, which respond differently to various wavelengths of light. Unlike conventional optoelectronic artificial synapses that require external power sources, the proposed synapse generates its electricity via solar energy conversion. This self-powering capability makes it particularly suitable for edge computing applications, where energy efficiency is crucial. As evidenced through extensive experiments, the resulting system can distinguish between colors with a resolution of 10 nanometers across the visible spectrum -- a level of discrimination approaching that of the human eye. Moreover, the device also exhibited bipolar responses, producing positive voltage under blue light and negative voltage under red light. This makes it possible to perform complex logic operations that would typically require multiple conventional devices. "The results show great potential for the application of this next-generation optoelectronic device, which enables high-resolution color discrimination and logical operations simultaneously, to low-power artificial intelligence (AI) systems with visual recognition," notes Dr. Ikuno. To demonstrate a real-world application, the team used their device in a physical reservoir computing framework to recognize different human movements recorded in red, green, and blue. The system achieved an impressive 82% accuracy when classifying 18 different combinations of colors and movements using just a single device, rather than the multiple photodiodes needed in conventional systems. The implications of this research extend across multiple industries. In autonomous vehicles, these devices could enable more efficient recognition of traffic lights, road signs, and obstacles. In healthcare, they could power wearable devices that monitor vital signs like blood oxygen levels with minimal battery drain. For consumer electronics, this technology could lead to smartphones and augmented/virtual reality headsets with dramatically improved battery life while maintaining sophisticated visual recognition capabilities. "We believe this technology will contribute to the realization of low-power machine vision systems with color discrimination capabilities close to those of the human eye, with applications in optical sensors for self-driving cars, low-power biometric sensors for medical use, and portable recognition devices," remarks Dr. Ikuno. Overall, this work represents a significant step toward bringing the wonders of computer vision to edge devices, enabling our everyday devices to see the world more like we do. Funding: This work was partially supported by the JST and the establishment of university fellowships for the creation of science and technology innovation (Grant Number JPMJFS2144). Additional support was provided by the JST SPRING (Grant Number JPMJSP2151). Author: Yoshimasa Iwasaki Source: Tokyo University of Science Contact: Yoshimasa Iwasaki - Tokyo University of Science Image: The image is credited to Neuroscience News Original Research: Open access. "Polarity-tunable dye-sensitized optoelectronic artificial synapses for physical reservoir computing-based machine vision" by Takashi Ikuno et al. Scientific Reports Abstract Polarity-tunable dye-sensitized optoelectronic artificial synapses for physical reservoir computing-based machine vision Conventional machine vision systems process huge time-series data per second, presenting significant challenges for edge-device applications due to limitations in data transfer and storage. Inspired by the human visual system, artificial optoelectronic synapses replicating synaptic responses have emerged as promising solutions. However, achieving color recognition comparable to human vision remains challenging. Moreover, most optoelectronic artificial synapses rely on photocurrent-based operation, producing low current values and necessitating external circuits. This study reports a self-powered optoelectronic artificial synapse capable of distinguishing wavelengths with a resolution of 10 nm by integrating dye-sensitized solar cells. The device exhibits synaptic responses to light pulses and bipolar responses when exposed to different wavelengths. The wavelength-dependent bipolar behavior enables exceptional separation capabilities, achieving six-bit resolution with 64 distinct states and supporting multiple logic operations, including AND, OR, and XOR, within a single device. Additionally, the device leverages distinct responses to red, green, and blue light irradiation for physical reservoir computing, facilitating the classification of color-coded human motion with an accuracy of 82%. These findings advance the development of optoelectronic artificial synapses for precise, human-eye-like color discrimination.
[4]
Color-smart AI device mimics human eye, powers with solar energy
The research team at the Tokyo University of Science developed the self-powered optoelectronic device, which operates entirely on light, to address the high power, storage and computational demands of current machine vision systems. Led by Associate Professor Takashi Ikuno, PhD, from the Department of Electronic Systems Engineering at the university's School of Advanced Engineering, the study was inspired by the human visual system, which they say is highly efficient at filtering visual data. "The results show great potential for the application of this next-generation optoelectronic device, which enables high-resolution color discrimination and logical operations simultaneously, to low-power artificial intelligence (AI) systems with visual recognition," Ikuno explained. The device reportedly mimics the way biological synapses, which are specialized connections between two neurons or between a neuron and a target cell, react to visual stimuli. The difference, according to the researchers, is that it runs completely on sunlight. For the research, the team integrated two dye-sensitized solar sells (DSSCs), and engineered each to respond to different wavelengths of light. These not only detect colors, but also generate the necessary electrical signals without an external power supply.
[5]
Self-powered artificial synapse mimics human color vision
As artificial intelligence and smart devices continue to evolve, machine vision is taking an increasingly pivotal role as a key enabler of modern technologies. Unfortunately, despite much progress, machine vision systems still face a major problem: Processing the enormous amounts of visual data generated every second requires substantial power, storage, and computational resources. This limitation makes it difficult to deploy visual recognition capabilities in edge devices, such as smartphones, drones, or autonomous vehicles. Interestingly, the human visual system offers a compelling alternative model. Unlike conventional machine vision systems that have to capture and process every detail, our eyes and brain selectively filter information, allowing for higher efficiency in visual processing while consuming minimal power. Neuromorphic computing, which mimics the structure and function of biological neural systems, has thus emerged as a promising approach to overcome existing hurdles in computer vision. However, two major challenges have persisted. The first is achieving color recognition comparable to human vision, whereas the second is eliminating the need for external power sources to minimize energy consumption. Against this backdrop, a research team led by Associate Professor Takashi Ikuno from the School of Advanced Engineering, Department of Electronic Systems Engineering, Tokyo University of Science (TUS), Japan, has developed a groundbreaking solution. Their paper, published in Scientific Reports on May 12, 2025, introduces a self-powered artificial synapse capable of distinguishing colors with remarkable precision. The study was co-authored by Hiroaki Komatsu and Norika Hosoda, also from TUS. The researchers created their device by integrating two different dye-sensitized solar cells, which respond differently to various wavelengths of light. Unlike conventional optoelectronic artificial synapses that require external power sources, the proposed synapse generates its electricity via solar energy conversion. This self-powering capability makes it particularly suitable for edge computing applications, where energy efficiency is crucial. As evidenced through extensive experiments, the resulting system can distinguish between colors with a resolution of 10 nanometers across the visible spectrum -- a level of discrimination approaching that of the human eye. Moreover, the device also exhibited bipolar responses, producing positive voltage under blue light and negative voltage under red light. This makes it possible to perform complex logic operations that would typically require multiple conventional devices. "The results show great potential for the application of this next-generation optoelectronic device, which enables high-resolution color discrimination and logical operations simultaneously, to low-power artificial intelligence (AI) systems with visual recognition," notes Dr. Ikuno. To demonstrate a real-world application, the team used their device in a physical reservoir computing framework to recognize different human movements recorded in red, green, and blue. The system achieved an impressive 82% accuracy when classifying 18 different combinations of colors and movements using just a single device, rather than the multiple photodiodes needed in conventional systems. The implications of this research extend across multiple industries. In autonomous vehicles, these devices could enable more efficient recognition of traffic lights, road signs, and obstacles. In health care, they could power wearable devices that monitor vital signs like blood oxygen levels with minimal battery drain. For consumer electronics, this technology could lead to smartphones and augmented/virtual reality headsets with dramatically improved battery life while maintaining sophisticated visual recognition capabilities. "We believe this technology will contribute to the realization of low-power machine vision systems with color discrimination capabilities close to those of the human eye, with applications in optical sensors for self-driving cars, low-power biometric sensors for medical use, and portable recognition devices," says Dr. Ikuno. Overall, this work represents a significant step toward bringing the wonders of computer vision to edge devices, enabling our everyday devices to see the world more like we do.
Share
Share
Copy Link
Researchers at Tokyo University of Science have developed a groundbreaking self-powered artificial synapse that can distinguish colors with near-human precision, potentially revolutionizing machine vision in edge devices.
Revolutionizing Machine Vision with Bio-Inspired Technology
Researchers at Tokyo University of Science have developed a groundbreaking self-powered artificial synapse that mimics human color vision, potentially transforming machine vision capabilities in edge devices. Led by Associate Professor Takashi Ikuno, the team's work addresses critical challenges in current machine vision systems, namely high power consumption and the need for extensive computational resources
1
2
.The Human Eye as a Model for Efficiency

Source: Interesting Engineering
Conventional machine vision systems process vast amounts of visual data, consuming significant power and computational resources. In contrast, the human visual system selectively filters information, achieving higher efficiency with minimal power consumption. This biological model inspired the researchers to explore neuromorphic computing as a solution to existing hurdles in computer vision
3
4
.Innovative Design: Self-Powered and Color-Smart
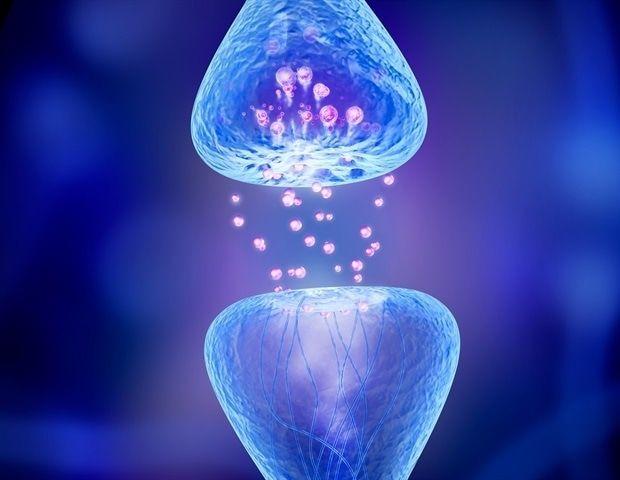
Source: News-Medical
The artificial synapse integrates two different dye-sensitized solar cells, each responding to various light wavelengths. Unlike traditional optoelectronic artificial synapses requiring external power, this device generates its own electricity through solar energy conversion. This self-powering capability makes it particularly suitable for edge computing applications where energy efficiency is crucial
1
2
5
.Key features of the device include:
- Color discrimination with 10-nanometer resolution across the visible spectrum
- Bipolar responses: positive voltage under blue light, negative under red light
- Ability to perform complex logic operations typically requiring multiple conventional devices
Real-World Application and Impressive Performance
To demonstrate practical applications, the team employed their device in a physical reservoir computing framework to recognize different human movements recorded in red, green, and blue. The system achieved an impressive 82% accuracy when classifying 18 different combinations of colors and movements using just a single device, outperforming conventional systems that require multiple photodiodes
1
3
4
.Related Stories
Wide-Ranging Implications Across Industries

Source: Neuroscience News
The potential applications of this technology span multiple sectors:
- Autonomous Vehicles: More efficient recognition of traffic lights, road signs, and obstacles
- Healthcare: Powering wearable devices for monitoring vital signs with minimal battery drain
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones and AR/VR headsets with improved battery life and sophisticated visual recognition capabilities
1
2
5
Dr. Ikuno expressed optimism about the technology's future: "We believe this technology will contribute to the realization of low-power machine vision systems with color discrimination capabilities close to those of the human eye, with applications in optical sensors for self-driving cars, low-power biometric sensors for medical use, and portable recognition devices"
1
3
.Funding and Future Prospects
The research was partially supported by the JST and the establishment of university fellowships for the creation of science and technology innovation (Grant Number JPMJFS2144), with additional support from the JST SPRING (Grant Number JPMJSP2151)
3
.As edge devices become increasingly prevalent in our daily lives, this breakthrough represents a significant step towards more efficient and capable machine vision systems. By mimicking the human eye's ability to process visual information selectively and efficiently, this self-powered artificial synapse opens up new possibilities for AI-driven visual recognition in a wide range of applications.
References
Summarized by
Navi
[1]
[3]
[4]
[5]
Related Stories
Novel Solar Cell-Based Device Revolutionizes Edge AI Processing with Human-Like Synaptic Behavior
26 Nov 2024•Science and Research

Revolutionary Light-Powered Chip Boosts AI Efficiency 100-Fold
09 Sept 2025•Science and Research
Revolutionary Light-Based AI Chip: Smaller Than a Speck of Dust, Faster Than Traditional Computing
08 Feb 2025•Technology

Recent Highlights
1
Google Gemini 3.1 Pro doubles reasoning score, beats rivals in key AI benchmarks
Technology

2
Meta strikes up to $100 billion AI chips deal with AMD, could acquire 10% stake in chipmaker
Technology

3
Pentagon threatens Anthropic with supply chain risk label over AI safeguards for military use
Policy and Regulation





