Microsoft Unveils Groundbreaking Microfluidic Cooling for AI Chips
14 Sources
14 Sources
[1]
Microsoft says this new cooling method could enable more powerful chips and efficient data centers
Microsoft is making advances with a new way to cool microchips that it says could lead to more energy-efficient data centers in the future. It's a method called microfluidics that involves liquid coolant flowing directly into the silicon. After lab tests, Microsoft found that this strategy can remove heat up to three times better than cold plates currently used in data centers today. The company announced this week that it was able to develop a microfluidic cooling system for a server running core services for a simulated Microsoft Teams meeting. If they can find the same success outside of a lab, microfluidics could cut down the amount of energy needed to cool a data center. It could also lead to more powerful chips that current cooling systems would struggle to keep from overheating. But there are still a lot of factors that could influence how impactful this new technology ultimately is in the real world. Compared to data centers of yore, the next generation being built to train and run new AI models house more powerful chips. Not only do those GPUs use a lot of energy, they also get very hot. Keeping them cool is a challenge that not only affects performance, but also makes data centers consume more energy. Typically, a data center might use fans to pass cool air over a chip. A more advanced technology that Microsoft employs for higher-powered chips involves cold plates made of copper with fluid flowing through them. Put that plate on top of a chip, and it whisks away the heat. With microfluidic cooling, liquid flows through channels etched onto the back of a chip. The trick is making sure the channels, about the width of a human hair, are deep enough to prevent clogging but not so deep that the chip becomes more likely to break. Microsoft says it used AI to figure out where to direct coolant onto a chip to chill it most efficiently. The etched designs are also inspired by nature -- mimicking the patterns of veins on leaves, for example -- that have already shown how practical they are at distributing water and resources. Using microfluidics, Microsoft documented a 65 percent reduction in the maximum temperature rise of the silicon of a GPU. The advantage with microfluidics is that it brings fluid straight to the chip, eliminating the need for protective layers of materials between the chip and the coolant when cold plates are used. Each layer, like a blanket, holds in some heat, and so the coolant needs to stay colder to work well within cold plates. Cold liquid flows into the plate; hot fluid flows out and needs to be cooled down again. With microfluidics, the coolant doesn't need to be chilled to as low of a temperature, conserving energy. Microfluidics can also allow a data center to more efficiently handle peaks in demand. Teams calls usually start every hour or half-hour, Microsoft gives as an example. To handle those spikes in demand, they might have to install more servers to have enough capacity on hand even if they won't be used all the time. The alternative would be to let existing servers work extra hard, called overclocking -- but that could lead to overheating and damaging the chip. Microfluidic cooling, because it's more efficient, can allow for more overclocking without the same risk of a chip melting down. In theory, if servers can work harder than they do now without melting chips down, a data center might not need as many of them. And by minimizing the risk of overheating, microfluidics could also allow for more tightly packed servers within a single data center. It could cut the costs, literal and environmental, of needing to build additional facilities. All these benefits could be key for next-generation microchips, which are expected to become so powerful that cold plates may fall short. Microsoft says that microfluidics could also enable 3D chip architecture. 3D chips would be even more powerful than today's semi-flat designs, but heat has been a stumbling block for making this happen. With microfluidics, however, there's the possibility of flowing coolant through the chip. Microsoft doesn't have a timeline for when this all might happen. After more lab testing comes the challenge of figuring out how to make the hardware and supply chain changes needed to allow for microfluidics -- for example, at what point in the manufacturing process will grooves be etched into the chips? Fortunately, they can use the same kind of coolant, a mix of water and propylene glycol, used today in cold plates. Other researchers have been studying microfluidics for years also. HP, for example, was awarded $3.25 million in funding from the Department of Energy last year to develop its own microfluidic cooling technology. "All these things are good to see, we're happy to see them, and where we can participate to move things faster we're happy to," says Husam Alissa, director of systems technology in Cloud Operations and Innovation at Microsoft. Microsoft says it "hopes to help pave the way for more efficient and sustainable next-generation chips across the industry" in its recent blog post touting its progress on microfluidics. Energy efficiency is crucial if the company wants to operate more sustainably. Like other tech companies, Microsoft's planet-heating carbon emissions have grown as it leaned into generative AI. But efficiency can also be a double-edged sword. As something becomes more efficient and affordable to use, people tend to use much more of it and that could ultimately lead to an even bigger environmental footprint. It's a phenomenon called the Jevons paradox, which even Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella has commented on as a force driving greater adoption of AI.
[2]
Microsoft Is Turning to the Field of Microfluidics to Cool Down AI Chips
One of the major reasons why AI data centers are sucking up so much power is the need to cool processors that run very hot. But Microsoft Corp. is trying out a possible solution: sending fluid directly through tiny channels etched into the chips. The technology is called microfluidics, and it's being used in prototype systems in test conditions at the company, said Husam Alissa, who oversees Microsoft's systems technology. The technique has been applied to server chips used for Office cloud apps and the graphics processing units that handle artificial intelligence tasks, he said.
[3]
Microsoft unveils new liquid-cooled computer chips -- they could prevent AI data centers from massively overheating
Channels etched into the silicon enable coolant to remove heat much more efficiently. (Image credit: Dan DeLong/ Microsoft) Microsoft engineers have devised a new way to keep data centers cool -- and it might help prevent the next generation of artificial intelligence (AI) hardware from cooking itself to death. The technology is based on "microfluidics" and involves pumping liquid coolant through tiny channels etched directly into silicon chips. In a statement, Microsoft representatives said the technology was up to three times more effective at removing heat compared with conventional "cold plate" methods for cooling data centers. The company hopes that microfluidics will make it possible for data centers to run more-intensive computational workloads without the risk of overheating, particularly as newer, more powerful AI processors enter the market. These generate far more heat than earlier generations of computer chips, with Microsoft warning that current cooling technology could max out data center performance in "just a few years." "If you're still relying heavily on traditional cold plate technology, you're stuck," Sashi Majety, senior technical program manager at Microsoft, said in the statement. "In as soon as five years, this could become a ceiling on performance." Graphics processing units (GPUs) are often used in data centers because they can run multiple calculations in parallel. This makes them ideal for powering AI and other computationally intensive workloads. To prevent them from overheating, GPUs are typically cooled using metal cold plates. These are mounted on top of the chip's housing and circulate coolant over and around it to draw heat away. However, cold plates are separated from the silicon by multiple layers, which limits how much heat they can extract from the chip. Microsoft's microfluidics technology involves etching grooves the size of a human hair directly into the silicon die -- the densely packed computational core of the chip. When coolant is sent directly to the die via this microscopic pipework, heat is carried away much more efficiently. The prototype chip went through four design iterations. Microsoft partnered with Swiss startup Corintis to develop a layout inspired by leaf veins and butterfly wings -- patterns that distribute liquid across branching paths rather than straight lines. The aim was to reach hotspots more precisely and avoid clogging or cracking the silicon. An AI model optimized these cooling paths by using heat maps to show where temperatures tended to be highest on the processor. Engineers then tested the design on a GPU running a simulated Microsoft Teams workload -- a mix of video, audio and transcription services used to reflect typical data center conditions. In addition to carrying away heat much more efficiently, the microfluidic cooling system reduced the peak temperature rise in the GPU's silicon by 65%, according to Microsoft representatives. Beyond better thermal control, Microsoft hopes microfluidics could allow for overclocking -- safely pushing chips beyond their normal operating limits without burning them out. "Whenever we have spiky workloads, we want to be able to overclock," Jim Kleewein, technical fellow at Microsoft 365 Core Management, said in the statement. "Microfluidics would allow us to overclock without worrying about melting the chip down because it's a more efficient cooler of the chip." The company is now exploring how to apply microfluidics to its custom Cobalt and Maia chips and will now work with fabrication partners to bring the technology into broader use. Future applications may include cooling 3D-stacked chips, which are notoriously hard to design due to the heat buildup between layers. "We want microfluidics to become something everybody does, not just something we do," Kleewein said. "The more people that adopt it the better, the faster the technology is going to develop, the better it's going to be for us, for our customers, for everybody."
[4]
Microsoft claims a 'breakthrough' in AI chip cooling
AI is an enormous energy drain, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions at a time when the planet desperately needs progress in the opposite direction. Although most of that comes from running GPUs, cooling them is another significant overhead. So, it's worth noting when a company of Microsoft's stature claims to have achieved a breakthrough in chip cooling. Microsoft's new system is based on microfluidics, a method long pursued but hard to implement. The company claims its approach could lead to three times better cooling than current methods. Many data centers rely on cold plates to prevent GPUs from overheating. Although effective to a degree, the plates are separated from the heat source by several layers of material, which limits their performance. "If you're still relying heavily on traditional cold plate technology [in five years], you're stuck," Microsoft program manager Sashi Majety is quoted as saying in the company's announcement. In microfluidics, the coolant flows closer to the source. The liquid in Microsoft's prototype moves through thread-like channels etched onto the back of the chip. The company also used AI to more efficiently direct the coolant through those channels. Another aspect separating this prototype from previous attempts is that it drew inspiration from Mother Nature. As you can see in the image above, the etchings resemble the veins in a leaf or a butterfly wing. Microsoft says the technique can reduce the maximum silicon temperature rise inside a GPU by 65 percent. (However, that number depends on the workload and chip type.) This would enable overclocking "without worrying about melting the chip down," Microsoft's Jim Kleewein said. It could allow the company to place servers closer together physically, reducing latency. It would also lead to "higher-quality" waste heat use. Although this sounds good for the environment in a general sense, Microsoft's announcement doesn't lean into that. The blog post primarily discusses the technique's potential for performance and efficiency gains. Green benefits are only alluded to briefly as "sustainability" and reduced grid stress. Let's hope that's only a case of a cynical observer overanalyzing framing. Our planet needs all the help it can get.
[5]
Microsoft unveils microfluidic cooling to handle hotter, denser AI workloads
Serving tech enthusiasts for over 25 years. TechSpot means tech analysis and advice you can trust. Forward-looking: Microsoft has taken a significant step toward addressing the thermal challenges of next-generation data processing hardware. The company has developed an in-chip microfluidic cooling system that routes liquid coolant directly through microscopic channels etched into the silicon itself. This method differs from conventional cold plate technologies, which are separated from the chip by several thermal layers and are reaching their efficiency limits as processors grow more powerful and heat-intensive. In practical terms, the new approach reduced GPU silicon temperatures by up to 65 percent, depending on chip type and workload. Its effectiveness hinges on the precise design of the microchannels - engineered with widths comparable to a human hair - to deliver coolant exactly where it is most needed. With the aid of artificial intelligence, the team was able to analyze and map the unique heat signatures across a chip, directing liquid flow to hotspots with greater accuracy. The prototypes were developed in collaboration with Swiss company Corintis, whose bio-inspired designs drew on natural structures such as leaf veins to optimize coolant distribution for heat removal. Channels are etched in the silicon that allow cooling liquid to flow directly onto the chip and more efficiently remove heat. Manufacturing this breakthrough posed significant engineering challenges. The microchannels had to deliver sufficient cooling capacity without weakening the silicon or creating leak risks. Microsoft conducted multiple iterations to refine the channel depth, etching methods, and sealing of the coolant pathways. The research also explored packaging for leak prevention, coolant formulations, and stepwise integration of microfluidics into chip fabrication. Early trials used existing silicon platforms, possibly including Intel Xeon processors, as test beds to validate both mechanical integrity and cooling performance. By allowing coolant to come into direct contact with the silicon, microfluidics also reduces reliance on heavily chilled coolant, offering potential gains in energy efficiency and operational costs. Microsoft expects this to improve power usage effectiveness in data centers. These efficiencies could enable higher server density, reducing the physical footprint required to support surging AI workloads. This microfluidics chip is covered and has tubing attached so the coolant can flow safely. The innovation reflects Microsoft's broader push to invest in infrastructure designed for the next generation of computing. This effort spans not only cooling technologies but also the development of proprietary chips such as the Cobalt and Maia lines, and a shift toward sustainable data center designs. The company has earmarked more than $30 billion in capital expenditures to support these initiatives. Looking ahead, Microsoft plans to explore how microfluidic cooling can be applied across future generations of its in-house chips as well as in collaboration with silicon manufacturers. The advancement could even influence new chip architectures, including stacked 3D configurations that would otherwise face insurmountable thermal barriers. In such designs, microfluidics could enable the vertical flow of coolant between layers, paving the way for higher compute density and more compact data center layouts.
[6]
Microsoft tames intense chip heat with liquid cooling veins, designed by AI and inspired by biology
REDMOND, Wash. -- About 5 minutes before each hour, and 5 minutes after it, Microsoft Teams gets busy with people joining meetings early or late. Yes, you know who you are. Those predictable spikes in demand are an example of a larger infrastructure challenge facing the industry: either build data centers full of chips and servers that sit idle for much of the time, waiting to handle peak loads, or risk performance issues during moments of high demand. Microsoft has come up with a different approach. The company said Tuesday that it has successfully prototyped new advances in the field of microfluidics that let its servers run hotter and faster -- a technique known as overclocking -- without the risk of melting down the silicon. "We've got these really spiky workloads -- I would dearly love to be able to overclock ... because then we would need way fewer servers and deliver a better experience," said Jim Kleewein, a Microsoft technical fellow and development director for core Office 365 services, recounting the challenge he originally brought to Microsoft's silicon development teams. Microfluidics overall is not a new concept. Instead of placing a cooling plate on top of a chip, the approach brings liquid coolant directly inside the processor itself through tiny channels. But Microsoft says it has developed a new approach that uses AI to customize the cooling system for the unique heat signatures of different chips running specific workloads. The design, inspired by biology, ends up resembling the veins in a leaf, delivering coolant with greater precision to a chip's hottest spots. The company says it's up to three times more effective at removing heat than current cold plates, making overclocking more feasible. 'Surface of the sun' Some of the hot spots on a chip "could have the same heat flux as the surface of the sun when you look at the very small scale," said Husam Alissa, Microsoft's director of systems technology, referring to a technical measure of heat intensity, or density in a specific area. While the working prototype was demonstrated on a commercially available Intel Xeon chip, Microsoft says the innovation is part of a broader strategy to improve its entire hardware fleet. As a next step, the company is looking to incorporate the cooling technology into future versions of its own silicon, potentially including its Azure Cobalt chip and Maia AI accelerator. Those first-party chips, unveiled in 2023, reflect Microsoft's efforts to gain control over the final piece in its cloud platform. The company is competing to efficiently train and run cutting-edge AI models against Amazon, Google, and others, which are also making their own chips. Microsoft still uses third-party chips, including industry-standard GPUs from Nvidia and other suppliers, but it says a more integrated approach is necessary to meet the challenges of the AI era. The goal isn't to replace partners but to advance the broader ecosystem, said Rani Borkar, the corporate vice president who leads Azure hardware systems and infrastructure. "The demands of Al are such that, frankly, hardware on its own cannot keep up," Borkar said during a recent media briefing and tour of Microsoft's Silicon Lab in Redmond. "We really are all about co-designing, co-optimizing every layer of the stack." Networking and steel The company made two related announcements Tuesday morning: * Microsoft is working with Corning and Heraeus to move to industrial scale production of its hollow core fiber technology, which transmits pulses of light through a hollow channel vs. a conventional solid glass core, letting data move faster and with lower latency. * In an initiative focused on sustainability, Microsoft said it will procure "green steel" from partner Stegra for use in datacenter construction. The steel is produced in a plant designed to reduce carbon emissions by up to 95% vs. traditional steelmaking. As for the newly announced microfluidics advances, Microsoft says it will work with partners and the broader tech community to make the technology an industry standard. Longer term, the company sees the cooling technology as a foundational step toward a revolutionary new type of chip architecture: 3D stacking. While stacking layers of silicon dramatically reduces latency by shortening the distance data has to travel, it has been largely unfeasible because of the immense challenge of removing heat from the inner layers. Microfluidics could eventually solve that by allowing coolant to flow between each layer of the silicon brick, a breakthrough that Microsoft's Kleewein believes could be transformative. "That is where this could move from, 'it's an interesting change that the rest of the industry should adopt,' to a 'holy shit' moment in the evolution of technology," he said.
[7]
Microsoft in-chip cooling breakthrough cuts GPU heat rise by 65%
Microsoft has announced a breakthrough in cooling technology that could reshape the future of artificial intelligence hardware. The company successfully tested microfluidic cooling, a system that channels liquid directly inside a chip to remove heat. Early results show it can outperform today's advanced cold plate systems by as much as three times. AI chips are growing hotter with each generation. Current systems like cold plates sit on top of chips but remain separated by layers that limit efficiency.
[8]
Microsoft wants to solve AI data center overheating with its latest cooling innovation - microfluidics
Microfluidics cooling promises denser, faster data centers while reducing energy costs for AI workloads Microsoft has revealed it is testing a new chip cooling approach called microfluidics, aiming to solve one of the biggest challenges for artificial intelligence hardware. As AI chips grow more powerful, they generate more heat than previous generations, pushing traditional cooling methods close to their limits. Most data centers today use cold plates, where liquid passes through a plate attached to the chip. That system is separated from the heat source by multiple layers that trap heat, limiting its effectiveness. Microsoft's new design takes a different path. With microfluidics, tiny grooves are etched directly into the back of the chip, allowing coolant to flow onto the silicon itself and remove heat more efficiently. Judy Priest, Corporate VP and CTO for Cloud Operations and Innovation at Microsoft, believes the new approach could reshape how future chips are built. "Microfluidics would allow for more power-dense designs that will enable more features that customers care about and give better performance in a smaller amount of space," she said in a blog post announcing the news. Priest added that having proved the technology and shown the design worked, the next step was to test its reliability. In lab experiments, microfluidics removed heat up to three times better than cold plates, depending on workload, and also reduced GPU temperature rise by 65%. By combining the channel design with AI that maps unique hotspots on the chip, Microsoft was able to direct coolant with greater precision. Sashi Majety, senior technical program manager at Microsoft, said heat is becoming a barrier. "If you're still relying heavily on traditional cold plate technology, you're stuck," he said, adding that within five years chips may run too hot to be cooled effectively with today's systems. Microsoft believes its breakthrough shows how new approaches could enable faster, denser data centers while also lowering energy use for cooling. The tech giant is collaborating with Swiss startup Corintis to refine the chip design. In a bid to to massively reduce its water usage, Microsoft previously revealed it was working on a closed loop cooling system for data centers. A number of other technology firms, including Lenovo, Dell, Supermicro and Giga Computing, are also racing to develop advanced cooling systems, as overheating risks putting a ceiling on the pace of AI progress.
[9]
Microsoft is turning to the field of microfluidics to cool down AI chips
One of the major reasons why AI data centers are sucking up so much power is the need to cool processors that run very hot. But Microsoft Corp. is trying out a possible solution: sending fluid directly through tiny channels etched into the chips. The technology is called microfluidics, and it's being used in prototype systems in test conditions at the company, said Husam Alissa, who oversees Microsoft's systems technology. The technique has been applied to server chips used for Office cloud apps and the graphics processing units that handle artificial intelligence tasks, he said. Because the cooling fluid is applied directly to chips, it can be a relatively high temperature -- as much as 70C (158F) in some cases -- while still being effective. The company demonstrated the technology under a microscope at its campus in Redmond, Washington, saying that testing so far has shown significant improvements over conventional approaches. Cooling in this way could also let Microsoft develop more powerful chips by stacking them on top of each other. News of the project weighed on shares of Vertiv Holdings Co., which makes cooling systems for data centers. The stock dropped as much as 8.4%, marking its worst intraday decline in more than two months. The technology is part of a broader effort to customize hardware in Microsoft's data centers, which are expanding rapidly. In the past year, the company has added more than 2 gigawatts' worth of capacity. "When you are operating at that scale, efficiency is very important," Rani Borkar, vice president for hardware systems and infrastructure at Microsoft's Azure data center arm, said in an interview. The new cooling technology can also let Microsoft deliberately overheat chips in order to get better performance. Called overclocking, this can be useful for handling brief surges in demand. For example, Microsoft's Teams conferencing software experiences spikes in use around the hour and half hour because that's when most meetings begin. Instead of using more chips, the company could just overclock ones for a few minutes, said Jim Kleewein, a Microsoft technical fellow who works with the hardware team on filling the needs of its Office software products. The company is also more widely deploying hollow-core fiber for networking to increase data transmission speeds. This approach uses air to deliver data rather than the traditional glass core. At the Microsoft lab, a piece of the material the size of a few inches can be stretched to connect several kilometers, said Jamie Gaudette, who works on cloud network engineering. The software giant has teamed up with Corning Inc. and Heraeus Covantics to boost production of the material. Microsoft is also aiming to develop hardware for memory chips, but hasn't yet unveiled any plans, Borkar said. "There are things happening on the memory side, but they are not to a point where we want to discuss it," she said. "Memory is something I can't ignore." A key industry focus is high-bandwidth memory, or HBM, a component used in artificial intelligence computing that's made by companies like Micron Technology Inc. Right now, Microsoft's Maia AI chip -- overseen by Borkar -- relies on commercially available HBM. It's a vital technology, she said. "Today, HBM is the end-all and be-all," Borkar said. "What's going to happen next? We are looking at all of that." 2025 Bloomberg News. Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.
[10]
Microsoft is resorting to laser etching AI-designed cooling channels directly into data center chips to tame their massive heat
If you think the power consumption of today's gaming graphics cards is bad, it's nothing compared to how energy the massive processors in AI and data systems use. All that power ends up as heat, resulting in chip cooling being a serious challenge. Microsoft reckons it has a great solution, though, and it's all about getting water into the processors themselves. The most complex direct-die, liquid cooling loops you'll see in a gaming PC all involve using a chamber that mounts on top of the CPU. At no point does the coolant ever touch the chip directly. In a recently published blog, Microsoft explains how it has developed a system that does precisely that. By etching the surface of the processor die with an intricate pattern of tiny channels, water can then be pumped directly into the silicon itself, albeit to a very shallow depth. The keyword to describe this is microfluidics, a technology that's been around for many decades, and if the history of consumer tech is anything to go by, it'll be a phrase plastered across every CPU cooler within a couple of years (though not actually do anything). This might all just seem like Microsoft is cutting a few grooves into the chip and having water to flow through it, but it's far more complicated than that. For a start, the channels themselves are no wider than a human hair, and they're not just simple lines either. Microsoft employed the services of Swiss firm Corintis, which used AI to determine the best pattern for maximum heat transfer. The end result is a network of microchannels that genuinely look organic, though at first glance, you'd be forgiven for thinking the complex patterns were just manufacturing defects. It certainly looks super cool (pun very much intended). Microsoft claims the tech is up to three times more effective at removing heat from a massive AI GPU than a traditional cold plate (aka waterblock), citing a 65% reduction in the maximum temperature rise of the silicon. Since all the coolant transfer apparatus doesn't need to be right on top of the microchannels, the system can also be applied to stacked chips, with each one etched before mounting. This way, each die within the stack is cooled individually, meaning they can operate closer to their maximum specifications than with a normal cold plate. Take AMD's X3D processors, for example. These all have one stacked chip underneath the heatsink: a Core Complex Die (CCD) bonded to a 3D V-Cache die. Each one acts as a thermal barrier to the other, though the CCD does generate much more heat than the cache die. If these could be both cooled via microfluidics, you'd be able to operate them both at higher clock speeds. Of course, such complex tech isn't cheap to develop or implement, and the likelihood of it ever appearing at the consumer level is very slim. But I wouldn't be surprised if somebody takes an RTX 5090, rips off the heatsink, and swaps it for a homebrewed microfluidic cooler. There again, if ramping up power consumption is the only way AMD, Intel, and Nvidia can keep improving chip performance, perhaps we might see etched processors and direct-die cooling being standard fare in our gaming PCs. After all, it wasn't that long ago when heatpipes and vapour chambers were phrases never to be uttered by a PC component manufacturer, but now they're in coolers of every kind.
[11]
Microsoft Develops New AI Chip Cooling System, says It's 3x Better Than Current Systems | AIM
"If you're still relying heavily on traditional cold plate technology, you're stuck." Microsoft has announced a new cooling system that can remove heat from AI chips up to three times more effectively thancurrent methods. The company tested the in-chip microfluidic cooling technology on a server running simulated Teams services, showing its potential to support next-generation data centres. A Microsoft Teams call might look simple, but it actually relies on hundreds of different services working together in the background. One service connects the user to the meeting, another hosts it, while others handle chat storage, merge audio, record conversations or create transcripts. Each of these tasks puts pressure on different parts of the server. "The more heavily utilised a server is, the more heat it generates, which makes sense," Jim Kleewein, technical fellow at Microsoft, explained. The system utilises microchannels etched directly into the silicon, enabling coolant to flow directly onto the chip, where heat is concentrated. "If you're still relying heavily on traditional cold plate technology, you're stuck," Sashi Majety, senior technical programme manager at Microsoft, said. The company expects the innovation to help overcome rising heat issues caused by increasingly powerful AI chips, as it expressed in its blog post. Judy Priest, corporate vice president and chief technical officer at the company, said the breakthrough "would allow for more power-dense designs that will enable more features that customers care about and give better performance in a smaller amount of space." To achieve this, the team combined microfluidics with AI to map unique heat signatures and direct coolant precisely. Microsoft also worked with Swiss startup Corintis to design bio-inspired channels that mimic veins in leaves to optimise cooling efficiency. The giant said the cooling method could improve energy efficiency and lower costs in data centres, where heat management is a growing challenge. "Microfluidics improves cost, reliability, speed, consistency of behaviour and sustainability," Kleewein said. The company is now exploring how to integrate the technology into future chip generations and data centre operations. It also plans to continue collaborating with silicon manufacturers to scale the system. "We want microfluidics to become something everybody does, not just something we do," Kleewein added.
[12]
Microsoft Uses Nature-Inspired Design for Chip-Level Cooling
Microsoft says it may have found a better way to keep future AI chips cool, and it involves letting coolant flow right through the chip itself. Instead of attaching a heat sink on top, which adds another layer for the heat to pass through, the new method uses tiny channels etched directly into the chip's surface. Liquid runs through these microchannels, removing heat far more efficiently -- Microsoft claims up to three times better cooling compared to what's used in its data centers today. The really interesting part is how AI gets involved. Modern chips don't heat up evenly; some areas run much hotter than others depending on what tasks they're handling. Microsoft's system uses AI to constantly track where those hot spots appear, then adjusts the coolant flow so more liquid gets pumped through the areas that need it most. That way, the chip stays balanced and avoids thermal throttling, which can drag down performance. The channels themselves are extremely small, about the width of a human hair. Their design was inspired by natural structures like the veins in leaves or the patterns on butterfly wings, which distribute fluids efficiently in living systems. Microsoft worked with Corintis, a Swiss startup, to design these pathways and integrate them into a test chip. The combination of biomimicry and AI control makes the system more adaptive than static cooling hardware. For now, this is still at the prototype stage, but it shows where cooling tech may be heading as AI accelerators continue to scale up in power and density. Cooling is already one of the biggest challenges in data centers -- not just in terms of keeping servers from overheating, but also when it comes to energy costs. Systems like this could cut down on the amount of extra cooling hardware needed, freeing up space and lowering power usage. If Microsoft's approach works at scale, it could sit alongside other advanced solutions like immersion cooling or cold-plate liquid cooling already being explored for AI servers. The difference here is that the cooling happens directly on the chip, right where the heat is being generated. That makes it especially appealing for the next generation of AI workloads, which demand both high performance and energy efficiency. Source: Microsoft
[13]
Microsoft is turning to the field of microfluidics to cool down AI chips
One of the major reasons why AI data centers are sucking up so much power is the need to cool processors that run very hot. But Microsoft is trying out a possible solution: sending fluid directly through tiny channels etched into the chips. The technology is called microfluidics, and it's being used in prototype systems in test conditions at the company, said Husam Alissa, who oversees Microsoft's systems technology. The technique has been applied to server chips used for Office cloud apps and the graphics processing units that handle artificial intelligence tasks, he said. Because the cooling fluid is applied directly to chips, it can be a relatively high temperature -- as much as 158 Fahrenheit in some cases -- while still being effective. The company demonstrated the technology under a microscope last week at its campus in Redmond, saying that testing so far has shown significant improvements over conventional approaches. Cooling in this way could also let Microsoft develop more powerful chips by stacking them on top of each other. News of the project weighed on shares of Vertiv Holdings, which makes cooling systems for data centers. The stock dropped as much as 8.4%, marking its worst intraday decline in more than two months. The technology is part of a broader effort to customize hardware in Microsoft's data centers, which are expanding rapidly. In the past year, the company has added more than 2 gigawatts' worth of capacity. "When you are operating at that scale, efficiency is very important," Rani Borkar, vice president for hardware systems and infrastructure at Microsoft's Azure data center arm, said in an interview. The new cooling technology can also let Microsoft deliberately overheat chips in order to get better performance. Called overclocking, this can be useful for handling brief surges in demand. For example, Microsoft's Teams conferencing software experiences spikes in use around the hour and half-hour because that's when most meetings begin. Instead of using more chips, the company could just overclock some for a few minutes, said Jim Kleewein, a Microsoft technical fellow who works with the hardware team on filling the needs of its Office software products. The company is also more widely deploying hollow-core fiber for networking to increase data transmission speeds. This approach uses air to deliver data rather than the traditional glass core. At the Microsoft lab, a piece of the material the size of a few inches can be stretched to connect several kilometers, said Jamie Gaudette, who works on cloud network engineering. The software giant has teamed up with Corning and Heraeus Covantics to boost production of the material. Microsoft is also aiming to develop hardware for memory chips, but hasn't yet unveiled any plans, Borkar said. "There are things happening on the memory side, but they are not to a point where we want to discuss it," she said. "Memory is something I can't ignore." A key industry focus is high-bandwidth memory, or HBM, a component used in artificial intelligence computing that's made by companies like Micron Technology. Right now, Microsoft's Maia AI chip -- overseen by Borkar -- relies on commercially available HBM. It's a vital technology, she said. "Today, HBM is the end-all and be-all," Borkar said. "What's going to happen next? We are looking at all of that."
[14]
Microsoft announces new microfluid technology breakthrough that helps cool next-gen AI chips
TL;DR: Microsoft is pioneering microfluidic cooling by embedding liquid channels directly into AI chip silicon, improving heat removal up to three times more effectively than traditional cold plates. This innovation reduces GPU temperatures by 65%, lowers datacenter power costs, and supports smaller, more efficient servers for next-gen AI hardware. Microsoft is experimenting with a totally different way to cool AI chips by using microfluidics to deliver liquid directly inside of the silicon. Check it out: Unlike using regular cold plates that are positioned on top of the chip and are blocked by packaging layers, Microsoft's new approach cuts tiny channels into the silicon itself, where coolant flows through the grooves and drags heat away from the source. Microsoft says that in its tests, the use of microfluidics removed heat up to 3x more effectively than cold plates, and that it also sliced the maximum GPU temperature rise by 65%, depending on the workload and the chip type. AI models were also used to map hotspots on the chip, and to direct the coolant with increased precision. The company adds that it would make new servers smaller, reduce datacenter power costs, and extend the lifespan of GPU and AI accelerators. As next-gen semiconductors continue to get hotter and hotter with each generation, Microsoft warns that cold plates might not be sufficient in the next 5 years, which is why there's work being done now with partners to refine this new technology, from packaging to coolant chemistry to full server integration. Judy Priest, corporate vice president and chief technical officer of Cloud Operations and Innovation at Microsoft, explains: "Microfluidics would allow for more power-dense designs that will enable more features that customers care about and give better performance in a smaller amount of space. But we needed to prove the technology and the design worked, and then the very next thing I wanted to do was test reliability".
Share
Share
Copy Link
Microsoft has developed a new microfluidic cooling system for computer chips that could revolutionize data center efficiency and enable more powerful AI processors. The technology, which involves etching tiny channels directly into silicon chips, has shown promising results in lab tests.
Microsoft's Microfluidic Breakthrough
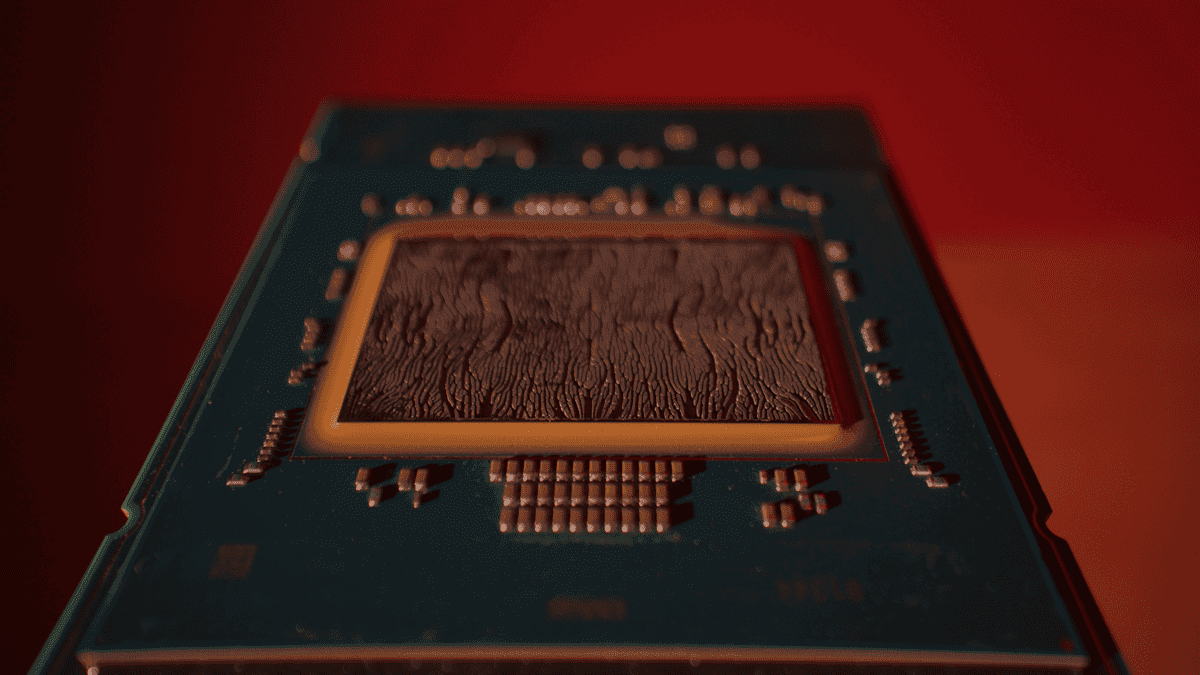
Microsoft has unveiled a groundbreaking cooling method for computer chips that could revolutionize the efficiency of data centers and enable the development of more powerful AI processors. The technology, known as microfluidics, involves etching tiny channels directly into silicon chips to allow liquid coolant to flow through them
1
2
.
Source: GeekWire
The Science Behind Microfluidic Cooling
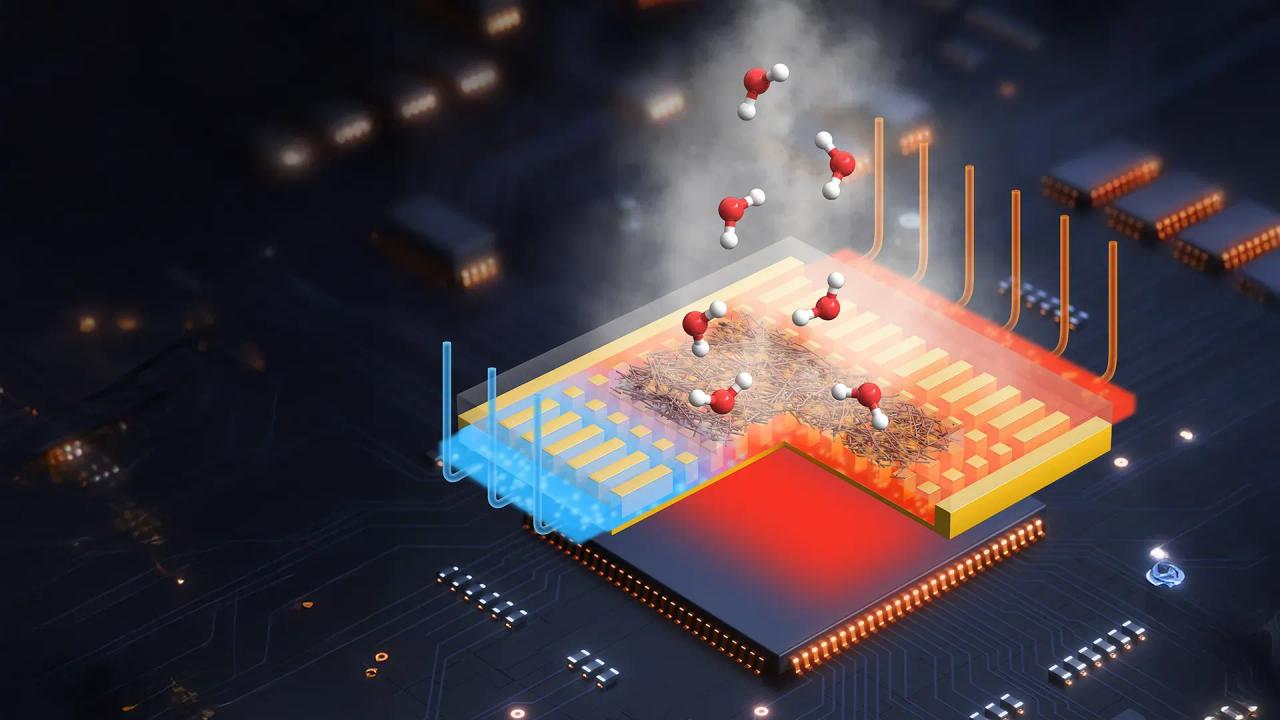
The microfluidic cooling system works by creating channels about the width of a human hair on the back of a chip. These channels allow coolant to come into direct contact with the silicon, eliminating the need for protective layers between the chip and the coolant, as is the case with current cold plate technology
1
3
.Microsoft partnered with Swiss startup Corintis to develop the channel layout, drawing inspiration from nature. The design mimics patterns found in leaf veins and butterfly wings, which are known for their efficient liquid distribution properties
3
5
.
Source: Guru3D
Impressive Performance and Potential
In lab tests, Microsoft found that this microfluidic cooling strategy can remove heat up to three times more effectively than cold plates currently used in data centers. The company successfully developed a microfluidic cooling system for a server running core services for a simulated Microsoft Teams meeting
1
.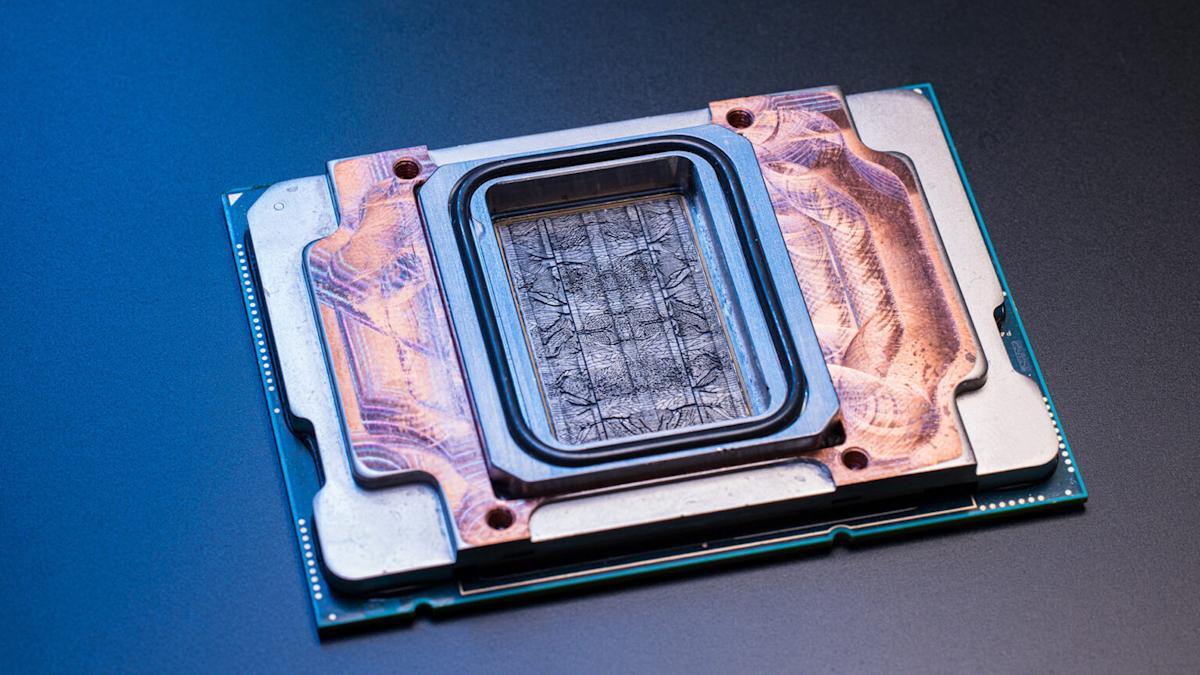
Source: Engadget
The prototype chip demonstrated a 65% reduction in the maximum temperature rise of the GPU's silicon, showcasing its potential for significantly improved thermal management
3
.Related Stories
Implications for AI and Data Centers
As AI models become more complex and demanding, the need for more powerful chips and efficient cooling systems grows. Microsoft's microfluidic technology could address several key challenges:
-
Energy Efficiency: By reducing the energy needed to cool data centers, microfluidic cooling could lead to more sustainable AI infrastructure
4
. -
Overclocking Potential: The improved cooling efficiency could allow for safer overclocking of chips, enabling them to handle spikes in demand without the risk of overheating
1
3
. -
Data Center Design: Microfluidic cooling could enable more tightly packed servers within data centers, potentially reducing the need for additional facilities
1
5
. -
Future Chip Architectures: The technology could pave the way for 3D chip architectures, which have been challenging to implement due to heat management issues
1
5
.
Challenges and Future Steps
While the results are promising, Microsoft acknowledges that there are still hurdles to overcome before microfluidic cooling can be widely implemented. These include adapting manufacturing processes to incorporate the etching of cooling channels and ensuring the structural integrity of the chips
1
5
.Microsoft plans to explore applying microfluidic cooling to its custom Cobalt and Maia chips and is working with fabrication partners to bring the technology into broader use. The company hopes that microfluidic cooling will become an industry standard, benefiting not just Microsoft but the entire tech ecosystem
3
5
.References
Summarized by
Navi
[1]
[3]
Related Stories
Microsoft Unveils Custom Chips and Infrastructure Upgrades to Boost AI Performance and Efficiency
20 Nov 2024•Technology

Microsoft Unveils Zero-Water Data Center Design to Reduce AI's Environmental Impact
10 Dec 2024•Technology

Breakthrough in Evaporative Cooling Technology Could Revolutionize Data Center Energy Efficiency
14 Jun 2025•Technology
Recent Highlights
1
Google Gemini 3.1 Pro doubles reasoning score, beats rivals in key AI benchmarks
Technology

2
Meta strikes up to $100 billion AI chips deal with AMD, could acquire 10% stake in chipmaker
Technology

3
Pentagon threatens Anthropic with supply chain risk label over AI safeguards for military use
Policy and Regulation





