Humanoid Robot Masters Waltz and More Through AI-Powered Human Movement Mirroring
2 Sources
2 Sources
[1]
Humanoid robot learns to waltz by mirroring people's movements
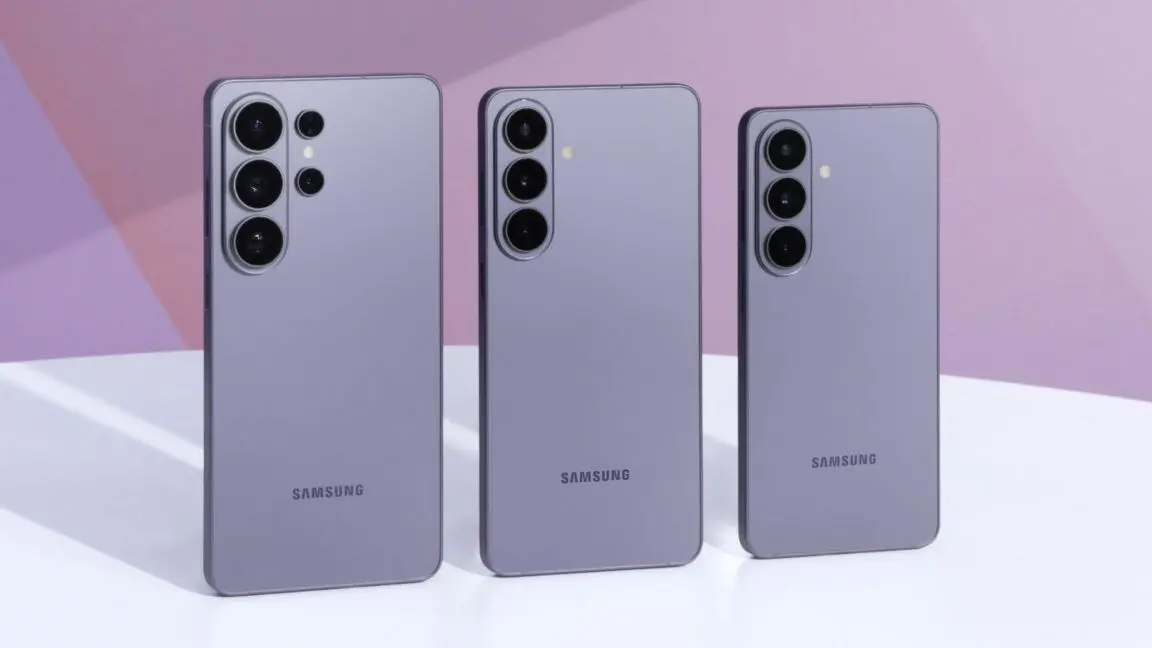
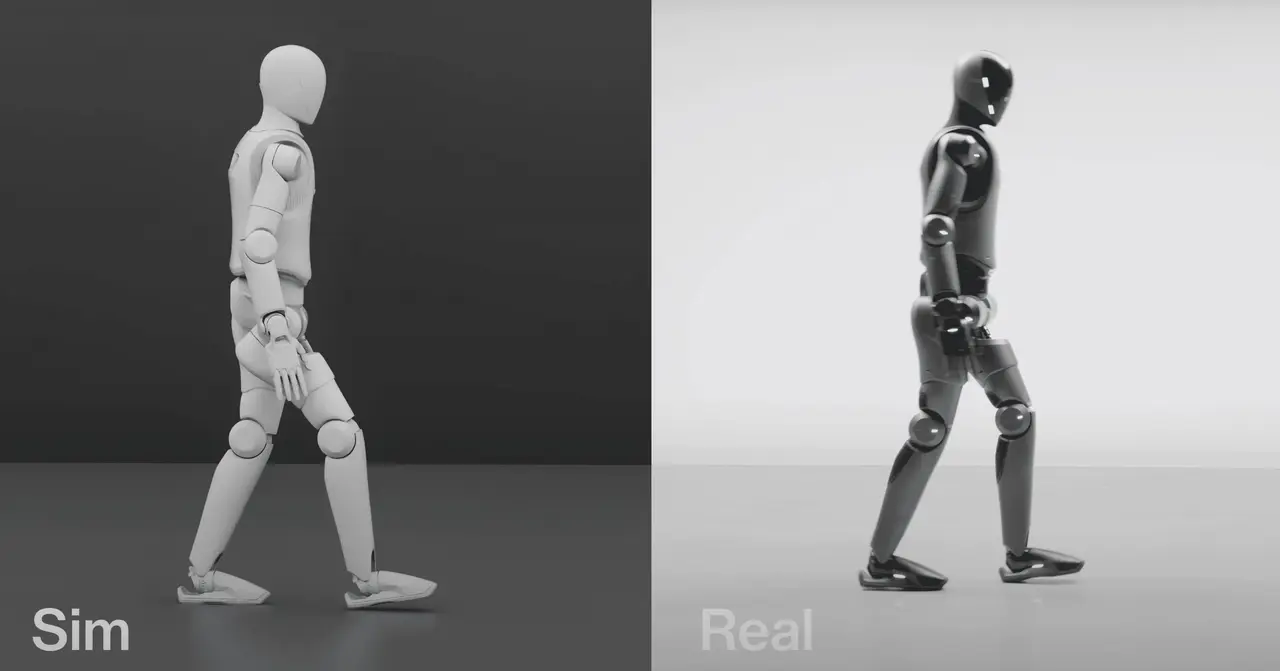
An AI trained on motion capture recordings can help robots smoothly imitate human actions, such as dancing, walking and fighting An AI that helps humanoid robots mirror a person's movement could allow robots to walk, dance and fight in more convincingly human ways. The most agile and fluid robotic movements, such as Boston Dynamic's impressive demonstrations of robot acrobatics, are typically narrow and pre-programmed sequences. Teaching robots to perform a wider repertoire of convincingly human movements is still difficult. To overcome this hurdle, Xuanbin Peng at the University of California, San Diego and his colleagues have developed an artificial intelligence system, called ExBody2, that lets robots copy and smoothly perform many different human movements in more lifelike ways. Peng and his team first created a database of actions that a humanoid robot might be capable of performing, from simple movements like standing or walking to more complex manoeuvres, such as tricky dance moves. The database included motion capture recordings of hundreds of human volunteers, collected by previous research projects. "Since humanoid robots share a similar physical structure with us, it makes sense to take advantage of the vast amounts of the human motion data already available," says Peng. "By learning to mimic this kind of motion, the robot can quickly pick up a wide variety of human-like behaviours. This means that whatever humans can do, the robot can potentially learn." To teach a simulated humanoid robot how to move, Peng and his team used reinforcement learning, where an AI is given an example of what a successful movement consists of and then tasked with figuring out how to do it itself by trial and error. They first had ExBody2 learn with complete access to all the data on the virtual robot, such as coordinates of each joint, so it could mimic the human actions as closely as possible. Then, they had it learn from these movements but only using data it would have access to in the real world, such as measurements of inertia or speed from sensors on the robot's body. After it had trained on the database, ExBody2 was put in control of two different commercial humanoid robots. It was able to smoothly string together simple movements, such as walking in a straight line and crouching, as well as perform trickier moves, such as following a 40-second dance routine, throwing punches and waltzing with a human. "Humanoid robots work best when they coordinate all their limbs and joints together," says Peng. "Many tasks and motions require the arms, legs and torso to work together, and full body coordination greatly expands the robot's range of capabilities."
[2]
Humanoid robot learns to Waltz with the grace of ... a robot
By mirroring humans, it can also punch and wave its arms around. Researchers from the University of California, San Diego have designed an AI-enabled robot that can perform a Waltz simply by mirroring the moves of its human partner. As far as we can tell, the robot was even able to pull off the ballroom dance without stepping on its partner's toes. To make their dancing robot, the team first designed an AI model trained on human motion capture videos and then integrated it into two bipedal Unitree G1 robots. Using another model, those robots were then able to analyze the motions of humans in front of them and mimic those movements themselves. The result was a humanoid robot able to seamlessly walk, dodge, squat, and dance by copying a human. [ Related: The 11 weirdest things humans did to robots in 2024 ] Robotics researchers aren't shy about having their machines perform over-the-top stunts. From intricate dance dance routines to impressive parkour moves, the internet is awash with robots behaving bizarrely. But most of those examples typically involve pre-programmed, highly choreographed scripts. In this case, researchers wanted to see if they could teach a robot to learn movements more organically. To do that, they first needed a powerful brain with a good baseline of knowledge. The researchers obtained a database of human motion capture data and used it to build out an AI model they called ExBody2. They trained the model in a simulation environment using reinforcement learning until it had a broad understanding of how to articulate and move many parts of a robot body. They then implemented ExBody2 into a pair of robots that were equipped with another model that sucked in real-world physical data captured by the robot's cameras. The robot was able to quickly compare the movements it was "seeing" in front of it against its baseline training. Videos of the robot in action show it pacing outdoors, sidestepping like an athlete (or attempting a foxtrot?), drawing circles with its arms, squatting, and throwing punches. Some of the demonstrations show one of the researchers besides the robot performing the initial movements. After just around a second delay, the robot dutifully repeats the motion. Researchers say this approach is useful because it means the robot is more adaptable than others that require new training sets every time it needs to perform a new movement. This isn't the first example of a copycat robot. Last year, researchers from Stanford used a similar AI model to teach a 5'9 humanoid robot how to box and play rudimentary tennis all by "shadowing" human movements. Like ExBody2, the robot also utilizes an AI trained on motion capture data. [ Related: Researchers tortured robots to test the limits of human empathy ] "By mimicking humans, humanoids can potentially tap into the rich repertoire of skills and motion exhibited by humans, offering a promising avenue towards achieving general robot intelligence," the authors wrote in a paper detailing their results. This approach to robot movement isn't just about novelty. Researchers believe mirroring or shadowing could cut down on the need to repeatedly train robots, which could help speed up their development and drive down costs. At the very least, the technology shows a rudimentary robot dance partner is within the realm of possibility.
Share
Share
Copy Link
Researchers develop an AI system enabling humanoid robots to mimic human movements, including dancing, walking, and fighting, potentially revolutionizing robot agility and adaptability.

AI-Powered Humanoid Robot Learns to Waltz and More
Researchers from the University of California, San Diego have developed an innovative AI system called ExBody2, enabling humanoid robots to mirror human movements with unprecedented fluidity and adaptability. This breakthrough could potentially revolutionize how robots perform a wide range of actions, from simple tasks to complex maneuvers like dancing and fighting
1
2
.The ExBody2 System
ExBody2 utilizes a database of human motion capture recordings, encompassing hundreds of volunteers performing various actions. By leveraging reinforcement learning techniques, the AI system teaches simulated humanoid robots to mimic these movements. The learning process occurs in two stages:
- Complete data access: The AI initially learns with full access to the virtual robot's data, including joint coordinates.
- Real-world constraints: The system then adapts to learn using only data available in real-world scenarios, such as inertia and speed measurements from the robot's sensors
1
.
Practical Applications and Demonstrations
The researchers implemented ExBody2 in two commercial Unitree G1 bipedal robots, showcasing impressive results:
- Basic movements: The robots successfully performed simple actions like walking in a straight line and crouching.
- Complex maneuvers: More intricate movements, including a 40-second dance routine, throwing punches, and waltzing with a human partner, were executed smoothly
1
2
.
Advantages of the Mirroring Approach
This innovative approach to robot movement offers several benefits:
- Adaptability: Robots can quickly learn new movements without requiring extensive reprogramming or additional training sets.
- Cost-effectiveness: The mirroring technique could potentially reduce development costs and accelerate robot training.
- Expanded capabilities: By coordinating all limbs and joints, humanoid robots can perform a wider range of tasks and motions
1
2
.
Related Stories
Comparison to Previous Work
While not the first example of a copycat robot, ExBody2 builds upon previous research. Last year, Stanford researchers used a similar AI model to teach a humanoid robot boxing and basic tennis skills through shadowing human movements
2
.Future Implications
The development of ExBody2 and similar systems could have far-reaching implications for robotics and AI:
- General robot intelligence: By tapping into the rich repertoire of human skills and motions, this approach may contribute to achieving more versatile and intelligent robots.
- Human-robot interaction: The ability to mirror human movements could enhance robots' capacity to work alongside humans in various settings.
- Potential applications: From healthcare and assistive technologies to entertainment and industrial uses, the improved agility and adaptability of humanoid robots could open up new possibilities
1
2
.
As research in this field progresses, we may soon see humanoid robots capable of performing an even wider range of human-like movements with greater precision and naturalness.
References
Summarized by
Navi
[1]
[2]
Related Stories
Figure AI's Humanoid Robot Achieves Natural Walking Through AI Simulation
26 Mar 2025•Technology
Boston Dynamics' Atlas Robot Showcases Advanced Mobility and AI-Driven Movements
20 Mar 2025•Technology

Humanoid Robots Face Training Gap as Industry Demands Practical Applications Over Demos
08 Jan 2026•Technology

Recent Highlights
1
Google Gemini 3.1 Pro doubles reasoning score, beats rivals in key AI benchmarks
Technology

2
Meta strikes up to $100 billion AI chips deal with AMD, could acquire 10% stake in chipmaker
Technology

3
Pentagon threatens Anthropic with supply chain risk label over AI safeguards for military use
Policy and Regulation





