AI-Powered Genetic Progression Score Revolutionizes Autoimmune Disease Prediction
3 Sources
3 Sources
[1]
Predicting the progression of autoimmune disease with AI
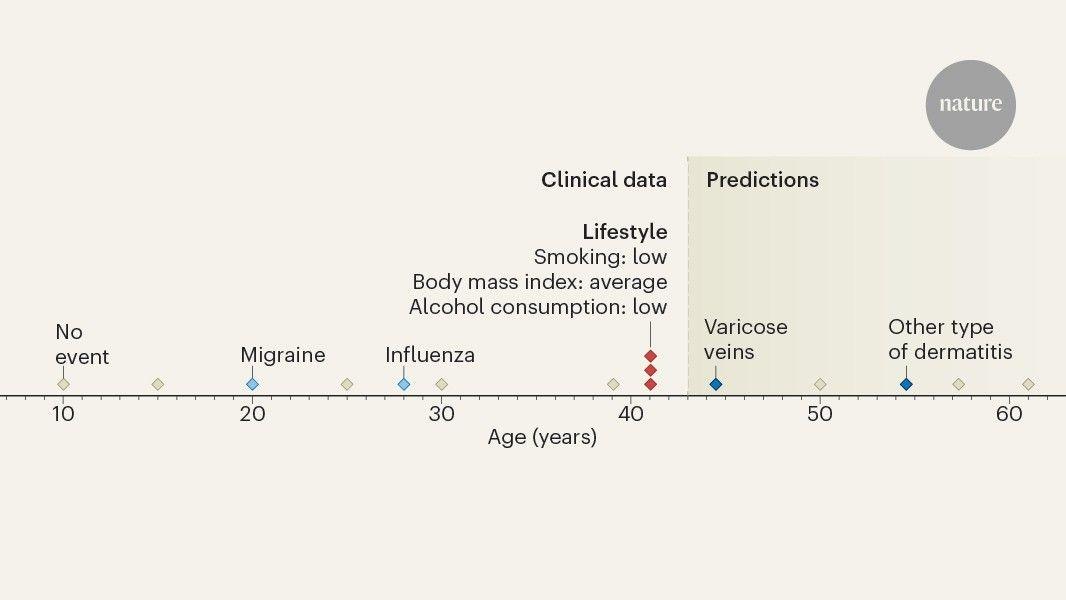
Autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own healthy cells and tissues, often have a preclinical stage before diagnosis that's characterized by mild symptoms or certain antibodies in the blood. However, in some people, these symptoms may resolve before culminating in the full disease stage. Knowing who may progress along the disease pathway is critical for early diagnosis and intervention, improved treatment and better disease management, according to a team led by researchers from the Penn State College of Medicine that has developed a new method to predict the progression of autoimmune disease among those with preclinical symptoms. The team used artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze data from electronic health records and large genetic studies of people with autoimmune disease to come up with a risk prediction score. When compared to existing models, this methodology was between 25% and 1,000% more accurate in determining whose symptoms would move to advanced disease. The research team published their findings this week (Jan. 2) in the journal Nature Communications. "By targeting a more relevant population -- people with family history or who are experiencing early symptoms -- we can use machine learning to identify patients with the highest risk for disease and then identify suitable therapeutics that may be able to slow down the progression of the disease. It's a lot more meaningful and actionable information," said Dajiang Liu, distinguished professor, vice chair for research and director of artificial intelligence and biomedical informatics at the Penn State College of Medicine and co-lead author of the study. Approximately 8% of Americans live with autoimmune disease, according to the National Institutes of Health, and the vast majority are women. The earlier you can detect the disease and intervene, the better, Liu said, because once autoimmune diseases progress, the damage can be irreversible. There are often signs of the disease before an individual receives a diagnosis. For example, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, antibodies can be detected in the blood five years before symptoms begin, the researchers explained. The challenge with forecasting disease progression is sample size. The population of individuals who have a specific autoimmune disease is relatively small. With less data available, it's harder to develop an accurate model and algorithm, Liu said. To improve prediction accuracy, the research team developed a new method, dubbed Genetic Progression Score or GPS, to foretell the progression from preclinical to disease stages. GPS leverages the idea behind transfer learning -- a machine learning technique where a model is trained on one task or dataset and then fine-tuned for a different but related task or dataset, explained Bibo Jiang, assistant professor of public health sciences at the Penn State College of Medicine and lead author of the study. It allows researchers to glean better information from smaller data samples. For example, in medical imaging, artificial intelligence models can be trained to tell whether a tumor is cancerous or non-cancerous. To create the training dataset, medical experts need to label images one-by-one, which can be time intensive and limited by the number of images available. Liu said, instead, transfer learning uses more numerous, easier-to-label images, such as cats and dogs and creates a much larger dataset. The task can also be outsourced. The model learns to differentiate between the animals, and then, it can be refined to distinguish between malignant and benign tumors. "You don't need to train the model from scratch," Liu said. "The way that the model segments elements from an image to determine whether it's a cat or dog is transferable. With some adaptation, you can refine the model to separate an image of a tumor from an image of normal tissue." GPS trains on data from large case-control genome-wide association studies (GWAS), a popular approach in human genetics research to identify genetic differences in people with a specific autoimmune disease from those without and to detect potential risk factors. It also incorporates data from electronic health record-based biobanks, which contain rich information about patients, including genetic variants, lab tests and clinical diagnoses. This data can help identify individuals in preclinical stages and characterize the stages of progression from preclinical to the disease stage. Data from both sources is then integrated to refine the GPS model, incorporating factors that are relevant to the actual development of disease. "Integrating large case-control studies and biobanks borrowed strengths from the large sample sizes of case-control studies and improved prediction accuracy," Liu said, explaining that people with high GPS scores have a higher risk of progressing from preclinical to disease stages. The team used real-world data from the Vanderbilt University biobank to predict the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and lupus and then validated the GPS risk scores with data from the All of Us biobank, a health data initiative of the National Institutes of Health. GPS better predicted disease progression than 20 other models that rely on biobank or case-control samples only and those combining biobank and case-control samples via other methods. Accurate prediction of disease progression using GPS can enable early interventions, targeted monitoring and personalized treatment decisions, leading to improved patient outcomes, Liu said. It could also improve clinical trial design and recruitment by identifying individuals who are most likely to benefit from new therapies. While this study focused on autoimmune conditions, the researchers said that a similar framework could be used to study other disease types. "When we talk about underrepresented populations, it's not just about race. It could also be a group of patients that are under-studied in the medical literature because they comprise only a small portion of typical data sets. AI and transfer learning can help us study these populations and help reduce health disparities," Liu said. "This work reflects the strength of Penn State's comprehensive research program in autoimmune disease." Liu and Jiang -- along with study co-authors Laura Carrel, professor of biochemistry and molecular biology; Galen Foulke, associate professor of dermatology; Nancy Olsen, H. Thomas and Dorothy Willits Hallowell Chair in Rheumatology -- formed the autoimmune working group and have collaborated for nearly a decade. They lead innovative clinical trials, perform research studies to understand the biological mechanisms of autoimmune diseases and develop AI methods to tackle various problems related to autoimmune diseases. Chen Wang, who earned a doctorate in bioinformatics and genomics from Penn State, and Havell Markus, joint degree student in the MD/PhD Medical Scientist Training Program, are co-first authors of the study. Other Penn State authors on the paper include: Avantika R. Diwadkar, graduate student; Chachrit Khunsriraksakul, who graduated from the MD/PhD Medical Scientist Training Program during the time of the study; and Xingyan Wang, who was a research assistant at Penn State College of Medicine during the time of the study. Other contributors include Bingshan Li, professor of molecular physiology and biophysics, and Xue Zhong, research assistant professor in genetic medicine, from Vanderbilt University School of Medicine; and Xiaowei Zhan, associate professor of public health at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. Funding from the National Institutes of Health, including the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Office of Data Science and Emerging Technologies, supported this research.
[2]
AI-based method predicts progression of autoimmune diseases
Penn StateJan 7 2025 Autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own healthy cells and tissues, often have a preclinical stage before diagnosis that's characterized by mild symptoms or certain antibodies in the blood. However, in some people, these symptoms may resolve before culminating in the full disease stage. Knowing who may progress along the disease pathway is critical for early diagnosis and intervention, improved treatment and better disease management, according to a team led by researchers from the Penn State College of Medicine that has developed a new method to predict the progression of autoimmune disease among those with preclinical symptoms. The team used artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze data from electronic health records and large genetic studies of people with autoimmune disease to come up with a risk prediction score. When compared to existing models, this methodology was between 25% and 1,000% more accurate in determining whose symptoms would move to advanced disease. The research team published their findings this week (Jan. 2) in the journal Nature Communications. "By targeting a more relevant population - people with family history or who are experiencing early symptoms - we can use machine learning to identify patients with the highest risk for disease and then identify suitable therapeutics that may be able to slow down the progression of the disease. It's a lot more meaningful and actionable information," said Dajiang Liu, distinguished professor, vice chair for research and director of artificial intelligence and biomedical informatics at the Penn State College of Medicine and co-lead author of the study. Approximately 8% of Americans live with autoimmune disease, according to the National Institutes of Health, and the vast majority are women. The earlier you can detect the disease and intervene, the better, Liu said, because once autoimmune diseases progress, the damage can be irreversible. There are often signs of the disease before an individual receives a diagnosis. For example, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, antibodies can be detected in the blood five years before symptoms begin, the researchers explained. The challenge with forecasting disease progression is sample size. The population of individuals who have a specific autoimmune disease is relatively small. With less data available, it's harder to develop an accurate model and algorithm, Liu said. To improve prediction accuracy, the research team developed a new method, dubbed Genetic Progression Score or GPS, to foretell the progression from preclinical to disease stages. GPS leverages the idea behind transfer learning - a machine learning technique where a model is trained on one task or dataset and then fine-tuned for a different but related task or dataset, explained Bibo Jiang, assistant professor of public health sciences at the Penn State College of Medicine and lead author of the study. It allows researchers to glean better information from smaller data samples. For example, in medical imaging, artificial intelligence models can be trained to tell whether a tumor is cancerous or non-cancerous. To create the training dataset, medical experts need to label images one-by-one, which can be time intensive and limited by the number of images available. Liu said, instead, transfer learning uses more numerous, easier-to-label images, such as cats and dogs and creates a much larger dataset. The task can also be outsourced. The model learns to differentiate between the animals, and then, it can be refined to distinguish between malignant and benign tumors. "You don't need to train the model from scratch," Liu said. "The way that the model segments elements from an image to determine whether it's a cat or dog is transferable. With some adaptation, you can refine the model to separate an image of a tumor from an image of normal tissue." GPS trains on data from large case-control genome-wide association studies (GWAS), a popular approach in human genetics research to identify genetic differences in people with a specific autoimmune disease from those without and to detect potential risk factors. It also incorporates data from electronic health record-based biobanks, which contain rich information about patients, including genetic variants, lab tests and clinical diagnoses. This data can help identify individuals in preclinical stages and characterize the stages of progression from preclinical to the disease stage. Data from both sources is then integrated to refine the GPS model, incorporating factors that are relevant to the actual development of disease. "Integrating large case-control studies and biobanks borrowed strengths from the large sample sizes of case-control studies and improved prediction accuracy," Liu said, explaining that people with high GPS scores have a higher risk of progressing from preclinical to disease stages. The team used real-world data from the Vanderbilt University biobank to predict the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and lupus and then validated the GPS risk scores with data from the All of Us biobank, a health data initiative of the National Institutes of Health. GPS better predicted disease progression than 20 other models that rely on biobank or case-control samples only and those combining biobank and case-control samples via other methods. Accurate prediction of disease progression using GPS can enable early interventions, targeted monitoring and personalized treatment decisions, leading to improved patient outcomes, Liu said. It could also improve clinical trial design and recruitment by identifying individuals who are most likely to benefit from new therapies. While this study focused on autoimmune conditions, the researchers said that a similar framework could be used to study other disease types. "When we talk about underrepresented populations, it's not just about race. It could also be a group of patients that are under-studied in the medical literature because they comprise only a small portion of typical data sets. AI and transfer learning can help us study these populations and help reduce health disparities," Liu said. "This work reflects the strength of Penn State's comprehensive research program in autoimmune disease." Liu and Jiang - along with study co-authors Laura Carrel, professor of biochemistry and molecular biology; Galen Foulke, associate professor of dermatology; Nancy Olsen, H. Thomas and Dorothy Willits Hallowell Chair in Rheumatology - formed the autoimmune working group and have collaborated for nearly a decade. They lead innovative clinical trials, perform research studies to understand the biological mechanisms of autoimmune diseases and develop AI methods to tackle various problems related to autoimmune diseases. Chen Wang, who earned a doctorate in bioinformatics and genomics from Penn State, and Havell Markus, joint degree student in the MD/PhD Medical Scientist Training Program, are co-first authors of the study. Other Penn State authors on the paper include: Avantika R. Diwadkar, graduate student; Chachrit Khunsriraksakul, who graduated from the MD/PhD Medical Scientist Training Program during the time of the study; and Xingyan Wang, who was a research assistant at Penn State College of Medicine during the time of the study. Other contributors include Bingshan Li, professor of molecular physiology and biophysics, and Xue Zhong, research assistant professor in genetic medicine, from Vanderbilt University School of Medicine; and Xiaowei Zhan, associate professor of public health at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. Funding from the National Institutes of Health, including the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Office of Data Science and Emerging Technologies, supported this research. Penn State
[3]
AI Predicts Autoimmune Disease Progression with New Genetic Tool - Neuroscience News
Summary: Researchers have developed a Genetic Progression Score (GPS) using artificial intelligence to predict the progression of autoimmune diseases from preclinical symptoms to full disease. The GPS model integrates genetic data and electronic health records to provide personalized risk scores, improving prediction accuracy by 25% to 1,000% over existing models. This method identifies individuals at higher risk earlier, enabling timely interventions and better disease management. The framework could also be adapted to study other underrepresented diseases, offering a breakthrough in personalized medicine and health equity. Autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own healthy cells and tissues, often have a preclinical stage before diagnosis that's characterized by mild symptoms or certain antibodies in the blood. However, in some people, these symptoms may resolve before culminating in the full disease stage. Knowing who may progress along the disease pathway is critical for early diagnosis and intervention, improved treatment and better disease management, according to a team led by researchers from the Penn State College of Medicine that has developed a new method to predict the progression of autoimmune disease among those with preclinical symptoms. The team used artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze data from electronic health records and large genetic studies of people with autoimmune disease to come up with a risk prediction score. When compared to existing models, this methodology was between 25% and 1,000% more accurate in determining whose symptoms would move to advanced disease. The research team published their findings this week (Jan. 2) in the journal Nature Communications. "By targeting a more relevant population -- people with family history or who are experiencing early symptoms -- we can use machine learning to identify patients with the highest risk for disease and then identify suitable therapeutics that may be able to slow down the progression of the disease. "It's a lot more meaningful and actionable information," said Dajiang Liu, distinguished professor, vice chair for research and director of artificial intelligence and biomedical informatics at the Penn State College of Medicine and co-lead author of the study. Approximately 8% of Americans live with autoimmune disease, according to the National Institutes of Health, and the vast majority are women. The earlier you can detect the disease and intervene, the better, Liu said, because once autoimmune diseases progress, the damage can be irreversible. There are often signs of the disease before an individual receives a diagnosis. For example, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, antibodies can be detected in the blood five years before symptoms begin, the researchers explained. The challenge with forecasting disease progression is sample size. The population of individuals who have a specific autoimmune disease is relatively small. With less data available, it's harder to develop an accurate model and algorithm, Liu said. To improve prediction accuracy, the research team developed a new method, dubbed Genetic Progression Score or GPS, to foretell the progression from preclinical to disease stages. GPS leverages the idea behind transfer learning -- a machine learning technique where a model is trained on one task or dataset and then fine-tuned for a different but related task or dataset, explained Bibo Jiang, assistant professor of public health sciences at the Penn State College of Medicine and lead author of the study. It allows researchers to glean better information from smaller data samples. For example, in medical imaging, artificial intelligence models can be trained to tell whether a tumor is cancerous or non-cancerous. To create the training dataset, medical experts need to label images one-by-one, which can be time intensive and limited by the number of images available. Liu said, instead, transfer learning uses more numerous, easier-to-label images, such as cats and dogs and creates a much larger dataset. The task can also be outsourced. The model learns to differentiate between the animals, and then, it can be refined to distinguish between malignant and benign tumors. "You don't need to train the model from scratch," Liu said. "The way that the model segments elements from an image to determine whether it's a cat or dog is transferable. With some adaptation, you can refine the model to separate an image of a tumor from an image of normal tissue." GPS trains on data from large case-control genome-wide association studies (GWAS), a popular approach in human genetics research to identify genetic differences in people with a specific autoimmune disease from those without and to detect potential risk factors. It also incorporates data from electronic health record-based biobanks, which contain rich information about patients, including genetic variants, lab tests and clinical diagnoses. This data can help identify individuals in preclinical stages and characterize the stages of progression from preclinical to the disease stage. Data from both sources is then integrated to refine the GPS model, incorporating factors that are relevant to the actual development of disease. "Integrating large case-control studies and biobanks borrowed strengths from the large sample sizes of case-control studies and improved prediction accuracy," Liu said, explaining that people with high GPS scores have a higher risk of progressing from preclinical to disease stages. The team used real-world data from the Vanderbilt University biobank to predict the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and lupus and then validated the GPS risk scores with data from the All of Us biobank, a health data initiative of the National Institutes of Health. GPS better predicted disease progression than 20 other models that rely on biobank or case-control samples only and those combining biobank and case-control samples via other methods. Accurate prediction of disease progression using GPS can enable early interventions, targeted monitoring and personalized treatment decisions, leading to improved patient outcomes, Liu said. It could also improve clinical trial design and recruitment by identifying individuals who are most likely to benefit from new therapies. While this study focused on autoimmune conditions, the researchers said that a similar framework could be used to study other disease types. "When we talk about underrepresented populations, it's not just about race. It could also be a group of patients that are under-studied in the medical literature because they comprise only a small portion of typical data sets. AI and transfer learning can help us study these populations and help reduce health disparities," Liu said. "This work reflects the strength of Penn State's comprehensive research program in autoimmune disease." Liu and Jiang -- along with study co-authors Laura Carrel, professor of biochemistry and molecular biology; Galen Foulke, associate professor of dermatology; Nancy Olsen, H. Thomas and Dorothy Willits Hallowell Chair in Rheumatology -- formed the autoimmune working group and have collaborated for nearly a decade. They lead innovative clinical trials, perform research studies to understand the biological mechanisms of autoimmune diseases and develop AI methods to tackle various problems related to autoimmune diseases. Chen Wang, who earned a doctorate in bioinformatics and genomics from Penn State, and Havell Markus, joint degree student in the MD/PhD Medical Scientist Training Program, are co-first authors of the study. Other Penn State authors on the paper include: Avantika R. Diwadkar, graduate student; Chachrit Khunsriraksakul, who graduated from the MD/PhD Medical Scientist Training Program during the time of the study; and Xingyan Wang, who was a research assistant at Penn State College of Medicine during the time of the study. Other contributors include Bingshan Li, professor of molecular physiology and biophysics, and Xue Zhong, research assistant professor in genetic medicine, from Vanderbilt University School of Medicine; and Xiaowei Zhan, associate professor of public health at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. Funding: Funding from the National Institutes of Health, including the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Office of Data Science and Emerging Technologies, supported this research. Author: Christine Yu Source: Penn State Contact: Christine Yu - Penn State Image: The image is credited to Neuroscience News Original Research: Open access. "Integrating electronic health records and GWAS summary statistics to predict the progression of autoimmune diseases from preclinical stages" by Dajiang Liu et al. Nature Communications Abstract Integrating electronic health records and GWAS summary statistics to predict the progression of autoimmune diseases from preclinical stages Autoimmune diseases often exhibit a preclinical stage before diagnosis. Electronic health record (EHR) based-biobanks contain genetic data and diagnostic information, which can identify preclinical individuals at risk for progression. Biobanks typically have small numbers of cases, which are not sufficient to construct accurate polygenic risk scores (PRS). Importantly, progression and case-control phenotypes may have shared genetic basis, which we can exploit to improve prediction accuracy. We propose a novel method Genetic Progression Score (GPS) that integrates biobank and case-control study to predict the disease progression risk. Via penalized regression, GPS incorporates PRS weights for case-control studies as prior and forces model parameters to be similar to the prior if the prior improves prediction accuracy. In simulations, GPS consistently yields better prediction accuracy than alternative strategies relying on biobank or case-control samples only and those combining biobank and case-control samples. The improvement is particularly evident when biobank sample is smaller or the genetic correlation is lower. We derive PRS for the progression from preclinical rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus in the BioVU biobank and validate them in All of Us. For both diseases, GPS achieves the highest prediction R2 and the resulting PRS yields the strongest correlation with progression prevalence.
Share
Share
Copy Link
Researchers at Penn State College of Medicine have developed a new AI-based method called Genetic Progression Score (GPS) to predict the progression of autoimmune diseases with unprecedented accuracy, potentially transforming early diagnosis and treatment strategies.

Breakthrough in Autoimmune Disease Prediction
Researchers from Penn State College of Medicine have developed a groundbreaking artificial intelligence (AI) method to predict the progression of autoimmune diseases with unprecedented accuracy. The new approach, called Genetic Progression Score (GPS), combines genetic data with electronic health records to forecast disease progression from preclinical stages to full-blown autoimmune conditions
1
.The Challenge of Autoimmune Disease Prediction
Autoimmune diseases, affecting approximately 8% of Americans, often have a preclinical stage characterized by mild symptoms or specific antibodies in the blood. Early detection and intervention are crucial, as the damage caused by these diseases can be irreversible once they progress
2
.The main challenge in predicting disease progression has been the limited sample size of individuals with specific autoimmune conditions. This scarcity of data has made it difficult to develop accurate predictive models and algorithms.
The Genetic Progression Score (GPS) Method
To overcome these limitations, the research team developed the GPS method, which leverages transfer learning techniques. GPS integrates data from two primary sources:
- Large case-control genome-wide association studies (GWAS)
- Electronic health record-based biobanks
This innovative approach allows researchers to extract valuable insights from smaller data samples, significantly improving prediction accuracy
3
.Unprecedented Accuracy in Disease Progression Prediction
When compared to existing models, the GPS methodology demonstrated remarkable improvements in accuracy:
- 25% to 1,000% more accurate in determining which patients' symptoms would progress to advanced disease stages
- Outperformed 20 other models relying on biobank or case-control samples alone
The team validated their findings using real-world data from the Vanderbilt University biobank and the National Institutes of Health's All of Us biobank initiative
1
.Related Stories
Implications for Patient Care and Research
The GPS method offers several potential benefits for both patients and the medical community:
- Early intervention: Identifying high-risk individuals earlier allows for timely therapeutic interventions.
- Personalized treatment: Enables more targeted monitoring and personalized treatment decisions.
- Improved clinical trials: Enhances clinical trial design and recruitment by identifying individuals most likely to benefit from new therapies.
Future Applications
While this study focused on autoimmune conditions, particularly rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, the researchers believe that a similar framework could be applied to study other disease types. This breakthrough has the potential to significantly impact personalized medicine and health equity, especially for underrepresented diseases
3
.References
Summarized by
Navi
[1]
[2]
[3]
Related Stories
Recent Highlights
1
Google Maps unveils Ask Maps with Gemini AI and 3D Immersive Navigation in biggest update
Technology

2
AI chatbots help plan violent attacks as safety guardrails fail, new investigation reveals
Technology

3
OpenAI secures $110 billion funding round as questions swirl around AI bubble and profitability
Business and Economy