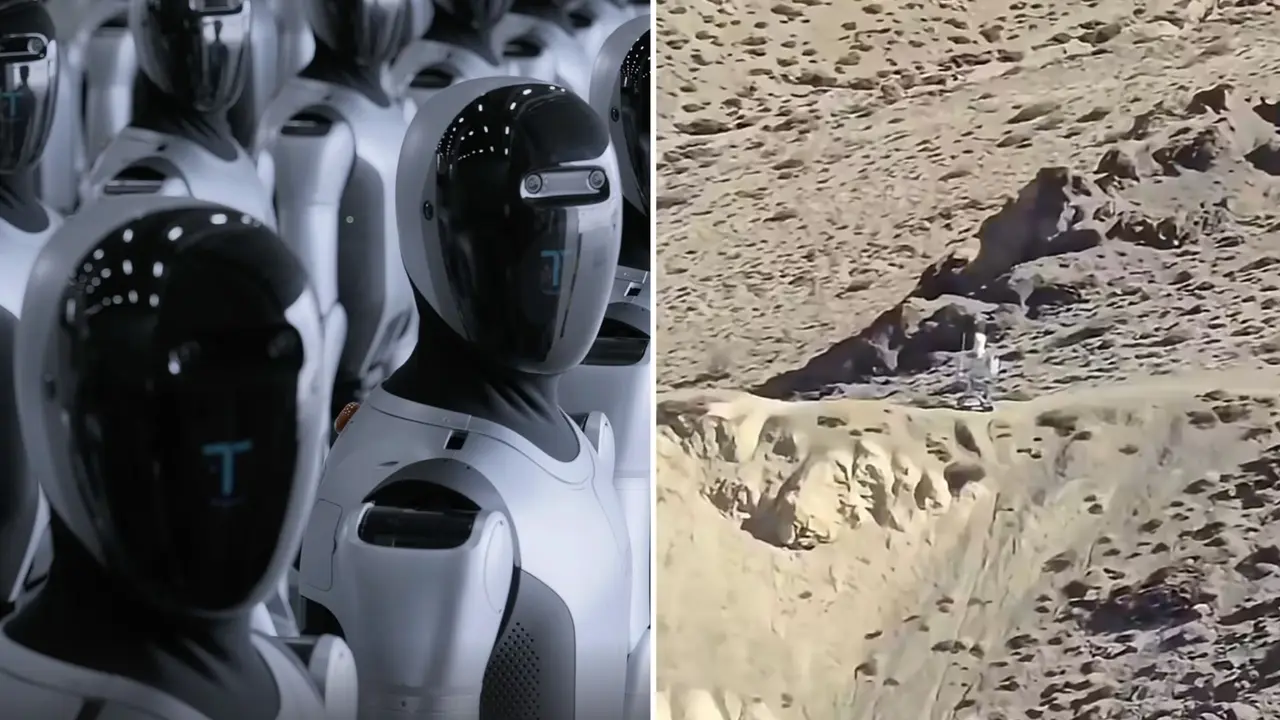
China Deploys AI-Powered Robotic Antelope for Wildlife Surveillance in Tibet
2 Sources
2 Sources
[1]
China deploys robot antelope in Tibet to surveil real herds
BEIJING, Aug 12 (Reuters) - To the wolves of Tibet, China's first 'robot antelope' may look as appetising as the real herds that roam the rugged tundra, but the "creature" is part of Beijing's growing surveillance that now even reaches into its most remote places. Its doe-like eyes and thick brown fur make the robotic ruminant nearly indistinguishable from the real antelope as the 5G- and AI-integrated imposter scans the Hoh Xil plateau with its sensors, footage from China's state news agency Xinhua shows. Developed by Xinhua, the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Hangzhou-based DEEP Robotics, the robot antelope is equipped with 5G connectivity and artificial intelligence vision systems, enabling real-time monitoring of the migration, feeding and mating behaviours of the endangered species endemic to Tibet. China is offering its robotics industry tens of billions in subsidies and was host to the 2025 World Robot Conference, which wrapped up on Tuesday. 5G arrived in Tibet in 2019, according to Chinese government documents, and the southwestern region reached 1 million users by 2022. With the completion of a 5G base station in the town of Gogmo in late 2023, every district in Tibet was covered, state media reported. Beyond transmitting live images and tracking data on rare antelope species, Tibet's 5G infrastructure now supports a growing range of AI applications -- from small drones that can operate in areas impenetrable to radar, to telemedicine consultations and smart yak herding technologies, according to Chinese state media reports. China has invested heavily in Tibet, boosting the at times restive region's role in President Xi Jinping's flagship Belt and Road infrastructure initiative by strengthening its trade ties with Central Asia, while also tightening surveillance over its population and extending Beijing's digital footprint towards neighbouring rival India. Analysts and human rights campaigners accuse Beijing of deploying "grey-zone" tactics against countries around the Tibetan plateau. A July report from the Center of Strategic and International Studies think tank documented instances of China leveraging local telecommunications networks to surveil dissidents living in neighbouring Nepal, alongside cases of cyber theft. Reporting by Joe Cash; Editing by Michael Perry Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles., opens new tab
[2]
China unveils antelope robot to study endangered Tibetan species
A lifelike robotic Tibetan antelope is now roaming the high-altitude wilderness of Hoh Xil National Nature Reserve in Northwest China's Qinghai Province. Equipped with 5G ultra-low latency networks and advanced artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, the bionic robot is being used to collect real-time data on Tibetan antelope populations without disturbing them. This is the first time such a robotic antelope has been deployed in the heart of Hoh Xil, which sits more than 15,092 feet (4,600 meters) above sea level.
Share
Share
Copy Link
China has introduced a 5G and AI-integrated robotic antelope in Tibet's Hoh Xil plateau to monitor endangered Tibetan antelope populations, showcasing advanced surveillance technology in remote areas.
China's Robotic Antelope: A Technological Marvel in Wildlife Conservation
In a groundbreaking move, China has deployed its first 'robot antelope' in the rugged tundra of Tibet's Hoh Xil plateau. This innovative creation, developed through a collaboration between Xinhua, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Hangzhou-based DEEP Robotics, represents a significant leap in wildlife surveillance technology
1
.Advanced Features and Capabilities

Source: Interesting Engineering
The robotic antelope is a marvel of modern technology, seamlessly blending into its natural surroundings. With its doe-like eyes and thick brown fur, it is nearly indistinguishable from real antelopes. The robot is equipped with state-of-the-art 5G connectivity and artificial intelligence (AI) vision systems, enabling real-time monitoring of the migration, feeding, and mating behaviors of endangered Tibetan antelope species
1
.Operating at an altitude of over 15,092 feet (4,600 meters) above sea level, this bionic robot utilizes ultra-low latency 5G networks and advanced AI algorithms to collect data without disturbing the natural behavior of the wildlife it observes
2
.Expanding Technological Footprint in Tibet
The deployment of the robotic antelope is part of China's broader technological expansion in Tibet. The region has seen significant advancements in its digital infrastructure, with 5G coverage reaching every district by late 2023. This technological leap supports a growing range of AI applications, including small drones for radar-impenetrable areas, telemedicine consultations, and smart yak herding technologies
1
.Related Stories
Implications and Concerns
While the robotic antelope represents a significant advancement in wildlife conservation efforts, it also raises questions about the extent of China's surveillance capabilities. The project is part of China's substantial investment in Tibet, which aims to boost the region's role in President Xi Jinping's Belt and Road initiative while also tightening surveillance over its population
1
.Some analysts and human rights campaigners have expressed concerns about China's use of "grey-zone" tactics in the region. A report from the Center of Strategic and International Studies documented instances of China leveraging local telecommunications networks to surveil dissidents living in neighboring Nepal, alongside cases of cyber theft
1
.The Future of Wildlife Monitoring
The introduction of the robotic antelope marks a new era in wildlife conservation technology. By allowing researchers to gather crucial data without disturbing the natural habitat, this innovation could potentially revolutionize our understanding of endangered species and their ecosystems. However, it also underscores the need for careful consideration of the ethical implications of such advanced surveillance technologies in both wildlife conservation and broader societal contexts.
References
Summarized by
Navi
[2]
Related Stories
Chinese spy robot video near India border sparks debate as China deploys humanoid patrols
03 Dec 2025•Technology
China Deploys AI-Powered Spherical Robot for Urban Policing
11 Dec 2024•Technology

Humanoid robots take center stage at China's Lunar New Year gala as Beijing pushes AI dominance
09 Feb 2026•Entertainment and Society

Recent Highlights
1
Trump bans Anthropic from government as AI companies clash with Pentagon over weapons and surveillance
Policy and Regulation

2
Nvidia pulls back from OpenAI investment as Jensen Huang cites IPO plans and complex dynamics
Technology

3
Samsung unveils Galaxy S26 lineup with Privacy Display tech and expanded AI capabilities
Technology