Paralyzed Man Flies Virtual Drone Using Brain-Computer Interface
6 Sources
6 Sources
[1]
Paralyzed Man Can Now Fly Drone Using Brain Implant
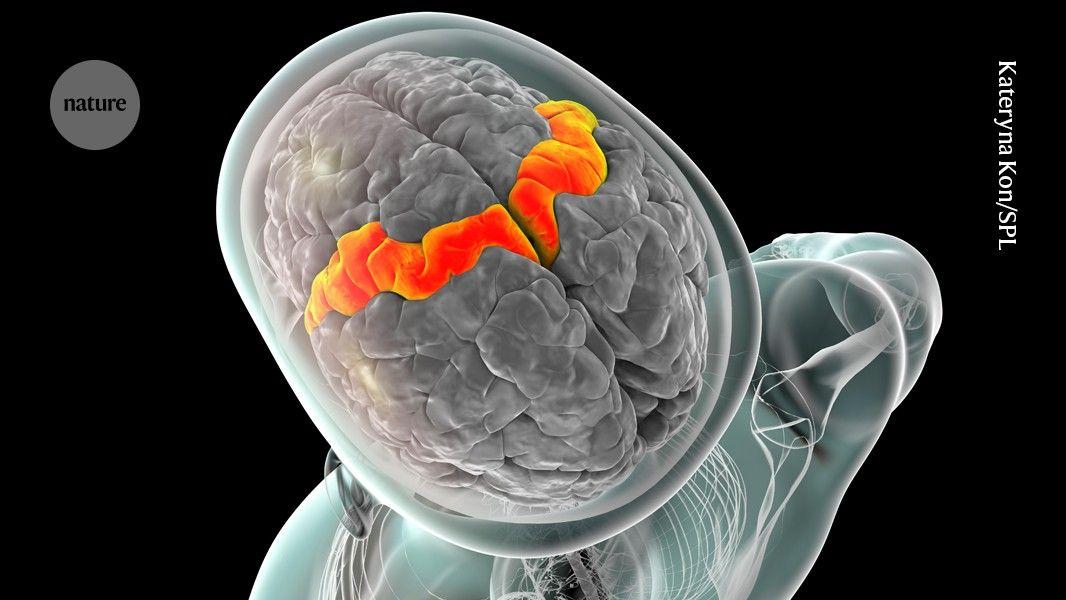
A groundbreaking brain implant has allowed a paralyzed man to control a virtual drone and fly it through an obstacle course. The feat, as detailed in a study published in the journal Nature Medicine, was achieved by mapping virtual inputs to signals sent by a region of the brain that controls the fingers, the left precentral gyrus, which is where the brain computer interface (BCI) was implanted. All the paralyzed patient had to do to exert control is simply think about moving the digits of his hand -- bringing a whole new meaning, we must report, to the expression of "not lifting a finger." "This is a greater degree of functionality than anything previously based on finger movements," said study lead author Matthew Willsey, an assistant professor of neurosurgery and biomedical engineering at the University of Michigan, in a statement about the work. Key to the BCI's success, the researchers argue, was the fact that it was a brain implant, and not a noninvasive alternative like a brain cap. The researchers believe that placing electrodes as close as possible to neurons is essential to achieve highly functional motor control. In this case, a total of 192 electrodes were surgically placed in the patient's brain, connecting to a computer. From there, a type of AI called a feed-forward neural network interprets the signals, assigning them to different finger movements. The AI system learned to distinguish the signals during a training stage in which the patient tried to perform motions with their fingers -- in their mind, to clarify -- in sync with a moving virtual hand. In total, the system provides four degrees of freedom: forwards and backwards, left and right, up and down, and horizontal rotation. Plenty to fly a drone or take control of any virtual environment. The researchers hope that their technique will open up vast recreational opportunities for people with paralysis and other severe disabilities -- like being able to play multiplayer video games, a feat already achieved by a Neuralink patient. "People tend to focus on restoration of the sorts of functions that are basic necessities -- eating, dressing, mobility -- and those are all important," co-author Jamie Henderson, a Stanford professor of neurosurgery, said in the statement. "But oftentimes, other equally important aspects of life get short shrift, like recreation or connection with peers. People want to play games and interact with their friends." Willsey's patient, a 69-year-old man who became quadriplegic after sustaining a devastating spine injury, has a passion for flying. With any luck, he may be able to play a full blown flight simulator -- or maybe even control a real drone -- in the near future.
[2]
Paralyzed man, 69, flies virtual drone with thoughts in brain-computer s
Participant says controlling the virtual drone felt like playing a musical instrument, evoking activity and socialization. In an advancement in brain-computer interface (BCI) technology, scientists enabled a 69-year-old man with paralysis to fly a virtual drone through a complex obstacle course using only his thoughts. The team of researchers from the University of Michigan and Stanford University developed a device that deciphers brain activity related to finger movements, allowing for precision in controlling external devices. According to Nature, the brain-computer interface was implanted in the participant's left precentral gyrus, the region of the brain responsible for controlling fine movements of the hand and fingers. By imagining moving his fingers, the participant could control the virtual drone in real time. The study marks a milestone in restoring fine motor functions for individuals with motor impairments. "The interface takes the signals created in the motor cortex that occur simply when the participant tries to move their fingers and uses an artificial neural network to interpret what the intentions are to control virtual fingers in the simulation," said Matthew Willsey, a neurosurgeon at the University of Michigan and first author of the study, according to Gizmodo. The participant, who became tetraplegic after a cervical spinal cord injury, expressed his passion for flying, which inspired the design of the quadcopter simulation. "The goal of doing the quadcopter was really kind of shared between our lab and the participant," said Willsey. Using machine learning algorithms, the researchers identified neural signals linked to specific finger movements. These signals were then decoded to control the speed and direction of the virtual drone, allowing the participant to maneuver through rings in a virtual basketball court. The brain-computer interface provided a level of precision and freedom of movement superior to previous systems. Jaimie Henderson, a professor of neurosurgery at Stanford University and co-author of the study, discussed the broader implications of the technology. "A person who can connect with a computer and manipulate a virtual vehicle simply by thinking could eventually be capable of much more," he said, according to Science Daily. The participant described the experience of piloting the drone as feeling like playing a musical instrument, which evoked a strong sense of activity, recreation, and socialization. "Flying [the virtual drone] is tiny little finesses off a middle line, a little bit up, a little bit down," he explained, as quoted by Nature. The study, published in the journal Nature Medicine, demonstrated the potential of brain-computer interfaces to restore autonomy to individuals with paralysis. Digital Trends noted that with practice, the participant was able to use the brain-computer interface to control the movement and speed of the virtual drone in a simulated obstacle course. The researchers used an artificial neural network to interpret the participant's brain signals, mapping complex neural activity to specific finger movements. As reported by New Scientist, the neural signals from the man were associated with finger movements, enabling him to pilot the virtual drone through the obstacle course by imagining moving three groups of digits. "This is a greater degree of functionality than anything previously based on finger movements," said Willsey, according to Popular Science. Stay updated with the latest news! Subscribe to The Jerusalem Post Newsletter Subscribe Now The success of the study opens new possibilities for people with paralysis to engage in leisure activities and social interactions that were previously inaccessible. "People want to play and connect with their peers," said the research team. "This technology could meet such needs, as it allows for human connection and fosters a healthy level of socialization." The participant, who had electrodes implanted in his motor cortex, worked closely with the research team, expressing enthusiasm and a desire for more "stick time" to improve his performance. Nature reported that he often requested video clips of his quadcopter flights to share with friends. While the results are promising, the researchers acknowledged that further work is needed to make BCI use safe in difficult tasks and to address health and psychological implications. As noted by ABP News, challenges remain with BCI technology, including medical risks from the surgery required to implant a BCI device. The ability to control multiple fingers in a coordinated manner opens the door to multifunctional applications, potentially enabling individuals with paralysis to perform a wider range of activities, such as typing or playing complex video games. The BrainGate2 clinical trials, of which the study is a part, intended to determine how people with tetraplegia can use a neural interface to control assistive devices and navigate communication software. This article was written in collaboration with generative AI company Alchemiq
[3]
Paralyzed man flies virtual drone by thought alone
A man with paralysis has been able to fly a virtual drone using only his thoughts. The feat was made possible by a brain-computer interface (BCI) that decoded the man's brain activity in real time, Nature reported this week. The neural signals were associated with finger movements that enabled control of the virtual drone. Recommended Videos "There's a lot of things that we enjoy or do as humans where we use multiple individuated finger movements, so like typing, sewing, playing a musical instrument," said Matthew Willsey, the study's co-author and a neurosurgeon at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. "That's what this line of work is focused on -- how we enable the control of multiple things at the same time." Please enable Javascript to view this content Willsey added that the experiment could've been performed with a real drone but the team decided to use a virtual one for ease and safety. The 69-year-old man who participated in the study told the researchers that controlling the virtual object felt like playing a musical instrument, saying: "Flying [the virtual drone] is tiny little finesses off a middle line, a little bit up, a little bit down." The man's BCI was fitted by Blackrock Neurotech and was implanted in the area of the brain that controls hand motion. An AI model was used to map the neural signals received by the BCI's electrodes to the man's thoughts, New Scientist explained. The participant first went through a process of learning how to imagine some of his fingers moving in a way that created electrical signals of varying strength, which later allowed him to pilot the virtual drone through an obstacle course. Willsey said that for the participant, the test was the realization of "a dream that he thought was lost once he suffered his injury. He had a passion and a dream for flying. He seemed very empowered and enabled -- he would have us take videos and send it to friends." BCI technology has made significant advancements in recent years, with companies like Elon Musk's Neuralink also developing a device that is currently undergoing human testing. Once fully developed, a slew of exciting applications could bring significant freedom and independence to those with paralysis. They include allowing people with severe paralysis or locked-in syndrome to communicate by translating neural activity into text or speech simply through their thoughts. It can also enable people to use computers, play games, and operate wheelchairs and robotic prosthetics, and even do things like grasp objects or scratch their face. However, challenges remain with the technology, including medical risks from the surgery required to implant a BCI device. High levels of concentration are also required from the person using the device, with current BCIs correctly recognizing mental commands only about 80% of the time, and up to 30% of users failing to get it to function at all. The health and psychological implications of the technology, including cognitive fatigue and long-term exposure to electromagnetic fields, are also not yet fully understood. These and other challenges highlight the need for continued research and development to improve BCI technology, deal with safety concerns, and create appropriate regulatory frameworks.
[4]
Paralyzed Man Controls Virtual Drone With His Mind - Decrypt
A 69-year-old man with paralysis and a brain implant was able to fly a virtual drone through complex obstacle courses, simply by thinking about moving his fingers, thanks to an experimental device developed by researchers from Stanford University. The participant, who has quadriplegia from a C4 spinal cord injury, navigated obstacle courses and random flight patterns using neural signals from two tiny electrode arrays implanted in his brain. His ability to combine multiple movements simultaneously represents a significant advance in brain-computer interface technology. For the experiment, researchers developed a system that can decode four distinct control dimensions from brain signals. This level of control matches what able-bodied gamers achieve with physical controllers, the researchers said. "Just as able-bodied users of digital systems use their fingers to manipulate keyboards and game controllers, this system allows an intuitive framework for a brain-controlled digital interface, providing opportunities for recreation and socialization as well as eliciting feelings of enablement." "He expressed on multiple occasions (even before enrollment in the clinical trial) that one of his most important personal priorities was to use a BCI to control a quadcopter," the researchers wrote in their paper. "He felt controlling a quadcopter would enable him, for the first time since his injury, to figuratively 'rise up' from his bed/chair." This motivation drove impressive results: after different tries, the unidentified subject was able to complete 12 laps around an obstacle course averaging 222 seconds per lap, and navigating through 28 randomly placed rings in just 10 minutes. When you think about moving your fingers, neurons (brain cells) in the motor cortex (the brain's movement control center) fire electrical signals. Even if the body is paralyzed, these signals still exist. Mind reading studies have been trying to decode these signals to trigger external devices capable of achieving what the brain wants to do. The system that helped this man fly a virtual drone relies on two 96-channel silicon microelectrode arrays placed in the "hand knob" area of the participant's motor cortex. The electrodes pick up spike-band power, a measure of how active neurons are. For example, when the participant imagines flexing their thumb, specific neurons fire rapidly and these electrodes detect the neural activity patterns. Then, a computer uses a machine learning algorithm (like a smart translator) to convert these signals into finger movements in real time. The algorithm was trained by having the participant watch a virtual hand move and try to mimic it mentally. Over time, the system learned patterns that associated specific electrical patterns to specific finger movements. The control scheme then learned to map different imagined finger movements to specific drone actions: "Flying it is tiny little finesses off a middle line, a little bit up, a little bit down," the patient explained. The system allows for smooth, simultaneous control across all dimensions, enabling complex maneuvers like combining forward movement with turns. Mind reading technology is not exactly new; AI has given a massive boost to the discipline. Recent advances across multiple labs and companies show how quickly the field is evolving. For instance, Neuralink, Elon Musk's brain-computer interface company, has made headlines with its first two human patients. Its second participant, known as "Alex," broke records for brain-computer interface cursor control and managed to play the video game Counter-Strike 2 and use 3D design software just one month after receiving the implant. Elon Musk expects to make brain-computer interface devices massive. "If all goes well, there will be hundreds of people with Neuralinks within a few years, maybe tens of thousands within five years, millions within ten years," Musk tweeted shortly after sharing the results of Alex's performance. However, some experts believe Neuralink's approach is too invasive. This led one of its researchers to leave the company and fund another brain-control interface startup: "Precision Neuroscience" which is working on a device that registers activity by "wrapping" the brain rather than sticking needles in it. Synchron, a New York-based company, has developed a less invasive brain implant called The Stentrode that avoids traditional brain surgery by being inserted through blood vessels. Their patient, a 64-year-old identified as "Mark," successfully controlled Amazon Alexa devices and interacted with an Apple Vision Pro headset using just his thoughts. The device is implanted via the jugular vein and positioned near the motor cortex. There are many other examples, from practical to more experimental. Unbabel has been able to convert thoughts directly into text, UC San Francisco researchers have developed a thoughts-to-speech system and even Meta has been working on non-invasive brain-machine interfaces for augmented reality applications, developing a system that converts thoughts into images almost in real time. In 2023, UC Berkeley researchers were able to reconstruct music directly from brain activity. Their system successfully recreated Pink Floyd's "Another Brick in the Wall, Part 1" by analyzing neural signals from epilepsy patients. The breakthrough suggests potential applications for helping speech-impaired patients communicate through thought.
[5]
Using Thoughts Alone, Paralyzed Man Flies Virtual Drone With Remarkable Precision
The brainâ€"computer interface allowed the participant to control the drone with six times the accuracy of EEG-based systems. It looks like a simple video game, but the innovative new system might one day restore physical control to the lives of people with paralysis. Neurosurgeons from Stanford and Brown University implanted microelectrodes in the brain of a paralyzed research participant, connecting him to a computer to enable electrical signal transmission. The test subject, through the microelectrodes, was able to pilot a virtual drone through a video game-like obstacle course using only his thoughts. The achievement, as detailed in a January 20 study published in the journal Nature Medicine, holds important implications for enabling people with paralysis to enjoy activities previously inaccessible to them, and perhaps one day regain autonomous movement. “We developed a high-performance, finger-based brainâ€"computer-interface system allowing continuous control of three [virtual] independent finger groups of which the thumb can be controlled in two dimensions, yielding a total of four degrees of freedom,†the researchers wrote in the study. Though scientists have used brain-computer technology for over a decade to assist people with paralysis, it has historically faced challenges in replicating complex movements, such as those of the fingers, according to a Nature statement. The participant in the study is a 69-year-old right-handed man who suffered a spinal cord injury that gave him tetraplegia, an extreme form of paralysis that impacts most of the body. As detailed in the new paper, microelectrodes were implanted into his left precentral gyrus, the part of the brain that controls hand movement. The neurosurgeons asked the participant to watch the movements of a virtual hand, and then used artificial intelligence to identify the electrical brain activity associated with particular finger movements. This association then allowed the AI system to predict the desired finger movements, even though the participant can't move his own fingers. The brainâ€"computer interface thus enabled him to control the movements of a virtual hand using his thoughts. The virtual hand was divided into three segments, which he could move vertically and horizontally, sometimes simultaneously: the thumb, index and middle finger, and ring and pinkie. “This is a greater degree of functionality than anything previously based on finger movements,†Matthew Willsey of Stanford University, who led the study and is also an assistant professor at the University of Michigan (U-M), Ann Arbor, said in a U-M statement. With practice, the participant was able to use this brainâ€"computer interface to control the movement and speed of a virtual drone in a simulated obstacle course, akin to how people without paralysis use game controllers to play video games. The interface “takes the signals created in the motor cortex [in the brain] that occur simply when the participant tries to move their fingers and uses an artificial neural network to interpret what the intentions are to control virtual fingers in the simulation,†Willsey added. “Then we send a signal to control a virtual quadcopter [drone].†“The quadcopter simulation was not an arbitrary choice," as the "research participant had a passion for flying,†said Donald T. Avansino of Stanford University, who also participated in the study. “While also fulfilling the participant’s desire for flight, the platform also showcased the control of multiple fingers.†The microelectrodes’ in the participant's brain are physically wired to a computer. Less invasive approaches, including electroencephalography (EEG, a painless technique that measures electrical brain activity without the need for surgery), have previously enabled patients with paralysis to play video games. However, the researchers suggest that fine motor control is better achieved by working more closely to neurons, according to the U-M statement. In fact, they noted in the study that their brainâ€"computer interface enabled the participant to control the drone six times more accurately than a similar previous study that used EEG. While the ability to play a video game enables patients with paralysis to socialize and engage in leisure activities, precise dexterous control has even greater potential. “Being able to move multiple virtual fingers with brain control, you can have multi-factor control schemes for all kinds of things,†explained Jaimie M. Henderson of Stanford University, who also participated in the study. “That could mean anything, from operating CAD software to composing music.†In other words, such technology could enable patients to pursue broader activities and even careers that were previously impossible for them. While Star Wars' characters use "the force" to control objects at a distance, scientists are leveraging technological advancements to help patients with paralysis regain control over their lives.
[6]
Paralyzed man controls virtual drone with his mind using brain chip
A view from the obstacle course game, in which a virtual drone is piloted using brain signals linked to finger movements. A virtual drone piloted only by a man's thought movements was brought to life through an innovative experiment. The AI model analyzes the man's brain activity when the individual imagines moving his fingers. In addition, this offers insight into the endless possibilities of brain-computer interface (BCI) technology. In this study, researchers explored the capabilities of BCIs to control complex systems. Unlike earlier work that focused on single inputs, such as controlling a cursor or virtual hand, this study marks a significant leap toward multi-input applications.
Share
Share
Copy Link
A 69-year-old man with paralysis successfully controlled a virtual drone through complex obstacle courses using only his thoughts, thanks to a brain-computer interface that interprets neural signals associated with finger movements.

Breakthrough in Brain-Computer Interface Technology
In a groundbreaking study published in Nature Medicine, researchers from the University of Michigan and Stanford University have enabled a 69-year-old man with paralysis to fly a virtual drone using only his thoughts
1
. This achievement marks a significant advancement in brain-computer interface (BCI) technology, offering new possibilities for individuals with severe motor impairments.The Brain Implant and Neural Network
The study involved implanting 192 electrodes in the participant's left precentral gyrus, the region of the brain responsible for controlling fine hand and finger movements
2
. A feed-forward neural network was then used to interpret the brain signals and assign them to different finger movements. This AI system learned to distinguish the signals during a training stage where the patient imagined performing motions with his fingers in sync with a moving virtual hand1
.Virtual Drone Control and Degrees of Freedom
The BCI system provided four degrees of freedom: forward/backward, left/right, up/down, and horizontal rotation
1
. This level of control matches what able-bodied gamers achieve with physical controllers4
. The participant successfully navigated the virtual drone through complex obstacle courses, completing 12 laps averaging 222 seconds per lap and navigating through 28 randomly placed rings in just 10 minutes4
.Implications for Quality of Life
This technology opens up vast recreational opportunities for people with paralysis and other severe disabilities. It could enable activities such as playing multiplayer video games, using computers, and potentially controlling real drones in the future
1
3
. The participant, who had a passion for flying before his injury, described the experience as feeling like playing a musical instrument2
.Related Stories
Comparison with Other BCI Technologies
The researchers argue that the success of this BCI is due to its invasive nature, placing electrodes as close as possible to neurons
1
. This approach allowed for six times greater accuracy compared to non-invasive EEG-based systems5
. However, less invasive approaches are also being developed by companies like Precision Neuroscience and Synchron4
.Future Potential and Challenges
While the results are promising, challenges remain in making BCI use safe for difficult tasks and addressing health and psychological implications
2
. The technology could potentially enable a wide range of activities, from typing to playing complex video games, significantly improving the quality of life for individuals with paralysis5
. However, further research is needed to address medical risks, improve accuracy, and develop appropriate regulatory frameworks3
.References
Summarized by
Navi
[2]
[3]
Related Stories
Breakthrough: AI-Powered Brain Implant Enables Paralyzed Man to Control Robotic Arm for Record 7 Months
07 Mar 2025•Science and Research

AI-Enhanced Brain-Computer Interface Boosts Performance for Paralyzed Users
02 Sept 2025•Technology
Neuralink's Second Brain Implant Patient Plays Video Games with Mind Control
23 Aug 2024

Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.4, New AI Model Built for Agents and Professional Work
Technology

2
Anthropic takes Pentagon to court over unprecedented supply chain risk designation
Policy and Regulation

3
Meta smart glasses face lawsuit and UK probe after workers watched intimate user footage
Policy and Regulation