Astrocytes: The Unsung Heroes of Brain Memory Storage
5 Sources
5 Sources
[1]
Overlooked cells might explain the human brain's huge storage capacity
The human brain contains about 86 billion neurons. These cells fire electrical signals that help the brain store memories and send information and commands throughout the brain and the nervous system. The brain also contains billions of astrocytes -- star-shaped cells with many long extensions that allow them to interact with millions of neurons. Although they have long been thought to be mainly supportive cells, recent studies have suggested that astrocytes may play a role in memory storage and other cognitive functions. MIT researchers have now put forth a new hypothesis for how astrocytes might contribute to memory storage. The architecture suggested by their model would help to explain the brain's massive storage capacity, which is much greater than would be expected using neurons alone. "Originally, astrocytes were believed to just clean up around neurons, but there's no particular reason that evolution did not realize that, because each astrocyte can contact hundreds of thousands of synapses, they could also be used for computation," says Jean-Jacques Slotine, an MIT professor of mechanical engineering and of brain and cognitive sciences, and an author of the new study. Dmitry Krotov, a research staff member at the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab and IBM Research, is the senior author of the open-access paper, which appeared May 23 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Leo Kozachkov PhD '22 is the paper's lead author. Memory capacity Astrocytes have a variety of support functions in the brain: They clean up debris, provide nutrients to neurons, and help to ensure an adequate blood supply. Astrocytes also send out many thin tentacles, known as processes, which can each wrap around a single synapse -- the junctions where two neurons interact with each other -- to create a tripartite (three-part) synapse. Within the past couple of years, neuroscientists have shown that if the connections between astrocytes and neurons in the hippocampus are disrupted, memory storage and retrieval are impaired. Unlike neurons, astrocytes can't fire action potentials, the electrical impulses that carry information throughout the brain. However, they can use calcium signaling to communicate with other astrocytes. Over the past few decades, as the resolution of calcium imaging has improved, researchers have found that calcium signaling also allows astrocytes to coordinate their activity with neurons in the synapses that they associate with. These studies suggest that astrocytes can detect neural activity, which leads them to alter their own calcium levels. Those changes may trigger astrocytes to release gliotransmitters -- signaling molecules similar to neurotransmitters -- into the synapse. "There's a closed circle between neuron signaling and astrocyte-to-neuron signaling," Kozachkov says. "The thing that is unknown is precisely what kind of computations the astrocytes can do with the information that they're sensing from neurons." The MIT team set out to model what those connections might be doing and how they might contribute to memory storage. Their model is based on Hopfield networks -- a type of neural network that can store and recall patterns. Hopfield networks, originally developed by John Hopfield and Shun-Ichi Amari in the 1970s and 1980s, are often used to model the brain, but it has been shown that these networks can't store enough information to account for the vast memory capacity of the human brain. A newer, modified version of a Hopfield network, known as dense associative memory, can store much more information through a higher order of couplings between more than two neurons. However, it is unclear how the brain could implement these many-neuron couplings at a hypothetical synapse, since conventional synapses only connect two neurons: a presynaptic cell and a postsynaptic cell. This is where astrocytes come into play. "If you have a network of neurons, which couple in pairs, there's only a very small amount of information that you can encode in those networks," Krotov says. "In order to build dense associative memories, you need to couple more than two neurons. Because a single astrocyte can connect to many neurons, and many synapses, it is tempting to hypothesize that there might exist an information transfer between synapses mediated by this biological cell. That was the biggest inspiration for us to look into astrocytes and led us to start thinking about how to build dense associative memories in biology." The neuron-astrocyte associative memory model that the researchers developed in their new paper can store significantly more information than a traditional Hopfield network -- more than enough to account for the brain's memory capacity. Intricate connections The extensive biological connections between neurons and astrocytes offer support for the idea that this type of model might explain how the brain's memory storage systems work, the researchers say. They hypothesize that within astrocytes, memories are encoded by gradual changes in the patterns of calcium flow. This information is conveyed to neurons by gliotransmitters released at synapses that astrocyte processes connect to. "By careful coordination of these two things -- the spatial temporal pattern of calcium in the cell and then the signaling back to the neurons -- you can get exactly the dynamics you need for this massively increased memory capacity," Kozachkov says. One of the key features of the new model is that it treats astrocytes as collections of processes, rather than a single entity. Each of those processes can be considered one computational unit. Because of the high information storage capabilities of dense associative memories, the ratio of the amount of information stored to the number of computational units is very high and grows with the size of the network. This makes the system not only high capacity, but also energy efficient. "By conceptualizing tripartite synaptic domains -- where astrocytes interact dynamically with pre- and postsynaptic neurons -- as the brain's fundamental computational units, the authors argue that each unit can store as many memory patterns as there are neurons in the network. This leads to the striking implication that, in principle, a neuron-astrocyte network could store an arbitrarily large number of patterns, limited only by its size," says Maurizio De Pitta, an assistant professor of physiology at the Krembil Research Institute at the University of Toronto, who was not involved in the study. To test whether this model might accurately represent how the brain stores memory, researchers could try to develop ways to precisely manipulate the connections between astrocytes' processes, then observe how those manipulations affect memory function. "We hope that one of the consequences of this work could be that experimentalists would consider this idea seriously and perform some experiments testing this hypothesis," Krotov says. In addition to offering insight into how the brain may store memory, this model could also provide guidance for researchers working on artificial intelligence. By varying the connectivity of the process-to-process network, researchers could generate a huge range of models that could be explored for different purposes, for instance, creating a continuum between dense associative memories and attention mechanisms in large language models. "While neuroscience initially inspired key ideas in AI, the last 50 years of neuroscience research have had little influence on the field, and many modern AI algorithms have drifted away from neural analogies," Slotine says. "In this sense, this work may be one of the first contributions to AI informed by recent neuroscience research."
[2]
Overlooked cells might explain the human brain's huge storage capacity
The human brain contains about 86 billion neurons. These cells fire electrical signals that help the brain store memories and send information and commands throughout the brain and the nervous system. The brain also contains billions of astrocytes -- star-shaped cells with many long extensions that allow them to interact with millions of neurons. Although they have long been thought to be mainly supportive cells, recent studies have suggested that astrocytes may play a role in memory storage and other cognitive functions. MIT researchers have now put forth a new hypothesis for how astrocytes might contribute to memory storage. The architecture suggested by their model would help to explain the brain's massive storage capacity, which is much greater than would be expected using neurons alone. "Originally, astrocytes were believed to just clean up around neurons, but there's no particular reason that evolution did not realize that, because each astrocyte can contact hundreds of thousands of synapses, they could also be used for computation," says Jean-Jacques Slotine, an MIT professor of mechanical engineering and of brain and cognitive sciences, and an author of the new study. Dmitry Krotov, a research staff member at the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab and IBM Research, is the senior author of the open-access paper, which appeared May 23 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Leo Kozachkov PhD '22 is the paper's lead author. Memory capacity Astrocytes have a variety of support functions in the brain: They clean up debris, provide nutrients to neurons, and help to ensure an adequate blood supply. Astrocytes also send out many thin tentacles, known as processes, which can each wrap around a single synapse -- the junctions where two neurons interact with each other -- to create a tripartite (three-part) synapse. Within the past couple of years, neuroscientists have shown that if the connections between astrocytes and neurons in the hippocampus are disrupted, memory storage and retrieval are impaired. Unlike neurons, astrocytes can't fire action potentials, the electrical impulses that carry information throughout the brain. However, they can use calcium signaling to communicate with other astrocytes. Over the past few decades, as the resolution of calcium imaging has improved, researchers have found that calcium signaling also allows astrocytes to coordinate their activity with neurons in the synapses that they associate with. These studies suggest that astrocytes can detect neural activity, which leads them to alter their own calcium levels. Those changes may trigger astrocytes to release gliotransmitters -- signaling molecules similar to neurotransmitters -- into the synapse. "There's a closed circle between neuron signaling and astrocyte-to-neuron signaling," Kozachkov says. "The thing that is unknown is precisely what kind of computations the astrocytes can do with the information that they're sensing from neurons." The MIT team set out to model what those connections might be doing and how they might contribute to memory storage. Their model is based on Hopfield networks -- a type of neural network that can store and recall patterns. Hopfield networks, originally developed by John Hopfield and Shun-Ichi Amari in the 1970s and 1980s, are often used to model the brain, but it has been shown that these networks can't store enough information to account for the vast memory capacity of the human brain. A newer, modified version of a Hopfield network, known as dense associative memory, can store much more information through a higher order of couplings between more than two neurons. However, it is unclear how the brain could implement these many-neuron couplings at a hypothetical synapse, since conventional synapses only connect two neurons: a presynaptic cell and a postsynaptic cell. This is where astrocytes come into play. "If you have a network of neurons, which couple in pairs, there's only a very small amount of information that you can encode in those networks," Krotov says. "In order to build dense associative memories, you need to couple more than two neurons. Because a single astrocyte can connect to many neurons, and many synapses, it is tempting to hypothesize that there might exist an information transfer between synapses mediated by this biological cell. That was the biggest inspiration for us to look into astrocytes and led us to start thinking about how to build dense associative memories in biology." The neuron-astrocyte associative memory model that the researchers developed in their new paper can store significantly more information than a traditional Hopfield network -- more than enough to account for the brain's memory capacity. Intricate connections The extensive biological connections between neurons and astrocytes offer support for the idea that this type of model might explain how the brain's memory storage systems work, the researchers say. They hypothesize that within astrocytes, memories are encoded by gradual changes in the patterns of calcium flow. This information is conveyed to neurons by gliotransmitters released at synapses that astrocyte processes connect to. "By careful coordination of these two things -- the spatial temporal pattern of calcium in the cell and then the signaling back to the neurons -- you can get exactly the dynamics you need for this massively increased memory capacity," Kozachkov says. One of the key features of the new model is that it treats astrocytes as collections of processes, rather than a single entity. Each of those processes can be considered one computational unit. Because of the high information storage capabilities of dense associative memories, the ratio of the amount of information stored to the number of computational units is very high and grows with the size of the network. This makes the system not only high capacity, but also energy efficient. "By conceptualizing tripartite synaptic domains -- where astrocytes interact dynamically with pre- and postsynaptic neurons -- as the brain's fundamental computational units, the authors argue that each unit can store as many memory patterns as there are neurons in the network. This leads to the striking implication that, in principle, a neuron-astrocyte network could store an arbitrarily large number of patterns, limited only by its size," says Maurizio De Pitta, an assistant professor of physiology at the Krembil Research Institute at the University of Toronto, who was not involved in the study. To test whether this model might accurately represent how the brain stores memory, researchers could try to develop ways to precisely manipulate the connections between astrocytes' processes, then observe how those manipulations affect memory function. "We hope that one of the consequences of this work could be that experimentalists would consider this idea seriously and perform some experiments testing this hypothesis," Krotov says. In addition to offering insight into how the brain may store memory, this model could also provide guidance for researchers working on artificial intelligence. By varying the connectivity of the process-to-process network, researchers could generate a huge range of models that could be explored for different purposes, for instance, creating a continuum between dense associative memories and attention mechanisms in large language models. "While neuroscience initially inspired key ideas in AI, the last 50 years of neuroscience research have had little influence on the field, and many modern AI algorithms have drifted away from neural analogies," Slotine says. "In this sense, this work may be one of the first contributions to AI informed by recent neuroscience research."
[3]
Astrocytes may contribute to memory storage in the brain
Massachusetts Institute of TechnologyMay 27 2025 The human brain contains about 86 billion neurons. These cells fire electrical signals that help the brain store memories and send information and commands throughout the brain and the nervous system. The brain also contains billions of astrocytes - star-shaped cells with many long extensions that allow them to interact with millions of neurons. Although they have long been thought to be mainly supportive cells, recent studies have suggested that astrocytes may play a role in memory storage and other cognitive functions. MIT researchers have now put forth a new hypothesis for how astrocytes might contribute to memory storage. The architecture suggested by their model would help to explain the brain's massive storage capacity, which is much greater than would be expected using neurons alone. Originally, astrocytes were believed to just clean up around neurons, but there's no particular reason that evolution did not realize that, because each astrocyte can contact hundreds of thousands of synapses, they could also be used for computation." Jean-Jacques Slotine, MIT professor of mechanical engineering and of brain and cognitive sciences, and study author Dmitry Krotov, a research staff member at the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab and IBM Research, is the senior author of the open-access paper, which appeared May 23 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Leo Kozachkov PhD '22 is the paper's lead author. Memory capacity Astrocytes have a variety of support functions in the brain: They clean up debris, provide nutrients to neurons, and help to ensure an adequate blood supply. Astrocytes also send out many thin tentacles, known as processes, which can each wrap around a single synapse - the junctions where two neurons interact with each other - to create a tripartite (three-part) synapse. Within the past couple of years, neuroscientists have shown that if the connections between astrocytes and neurons in the hippocampus are disrupted, memory storage and retrieval are impaired. Unlike neurons, astrocytes can't fire action potentials, the electrical impulses that carry information throughout the brain. However, they can use calcium signaling to communicate with other astrocytes. Over the past few decades, as the resolution of calcium imaging has improved, researchers have found that calcium signaling also allows astrocytes to coordinate their activity with neurons in the synapses that they associate with. These studies suggest that astrocytes can detect neural activity, which leads them to alter their own calcium levels. Those changes may trigger astrocytes to release gliotransmitters - signaling molecules similar to neurotransmitters - into the synapse. "There's a closed circle between neuron signaling and astrocyte-to-neuron signaling," Kozachkov says. "The thing that is unknown is precisely what kind of computations the astrocytes can do with the information that they're sensing from neurons." The MIT team set out to model what those connections might be doing and how they might contribute to memory storage. Their model is based on Hopfield networks - a type of neural network that can store and recall patterns. Hopfield networks, originally developed by John Hopfield and Shun-Ichi Amari in the 1970s and 1980s, are often used to model the brain, but it has been shown that these networks can't store enough information to account for the vast memory capacity of the human brain. A newer, modified version of a Hopfield network, known as dense associative memory, can store much more information through a higher order of couplings between more than two neurons. However, it is unclear how the brain could implement these many-neuron couplings at a hypothetical synapse, since conventional synapses only connect two neurons: a presynaptic cell and a postsynaptic cell. This is where astrocytes come into play. "If you have a network of neurons, which couple in pairs, there's only a very small amount of information that you can encode in those networks," Krotov says. "In order to build dense associative memories, you need to couple more than two neurons. Because a single astrocyte can connect to many neurons, and many synapses, it is tempting to hypothesize that there might exist an information transfer between synapses mediated by this biological cell. That was the biggest inspiration for us to look into astrocytes and led us to start thinking about how to build dense associative memories in biology." The neuron-astrocyte associative memory model that the researchers developed in their new paper can store significantly more information than a traditional Hopfield network - more than enough to account for the brain's memory capacity. Intricate connections The extensive biological connections between neurons and astrocytes offer support for the idea that this type of model might explain how the brain's memory storage systems work, the researchers say. They hypothesize that within astrocytes, memories are encoded by gradual changes in the patterns of calcium flow. This information is conveyed to neurons by gliotransmitters released at synapses that astrocyte processes connect to. "By careful coordination of these two things - the spatial temporal pattern of calcium in the cell and then the signaling back to the neurons - you can get exactly the dynamics you need for this massively increased memory capacity," Kozachkov says. One of the key features of the new model is that it treats astrocytes as collections of processes, rather than a single entity. Each of those processes can be considered one computational unit. Because of the high information storage capabilities of dense associative memories, the ratio of the amount of information stored to the number of computational units is very high and grows with the size of the network. This makes the system not only high capacity, but also energy efficient. "By conceptualizing tripartite synaptic domains - where astrocytes interact dynamically with pre- and postsynaptic neurons - as the brain's fundamental computational units, the authors argue that each unit can store as many memory patterns as there are neurons in the network. This leads to the striking implication that, in principle, a neuron-astrocyte network could store an arbitrarily large number of patterns, limited only by its size," says Maurizio De Pitta, an assistant professor of physiology at the Krembil Research Institute at the University of Toronto, who was not involved in the study. To test whether this model might accurately represent how the brain stores memory, researchers could try to develop ways to precisely manipulate the connections between astrocytes' processes, then observe how those manipulations affect memory function. "We hope that one of the consequences of this work could be that experimentalists would consider this idea seriously and perform some experiments testing this hypothesis," Krotov says. In addition to offering insight into how the brain may store memory, this model could also provide guidance for researchers working on artificial intelligence. By varying the connectivity of the process-to-process network, researchers could generate a huge range of models that could be explored for different purposes, for instance, creating a continuum between dense associative memories and attention mechanisms in large language models. "While neuroscience initially inspired key ideas in AI, the last 50 years of neuroscience research have had little influence on the field, and many modern AI algorithms have drifted away from neural analogies," Slotine says. "In this sense, this work may be one of the first contributions to AI informed by recent neuroscience research." Massachusetts Institute of Technology Journal reference: Kozachkov, L., et al. (2025). Neuron-astrocyte associative memory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2417788122.
[4]
Astrocytes May Hold the Key to Brain's Vast Memory Capacity - Neuroscience News
Summary: New research proposes that astrocytes -- long thought to be merely supportive cells -- may significantly enhance the brain's ability to store memories. Unlike neurons, astrocytes cannot fire electrical signals but can influence synaptic activity through calcium signaling and gliotransmitters. A computational model based on dense associative memory suggests astrocytes could link multiple neurons at once, greatly boosting storage capacity. This model also frames astrocytic processes as individual computational units, offering a more efficient memory system than neuron-only networks. The human brain contains about 86 billion neurons. These cells fire electrical signals that help the brain store memories and send information and commands throughout the brain and the nervous system. The brain also contains billions of astrocytes -- star-shaped cells with many long extensions that allow them to interact with millions of neurons. Although they have long been thought to be mainly supportive cells, recent studies have suggested that astrocytes may play a role in memory storage and other cognitive functions. MIT researchers have now put forth a new hypothesis for how astrocytes might contribute to memory storage. The architecture suggested by their model would help to explain the brain's massive storage capacity, which is much greater than would be expected using neurons alone. "Originally, astrocytes were believed to just clean up around neurons, but there's no particular reason that evolution did not realize that, because each astrocyte can contact hundreds of thousands of synapses, they could also be used for computation," says Jean-Jacques Slotine, an MIT professor of mechanical engineering and of brain and cognitive sciences, and an author of the new study. Dmitry Krotov, a research staff member at the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab and IBM Research, is the senior author of the open-access paper, which appeared May 23 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Leo Kozachkov PhD '22 is the paper's lead author. Memory capacity Astrocytes have a variety of support functions in the brain: They clean up debris, provide nutrients to neurons, and help to ensure an adequate blood supply. Astrocytes also send out many thin tentacles, known as processes, which can each wrap around a single synapse -- the junctions where two neurons interact with each other -- to create a tripartite (three-part) synapse. Within the past couple of years, neuroscientists have shown that if the connections between astrocytes and neurons in the hippocampus are disrupted, memory storage and retrieval are impaired. Unlike neurons, astrocytes can't fire action potentials, the electrical impulses that carry information throughout the brain. However, they can use calcium signaling to communicate with other astrocytes. Over the past few decades, as the resolution of calcium imaging has improved, researchers have found that calcium signaling also allows astrocytes to coordinate their activity with neurons in the synapses that they associate with. These studies suggest that astrocytes can detect neural activity, which leads them to alter their own calcium levels. Those changes may trigger astrocytes to release gliotransmitters -- signaling molecules similar to neurotransmitters -- into the synapse. "There's a closed circle between neuron signaling and astrocyte-to-neuron signaling," Kozachkov says. "The thing that is unknown is precisely what kind of computations the astrocytes can do with the information that they're sensing from neurons." The MIT team set out to model what those connections might be doing and how they might contribute to memory storage. Their model is based on Hopfield networks -- a type of neural network that can store and recall patterns. Hopfield networks, originally developed by John Hopfield and Shun-Ichi Amari in the 1970s and 1980s, are often used to model the brain, but it has been shown that these networks can't store enough information to account for the vast memory capacity of the human brain. A newer, modified version of a Hopfield network, known as dense associative memory, can store much more information through a higher order of couplings between more than two neurons. However, it is unclear how the brain could implement these many-neuron couplings at a hypothetical synapse, since conventional synapses only connect two neurons: a presynaptic cell and a postsynaptic cell. This is where astrocytes come into play. "If you have a network of neurons, which couple in pairs, there's only a very small amount of information that you can encode in those networks," Krotov says. "In order to build dense associative memories, you need to couple more than two neurons. Because a single astrocyte can connect to many neurons, and many synapses, it is tempting to hypothesize that there might exist an information transfer between synapses mediated by this biological cell. "That was the biggest inspiration for us to look into astrocytes and led us to start thinking about how to build dense associative memories in biology." The neuron-astrocyte associative memory model that the researchers developed in their new paper can store significantly more information than a traditional Hopfield network -- more than enough to account for the brain's memory capacity. Intricate connections The extensive biological connections between neurons and astrocytes offer support for the idea that this type of model might explain how the brain's memory storage systems work, the researchers say. They hypothesize that within astrocytes, memories are encoded by gradual changes in the patterns of calcium flow. This information is conveyed to neurons by gliotransmitters released at synapses that astrocyte processes connect to. "By careful coordination of these two things -- the spatial temporal pattern of calcium in the cell and then the signaling back to the neurons -- you can get exactly the dynamics you need for this massively increased memory capacity," Kozachkov says. One of the key features of the new model is that it treats astrocytes as collections of processes, rather than a single entity. Each of those processes can be considered one computational unit. Because of the high information storage capabilities of dense associative memories, the ratio of the amount of information stored to the number of computational units is very high and grows with the size of the network. This makes the system not only high capacity, but also energy efficient. "By conceptualizing tripartite synaptic domains -- where astrocytes interact dynamically with pre- and postsynaptic neurons -- as the brain's fundamental computational units, the authors argue that each unit can store as many memory patterns as there are neurons in the network. "This leads to the striking implication that, in principle, a neuron-astrocyte network could store an arbitrarily large number of patterns, limited only by its size," says Maurizio De Pitta, an assistant professor of physiology at the Krembil Research Institute at the University of Toronto, who was not involved in the study. To test whether this model might accurately represent how the brain stores memory, researchers could try to develop ways to precisely manipulate the connections between astrocytes' processes, then observe how those manipulations affect memory function. "We hope that one of the consequences of this work could be that experimentalists would consider this idea seriously and perform some experiments testing this hypothesis," Krotov says. In addition to offering insight into how the brain may store memory, this model could also provide guidance for researchers working on artificial intelligence. By varying the connectivity of the process-to-process network, researchers could generate a huge range of models that could be explored for different purposes, for instance, creating a continuum between dense associative memories and attention mechanisms in large language models. "While neuroscience initially inspired key ideas in AI, the last 50 years of neuroscience research have had little influence on the field, and many modern AI algorithms have drifted away from neural analogies," Slotine says. "In this sense, this work may be one of the first contributions to AI informed by recent neuroscience research." Astrocytes, the most abundant type of glial cell, play a fundamental role in memory. Despite most hippocampal synapses being contacted by an astrocyte, there are no current theories that explain how neurons, synapses, and astrocytes might collectively contribute to memory function. We demonstrate that fundamental aspects of astrocyte morphology and physiology naturally lead to a dynamic, high-capacity associative memory system. The neuron-astrocyte networks generated by our framework are closely related to popular machine learning architectures known as Dense Associative Memories. Adjusting the connectivity pattern, the model developed here leads to a family of associative memory networks that includes a Dense Associative Memory and a Transformer as two limiting cases. In the known biological implementations of Dense Associative Memories, the ratio of stored memories to the number of neurons remains constant, despite the growth of the network size. Our work demonstrates that neuron-astrocyte networks follow a superior memory scaling law, outperforming known biological implementations of Dense Associative Memory. Our model suggests an exciting and previously unnoticed possibility that memories could be stored, at least in part, within the network of astrocyte processes rather than solely in the synaptic weights between neurons.
[5]
Cells called 'astrocytes' help human brains store so much data - Earth.com
Astrocytes are the brain's star-shaped support cells, and they might be doing more than just backing up neurons. While we usually credit neurons for storing memories and processing thoughts, astrocytes are just as abundant and far more involved than was once believed. The human brain contains about 86 billion neurons, each firing electrical signals that help us think, feel, and remember. But alongside them, astrocytes quietly handle cleanup, deliver nutrients, and manage blood flow. For a long time, these cells were seen as background players. Now, scientists are starting to see them in a new light. A recent study from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) suggests astrocytes could play a central role in how the brain stores memories, potentially changing how we understand this process. Unlike neurons, astrocytes don't generate electrical impulses. Instead, they use calcium signals to communicate. These signals travel through thin extensions, called processes, that can wrap around the junctions where neurons connect - known as synapses. This forms what's called a "tripartite synapse" involving a presynaptic neuron, a postsynaptic neuron, and the astrocyte process. For years, the exact role astrocytes played in memory remained a mystery. But new imaging technology has revealed that calcium signaling allows astrocytes to sync their activity with neurons. This means they don't just observe what's happening - they're actively participating by releasing chemical messengers called gliotransmitters, which affect synaptic function. "There's a closed circle between neuron signaling and astrocyte-to-neuron signaling," said Leo Kozachkov, the paper's lead author. "The thing that is unknown is precisely what kind of computations the astrocytes can do with the information that they're sensing from neurons." Inspired by this feedback loop, MIT researchers built a model to test what astrocytes might be doing with the information they receive. They based their approach on a type of artificial neural network called a Hopfield network. While useful in theory, Hopfield networks don't have enough storage capacity to explain how the brain actually works. A newer version called dense associative memory boosts this capacity by linking more than two neurons at a time. But there's a catch - in real life, synapses usually only connect two neurons. That's where astrocytes come in. "If you have a network of neurons, which couple in pairs, there's only a very small amount of information that you can encode in those networks," explained Dmitry Krotov, a research staff member at the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab and IBM Research. According to Krotov, in order to build dense associative memories, you need to couple more than two neurons. Because a single astrocyte can connect to many neurons, and many synapses, it is tempting to hypothesize that there might exist an information transfer between synapses mediated by this biological cell. "That was the biggest inspiration for us to look into astrocytes and led us to start thinking about how to build dense associative memories in biology," Krotov continued. The result? A hybrid model that treats astrocytes as computing units in their own right. Each process of an astrocyte is considered a unit capable of interacting with many synapses. Together, they help form a system that can store far more information than traditional neuron-only models. One unique feature of this model is how it views astrocytes. Instead of seeing them as a single cell, it breaks them down into many processes - each one acting like its own little calculator. This division helps explain how the brain might pack in so much memory with relatively low energy use. "By careful coordination of these two things - the spatial temporal pattern of calcium in the cell and then the signaling back to the neurons - you can get exactly the dynamics you need for this massively increased memory capacity," Kozachkov explained. Supporting this theory is the physical layout of astrocytes. Each one touches hundreds of thousands of synapses. The researchers believe that patterns in calcium flow within astrocytes could encode memories. These patterns could then influence neurons by releasing gliotransmitters at key synapses. "By conceptualizing tripartite synaptic domains - where astrocytes interact dynamically with pre- and postsynaptic neurons - as the brain's fundamental computational units, the authors argue that each unit can store as many memory patterns as there are neurons in the network," said Professor Maurizio De Pitta from the Krembil Research Institute, University of Toronto, who was not involved in the study. "This leads to the striking implication that, in principle, a neuron-astrocyte network could store an arbitrarily large number of patterns, limited only by its size," he added. To find out if this model reflects reality, researchers hope to test it by manipulating the connections between astrocyte processes and observing the impact on memory. "We hope that one of the consequences of this work could be that experimentalists would consider this idea seriously and perform some experiments testing this hypothesis," Krotov said. This theory also holds promise beyond neuroscience. It could change how artificial intelligence systems are designed. By mimicking how astrocytes link various neurons together, future AI models might unlock more efficient memory storage. "While neuroscience initially inspired key ideas in AI, the last 50 years of neuroscience research have had little influence on the field, and many modern AI algorithms have drifted away from neural analogies," remarked Slotine. "In this sense, this work may be one of the first contributions to AI informed by recent neuroscience research." The quiet stars of the brain may hold more memory power than anyone imagined. With a better understanding of astrocytes, both brain science and artificial intelligence could be in for a rethink. The full study was published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. -- - Like what you read? Subscribe to our newsletter for engaging articles, exclusive content, and the latest updates.
Share
Share
Copy Link
MIT researchers propose a new model suggesting astrocytes, long thought to be mere support cells, may play a crucial role in the brain's vast memory storage capacity.
The Overlooked Stars of Brain Function
For decades, neurons have been the stars of brain research, credited with storing memories and processing thoughts. However, recent studies are shedding light on another abundant cell type in the brain: astrocytes. These star-shaped cells, long considered mere support staff, may play a crucial role in the brain's vast memory storage capacity
1
.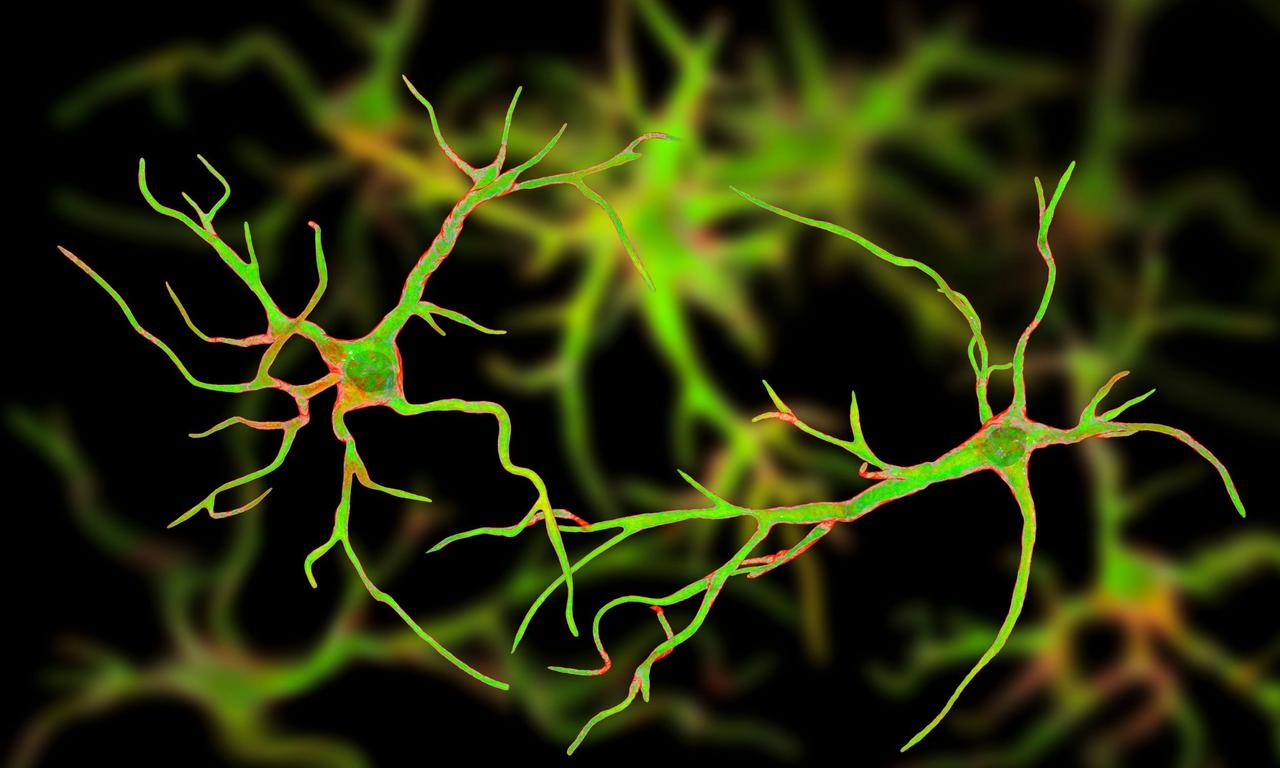
Source: Earth.com
Astrocytes: More Than Just Support Cells
The human brain contains approximately 86 billion neurons and a similar number of astrocytes. While neurons fire electrical signals to transmit information, astrocytes use calcium signaling to communicate with other cells. Recent research has shown that disrupting the connections between astrocytes and neurons in the hippocampus impairs memory storage and retrieval
2
.The Tripartite Synapse: A New Perspective on Neural Connections
Astrocytes extend thin processes that can wrap around synapses, forming what's known as a "tripartite synapse." This structure involves a presynaptic neuron, a postsynaptic neuron, and an astrocyte process. Through calcium signaling, astrocytes can detect neural activity and respond by releasing gliotransmitters, potentially influencing synaptic function
3
.
Source: Neuroscience News
A New Model for Memory Storage
MIT researchers have proposed a novel hypothesis for how astrocytes might contribute to memory storage. Their model, based on dense associative memory networks, suggests that astrocytes could link multiple neurons at once, significantly boosting storage capacity beyond what traditional neuron-only models can explain
4
.Astrocytes as Computational Units
One key feature of the new model is that it treats astrocytes as collections of processes, rather than single entities. Each process is considered a computational unit, capable of interacting with many synapses. This approach helps explain how the brain might store vast amounts of information with relatively low energy consumption
5
.Related Stories
Implications for Neuroscience and AI
The researchers hypothesize that within astrocytes, memories are encoded by gradual changes in calcium flow patterns. This information is then conveyed to neurons through gliotransmitters released at connected synapses. If proven correct, this theory could not only revolutionize our understanding of brain function but also inspire new approaches in artificial intelligence design
1
.Future Research Directions
Source: News-Medical
To validate this model, researchers aim to conduct experiments manipulating the connections between astrocyte processes and observing the impact on memory. The findings could lead to new avenues for understanding and treating memory-related disorders, as well as developing more efficient AI systems inspired by the brain's intricate memory storage mechanisms
5
.References
Summarized by
Navi
[3]
[4]
Related Stories
New Input-Driven Plasticity Model Revolutionizes Understanding of Memory Retrieval in AI
15 May 2025•Science and Research

Neuroscientists Discover Stable Synapses in the Brain's Adaptable Zone
17 Sept 2024

AI-Assisted Study Reveals Structural Basis of Memory Formation in Mouse Brain
21 Mar 2025•Science and Research

Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.4, New AI Model Built for Agents and Professional Work
Technology

2
Anthropic sues Pentagon over supply chain risk label after refusing autonomous weapons use
Policy and Regulation

3
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round as questions swirl around AI bubble and profitability
Business and Economy