xMEMS Labs' Tiny Cooling Chip Set to Revolutionize AI Data Center Efficiency
2 Sources
2 Sources
[1]
xMEMS Makes Tiny Coolers for Big Data Centers
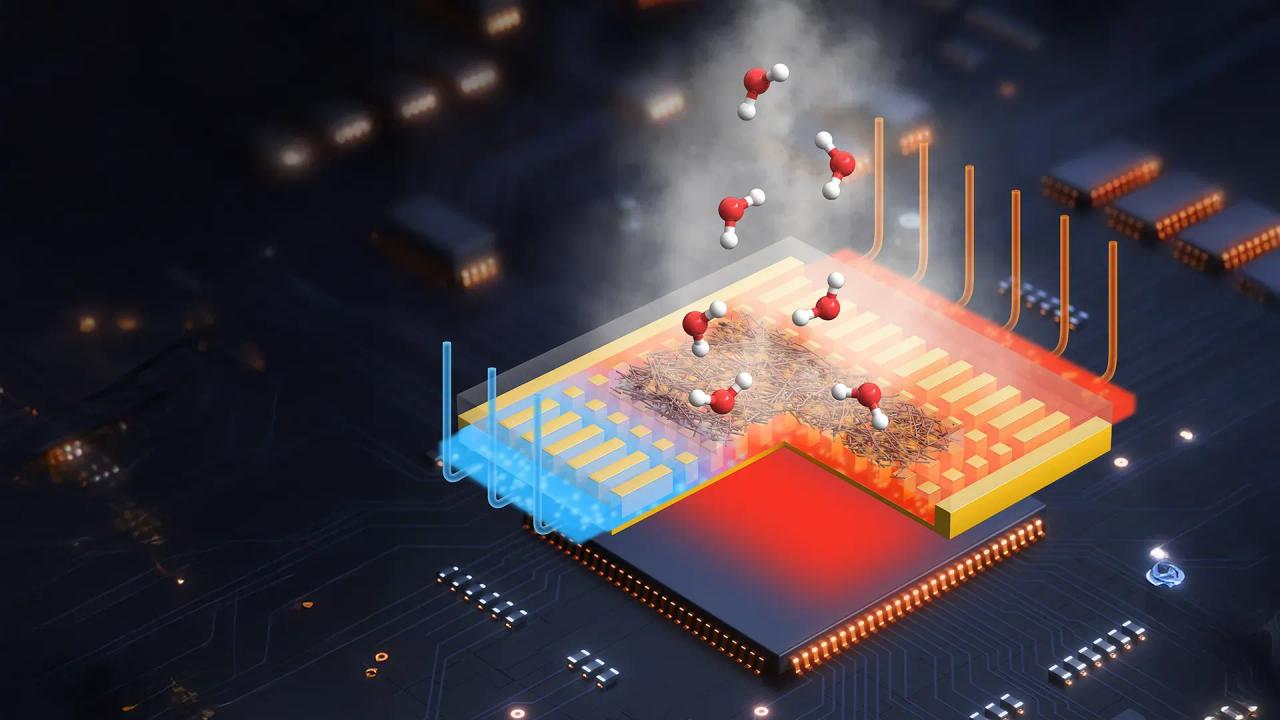
In data centers, pluggable optical transceivers convert electronic bits to photons, fling them across the room, and then turn them back to electronic signals, making them a technological linchpin to controlling the blizzard of data used in AI. But the technology consumes quite a bit of power. In a data center containing 400,000 GPUs, Nvidia estimates that optical transceivers burn 40 megawatts. Right now, the only way to deal with all that heat is to hope you can thermally connectthese transceivers to the switch system's case and cool that. It's not a great solution, says Thomas Tarter, principle thermal engineer at startup xMEMs Labs, but because these transceivers are about the size of an overlarge USB stick, there's no way to stick a conventional cooling fan in each. Now, xMEMs says it has adapted its upcoming ultrasonic microelectromechanical (MEMS) "fan-on-a-chip" to fit inside a pluggable optical transceiver so it drives air through and cools the transceiver's main digital part, the digital signal processor (DSP). Keeping the DSP cool is critical to its longevity, says Tarter. At upwards of US $2,000 per transceiver, getting an extra year or two from a transceiver is well worth it. Cooling should also improve integrity of the transceivers' signals. Unreliable links are blamed for extending already-lengthy training runs for new large language models. Smartphones, which are too slim to carry a fan, were the first obvious application for the MEMScooler, but cooling the fast-growing data-center-scale AI systems seemed out of reach for MEMS technology, because it can't come near matching the liquid cooling systems removing thousands of watts of heat from GPU servers. "We were pleasantly surprised by the approach by data center customers," says Mike Housholder, xMEMS vice president of marketing. "We were focused on low power. So we didn't think we had a slam dunk." Pluggable optical transceivers turn out to be a data center technology that is squarely in the fan-on-a-chip's wheelhouse. Today, heat from a transceiver's DSP, photonics IC, and lasers is thermally coupled to the network switch computers they are plugged into. (These usually sit at the top of a rack of computers.) Then air moving over fins built into the switch's face remove the heat. In collaboration with partners they would not name, xMEMS began exploring how to get air flowing through the transceiver. These parts consume 18 watts or more. But by situating the company's MEMS chip within an airflow channel that is thermally connected to the transceiver chips but physically isolated from them, the company predicts it will be able to drop the DSP's temperature by more than 15 percent. xMEMS has been making prototype MEMS chips at Stanford's nanofabrication facility, but it will have its first production silicon from TSMC in June, says Housholder. The company expects to be in full production in the first quarter of 2026. "That aligns well with our early customers," he says. Transceiver shipments are growing fast, according to Dell'Oro Group. The market analyst predicts that shipments of 800 gigabit per second and 1.6 terabit per second parts will grow at more than 35 percent per year through 2028. Other innovations in optical communications that could affect heat and power are also in the offing. In March, Broadcom unveiled a new DSP that could lead to a more than 20 percent power reduction for 1.6 Tbps transceivers, due in part to use of a more-advanced chip manufacturing process. The latter company and Nvidia, separately, have developed network switches that do away with pluggable transceivers altogether. These new "co-packaged optics" do the optical/electronic conversion on silicon within the switch chip's package. But Tarter, who has been working on cooling chips since the 1980s, predicts there will be more applications both inside and outside the data center for the MEMS chip to come. "We're learning a lot about applications," he says. "I've come up with 20 or 30 basic applications for it, and hopefully that inspires designers to say 'Oh, this is how I can use this in my system.'"
[2]
Tiny cooling fan-on-a-chip designed for phones to be deployed in AI data centers
AI data centers will start using xMEMS Labs' tiny, all-silicon, active fan-on-a-chip cooling solution, µCooling, initially designed for smartphones and mobile devices. According to GamesBeat, this technology will be deployed in small high-performance optical transceiver DSPs with a maximum TDP of 18W or higher. The tiny cooling chip can deliver up to 5 watts of localized cooling, and its small size and lack of moving parts mean it can be reliably deployed in hard-to-reach places and require no maintenance at all. Although the amount of heat these fans remove might seem small, it is still significant enough to reduce DSP temperatures by 15%. This decreases the thermal load on the system, allowing it to operate faster for much longer, reduce errors, and increase its service life. xMEMS Labs also isolated the airflow channel from the transceiver's optical and core electronic components. This ensures that any dust or contaminant picked up by its micro fan will have no way to interfere with the DSP's operation. "As data center interconnect demands scale rapidly with AI workloads, thermal bottlenecks are emerging at the component level -- especially in optical modules that are sealed, power-dense, and space-constrained," xMEMS Labs Marketing VP Mike Housholder said in a statement. "µCooling is uniquely positioned to solve this by providing true in-module active cooling with no compromise to optics or form factor." xMEMS Labs might be the first to deploy a micro cooling solution in an AI data center, but it isn't the only one working on an extremely compact fan with few or no moving parts. Frore System has been working on its solid-state cooling chip since 2022, which uses piezoelectric vibrations to drive airflow, similar to xMEMS Labs' µCooling chip. It has even introduced slimmer versions called the AirJet Mini Slim and applied them to an SSD, which doubled its performance. On the other hand, Ventivia is taking a different approach with its Ionic Cooling Engine, which uses an electric field to ionize air particles and force them to flow in one direction, creating cooling. As chips and devices become smaller and more power-dense, these tiny cooling solutions will be crucial for helping our tech keep its cool. And while we might not yet see these fans in phones and laptops this year, they're slowly coming online in different components that most people may never see.
Share
Share
Copy Link
xMEMS Labs adapts its ultrasonic MEMS "fan-on-a-chip" technology for cooling optical transceivers in AI data centers, potentially improving performance and longevity of critical components.

xMEMS Labs Introduces Innovative Cooling Solution for AI Data Centers
xMEMS Labs, a startup specializing in microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), has adapted its ultrasonic "fan-on-a-chip" technology to address a critical cooling challenge in AI data centers. Originally designed for smartphones, this tiny cooling solution is now set to make a significant impact on the efficiency and reliability of optical transceivers in data center environments
1
.The Challenge of Data Center Cooling
In modern data centers, particularly those focused on AI workloads, optical transceivers play a crucial role in converting electronic signals to photons and back. However, these components consume substantial power and generate significant heat. Nvidia estimates that in a data center with 400,000 GPUs, optical transceivers alone can consume up to 40 megawatts of power
1
.xMEMS' Innovative Solution
The xMEMS cooling chip, known as µCooling, is designed to fit inside pluggable optical transceivers, specifically targeting the digital signal processor (DSP). This active cooling solution can deliver up to 5 watts of localized cooling, which is expected to reduce DSP temperatures by more than 15%
2
.Key Features and Benefits
-
Size and Integration: The fan-on-a-chip is small enough to fit within the confined space of an optical transceiver, addressing a problem that conventional cooling fans cannot solve due to size constraints
1
. -
Improved Longevity: By keeping the DSP cooler, the solution aims to extend the lifespan of optical transceivers, which can cost upwards of $2,000 each
1
. -
Enhanced Signal Integrity: Cooler operating temperatures are expected to improve the reliability of data links, potentially reducing delays in AI model training
1
. -
Isolated Design: xMEMS has designed the cooling system with an isolated airflow channel, preventing dust or contaminants from interfering with the DSP's operation
2
.
Related Stories
Market Potential and Future Outlook
The optical transceiver market is experiencing rapid growth, with Dell'Oro Group predicting that shipments of high-speed transceivers will grow at over 35% annually through 2028
1
. This growth, coupled with the increasing demands of AI workloads, positions xMEMS' cooling solution as a potentially critical technology for future data center designs.Industry Competition and Alternative Approaches
While xMEMS may be the first to deploy a micro cooling solution in AI data centers, other companies are also working on compact cooling technologies:
-
Frore Systems: Developing a solid-state cooling chip using piezoelectric vibrations, similar to xMEMS' approach
2
. -
Ventivia: Taking a different approach with its Ionic Cooling Engine, which uses an electric field to create airflow
2
.
As the demand for more powerful and efficient AI systems continues to grow, these innovative cooling solutions are likely to play an increasingly important role in managing heat dissipation in compact, high-performance computing environments.
References
Summarized by
Navi
Related Stories
Microsoft Unveils Groundbreaking Microfluidic Cooling for AI Chips
23 Sept 2025•Technology

Breakthrough in Evaporative Cooling Technology Could Revolutionize Data Center Energy Efficiency
14 Jun 2025•Technology
Supermicro Unveils Comprehensive Liquid Cooling Solution for AI-Driven Data Centers
08 Oct 2024•Technology

Recent Highlights
1
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.4, New AI Model Built for Agents and Professional Work
Technology

2
Pentagon's Anthropic showdown exposes who controls AI guardrails in military contracts
Policy and Regulation

3
Anthropic challenges Pentagon supply chain risk label in court over AI usage restrictions
Policy and Regulation





