Stanford Researchers Leverage AI to Enhance Gene Therapy Safety and Efficacy
2 Sources
2 Sources
[1]
Researchers use machine learning to improve gene therapy
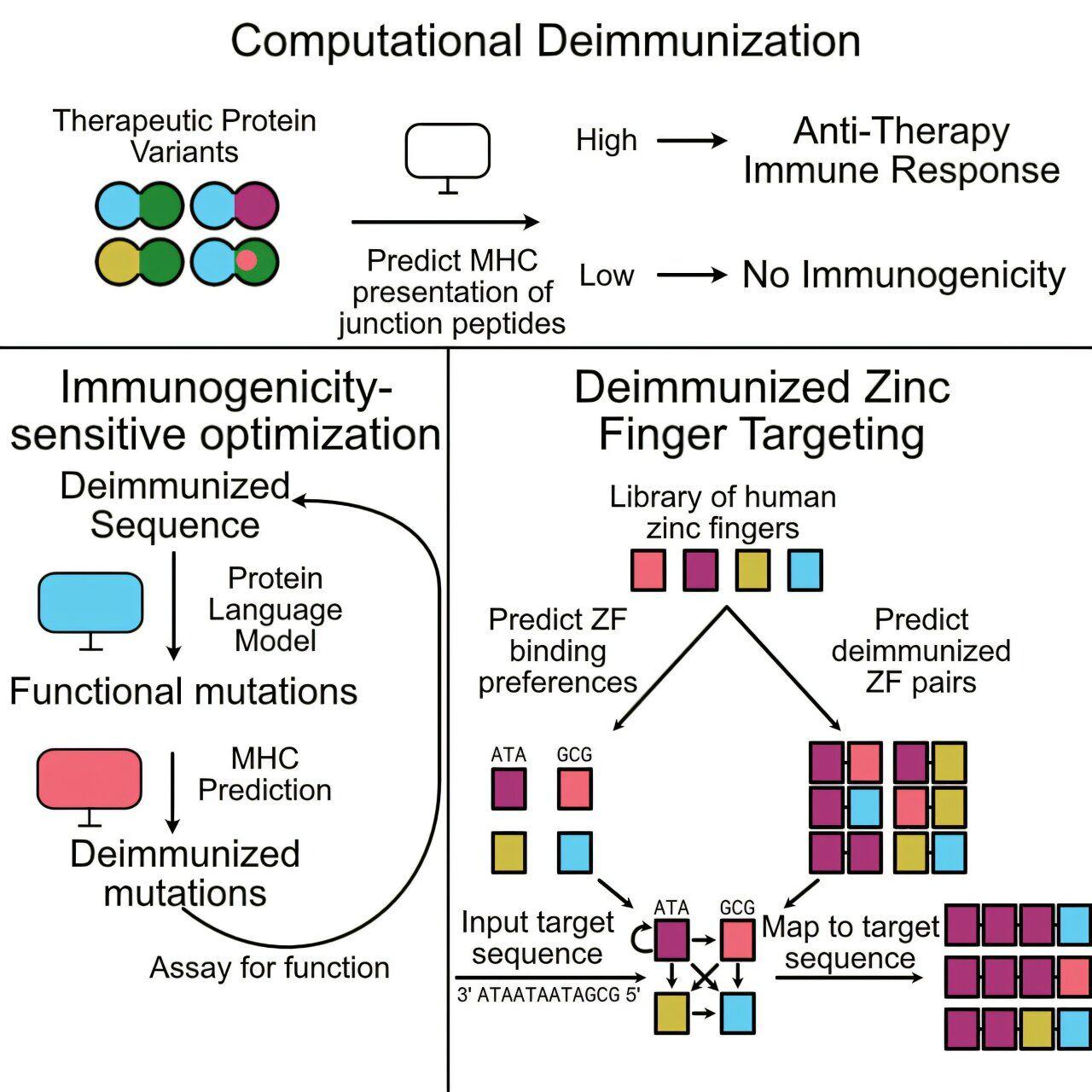
Stanford's Gao Lab is leveraging AI to optimize the efficacy and safety of targeted cell and gene therapies. Machine learning models have seeped into the fabric of our lives, from curating playlists to explaining hard concepts in a few seconds. Beyond convenience, state-of-the-art algorithms are finding their way into modern-day medicine as a powerful potential tool. In one such advance, published June 3 in Cell Systems, Stanford researchers are using machine learning to improve the efficacy and safety of targeted cell and gene therapies by potentially using our own proteins. Most human diseases occur due to the malfunctioning of proteins in our bodies, either systematically or locally. Naturally, introducing a new therapeutic protein to cure the one that is malfunctioning would be ideal. Although nearly all therapeutic protein antibodies are either fully human or engineered to look human, a similar approach has yet to make its way to other therapeutic proteins, especially those that operate in cells, such as those involved in CAR-T and CRISPR-based therapies. The latter still runs the risk of triggering immune responses. To solve this problem, researchers at the Gao Lab have now turned to machine learning models. "In this paper, we raise the question: Why not design treatments that avoid immune reactions from the start? With advances in computational tools, we're now trying to predict which changes to a protein could trigger an immune response, and only move forward with designs that are less likely to be rejected by the body," said Xiaojing Gao, the senior author of the paper and assistant professor of chemical engineering in the School of Engineering at Stanford. By combining three independent machine learning algorithms, the team has made significant progress toward a tool for efficiently designing proteins that avoid such immune response issues and maintain their functionality when introduced into the human body. One way to go about reducing immune reactions to these therapeutics is by starting with proteins that already exist in the human body. So, the Gao team chose tiny proteins called zinc fingers, which are among the most abundant proteins found in eukaryotic organisms and are responsible for regulating gene expression. Because of their ability to bind naturally with human DNA, they are a good alternative to existing technologies like CRISPR, which is more likely to trigger immune reactions because it comes from bacteria. "The most significant part of our work is our progress in designing zinc finger DNA-binding domains that can target any genomic site we choose while maintaining a low predicted risk of triggering immune responses," said Eric Wolsberg, PhD student in chemical engineering and the lead author of the paper. Naturally occurring zinc fingers are bound to a specific sequence in the human genome, as a result of evolutionary processes. However, in order to repurpose them for cell or gene therapy, the team used the first algorithm to predict new DNA targets - such as a disease-causing gene - that could bind to combinations of zinc fingers. Since zinc fingers are typically linked together to recognize longer DNA stretches, the team assembled them into arrays, creating new junctions between the individual zinc finger units. But there was a complication. "These junctions are unnatural, they don't occur in our bodies," said Gao. "That meant the immune system might recognize them as foreign and respond." The team then leveraged a second machine learning algorithm, MARIA - developed by the paper's co-authors, Binbin Chen, a former Stanford grad student, and Ash Alizadeh, the Moghadam Family Professor of Medicine, Oncology, in the School of Medicine. MARIA was designed to predict the immunogenicity of these zinc protein junctions to design cancer vaccines. The preference is for the vaccine to be highly immunogenic, which means the team used MARIA in reverse, to screen for junctions or mutations that would avoid immune detection. If MARIA predicted that the engineered zinc fingers weren't likely to be seen by the immune system, the design was considered safer. While the combination of these two models did yield functional zinc finger arrays, they show limited efficacy, probably due to the limitations in the algorithms used for predicting zinc finger binding sequences. To preserve lowered immunogenicity yet further improve the functionality of the engineered zinc fingers, the team applied their third algorithm: a powerful protein language model called ESM-IF1. Drawing on its training from millions of natural protein sequences, ESM-IF1 acted like a seasoned editor, suggesting with a high success rate which single-letter genetic tweaks would sharpen the zinc finger's performance. "In the past, researchers tried random mutations to improve zinc fingers, but that was slow and inefficient - and they are also incompatible with the MARIA filtering," Gao said. "With this language model, we could focus on smart, targeted changes." After suggesting potential mutations with ESM-IF1, the team once again ran the modified sequences through MARIA to ensure the changes wouldn't introduce new immunogenic properties. "We only moved forward with mutations that passed both tests - high functionality and low immunogenicity," said Gao. The team compared original zinc finger proteins to the versions with AI-suggested mutations by evaluating both computer-based predictions and lab-based tests to confirm their performance improvement. The original proteins increased the production of human genes by two to four times, while the AI enhancements further increased it by two- to six-fold in the lab-based tests. "We have taken the engineering of zinc fingers to a hitherto unvisited place, while simultaneously conserving function and lowering immunogenicity," said Gao. The researchers plan to build on this method, aiming for an end-to-end algorithm that could someday help design zinc-finger gene therapies for humans.
[2]
AI used to design immune-safe 'zinc finger' proteins for gene therapy
Machine learning models have seeped into the fabric of our lives, from curating playlists to explaining hard concepts in a few seconds. Beyond convenience, state-of-the-art algorithms are finding their way into modern-day medicine as a powerful potential tool. In one such advance, published in Cell Systems, Stanford researchers are using machine learning to improve the efficacy and safety of targeted cell and gene therapies by potentially using our own proteins. Most human diseases occur due to the malfunctioning of proteins in our bodies, either systematically or locally. Naturally, introducing a new therapeutic protein to cure the one that is malfunctioning would be ideal. Although nearly all therapeutic protein antibodies are either fully human or engineered to look human, a similar approach has yet to make its way to other therapeutic proteins, especially those that operate in cells, such as those involved in CAR-T and CRISPR-based therapies. The latter still runs the risk of triggering immune responses. To solve this problem, researchers at the Gao Lab have now turned to machine learning models. "In this paper, we raise the question: Why not design treatments that avoid immune reactions from the start? With advances in computational tools, we're now trying to predict which changes to a protein could trigger an immune response, and only move forward with designs that are less likely to be rejected by the body," said Xiaojing Gao, the senior author of the paper and assistant professor of chemical engineering in the School of Engineering at Stanford. By combining three independent machine learning algorithms, the team has made significant progress toward a tool for efficiently designing proteins that avoid such immune response issues and maintain their functionality when introduced into the human body. Designing zinc fingers One way to go about reducing immune reactions to these therapeutics is by starting with proteins that already exist in the human body. So, the Gao team chose tiny proteins called zinc fingers, which are among the most abundant proteins found in eukaryotic organisms and are responsible for regulating gene expression. Because of their ability to bind naturally with human DNA, they are a good alternative to existing technologies like CRISPR, which is more likely to trigger immune reactions because it comes from bacteria. "The most significant part of our work is our progress in designing zinc finger DNA-binding domains that can target any genomic site we choose while maintaining a low predicted risk of triggering immune responses," said Eric Wolsberg, Ph.D. student in chemical engineering and the lead author of the paper. Naturally occurring zinc fingers are bound to a specific sequence in the human genome, as a result of evolutionary processes. However, in order to repurpose them for cell or gene therapy, the team used the first algorithm to predict new DNA targets -- such as a disease-causing gene -- that could bind to combinations of zinc fingers. Since zinc fingers are typically linked together to recognize longer DNA stretches, the team assembled them into arrays, creating new junctions between the individual zinc finger units. But there was a complication. "These junctions are unnatural, they don't occur in our bodies," said Gao. "That meant the immune system might recognize them as foreign and respond." The team then leveraged a second machine learning algorithm, MARIA -- developed by the paper's co-authors, Binbin Chen, a former Stanford grad student, and Ash Alizadeh, the Moghadam Family Professor of Medicine, Oncology, in the School of Medicine. MARIA was designed to predict the immunogenicity of these zinc protein junctions to design cancer vaccines. The preference is for the vaccine to be highly immunogenic, which means the team used MARIA in reverse, to screen for junctions or mutations that would avoid immune detection. If MARIA predicted that the engineered zinc fingers weren't likely to be seen by the immune system, the design was considered safer. While the combination of these two models did yield functional zinc finger arrays, they show limited efficacy, probably due to the limitations in the algorithms used for predicting zinc finger binding sequences. To preserve lowered immunogenicity yet further improve the functionality of the engineered zinc fingers, the team applied their third algorithm: a powerful protein language model called ESM-IF1. Machine guides the enhancement Drawing on its training from millions of natural protein sequences, ESM-IF1 acted like a seasoned editor, suggesting with a high success rate which single-letter genetic tweaks would sharpen the zinc finger's performance. "In the past, researchers tried random mutations to improve zinc fingers, but that was slow and inefficient -- and they are also incompatible with the MARIA filtering," Gao said. "With this language model, we could focus on smart, targeted changes." After suggesting potential mutations with ESM-IF1, the team once again ran the modified sequences through MARIA to ensure the changes wouldn't introduce new immunogenic properties. "We only moved forward with mutations that passed both tests -- high functionality and low immunogenicity," said Gao. The team compared original zinc finger proteins to the versions with AI-suggested mutations by evaluating both computer-based predictions and lab-based tests to confirm their performance improvement. The original proteins increased the production of human genes by two to four times, while the AI enhancements further increased it by two- to six-fold in the lab-based tests. "We have taken the engineering of zinc fingers to a hitherto unvisited place, while simultaneously conserving function and lowering immunogenicity," said Gao.
Share
Share
Copy Link
Stanford's Gao Lab combines machine learning algorithms to design immune-safe 'zinc finger' proteins for targeted cell and gene therapies, potentially revolutionizing treatment approaches for various diseases.
Stanford Researchers Harness AI for Safer Gene Therapies
In a groundbreaking study published in Cell Systems, Stanford University researchers have successfully employed artificial intelligence to enhance the safety and efficacy of targeted cell and gene therapies. The team, led by Xiaojing Gao, assistant professor of chemical engineering at Stanford's School of Engineering, has developed a novel approach using machine learning to design proteins that can potentially revolutionize treatment methods for various diseases
1
2
.
Source: Stanford
The Challenge of Immune Reactions in Gene Therapy
Most human diseases stem from malfunctioning proteins in our bodies. While introducing therapeutic proteins to address these issues seems logical, current approaches, especially those involving CAR-T and CRISPR-based therapies, still risk triggering immune responses. This challenge prompted the Gao Lab to explore innovative solutions using machine learning models
1
.Zinc Fingers: A Promising Alternative
The researchers focused on tiny proteins called zinc fingers, which are abundant in eukaryotic organisms and regulate gene expression. These proteins can naturally bind with human DNA, making them a safer alternative to technologies like CRISPR, which originates from bacteria and is more likely to provoke immune reactions
1
2
.Three-Pronged AI Approach
The team employed a combination of three independent machine learning algorithms to design zinc finger proteins that can target specific genomic sites while maintaining a low risk of triggering immune responses:
- The first algorithm predicted new DNA targets that could bind to combinations of zinc fingers
1
. - MARIA, the second algorithm, was used in reverse to screen for protein junctions or mutations that would avoid immune detection
2
.
Source: Phys.org
- ESM-IF1, a powerful protein language model, suggested genetic tweaks to enhance the zinc fingers' performance
1
2
.
Balancing Functionality and Safety
Eric Wolsberg, the lead author of the paper, emphasized the significance of their work in designing zinc finger DNA-binding domains that can target chosen genomic sites while maintaining a low predicted risk of immune responses
1
2
.The team faced a challenge when assembling zinc fingers into arrays, as the new junctions created between individual units were unnatural and potentially recognizable by the immune system as foreign. This is where the MARIA algorithm played a crucial role in screening for safer designs
2
.Related Stories
AI-Driven Enhancements
The ESM-IF1 model, trained on millions of natural protein sequences, acted as a sophisticated editor, suggesting targeted genetic changes to improve the zinc fingers' functionality. The team then re-evaluated these modifications using MARIA to ensure they didn't introduce new immunogenic properties
1
2
.Promising Results
Laboratory tests revealed significant improvements in the AI-enhanced zinc finger proteins:
- Original proteins increased human gene production by 2-4 times
- AI-enhanced versions further increased production by 2-6 fold
1
2
Future Implications
This research represents a significant step forward in the field of gene therapy. By combining AI algorithms to design immune-safe and highly functional zinc finger proteins, the team has opened up new possibilities for developing more effective and safer treatments for a wide range of diseases
1
2
.As Gao concluded, "We have taken the engineering of zinc fingers to a hitherto unvisited place, while simultaneously conserving function and lowering immunogenicity"
1
2
. This breakthrough could pave the way for a new generation of targeted cell and gene therapies with reduced risks of immune rejection.References
Summarized by
Navi
Related Stories
CRISPR-GPT: AI-Powered Gene Editing Assistant Accelerates Drug Development
17 Sept 2025•Science and Research

AI-Powered Protein Engineering: EVOLVEpro Revolutionizes Protein Design for Medical and Environmental Applications
22 Nov 2024•Science and Research

AI-Designed Proteins Revolutionize Cancer Immunotherapy: A Breakthrough in Precision Treatment
25 Jul 2025•Science and Research
Recent Highlights
1
Google Gemini 3.1 Pro doubles reasoning score, beats rivals in key AI benchmarks
Technology

2
Pentagon Summons Anthropic CEO as $200M Contract Faces Supply Chain Risk Over AI Restrictions
Policy and Regulation

3
Canada Summons OpenAI Executives After ChatGPT User Became Mass Shooting Suspect
Policy and Regulation